Chapter 21 - Nuclear Chemistry
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
69 Terms
Radioactivity:
the spontaneous emission of particles or electromagnetic radiation
All elements with Z __ are radioactive
> 83
What is Z?
atomic number — the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom
In nuclear reactions, elements are:
converted to other elements or isotopes
In nuclear reactions, what subatomic particles are involved?
protons, neutrons, and α particles
What are α particles?
a type of radiation emitted during alpha decay, a process by which unstable atoms release excess energy
In nuclear reactions, reactions are accompanied by:
the absorption or release of tremendous amounts of energyr
In nuclear reactions, rates of reaction are:
normally not affected by temperature, pressure, or catalysts
What is a positron?
a type of subatomic particle that is the antiparticle of an electron
What does antiparticle mean?
a particle that has the same mass as a corresponding particle but has opposite charge and other quantum properties
How do you balance a nuclear reaction?
simply balance the total of all atomic numbers and total of all mass numbers for the products and reactants
Principle factor for nuclear stability is:
neutron - to - proton ratio (n/p)
There are more stable nuclei with 2:
8, 20, 50, 82, or 126 protons or neutrons (Magic Numbers)
All with atomic number > 83 are:
radioactive
All isotopes of _ and _ are radioactive
Tc and Pm
The conversion of one nuclide into another is called:
nuclear transmutation
What are the 5 types of radioactivity?
alpha decay
beta decay
gamma decay
positron emission (β + decay)
electron capture
Alpha particles can be stopped by:
a piece of paper
Alpha decay:
occurs when an unstable nucleus emits a particle composed of two protons and two neutrons (called an α particle)
nucleus loses protons and neutrons
Beta decay/emission:
occurs when an unstable nucleus emits an electron (called an β particle )
nucleus loses neutron and electron, gains proton
Beta particles are stopped by:
few millimeters of Al
Gamma radiation:
significantly different from alpha/beta decays, gamma ray emission is the emission of gamma radiation, a form of electromagnetic radiation
excited nuclei lose this extra energy in the form of light
high energy nuclei lower their energy by emitting gamma rays
Gamma rays easily pass through:
1cm of Pb
Positron emission ( β + decay):
the emission of a positron from the nucleus
nucleus loses proton; gains neutron and emits positron
Electron capture:
occurs when an inner electron in an atom is captured by the atom’s nucleus
generally occurs when the inner electron combines with a proton to make a neutron
nucleus loses a proton and electron, gains a neutron
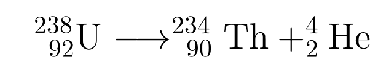
What type is this?
alpha decay
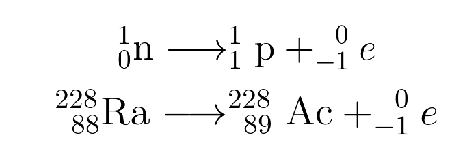
What type is this?
beta decay/emission
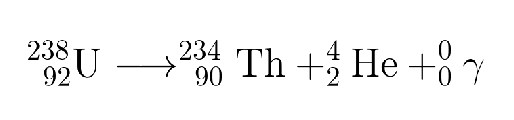
What type is this?
Gamma ray emission
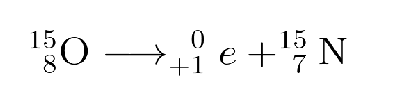
What type is this?
Positron emission
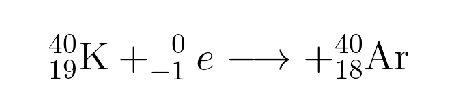
What type is this?
Electron capture
EC processes produce:
x-rays
In a nuclear stability graph, stable nuclei are in an area of the graph known as:
belt of stability
In a nuclear stability graph, the most radioactive nuclei lie:
outside the belt
In a nuclear stability graph, above the belt the nuclei have:
higher neutron - to - proton ratio
In a nuclear stability graph, below the belt:
isotopes mostly decay by beta emission
In a nuclear stability graph, above the belt isotopes mostly decay by:
positron emission or electron capture
Nuclear Binding Energy:
A quantitative measure of nuclear stability — the energy required to break up a nucleus into its component protons and neutrons
Proton mass =
1.0073 amu
Electron mass =
5.4858x10^-4 amu
Neutron mass =
1.0087 amu
The difference between the mass of an atom and the sum of the masses of its protons, neutrons, and electrons is called the:
mass defect
The disintegration of a radioactive nucleus often is the beginning of a:
radioactive decay series
Radioactive decay series:
a sequence of nuclear reactions that ultimately result in the formation of a stable isotope
The beginning radioactive isotope is called the:
parent
The product isotope is called the:
daughter
All radioactive decays obey:
first - order kinetics
What is k in radioactive decay?
decay constant
High k =
faster decay
Low k =
slower decay
Common dating methods:
Radiocarbon
Uranium – lead
Rubidium – strontium
Potassium – argon
Nuclear transmutation differs from radioactive decay in that transmutation is brought about by:
the collision of two particles
What make is possible to synthesize the so called transuranium elements?
particle accelerators
What are transuranium elements?
elements with atomic numbers greater than 92
Nuclear fission:
the process in which a heavy nucleus (mass number > 200) divides to form smaller nuclei and one or more neutrons
Critical Mass =
The minimum mass of fissionable material required to generate a self - sustaining nuclear chain reaction
Nuclear fusion =
the process of combining small nuclei into larger ones
Because fusion reactions take place at very high temperatures, they are often called
thermonuclear reactions
In medicine, radioactive isotopes are used as:
tracers
Sodium - 24 –
blood flow
Iodine - 131 —
thyroid conditions
Iodine - 123 —
brain imaging
Fluorine - 18 as [ 18 F]fluorodeoxyglucose –
PET scans
What is Internal therapy/Brachytherapy:
“radioactive seeds” Implant Ti capsules containing iodine - 125 can be implanted next to a tumor to kill the cancer cells
The fundamental unit of radioactivity is the:
curie (Ci)
1 Cu =
3.70 x 10^10 disintegrations per second
A common unit for the absorbed dose of radiation is the:
rad ( radiation absorbed dose)
1 rad =
1 x 10^-5 J/g of tissue irradiated
The rem ( roentgen equivalent for man) is:
determined from the number of rads
Number of rems =
number of rads x 1 RBE
RBE = the relative biological effectivness