L7 Neurobiology ✅
1/3
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
4 Terms
Multipolar
Bipolar
Unipolar or pseudounipolar
Sensory neuron
Interneuron
Motor neuron
What cells depend on ion movement across membranes?
What creates the membrane potential?
Many processes from cell body multiple dendrites & one axon
Two main processes
One main process from cell body
Transmit information about sensory stimuli from receptors to the central nervous system
Connect neurons to one another, often short, unmyelinated axons and complex dendrite
Carry impulses from central nervous system to effector organ and Initiate contractions or secretions
Neurons/muscles
Facilitated diffusion of ions across cell membranes
Membrane potential
What charge does cytoplasm have?
Plasma membrane
Define electrochemical gradient
Voltage difference across cell membrane measured in V or mV with inside of cell negative relative to outside of cell that arises from unequal distribution of ions across membrane
Net neutral charge
Functions as capacitor that stores electrical energy by accumulating charges on two closely spaced surfaces insulated from each other
Gradient independent from membrane potential that is based on concentration that moves ions according to the net effect of concentration and charge
Equilibrium potential (reversal potential of an ion)
What can be used to calculate equilibrium potential?
Resting membrane potential
What helps maintain RMP?
How do resting neurons maintain concentration gradients?
What are leaky channels?
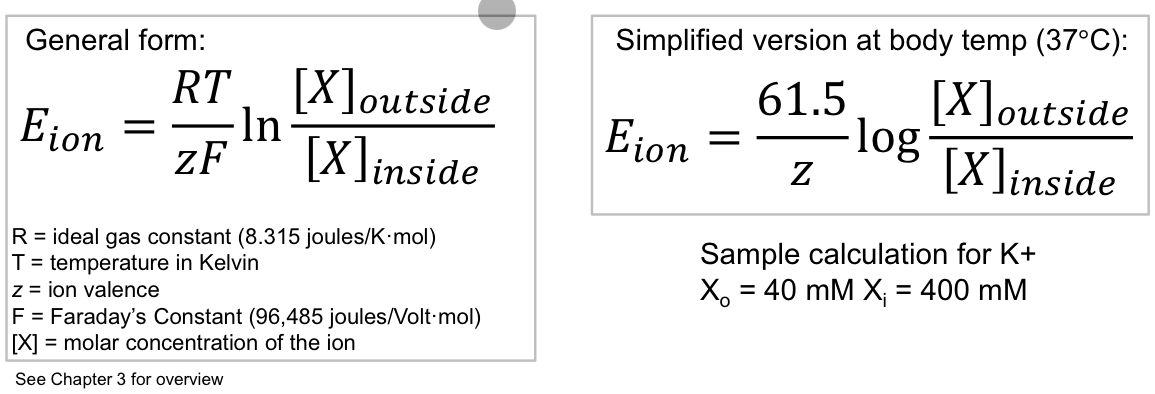
The membrane voltage at which an ion is at equilibrium where no net movement occurs, and if the membrane potential changes from this value, the driving force (net electrochemical gradient) causes the ion to flow into or out of the cell, depending on which gradient (electrical or concentration) is stronger.
Nernst equation:
In neurons, -70 mV where its actively maintained using dynamic equilibrium
More + ions outside, with more - inside the plasma membrane
Na/K pump: maintains ionic gradients by active transport
Leaky channels: predominant determinant of RMP
Active transport
Constitutively active channels that allow facilitated diffusion and leak based on gradients
What causes electrical signals?
What changes membrane potential?
Driving force
Depolarization
Hyperpolarization
Repolarization
Changes in membrane permeability
Opening and closing ion channels
Governs predominant ion flow as the difference between membrane potential and ion equilibrium potential with larger difference meaning larger driving force
Membrane potential becomes less negative with +ions entering and -ions exiting
Membrane potential becomes more negative with +ions exiting and -ions entering
Membrane potential returns toward RMP