ATD QUIZ 2
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
Prevailing Winds
Amihan (Northeast Monsoon) and Habagat (Southwest Monsoon)
Amihan
Cold and Low Velocity Wind (Winter Monsoon)
October to April
Month range of Amihan
Northeast
Direction of Winter Monsoon (Amihan)
The positive (+) zone
Trade Winds
Constant winds (present throughout the year)
They are Easterly winds (winds coming from the east)
Habagat
Hot and Humid, and High Velocity Wind (Summer Monsoon)
It comes along with rain (Tagulan and Typhoons)
May to September
Month range of Habagat
Southwest
Direction of summer monsoon (Habagat)
The negative (-) zone
Trees
Wind breakers, a solution to break wind from typhoons caused by Habagat
Amihan
desirable wind for buildings
Habagat
undesirable wind and should be avoided in buildings
6:1
Ratio of roofing
West-East
Best orientation of roofing
Windward
Positive Zone (+) (Northeast), where the wind enters or originates
Leeward
Negative Zone (-) (Southwest), where the wind exits
High Pressure to Low Pressure
What happens to wind pressure if wind enters (Windward) a building (Leeward)
Windward to Leeward
Flow of Wind: From positive zone to negative zone
Awning Windows
Best window considering Tropical Design
Casement Windows
If wind is sideways, wind cannot enter this type of window because it is only open upfront
Least resistance
Wind flows through areas with what?
Screens
They offer wind resistance. Remove for Stronger wind current
Lower and Higher
Ideally, Windows in windward should be _____ and ______ on Leeward. (Hot air rises)
above and below
Hot air is always _____ and cold air stays ______
Materials Recovery Facility
MRF
Habagat (Southwest Monsoon)
MRF is an exception, it needs this type of wind
Ground Level windows
This window level works best with Tropical design. However, it is not recommended considering electrical, privacy, and child safety
Artificial Ventilation
Ventilation that requires energy
Active Ventilation
another term for artificial ventilation
2.4 meters
minimum ceiling height for atificially ventilated spaces
For faster process of cooling a space. (Lesser volume, faster cooling)
Why are standard ceiling heights lower in artificially ventilated spaces?
Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning
HVAC
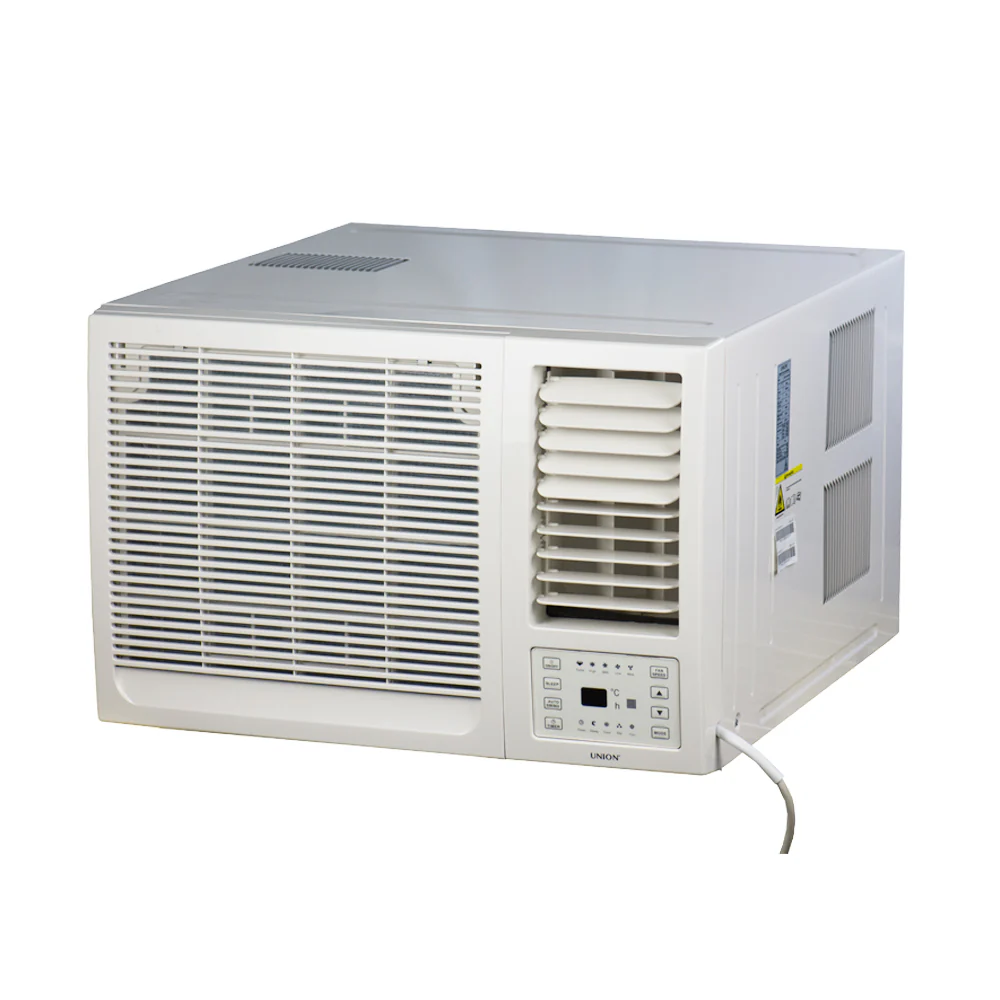
Window-type aircon

Cabinet-type aircon

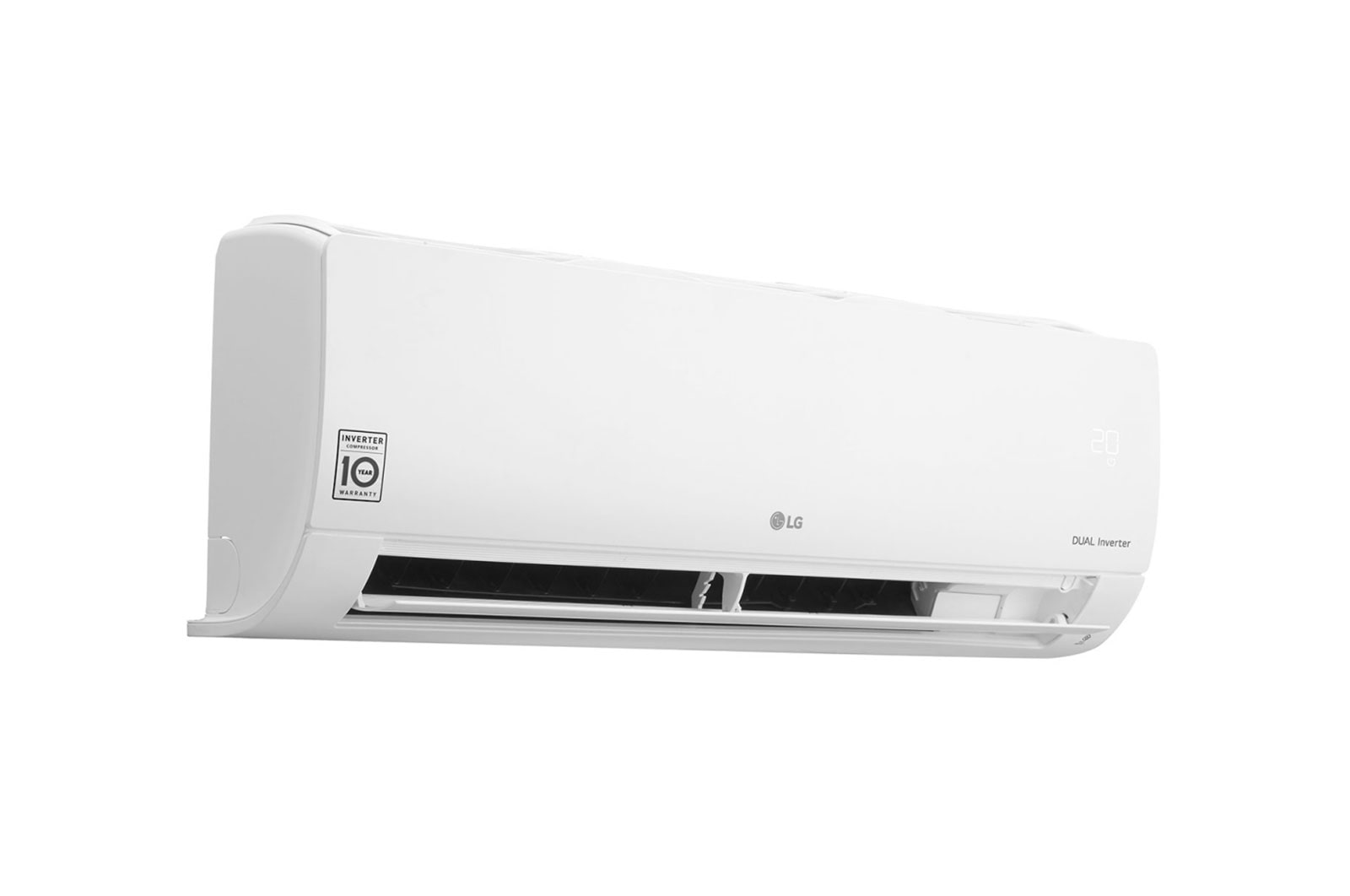
Split-type aircon

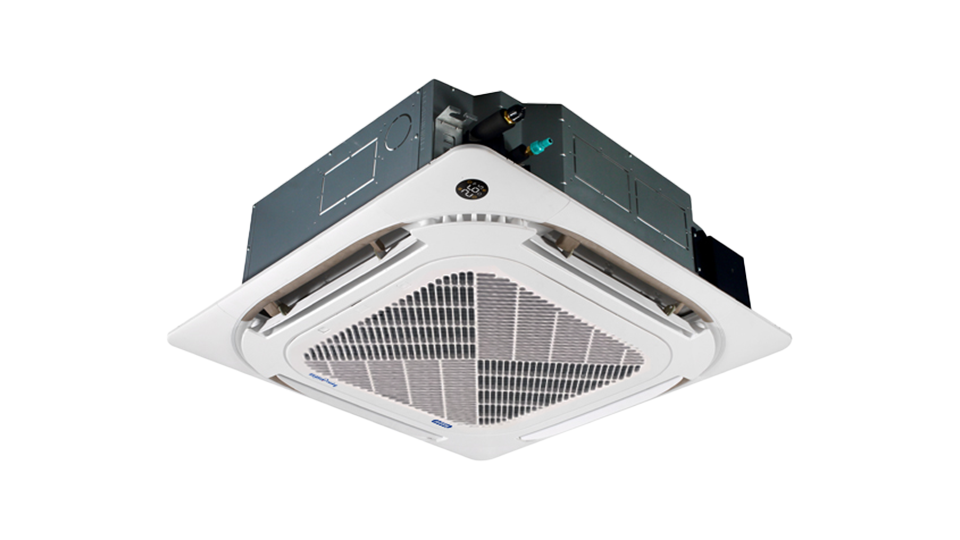
Cassette-type aircon

Energy Efficiency Ratio (ERR)
Identifies an aircon’s rating of energy consumption (Higher rating = Lesser energy consumption)
Natural Ventilation
Ventilation that does not require energy to work
Passive Ventilation
Another term for natural ventilation
2.7 meters
minimum ceiling height for naturally ventilated spaces
Primarily to separate hot air from spaces that are accessible to users (hot air circulates upwards). Also, for better air circulation.
Why are standard ceiling heights higher in naturally ventilated spaces?
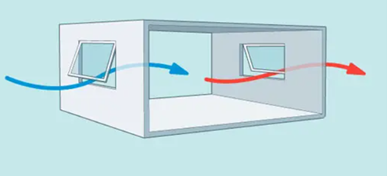
Cross-ventilation
2-opposite windows in a single space
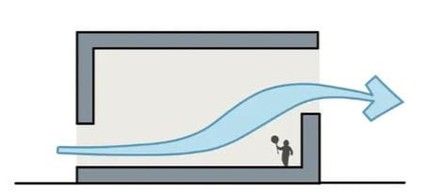
Single-sided ventilation
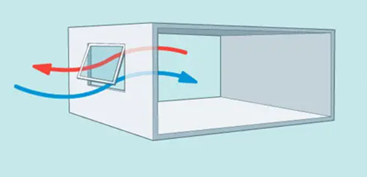
smaller, larger
2 separate _______ windows (for entry and exit) are more preferrable than 1 _______ window in a single-sided ventilation
Wind Catcher (Concrete Ledge)
an exterior element that helps redirect wind into the windows.

Stack effect Ventilation
Use of hot air pressure to suction heat from the building outside through a space in the middle called the atrium.
Mostly used in high-rise buildings
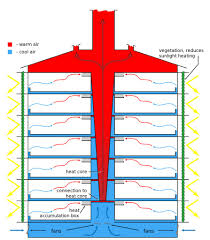
Chimney Effect ventilation
Another term for Stack effect Ventilation
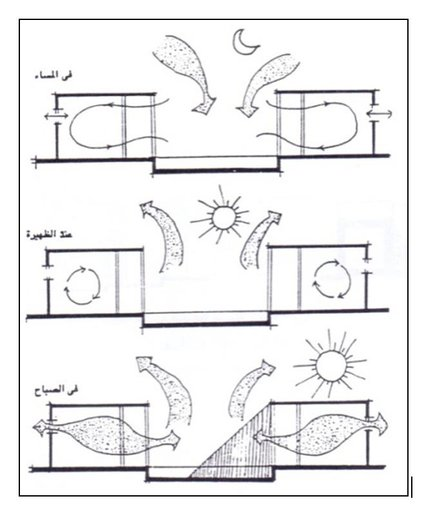
Courtyard Ventilation
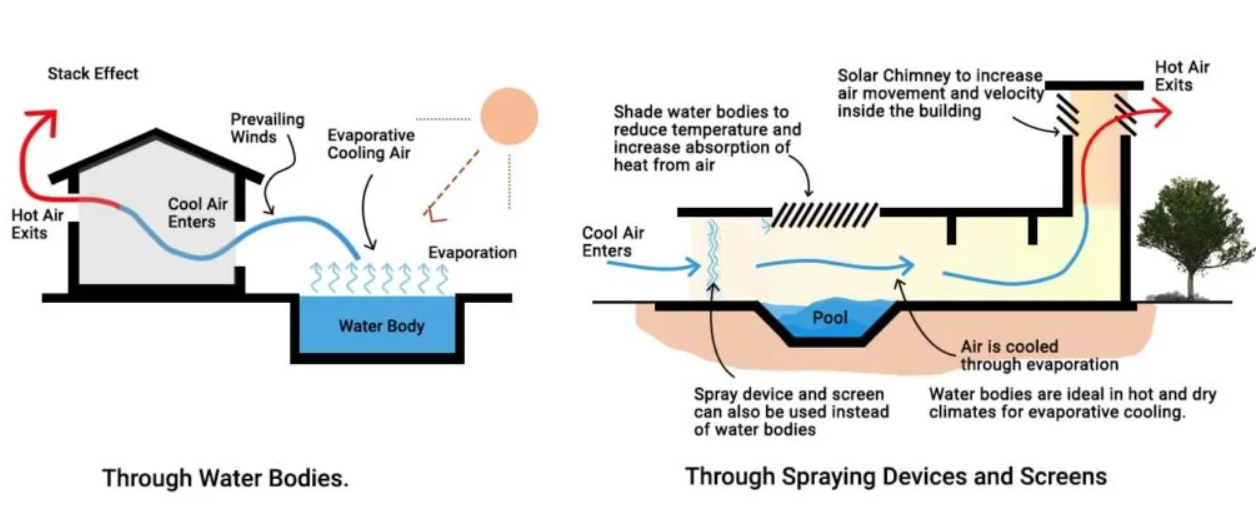
Evaporative Cooling
Use of any forms of water through evaporation to cool the building
Roof Ventilation
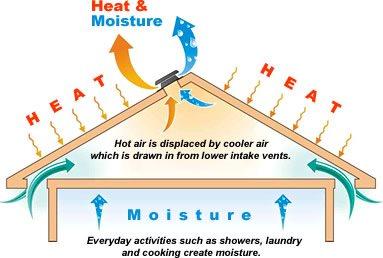
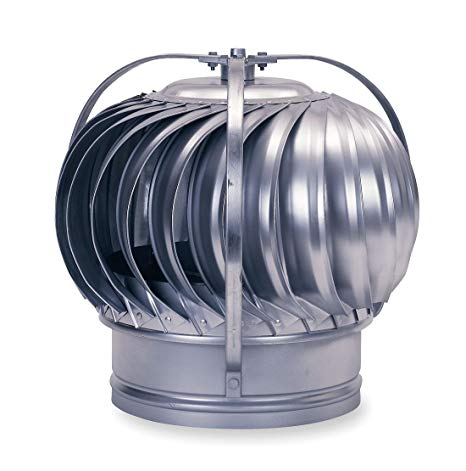
Turbine Ventilator
A device that spins by using the force of the wind and utilizing that spinning motion to act on a fan that suctions hot air from the roof outside to the air.
Not recommended by Sir Sotto
