MMI 188A: Midterm #2
1/143
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
144 Terms
where do T-cell precursors develop
The thymus
Where are T cells generated
stem cells in the bone marrow
What type of T cells are found in the cortex of the thymus
Immature T cells
What type of T cells are found in the Medulla
Mature T cells
Notch 1
- Found on suface membrane of T cell
- Binds to ligand thymic epithilium
- Interaction between the two is cleaved as Notch1 intracellular domain is sent to Nucleus
- Turns on expression of :
Removal of repressive transcription factors
Recruiting coactivating factors
What happens to apopotic T cells in the thymus
- Macrophages in cortex ingest apopotic T cells that failed further development
- Most T cells die in thymic cortex
What lineage are most T cells
Alpha-Beta
Alpha-Beta T cell development vs Gamma-Delta T cell development
- Commited double negative T cell progenitor has 2 choices
Gamma and delta rearrangement or B chain rearrangement
( B chain rearrangement more common b/c only 1)
2nd chance for gamma delta rearrangement or alpha chain rearrangement
alpha chain gene rearangement produces double positive CD4 and CD8 alpha-beta T cells
pre-TCR
surrogate alpha chain
placeholder after successful Beta chain rearrangement
placeholder until successful Alpha chain rearrangement
pre-TCR development
Step 1: 2 heterodimers of a B chain and PT-alpha chain form the pre-TCR
Step 2: Heterodimers form superdimer together
Step 3: Interactions with CD3 complex and Theta chain (intracellular) form a functional pre-TCR - signal for alpha chain rearrangement to take place
Step 4: After functional alpha chain rearrangement, association with complex to form T-cell receptor
B chain rearrangement
- similar to Ig heavy chain
-contain all three segments V-D-J
- 2 genes per chromosome and only 1 needed meaning 4 chances for beta chain rearrangements
alpha chain rearrangement
- similiar to Ig light chain
- contain 2/3 segments V-J
- can undergo several rearrangements due to 61 J segments
- only need one successfull rearrangement
- delta chain is lost during alpha chain rearrangement
Positive selection
- T cells must be able to work effectively with own MHC molecules
- After a double positive T cell interacts with epithelial cells in thymus it will only express CD4 or CD8
- Mature into Single Positive T Cells
negative selection
T cell receptors must not recognize self antigens from healthy cells
Central Tolerance
Removal of T cells with autoreactive TCRs in Thymus
Peripheral Tolerance
Treg Cells suppress autoreactive T cells outside of Thymus
AIRE
Autoimmune Regulator
- Induces expression of tissue specfiic genes in thymus to allow for negative selection
- Mutations in AIRE lead to autoimmunity
- autoimmunity: autoreactive T cells wont be targeted for apoptosis/phagocytosis
FOX P3
- type of transcription factor
- Expressed by T reg cells that suppress auto reactive T cells
T reg cells
- secrete transcription factor FOX P3
- Secrete suppressor cytokines IL-10, and TGF-beta
- suppress auto reactive t cells outside of thymus (peripheral tolerance)
T cell vs B cell facts
- Very few T cells in the body are specific for any one microbe
- B cells differentiate into plasma cells and send antibodies to infection
- T cells must physically go to infection site
TCRs and antigen specificity
- Each T cell has only one TCR specificity
- Diversity is from gene rearrangement in the receptor binding site
- TCR antigen binding domain is made from V-alpha and V-beta regions
CD3
- All T cells express CD3
- Associates with TCRs
- facilitates transport to the cell surface
- Allows for signal transduction due to having transmembrane domains after TCR encounters antigen
gamma-delta receptors
- gamma delta t cells can recognize antigens without MHC
- only 1-5% of t cells
- fever V and J gene segments
CD8 T cells function and ligand
- kill virus infected cells
- more effective on intracellular pathogens
- Bind to MHC class I
CD4 T cells function and ligand
- Bind to macrophages, release cytokines, induce higher capacity to kill bacteria inside
- Bind to B cells, release cytokines, drive differentiation into plasma cells to release more antibodies
- more effective on extracellular pathogens
- Bind to MHC class II
TH1 cells provide help to ________ and are a _______ type of T cell
macrophages
CD8 T cell
TH2 cells provide help _______ and are a ______type of T cell
B cells
CD4 T cell
Human Leukocyte Antigen (HLA)
Same as Major Histocompatability Complx (MHC)
Interchangeable name of MHC
HLA - Human Leukocyte Antigens
MHC class I binding domain
- CD8 co receptor binds to Alpha 3 domain of MHC class 1 heavy chain
- peptides bind to domain via their ends
- usually 8-10 aa
MCH class II binding domain
- CD4 coreceptor binds to Beta 1 domain of MHC class II
- peptide is longer than peptide binding groove and is thus held by interactions along its length
- 13-25 aa in length
Antigen processing
The intracellular degradation of proteins into peptides
Antigen presentation
loading of peptides onto MHC molecules
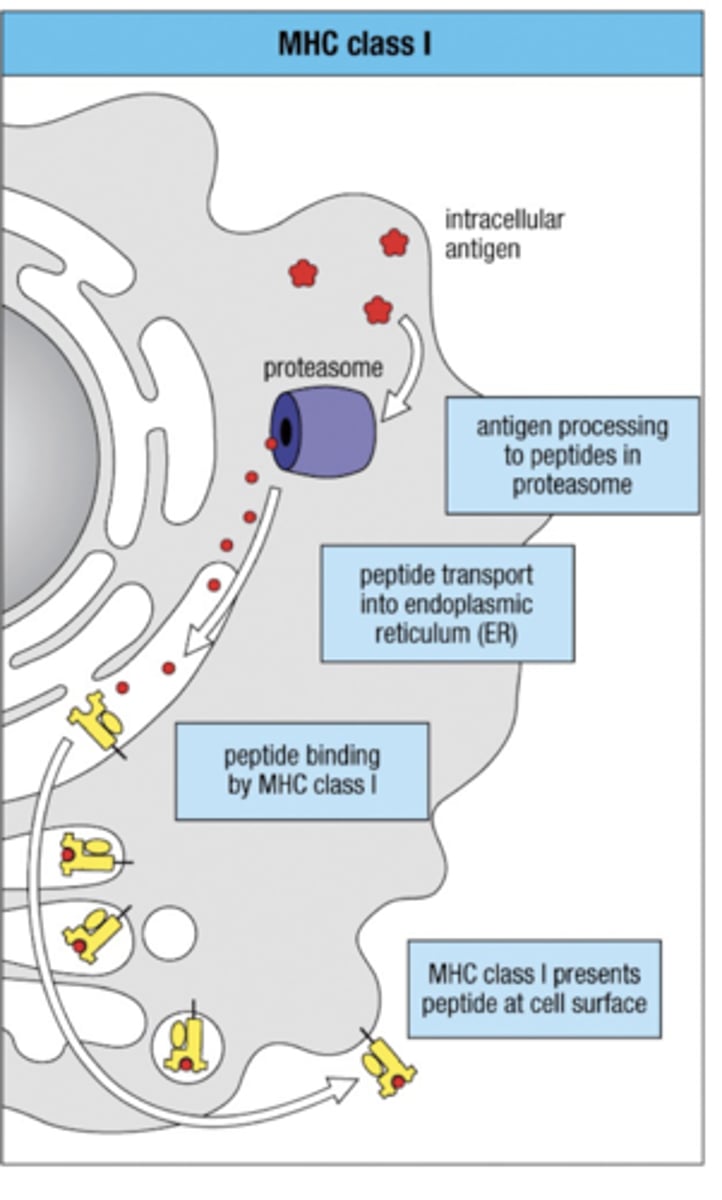
Endogenous pathway
Antigen processing pathway
- 1. intracellular antigen cut up into peptides via proteasome
- 2. Peptides allowed to enter ER via TAP (transporter associated w/ antigen processing)
- 3. Peptides meet and bind to MHC class I in Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
- 4. Bound MHC class 1 leaves via Golgi Apparatus to present antigen peptide on cell surface
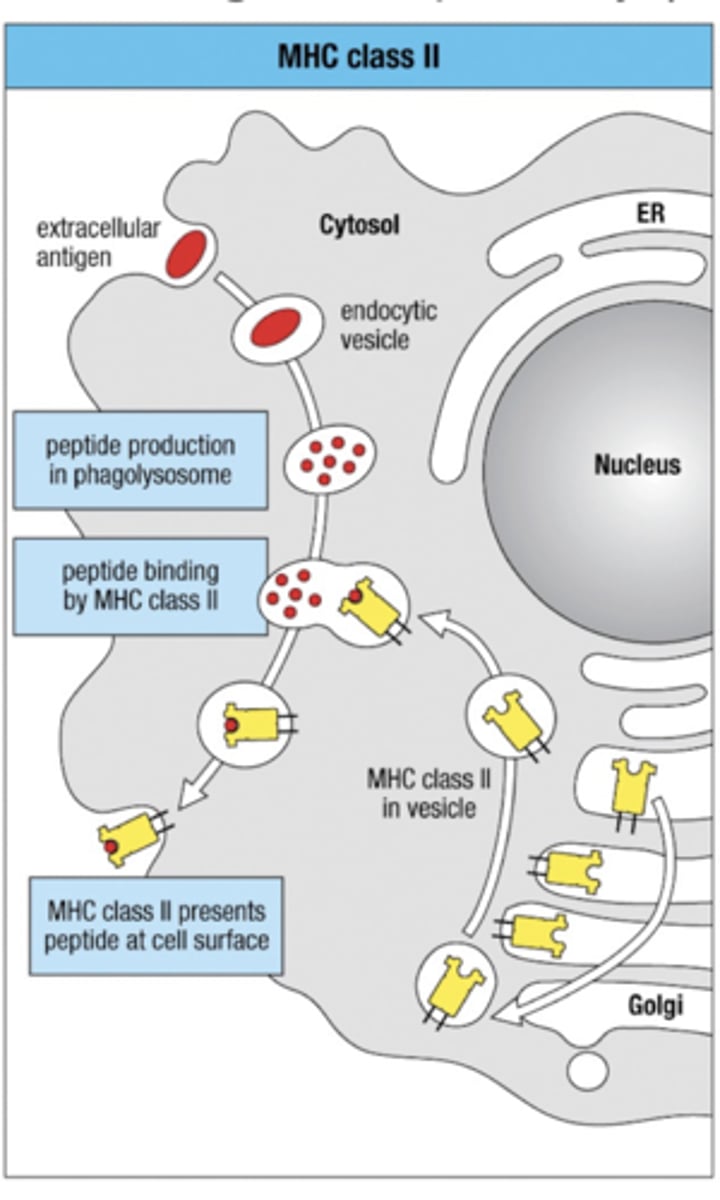
Exogenous Pathway
Antigen Processing Pathway
-1. Extracellular antigen enters and placed in vesicle
-2. Peptide production contained to phagolysosome
3. MHC class II leaves Golgi Apparatus in vesicle to go meet extracellular antigen peptides
4. fuse and bind together
5. MHC class II presents antigen peptide at cell surface
TAP
transporter associated with antigen processing
- found in endogenous pathway
- allows for peptides to pass from proteasome into ER
- peptides then meet MHC class I inside ER
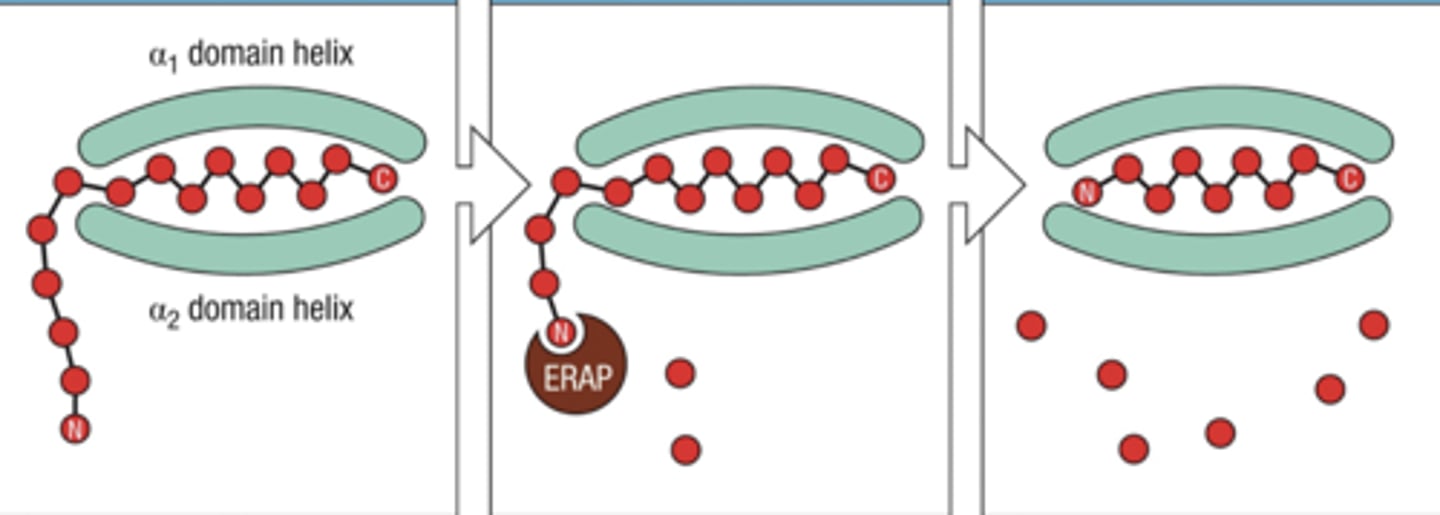
ERAP
trims peptides bound to MHC class I to improve binding affinity
What would a mutation on TAP cause
Bare lymphocyte syndrome
- MHC class I proteins would not present any antigens
Tapasin
- binds to MHC class I causing a conformational change that allows low affinity peptides to leave
- If a high affinity peptide binds to MHC class I then tapasin unbinds and binding domain closes
peptide loading complex
MHC class I peptide loading complex includes chaperones :
- calreticulin
-ERp57
- tapasin
MHC class II endocytic vesicles
endosomes contain proteases that are only activated after pH is lowered
proteases then cut up antigens into peptides for MHC class II
MHC class II Assembly
- while in ER invariant chain blocks peptides from binding, also directs MHC class II into endocytic vesicles
- once in vesicles, invariant chain is cleaved and CLIP is left in MHC class II to block other peptides
- HLA-DM facilitates removal of CLIP to allow for peptide binding
Invariant chain
- prevents peptide loading while in ER
- Directs MHC class II into endocytic vesicles
HLA-DM
facilitates release of CLIP, allowing peptides to bind
cross-presentation (cross-priming)
ingested antigens (typically leading to MHC class II/endogenous pathway) are transported from phagolysosome, where peptides are degraded to proteasomes ( MHC class I) can then enter the ER to bind to MHC class I and present to CD8 T cells
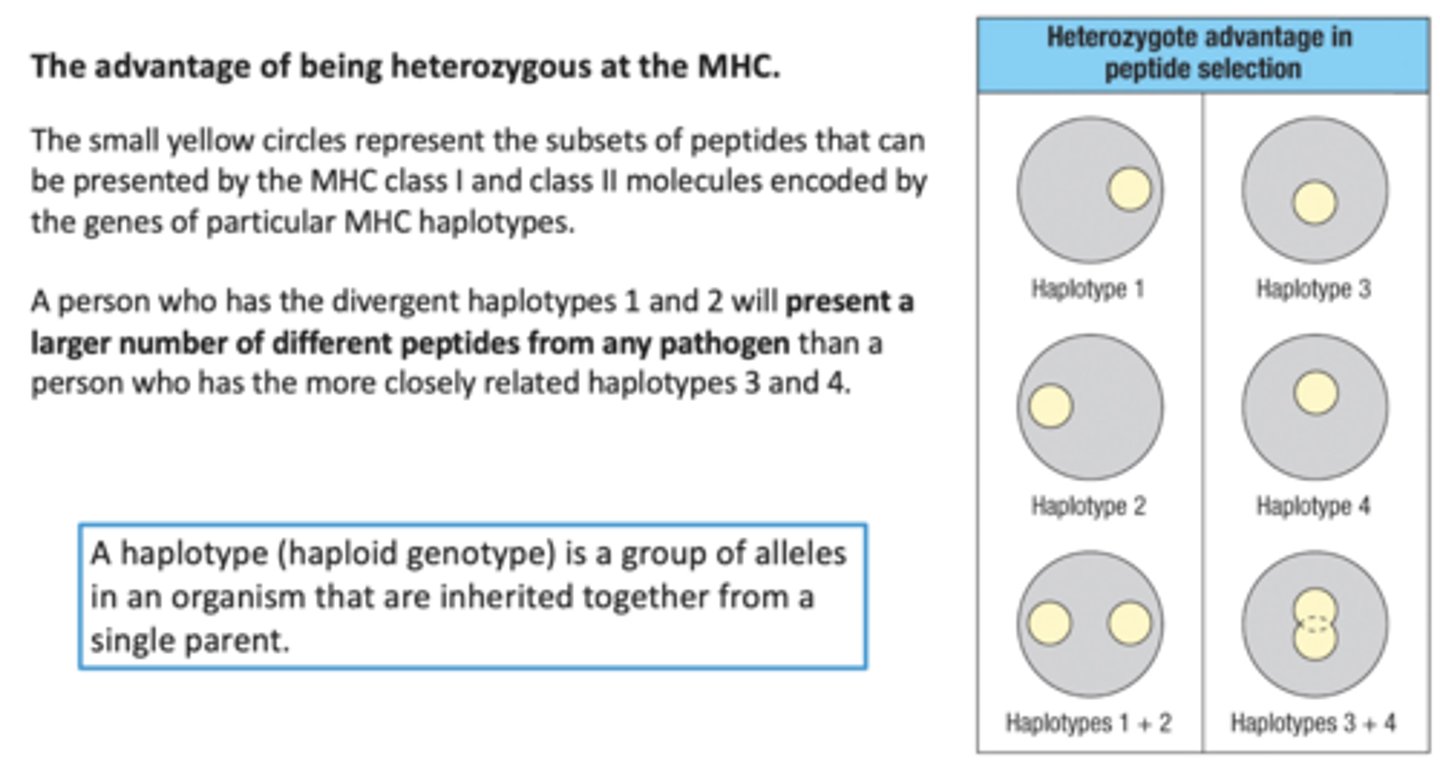
How does Achieving MHC Binding Diversity occur
Polygenic - Multiple genes encode MHC class I, II, and Beta proteins
Polymorphic - Multiple alleles of each gene are found in any population
Advantage of being Heterozygous at the MHC
How are new MHC alleles generated?
Interallelic conversion/ gene conversion
recombination between alleles of the same gene, typically from different parents
result is random and thus can either be beneficial or negative
Naive T lymphocytes
- T cells that have not yet been stimulated by antigen
- Recirculate through peripheral lymphoid organs
- Express L-selectin that binds to ligand on high endothelial venules
- Express TCR, but do not engage in effector fxns (cytokine production, cytolysis)
Effector T lymphocytes
- T cells that have differentiated in response to an antigen
- Perform effector fxns (cytokine production, cytolysis [cytotoxic t cells])
Immature Dendritic Cells
present in tissues
Mature dendritic cells
found in lymph nodes
What is the exit of the lymph node
efferent lymphatic vessels
High endothelial venules
entry point for T and B cells into the lymph nodes
What are the 'Main players' in binding naive t cells through to the HEV
- L-selectin (on naive T cells)
- CD34 and GlyCAM-1 (vascular addressins ) on HEVs
how do circulation naive T cells enter lymph nodes
- naive T cell enters HEV
- L-selectin from N. T cell binds to GlyCAM-1 and CD34 on HEV endothelium
- LFA-1 activated by chemokine and binds to ICAM-1
- T cell enters lymph node
Functions of T cell Integrins like LFA-1
- Adhesion of T cells to APCS
- Binding of T cells to endothelium
- Inflammatory cytokines and microbes
- Affinity of integrins and ligand is increased by chemokines and TCR ligation
CD34
vascular addressins on HEVs
bind to L-selectin
GlyCAM-1
vascular addressins on HEVs
bind to L-selectin
LFA-1
- receptor on naive T cell surface
- binds to ICAM-1,-2,-3 on HEVS endothelium
-Promotes adhesion and cytoskeletal reorganization during T cell activation
- Promotes stable TCR:MHC interaction (Anchor)
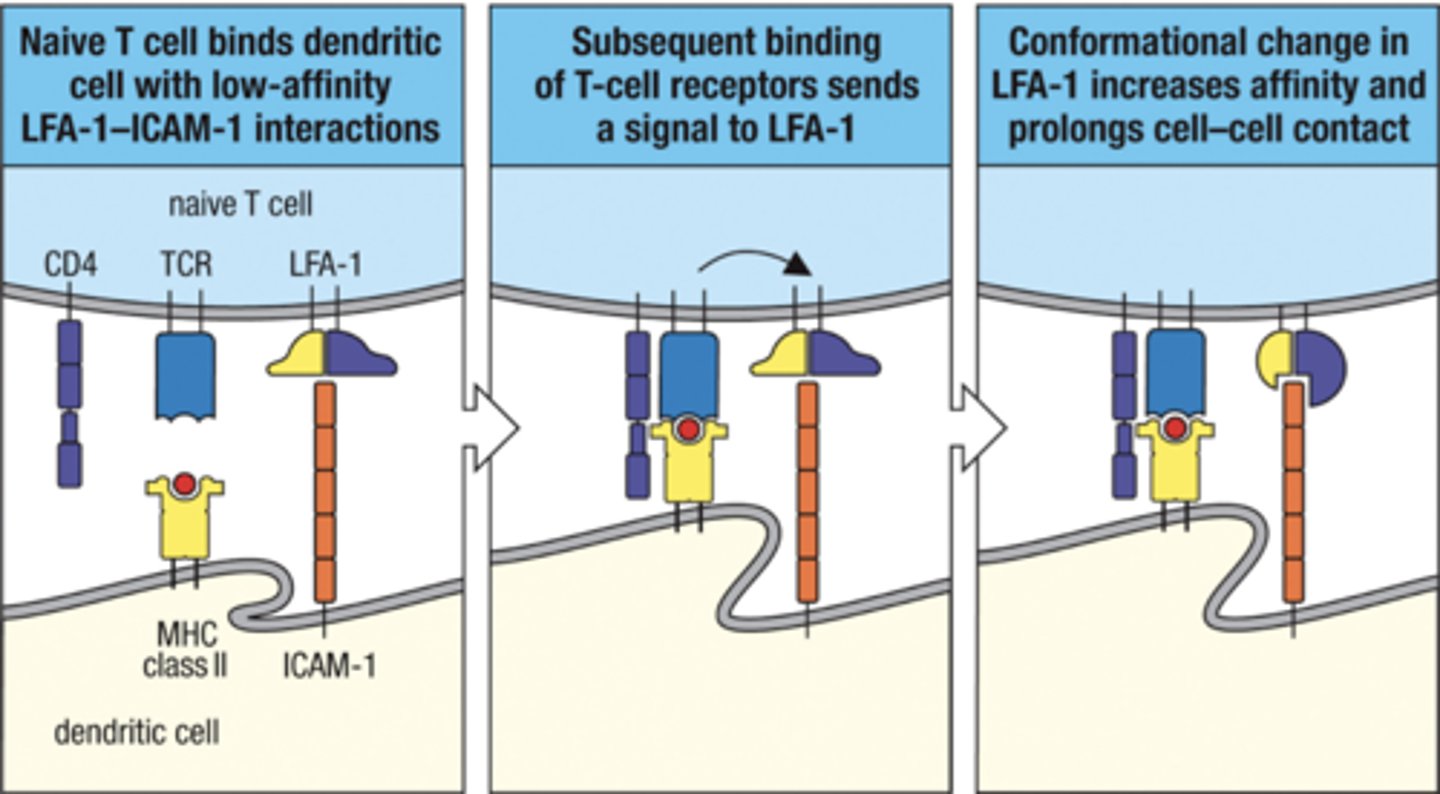
What are the 3 signals for T cell Activation
1) Antigen
-determines specificity of response
- mediated by TCR:MHC-peptide interactions
2) Co-Stimulators
- surface molecules expressed by APCs and T cells
- provide amplification
-determine type of response
3) Cytokines
- growth and differentiation factors for T cells
- provide amplification
- determine type of response
CD28
- co-stimulator
- receptor on T cell
- binds to B7 on APC's
B7
co-stimulatory molecule on APCs
"accelerator" for T cell
CD28/B7 interaction
Induce activation of PI-3 kinase and NKkappaB signal transduction pathway
promotes cell survival through upregulation of Bcl-xL
Increases production of IL-2
Promotes IL-4 production and T cell differentiation
IL-2
-Secreted by all T cells
- production increased by CD28/B7 interaction
-Stimulates growth of helper, cytotoxic, and regulatory T cells, and NK cells.
Bcl-xL
transmembrane molecule in mitochondria
anti-apoptotic protein
- activated via CD28/B7 interaction (naive T cells)
CTLA-4
Brake for T cells
CTLA4 when expressed inhibits both the activation and proliferation of T cells
CTLA4 in already active T cells, bind to B7 20x strongly than CD28
ITAM
Immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif
the prongs from CD3 that go intracellularly into the T cell and send signals towards nucleus
Immunological synapse
region of contact between t cell and APC
How to TCRs and coreceptors initiate signaling within a T cell
- MHC and CD bind
- tyrosine kinase (Lck) phosphorylates ITAMS of CD3 and zeta chains from TCR
- Lck activates ZAP-70 which goes and transmits cell signal pathways
What 3 transcription factors are activated via ZAP-70
NFAT
NF kappa B
AP-1
these transcription factors activate cytokine IL-2
Why is IL-2 important?
- drives proliferation and differentiation of ACTIVATED T cells
- costimulation along with CD28 increases synthesis of IL-2 100x
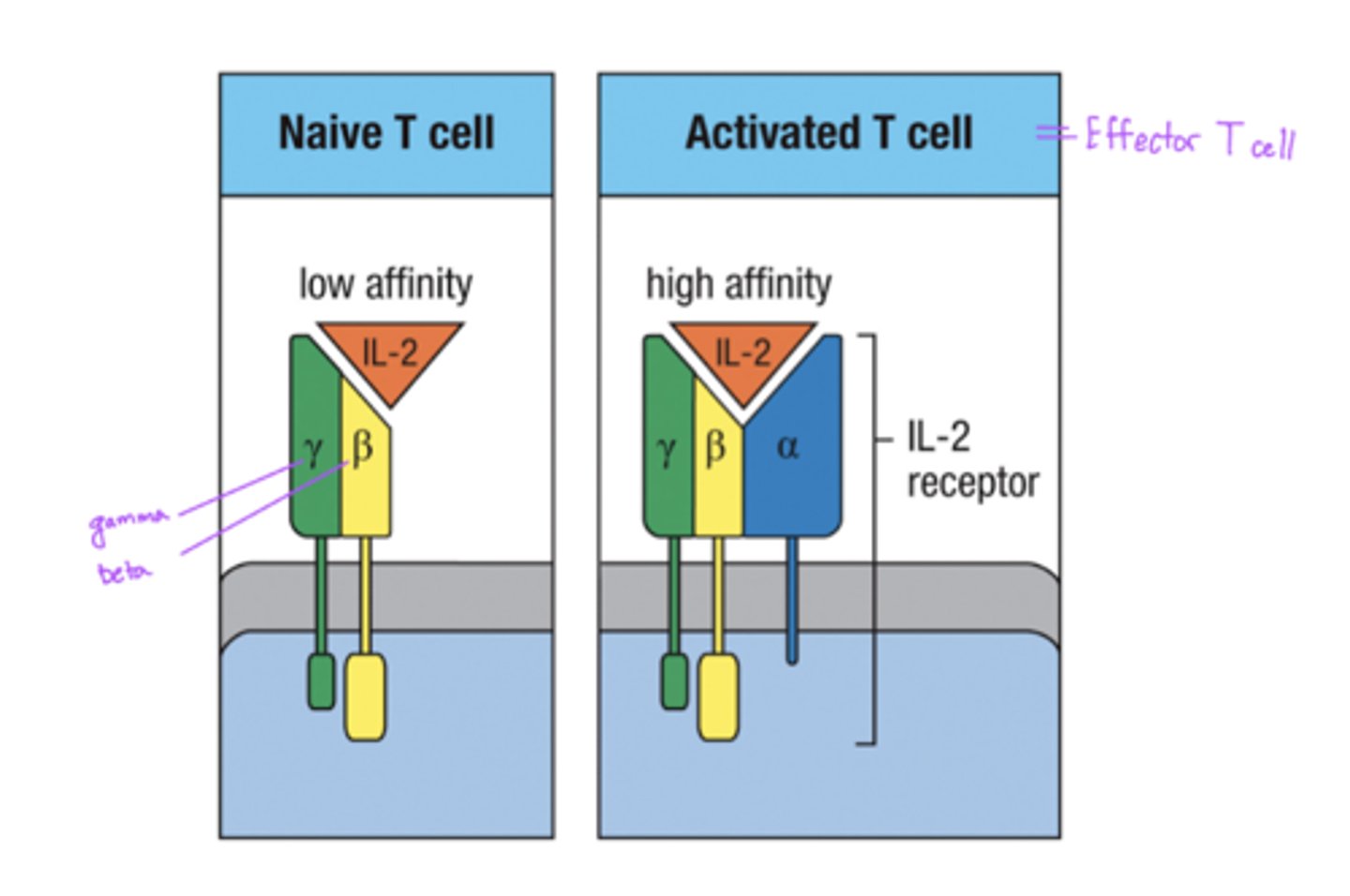
Difference between Naive T cell and Activated T cell IL-2 Receptors
Naive T cells
- low affinity
- made of only gamma, beta chains
Activated T cells
- high affinity
- made of gamma, beta, and alpha chains
Antigen recognition without costimulation may result in :

CD40
- Costimulator
- expressed on APCs (B cells too)
CD40L
- Costimulator
-expressed on T cells
CD40/CD40L interaction
- expressed only on activated T cells
- Induces upregulation of B7 on APCs
- promotes IL-12 production (contributing to TH1 differentiation)
- CD40 signaling required for Ig class switching
Function of TH1 cells
activate macrophages
Cytokine of TH1 cells
IFN-gamma
Cytokine of TH2 cells
IL-4
Cytokine of TH17 cells
IL-17
Cytokine of TFH cells
IL-21
Cytokine of T reg cells
TGF-beta
TH2 cell function
activate cellular and antibody response to parasites
TH17 functions
enhance neutrophil response
TFH functions
Activate B cells to refine antibody response
Treg functions
Suppress autoreactive effector T cells via IL-10 and TGF-beta cytokines
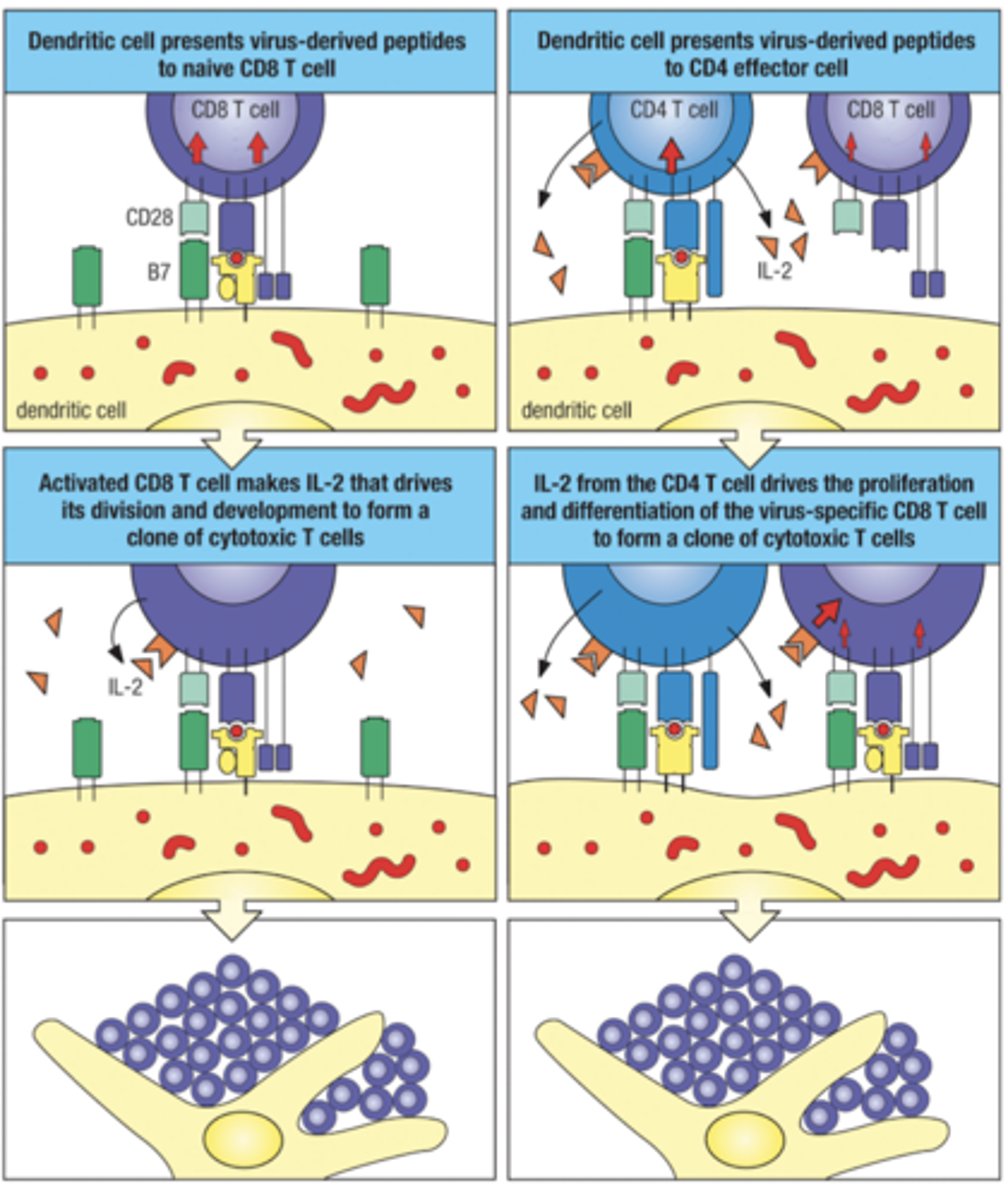
Activation of CD8 T cells
2 methods
1. Naive CD8 T cell can be activated directly by a virus-infected dendritic cell
2. Virus infected dendritic cell induces insufficient costimulation, leads to needing to be helped by CD4 effector T cells (done via IL-2 secreted)
What key surface molecule is not expressed on activated T cells but is on naive ones
Naive T cells express L-selectin allowing them to enter lymph nodes through HEV
Activated T cells express VLA-4 enablling them to enter infected tissue
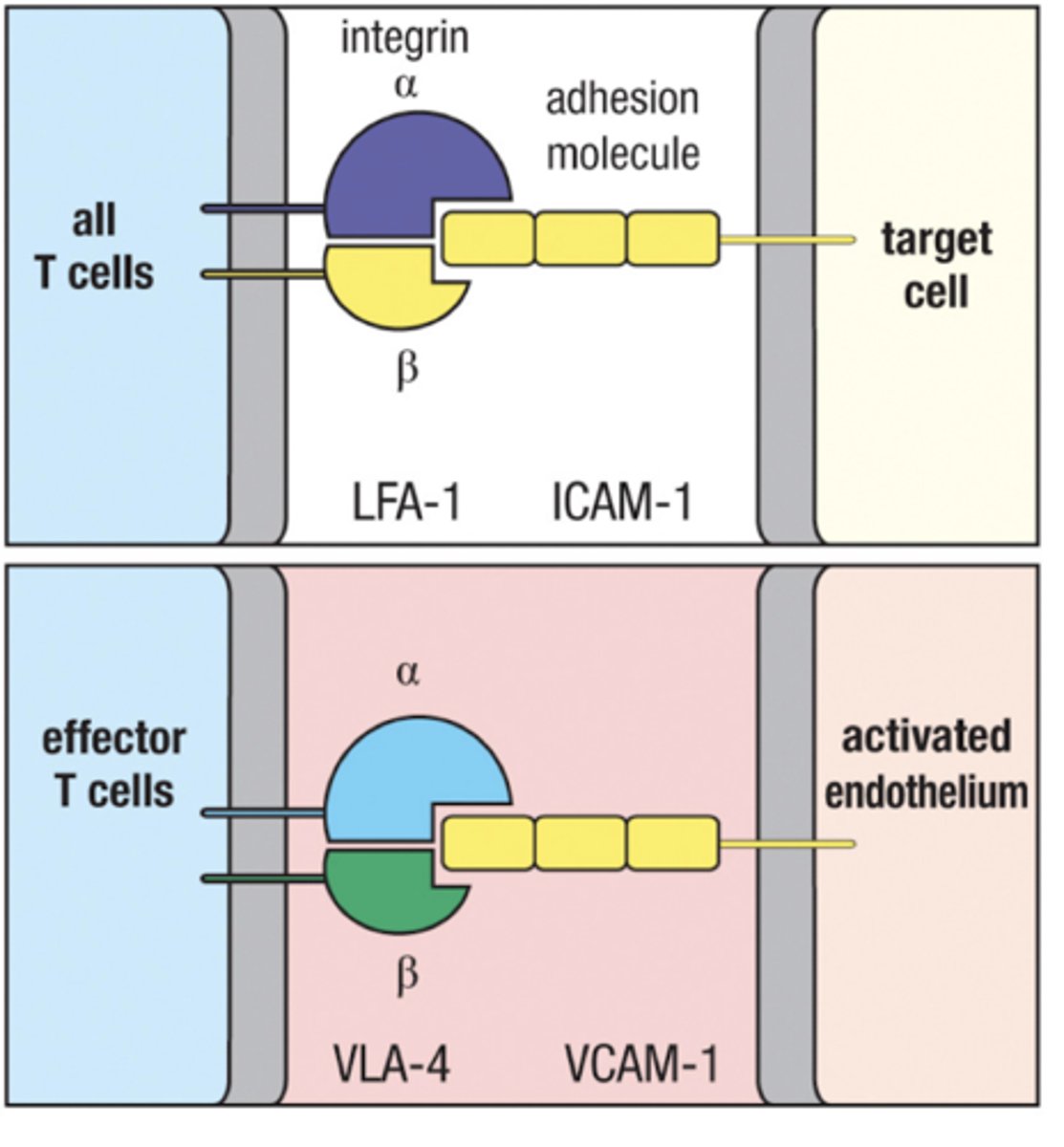
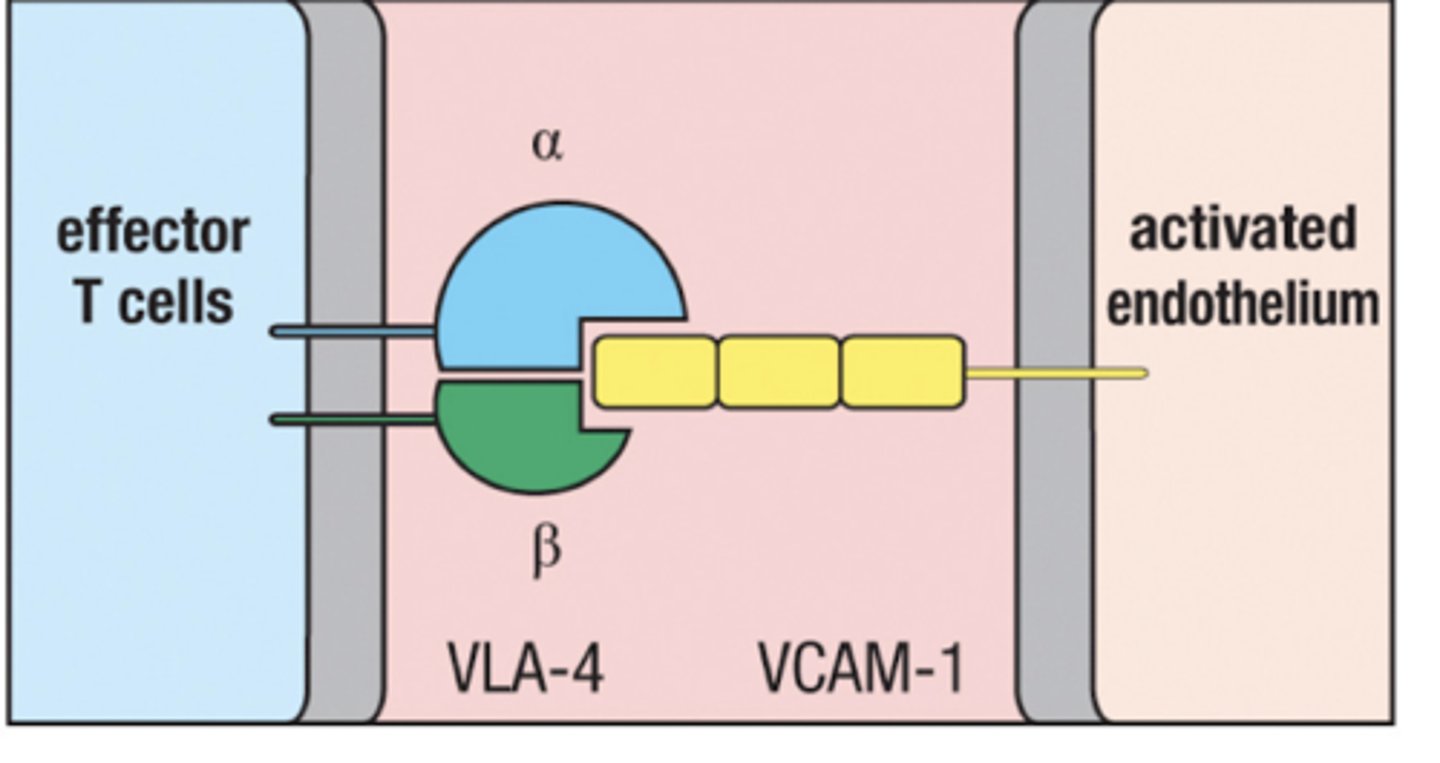
VLA-4
expressed on activated T cells
Binds to VCAM-1 on inflamed tissue in blood vessels
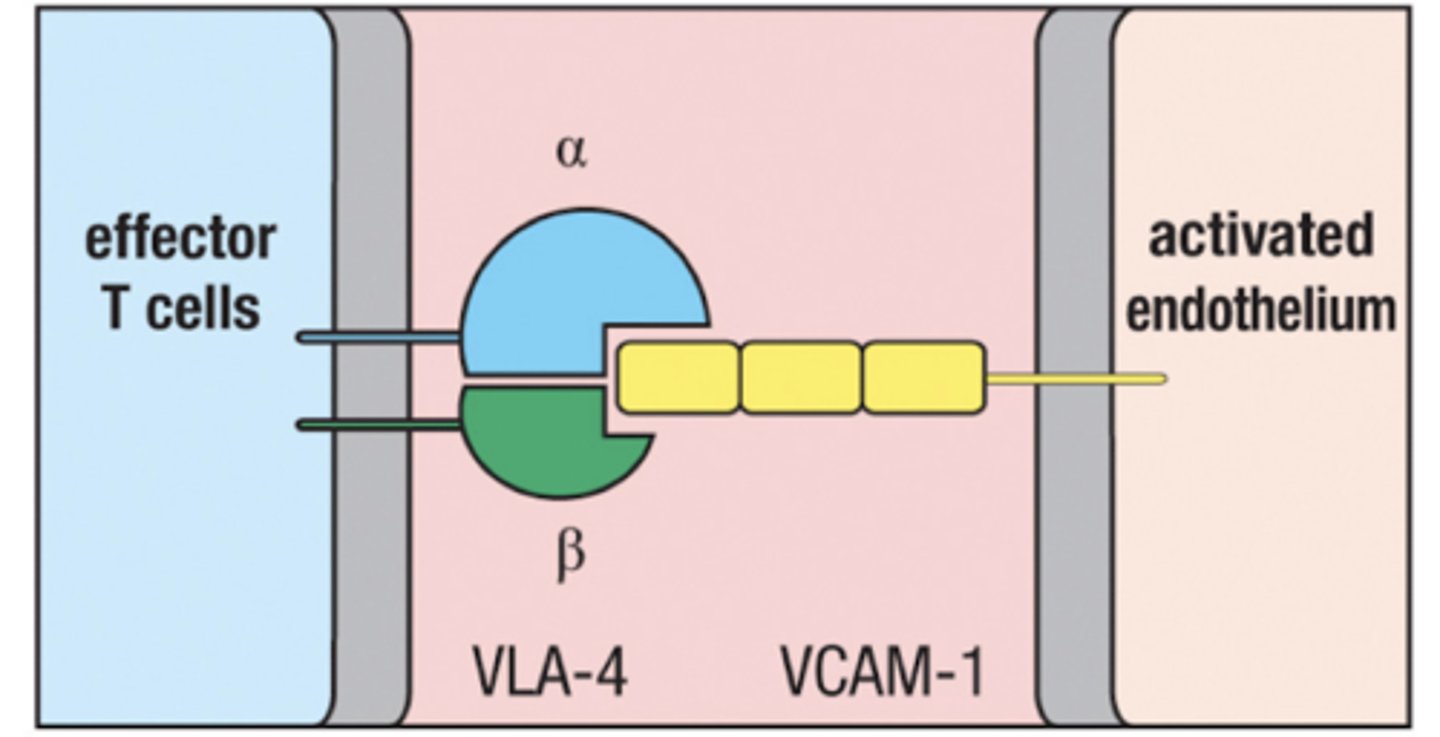
VCAM-1
expressed on endothelium of blood vessels in inflamed tissue
Recruits T cells from the blood by binding with VLA-4
Cytokines are
pleiotrophic - each one has multiple actions
redundant- different cytokines may have similar effects
Cytotoxins
secreted proteins used to kill target cells by apoptosis
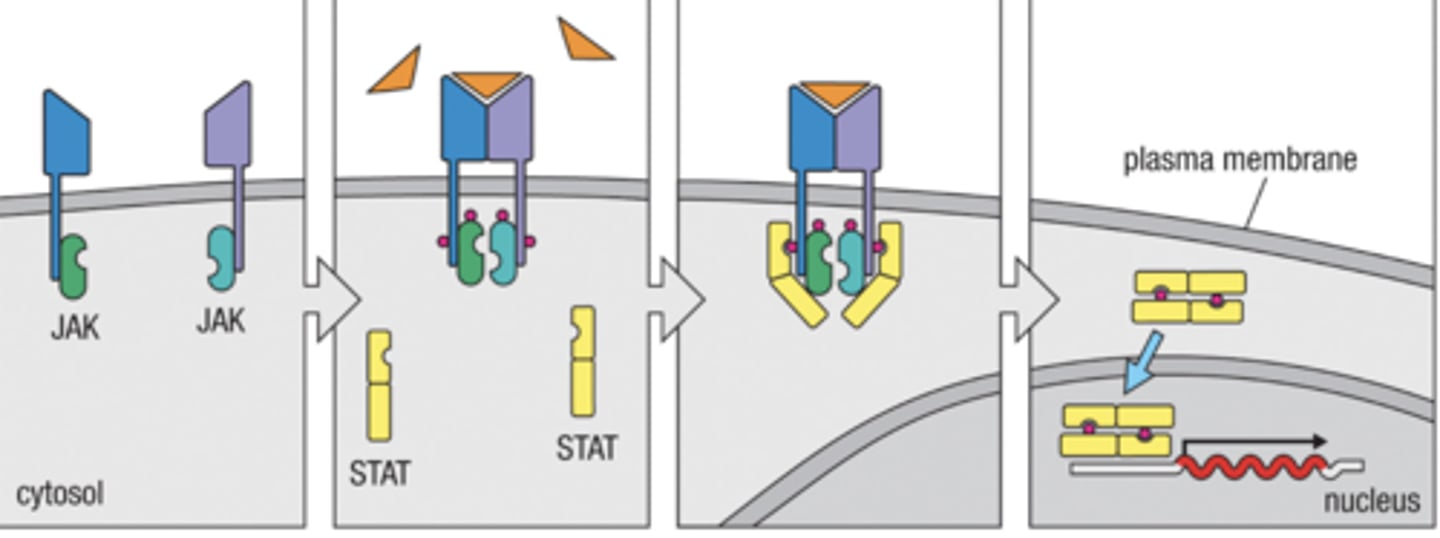
how does cytokine receptor signaling work ?
1. Cytokine receptors bind their JAKS together
2. Cytokine binds to receptor phosphorylating JAKS
3. JAKS bind to and phosphorylate STATs
4. Phosphorylated STAT dimers enter the nucleus to start gene expression
What T cells enter circulation seeking sites of infection after activation in lymph nodes?
CD8+ CTLs and ,CD4+ TH1 cells enter the circulation seeking sites of infection
What T cells do not enter circulation after activation in lymph nodes
CD4+ T FH cells remain in secondary lymphoid tissues to help B cells become
plasma cells or memory cells
Do T cells always require costimulation ?
No
Naive T cells require costimulators (CD40/CD40L and BT/CD28 ) for activation
Activated T cells do not require costimulation MHC only is okay
CD4+ Helper T cells have what key functions
- Help B cells produce antibody and isotype switch
- Help activate CD8+ cytotoxic T cells
- Help activate APCs
- Enhance macrophage and neutrophil response
What is the lifespan of a naive T cell
up to 9 years
What is the lifespan of an activated T cell
Weeks