To determine the heat of reaction of hydrochloric acid with sodium hydroxide i.e. the heat of neutralisation
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
Theory
• A known volume and concentration of hydrochloric acid (HCl) is reacted with the same volume and same concentration of sodium hydroxide (NaOH)
HCl + NaOH → NaCl + H2O
• This is an exothermic reaction. The rise in temperature is measured and from this the heat of reaction can be calculated
Procedure
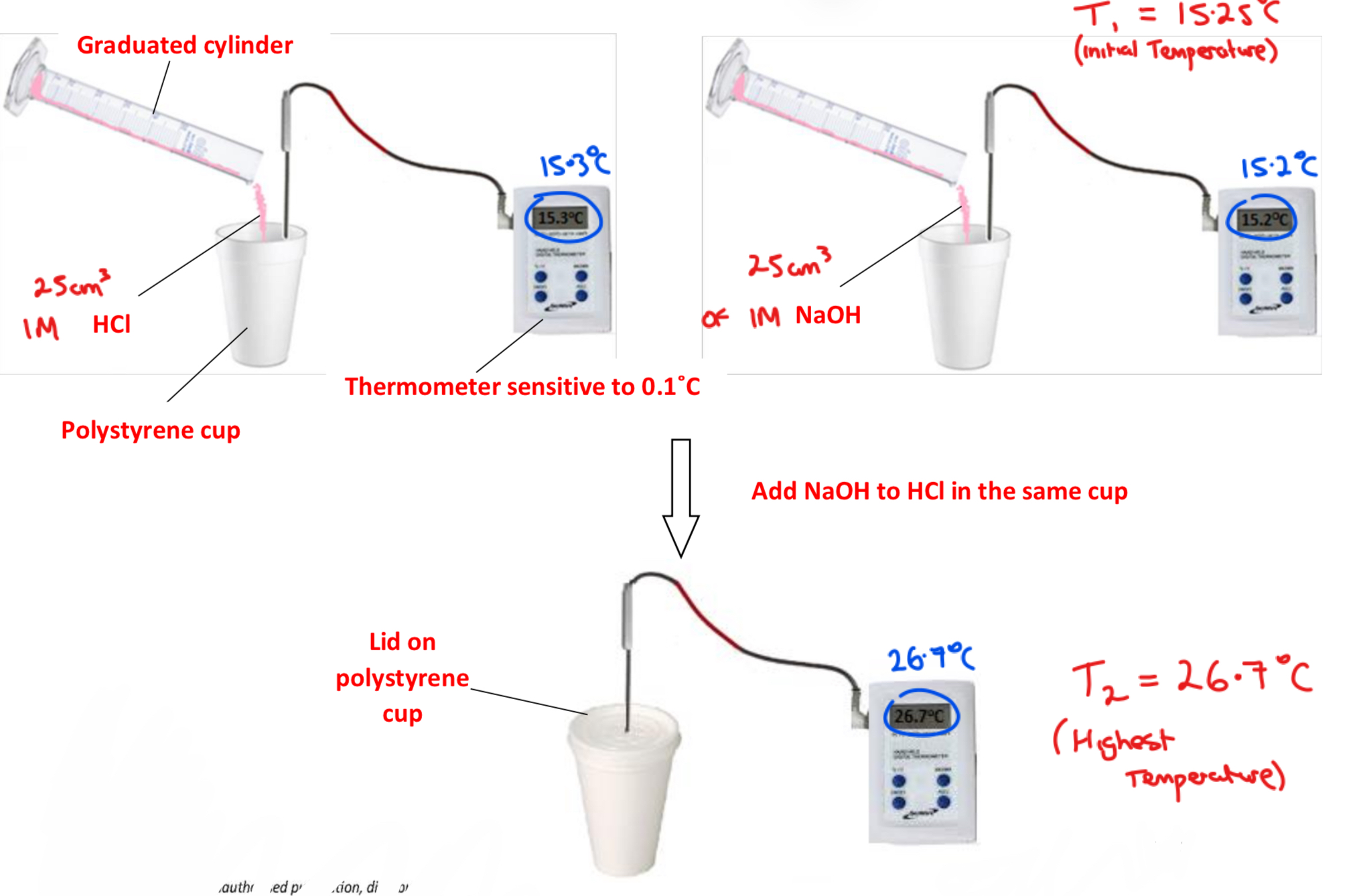
➢ Using a graduated cylinder, add 25 cm3 of 1 M hydrochloric acid (HCl) to a polystyrene cup and add 25 cm3 of 1 M sodium hydroxide (NaOH) to a separate polystyrene cup
➢ Record the temperature T1 of each solution using a thermometer sensitive to 0.1˚C - if the temperature of the two solutions are not equal, calculate their average
➢ Quickly pour the NaOH into the HCl, apply the lid quickly and continuously stir the solutions
➢ Record the maximum temperature obtained T2
➢ Record the rise in temperature T2 – T1, and calculate the heat for the reaction using m X c X ΔT and hence the heat of reaction/neutralisation
Why are polystyrene cups used in this experiment?
Polystyrene cups are used as:
i) They are excellent insulators and will only allow a minimal heat loss to the surroundings
ii) They have a negligible heat capacity – they will absorb a negligible amount of heat away from the reaction
Give an advantage and disadvantage to using a pipette/burette to measure out the solutions
Advantage: A pipette/burette is more accurate than a graduated cylinder
Disadvantage: A pipette/burette is very slow to measure out solutions
Note: A graduated cylinder is generally used and not a pipette
If the hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide solutions had been stored at slightly different temperatures, explain how the initial temperature of the reaction mixture could have been obtained
An average temperature of the two solutions could have been calculated
How do we know that the reaction of HCl and NaOH is exothermic?
The temperature rises; exothermic reactions are associated by a rise in temperature
Give two reasons continuous stirring of the solutions is essential
1) To distribute the heat evenly and take accurate temperature readings
2) To ensure the solutions react completely
Give three precautions that should be taken to accurately measure the change in temperature
1) Once the solutions are mixed quickly cover the polystyrene cup with a lid to avoid heat loss to surroundings.
2) Ensure no splashing and loss of volume of liquid occurs - leads to inaccurate results
3) A sensitive thermometer should be used – one that reads to at least 0.1 °C / 0.1 K
After the temperature of the mixed acid and base solution rises, the temperature will then gradually drop. What is the reason for this?
The temperature of the solutions after mixing will be greater than room temperature, heat will be lost to the surroundings
Why are concentrated solutions of hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide used? i.e. 1 Molar solution
Concentrated (1 M) HCl and NaOH are used to ensure a sufficiently large, measurable temperature change, reduce experimental error, and allow simple, accurate calculations of the heat of reaction.
Give two safety precautions in this experiment
- As concentrated solutions of HCl and NaOH are being used, they are corrosive and cause burns
1) Safety glasses should be worn to avoid them coming into contact with eyes
2) Gloves and a lab coat should be worn to avoid them coming into contact with skin
State and explain two further modifications that could be made if the value for heat of neutralisation between hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide was lower than the expected value
1) More insulation could be placed around the polystyrene cup to prevent heat loss – a more accurate rise in temperature would be recorded Example: Cotton wool
2) Greater volumes of acid and base could be used – would result in a greater temperature rise which is easier to measure accurately
Define specific heat capacity (c)
• Specific heat capacity is the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 kg of a substance by 1 Kelvin
Note: Specific heat capacity X mass = total heat capacity
c X m = C