SQL - Basics
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
What is the difference between DBMS and RDBMS?
Feature | DBMS | RDBMS |
|---|---|---|
Data Storage | Stores data as files | Stores data in tabular form (tables) |
Data Relationships | No relationships between data | Tables are related (e.g., via foreign keys) |
Normalization | Not supported | Supported to reduce redundancy |
Data Volume | Handles small amounts of data | Handles large amounts of data |
Examples | XML, file systems | MySQL, PostgreSQL, SQL Server, Oracle, MS Access |
What is a Constraint in SQL?
SQL constraints are used to specify rules for the data in a table.
What are the types of constraints?
Constraint | Description |
|---|---|
PRIMARY KEY | Uniquely identifies each row in a table |
NOT NULL | Prevents storing |
FOREIGN KEY | Links to a primary key in another table to enforce referential integrity |
CHECK | Validates column values against a specified condition |
DEFAULT | Assigns a default value when no value is provided by the user |
UNIQUE | Ensures all values in the column are distinct |
What is the difference between Primary key and Unique key?
Feature | Primary Key | Unique Key |
|---|---|---|
Null Values | Cannot accept | Allows one |
Index Type | Creates a clustered index automatically | Creates a non-clustered index |
Count per Table | Only one primary key allowed | Multiple unique keys can exist |
What are Triggers?
Triggers are stored programs, which are AUTOMATICALLY executed or fired when some events (insert, delete and update) occur.
Types of triggers
DML
DDL
Log ON
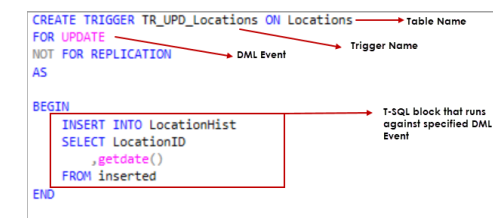
CREATE TRIGGER TR_UPD_Locations
ON Locations
FOR UPDATE
NOT FOR REPLICATION
AS
BEGIN
INSERT INTO LocationHist (LocationID, UpdateDate)
SELECT LocationID, GETDATE()
FROM inserted
END
An INSTEAD OF trigger is a trigger that allows you to skip an INSERT , DELETE , or UPDATE statement to a table or a view and execute other statements defined in the trigger.
What is a View?
A view is a VIRTUAL table which consists of a subset of data contained in single table or more than one table.
CREATE VIEW [India-Customers] AS
SELECT CustomerName, ContactName
FROM Customers
WHERE Country = ’India’;
What are advantages of View?
1. Indexed Views to improve the performance.
2. Extra security – DBA can hide the actual table names and expose views for Read operations only
Query is stored but the actual data is never stored like a table
What is the difference between Having clause and Where clause?
1. WHERE Clause is used before GROUP BY Clause. HAVING Clause is used after GROUP BY Clause.
SELECT COUNT(CustomerID), Country
FROM Customers
WHERE Country = 'India'
GROUP BY Country
HAVING COUNT(CustomerID) > 5;2. WHERE Clause cannot contain AGGREGATE function. HAVING Clause can contain aggregate function.
SELECT EmpName FROM Employee
GROUP BY EmpName
HAVING SUM(EmpSalary) <30000What is Sub query or Nested query or Inner query in SQL?
A Subquery/ Inner query/ Nested query is a query within another SQL outer query and embedded within the WHERE clause.
What is Auto Increment/ Identity column in SQL Server?
Auto-increment allows a unique number to be generated automatically when a new record is inserted into a table.
Mostly auto increment is set on the primary key only.