exercise physiology chapter 4: hormonal control during exercise
1/158
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
159 Terms
what are the three components of the endocrine system?
1) gland of origin
2) hormone
3) target tissue
the nervous system is _____ communication while the endocrine system is ____ communication.
- nervous system = electrical communication
- endocrine system = chemical communication
is the endorcrine system slower or faster than the nervous system in their response? why?
slower (the nervous system has myelin to accelerate it)
is the endocrine system shorter lasting than the nervous system?
NO! it's longer lasting
what is the role of the endocrine system?
maintains homeostasis via hormones
how does the endocrine system constantly monitor internal environment?
negative feedback loop! meaning that nervous system fell out of balance so endocrine has to bring it back to normal!
list all the glands of origin in the endocrine system
- hypothalamus
- pituitary plane
- thyroid gland
- parathyroid gland
- thymus gland
- adrenal glands
- pancreas
- kidneys
- ovaries in women and testes in men
-stomach
what are steroid hormones derived from?
cholesterol
are steroid hormones lipid soluble?
yes, they diffuse through membranes with a carrier protein
what 4 major glands are steroid hormones secreted by?
- adrenal cortex
- ovaries
- testes
- placenta
what steroid hormones are released from the adrenal cortex?
cortisol and aldosterone
what steroid hormones are released from the ovaries?
estrogen and progesterone
what steroid hormone is released from the testes?
testosterone
what steroid hormones are released from the placenta?
estrogen and progesterone
are nonsteroid hormones lipid soluble?
NO! they can not cross membranes on their own and require a protein carrier and receptor to bind to and get into the membrane
what two groups are nonsteroid hormones divided into?
- protein/peptide hormones
- amino-acid derived hormones
most non-steroid hormones are ____ hormones.
protein/peptide based !!!
where are nonsteroid hormones secreted from?
pancreas, hypothalamus, pituitary gland
what are the 2 kinds of amino acid-derived hormones?
- thyroid hormones (T3, T4)
- adrenal medulla hormones (epinephrine, norepinephrine)
what is the term used to define how hormones are secreted in bursts?
pulsatile
over what periods of time does plasma concentrations fluctuate?
- over minutes/hours
- over days/weeks
what triggers or regulates hormone bursts?
negative feedback!
how is hormone secretion regulated by negative feedback?
- high levels of downstream change = decrease secretion
- low levels of downstream change = increase secretion
what is an example of a negative feedback?
home thermostat
(when temperature in the house increases = thermostat sets to a decreased temperature to cool the house down)
what can be a poor indicator of hormone activity?
plasma concentration
why is plasma concentraion a poor indicator of hormone activity?
- cells change sensitivity to hormones
- the number of receptors on the cell surface can change
define downregulation in relation to hormone-receptor interactions
- decreased number of receptors during high plasma concentration = desensitization of hormones to bind to receptors on the cell surface
define upregulation in relation to hormone-receptor interacions
- increased number of receptors during high plasma concentration = sensitization of hormones to bind to receptors on the cell surface
what do hormones regulate?
homeostasis!
define homeostasis!!!
the maintenance of the body's internal environment with narrow limits via a dynamic equilibrium (constant check and balance system)
how do hormones limit the scope of their effects?
by using hormone-specific receptors
what are hormone-specific receptors? !!!
receptors that can differentiate hormones that can bind to if from hormones that can not bind to them
no receptor on cell surface = ?
no hormone effect
t or f: hormones only affect tissues with specific receptors
true!
about how many receptors does a typical cell have?
2,000 to 10,000 receptors
define hormone-receptor complex
- when a hormone binds to a receptor
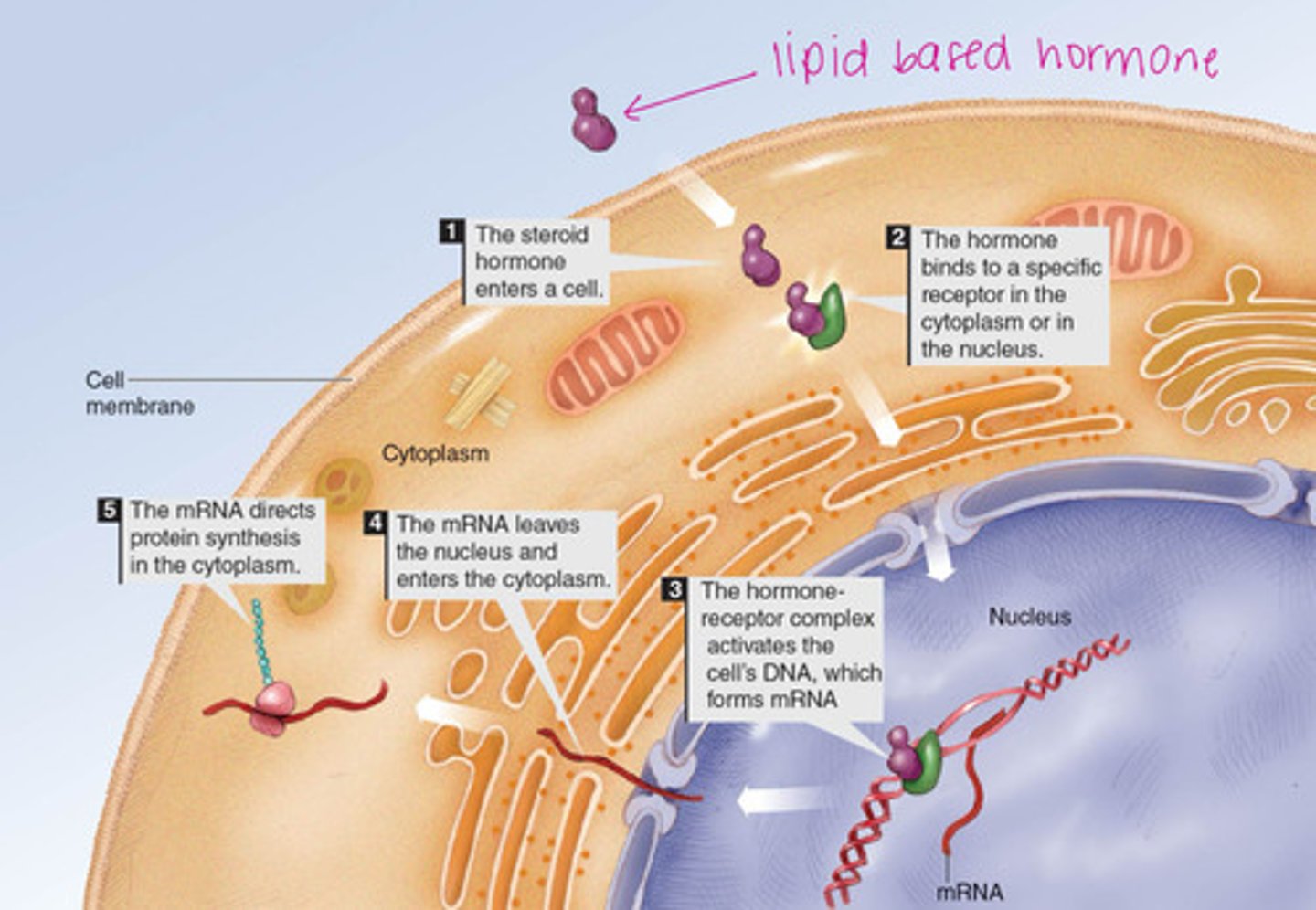
where are steroid hormone receptors found?
inside the cell in the cytoplasm or nucleus
what happens once the hormone binds to its receptor?
the hormone-receptor complex enters into the nucleus
what does the hormone-receptor complex do in the nucleus?
- binds to DNA, for direct gene activation
- regulates mRNA synthesis (protein synthesis)
explain this image in relation to steroid hormones
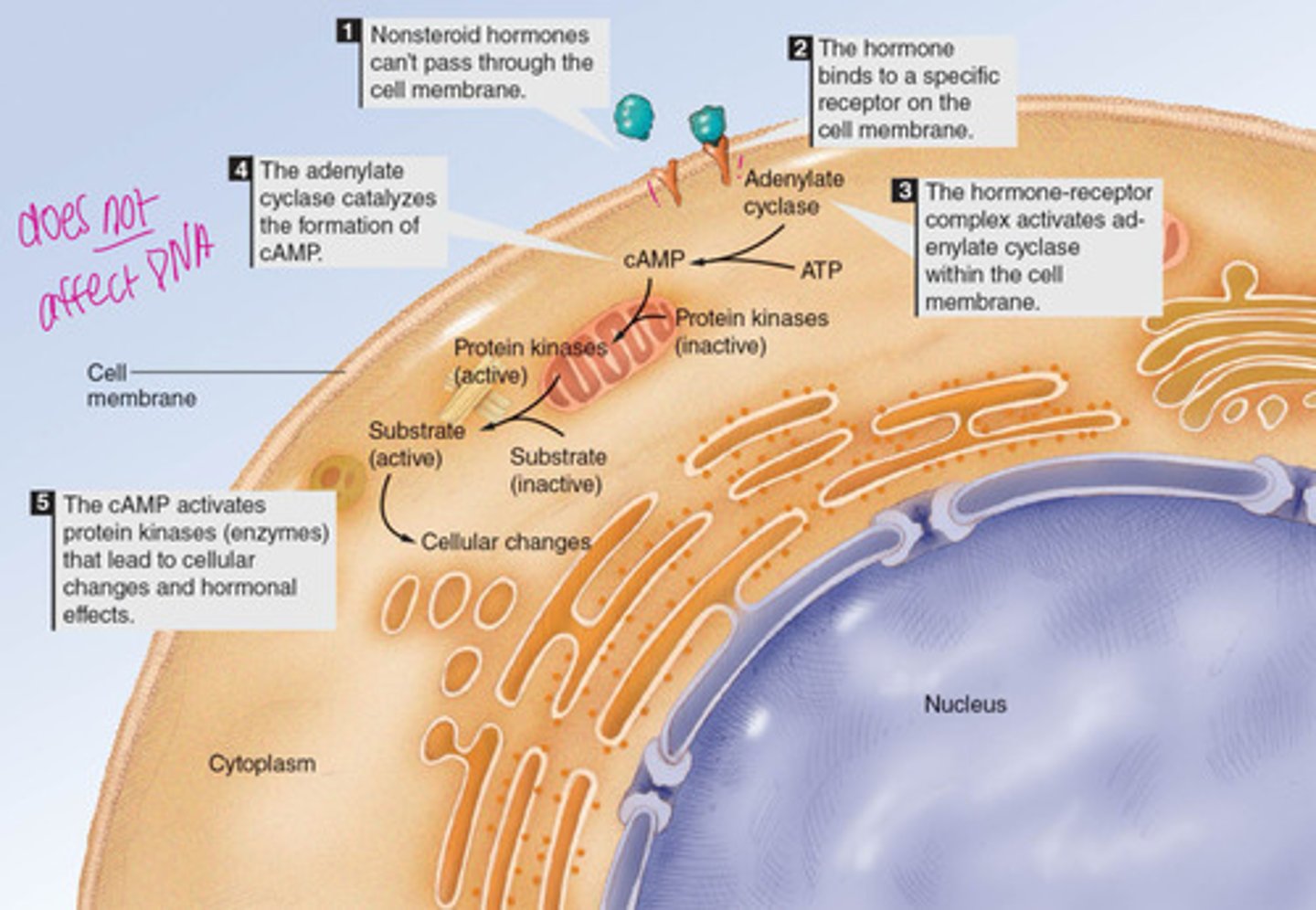
what are the receptors on the cell membrane considered for nonsteroid hormones?
second messengers that carry out hormone effects and intensify the strength of the hormone signal
what are the three most common second messengers?
- cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP)
- cyclic guanine monophosphate (cGMP)
- inositol triphosphate (IP3), diacylglycerol (DAG)
explain this image and how it relates to non-steroid hormone action
- needs receptor
- does NOT affect DNA
what is the third class of (pseudo) hormones
- prostaglandins
what are prostaglandins derived from?
arachidonic acid
prostaglandins act as ____ hormones, ____ area
local, immediate
what are the 2 kinds of responses that prostaglandins illicit/produce?
- inflammatory response!!! (swelling, vasodilation)
(ex: eye swells when you get punched in the eye)
- sensitize nociceptor-free nerve endings (pain)
can endocrine glands produce more than one hormone?
yes!
what are the major endocrine glands responsible for metabolic regulation? !!!!
- anterior pituitary gland
- thyroid gland
- adrenal gland
- pancreas
(APTA haha)
what do the hormones released from these glands affect during exercise?
metabolism of carbohydrate and fat during exercise
what is the anterior pituitary gland attached to?
inferior hypothalamus
what are the three lobes of the anterior pituitary
anterior, intermediate, posterior
which lobe of the anterior pituitary gland is blood rich?
anterior
which lobe of the anterior pituitary gland is free of blood and very neurological?
posterior
what does the anterior pituitary gland secrete hormones in response to?
hypothalamic hormone factors
what has to happen for anything to happen in the anterior pituitary?
secretion of releasing factors from the hypothalamus
does exercise decrease or increase the secretion of all anterior pituitary hormones?
increase
what hormone is released from the anterior pituitary gland?
growth hormone (human growth hormone) and thyrotropin/thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)
what is important to note about GH?
- potent anabolic hormone (anabolic androgenic - deeper voice, sharper jaw)
- builds tissue, organs
- promotes muscle growth (hypertrophy)
- stimulates fat metabolism
what is GH release proportional to?
exercise intensity
what hormones does the thyroid gland release?
triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4)
what does secretion of T3 and T4 increase when you exercise?
- metabolic rate of all tissues
- protein synthesis
- number and size of mitochondria (more ATP, more oxygen carrying capacity - mitochondrial biogenesis)
- glucose uptake by cells
- rate of glycolysis, gluconeogenesis
- FFA mobilization
besides GH hormone, what other hormone is released by the anterior pituitary gland?
thyrotropin/thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH)
what happens to TSH once it is released?
- it travels to the thyroid gland and stimulates T4 and T3 release
does exercise increase TSH release?
yes
short term exercise ____ T4.
increases (delayed release)
what does prolonged exercise do to T4 levels? what does it do to T3 levels?
T4 levels stay constant while T3 levels decrease
what does the adrenal medulla release?
catecholamines (epinephrine and norepinephrine)
what are catecholamines?
hormones for fight or flight (EP and NE)
what percent of catecholamines are epinephrine? what percent are norepinephrine?
- EP = 80%
- NE = 20%
does exercise increase or decrease sympathetic nervous system response and in turn EP and NE production?
increase
what things in the body increase because of catecholamine release?
- heart rate, contractile force of skeletal muscle, blood pressure (sympathetic nervous system), glycogenolysis (Ca+), FFA, and blood flow to skeletal muscle
where is the adrenal cortex located?
sitting on top of the kidney
what hormone does the adrenal cortex release?
corticosteroids/glucocorticoids, mineralcorticoids, gonadcorticoids: CORTISOL
why are corticosteroids also called glucocorticoids?
because corticosteroids stimulate the production of glucose
what is the major glucocorticoid?
cortisol
what is cortisol known as?
the "stress hormone"
what affect does cortisol have on gluconeogeneisis?
increases gluconeogenesis (we crave sweets when we're stressed because of this release of sugar)
what other processes does cortisol increase?
FFA mobilization and protein catabolism (Krebs cycle if we can't make enough glucose)
what two hormones are released from the pancreas?
insulin and glucagon
does insulin raise or lower blood glucose levels?
lowers blood glucose
when is insulin released in the body?
- whenever we eat food for some of the glucose to be stored in muscle or the liver
is there more glucose stored in the liver or in muscle?
in the liver (even though there is a lot in muscle too being that there is more muscle throughout the body)
(liver relative muscle absolute)
what does insulin counter and what does is oppose?
- insulin counters hyperglycemia, opposes glucagon (cortisol)
does insulin increase or decrease glucose transport into cells?
- increase
does insulin increase or decrease the synthesis of glycogen, protein, and fat?
- increase
does insulin inhibit or promote gluconeogenesis?
inhibits
does glucagon raise or lower blood glucose levels?
raises blood glucose
what does glucagon counter and what does it oppose?
- counters hypoglycemia, opposes insulin
when is glucagon released?
- when our bodies are in a fasting state (when we don't eat enough like when you're class and you don't eat breakfast in the am) and need blood sugar to go up
are glycogenolysis and gluconeogensis increased or decreased with the release of glucagon?
increased
what is glycogen broken down into in glycogenolysis?
glucose
what are FFAs and proteins turned into in gluconeogenesis?
glucose
what substance is broken down into glucose in glycogenolysis?
glycogen
what substances turn into glucose in gluconeogenesis?
FFAs and proteins
what two things does adequate glucose during exercise require?
- glucose release by liver
- glucose uptake by muscles
what are the 4 hormones that increase glucose circulation during exercise?
- glucagon
- epinephrine
- norepinephrine
- cortisol
how does GH affect FFA mobilization and cellular glucose uptake during exercise?
- increase FFA mobilization, decrease cellular glucose uptake
how does T3 and T4 affect glucose catabolism and fat metabolism?
- increase glucose catabolism and fat metabolism
what does the amount of glucose released from the liver depend on?
exercise intensity and duration
(ex: drive over speed limit = willl run out of gas quicker)