All Nuclei of the CNS
1/52
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Neuroanatomy
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
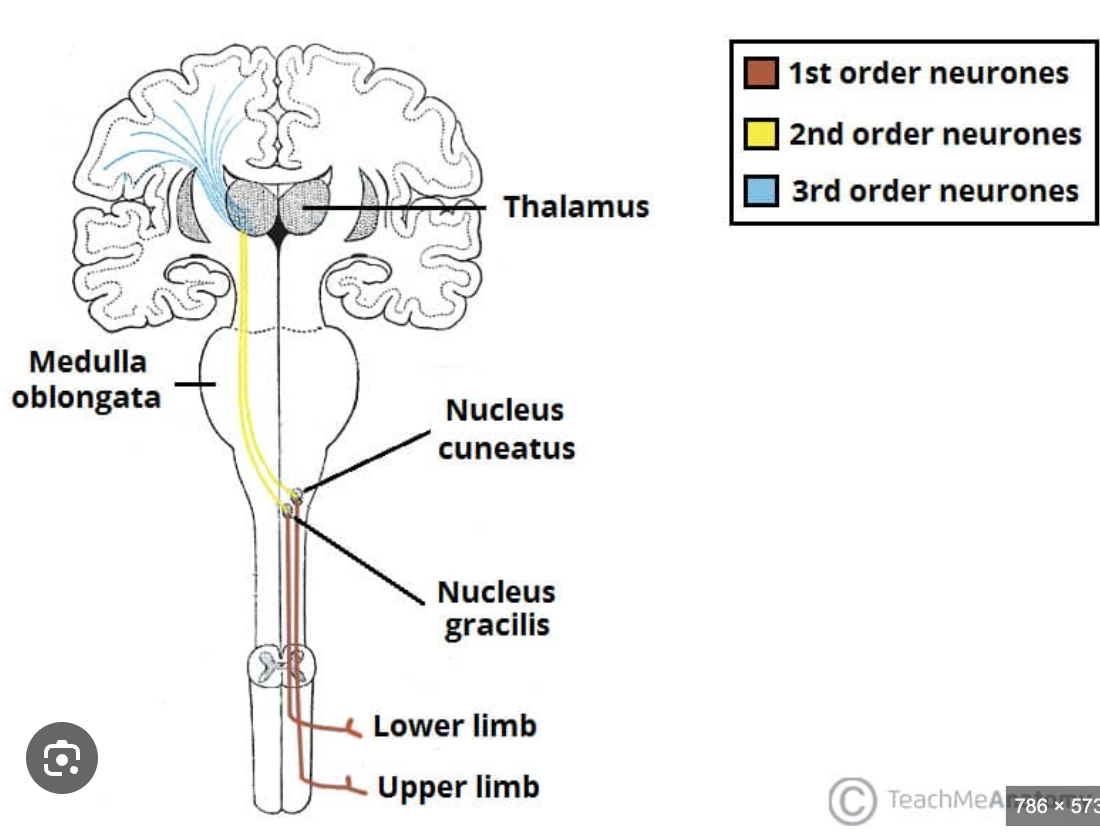
Nucleus gracilis
Located in the medulla oblongata (posterior column);
relays fine touch and proprioception from the lower limbs;
forms the medial lemniscus after decussation to the thalamus (VPL)
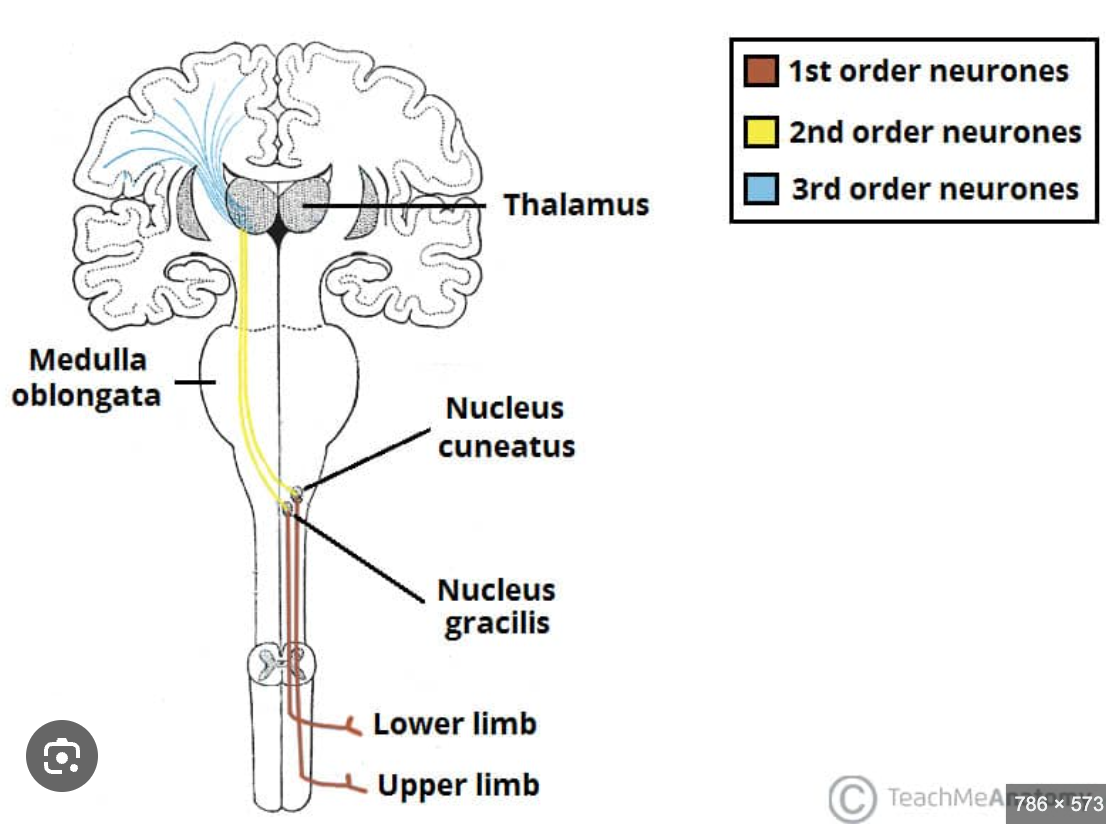
Nucleus cuneatus
Located in the medulla oblongata (posterior column);
relays fine touch and proprioception from the upper limbs;
forms the medial lemniscus to the thalamus (VPL)
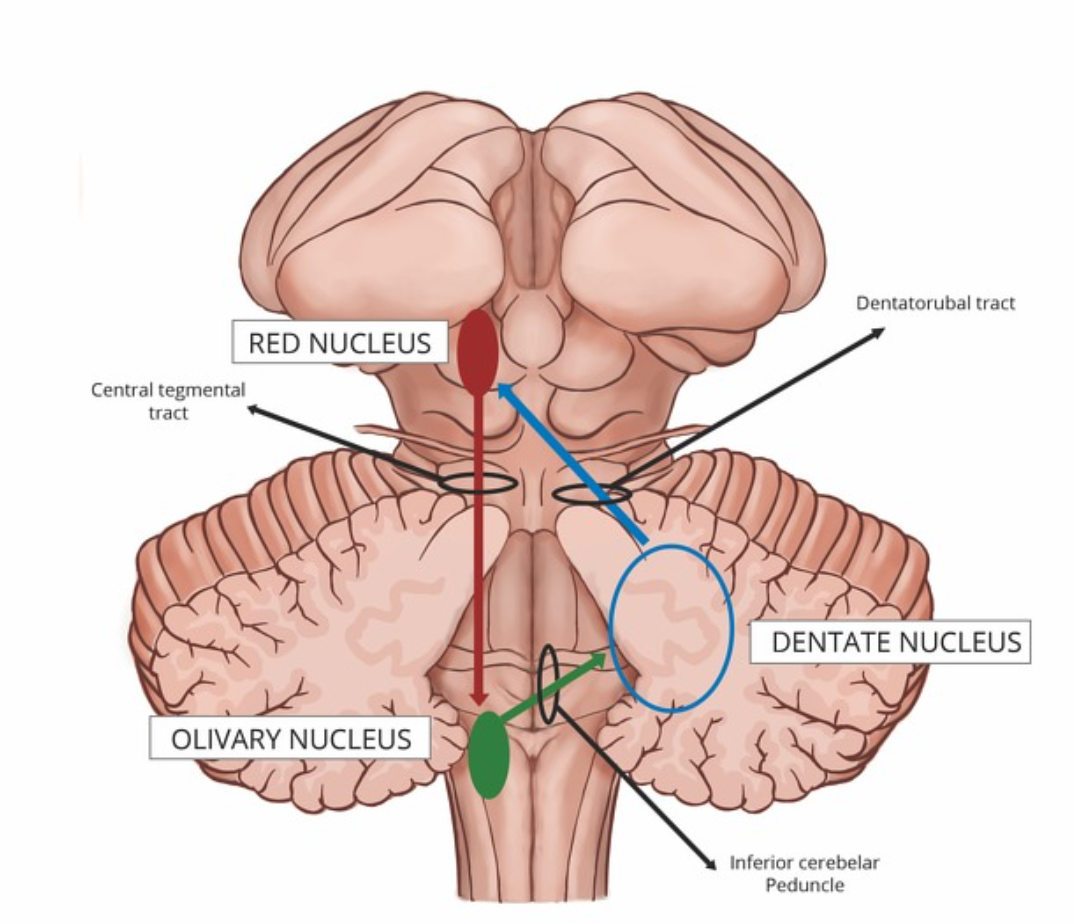
Inferior olivary nucleus
Located in the medulla oblongata (tegmentum);
coordinates motor activity and learning;
sends olivocerebellar fibers to the contralateral cerebellar cortex
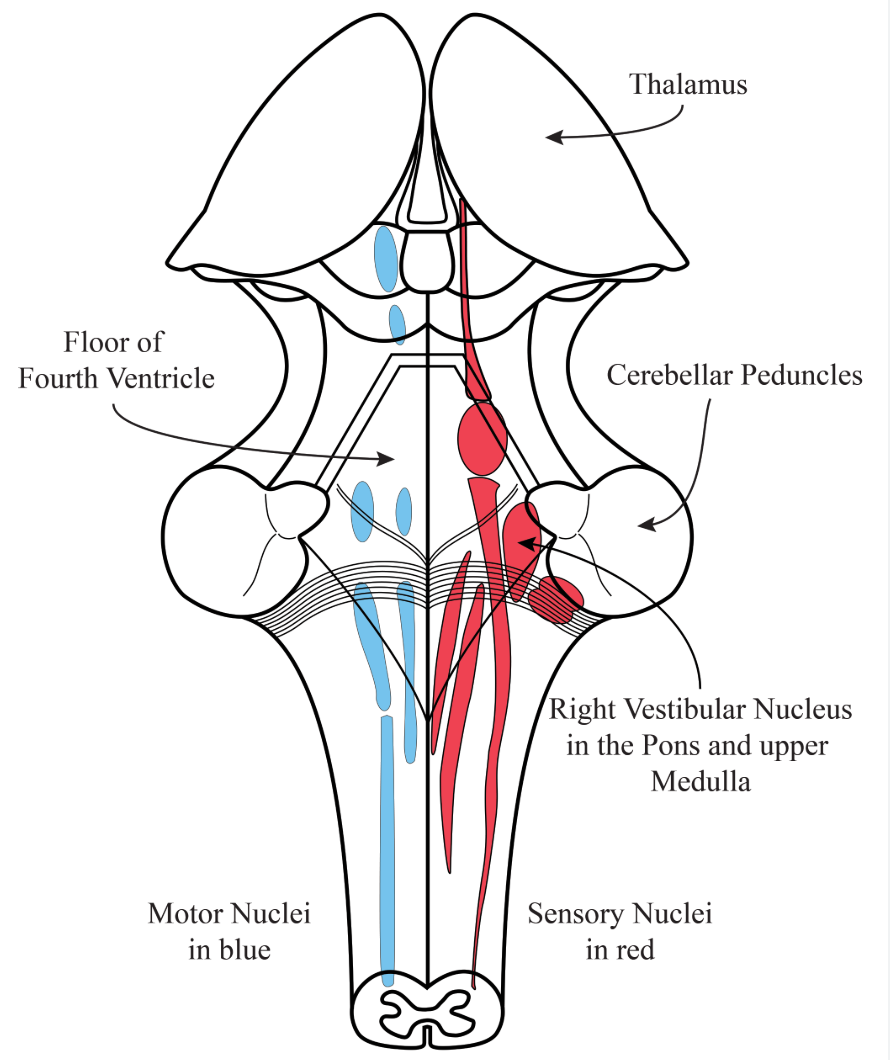
Vestibular nuclei
Located in the pons and medulla (floor of the fourth ventricle);
maintain balance, posture, and eye coordination;
connect via vestibulospinal and vestibulocerebellar tracts
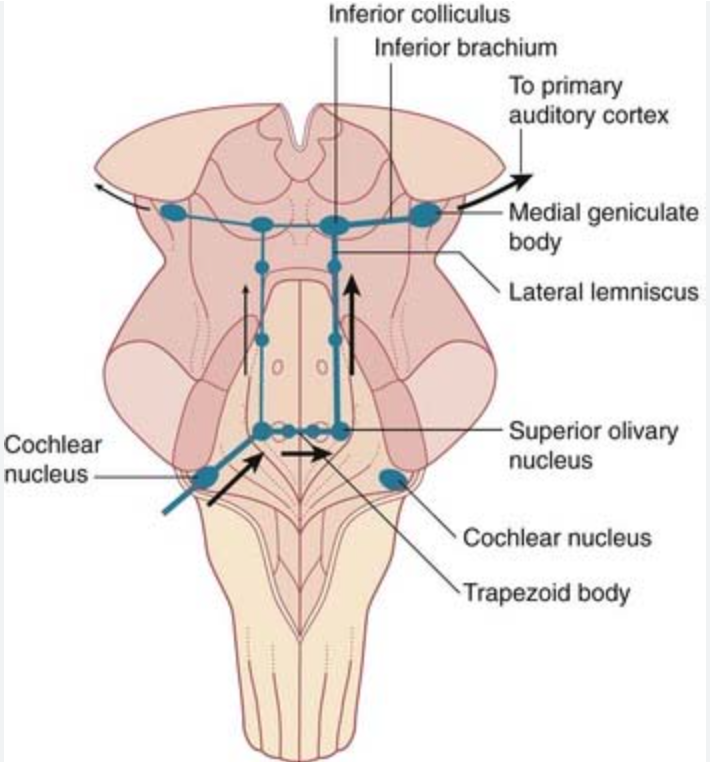
Cochlear nuclei
Located at the junction of pons and medulla;
relay auditory information from the cochlea;
project via trapezoid body to superior olivary nucleus and lateral lemniscus
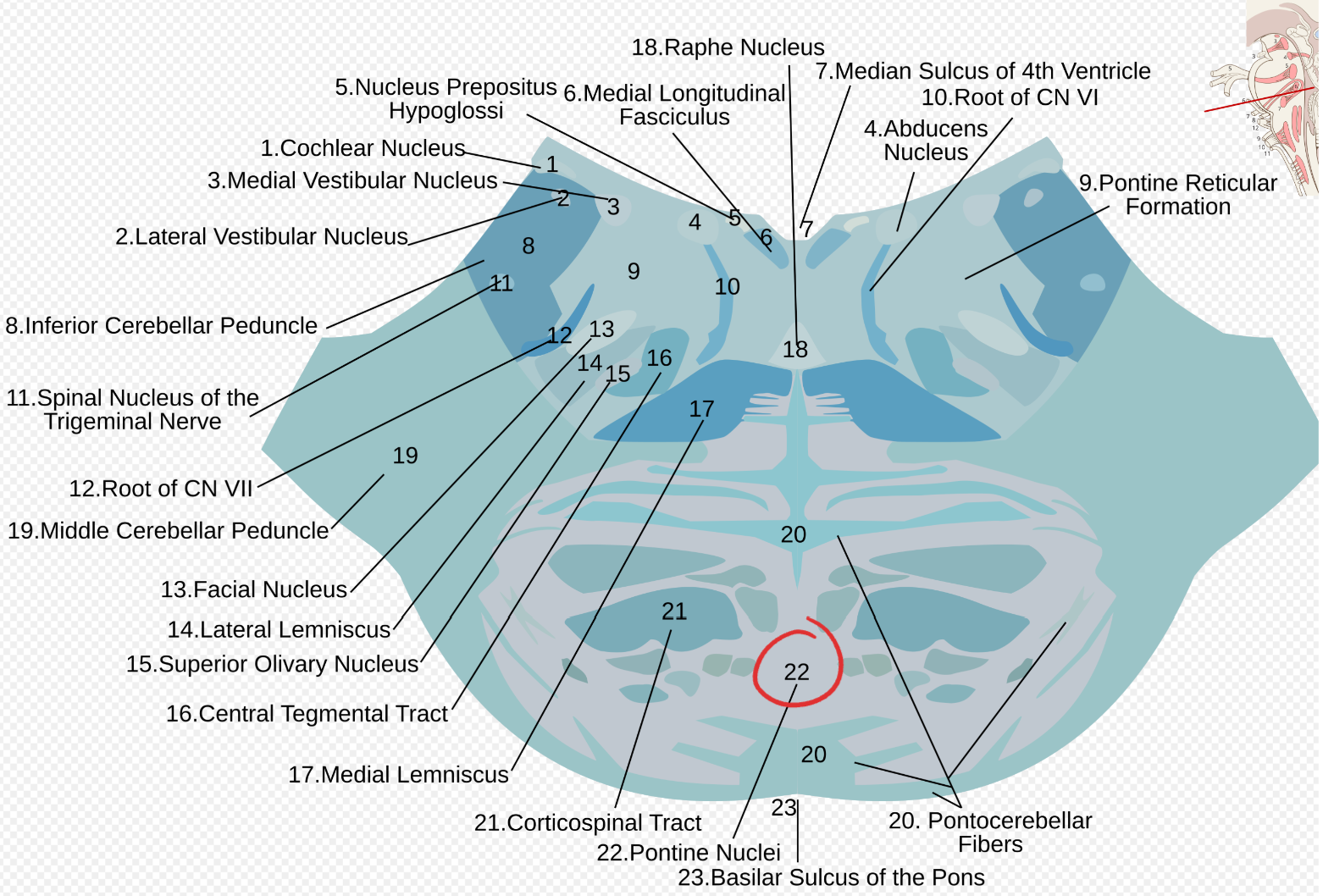
Pontine nuclei
Located in the basis pontis of the pons;
relay motor information from the cerebral cortex to the cerebellum through corticopontine and pontocerebellar fibers
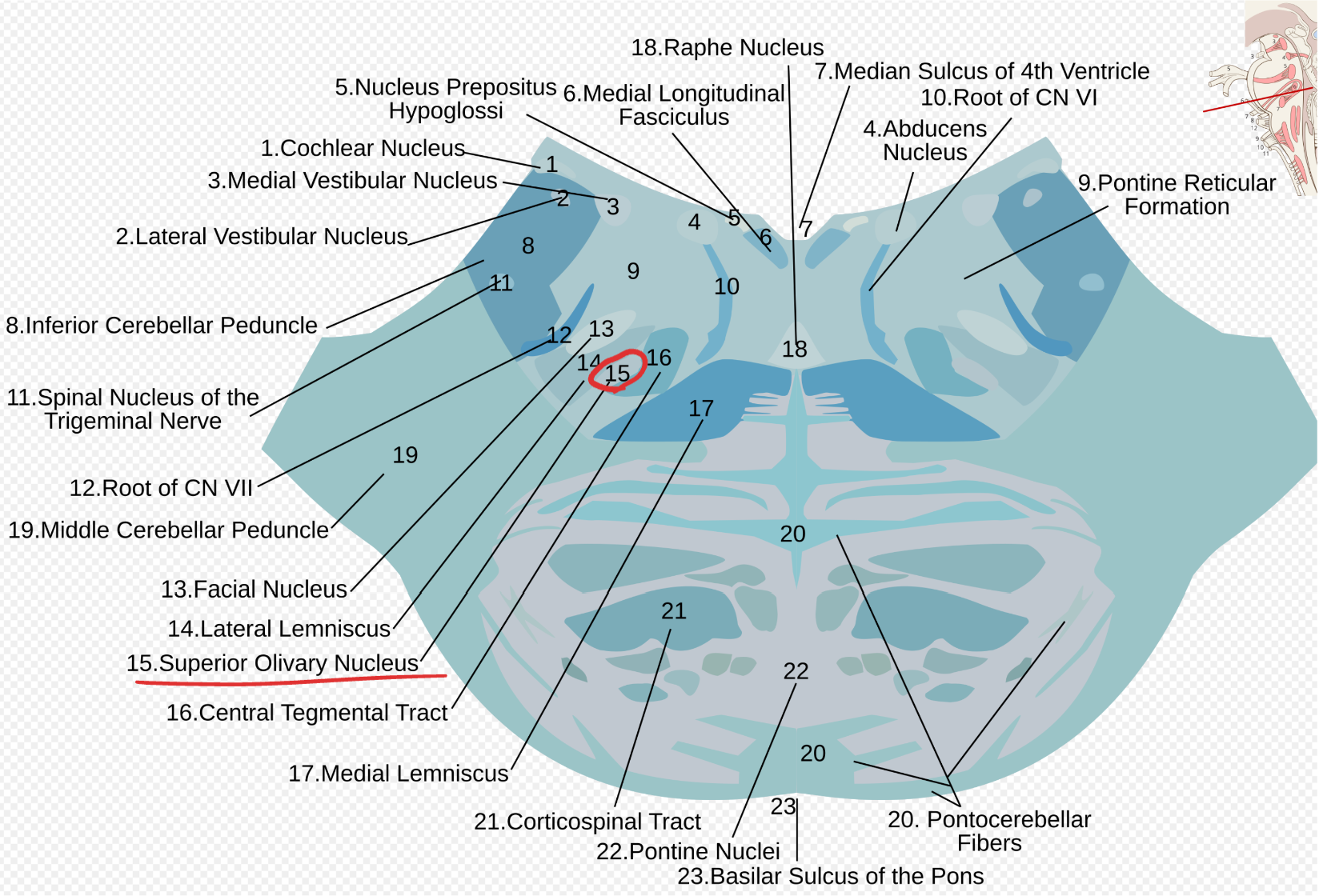
Superior olivary nucleus
Located in the pons (tegmentum);
processes binaural auditory input for sound localization;
part of trapezoid body and lateral lemniscus pathway
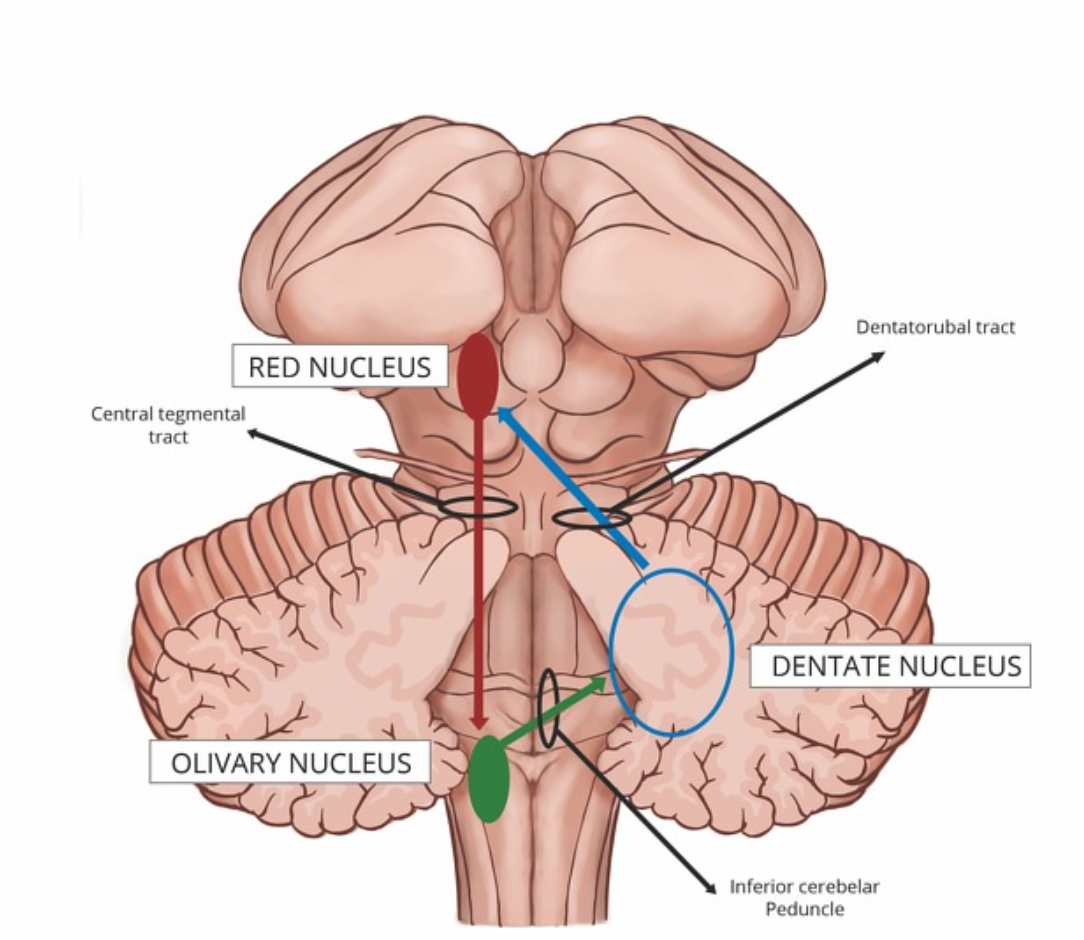
Red nucleus
Located in the midbrain (tegmentum);
controls motor coordination and muscle tone;
connects via cerebellorubral and rubrospinal tracts
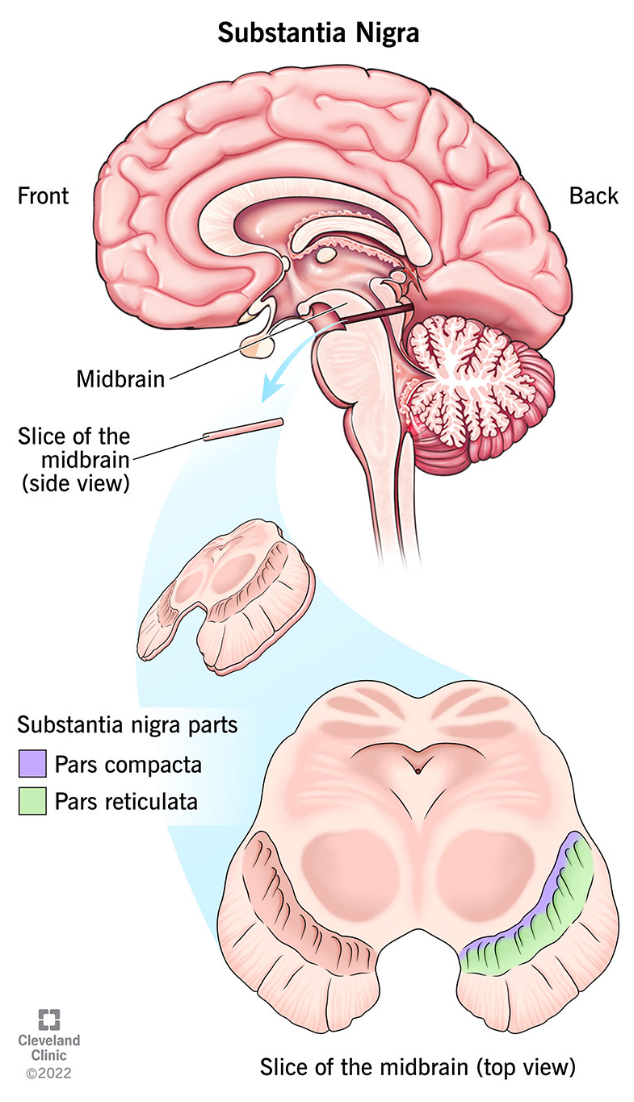
Substantia nigra
Located in the midbrain (basis pedunculi);
produces dopamine for motor control;
part of the nigrostriatal pathway to the striatum
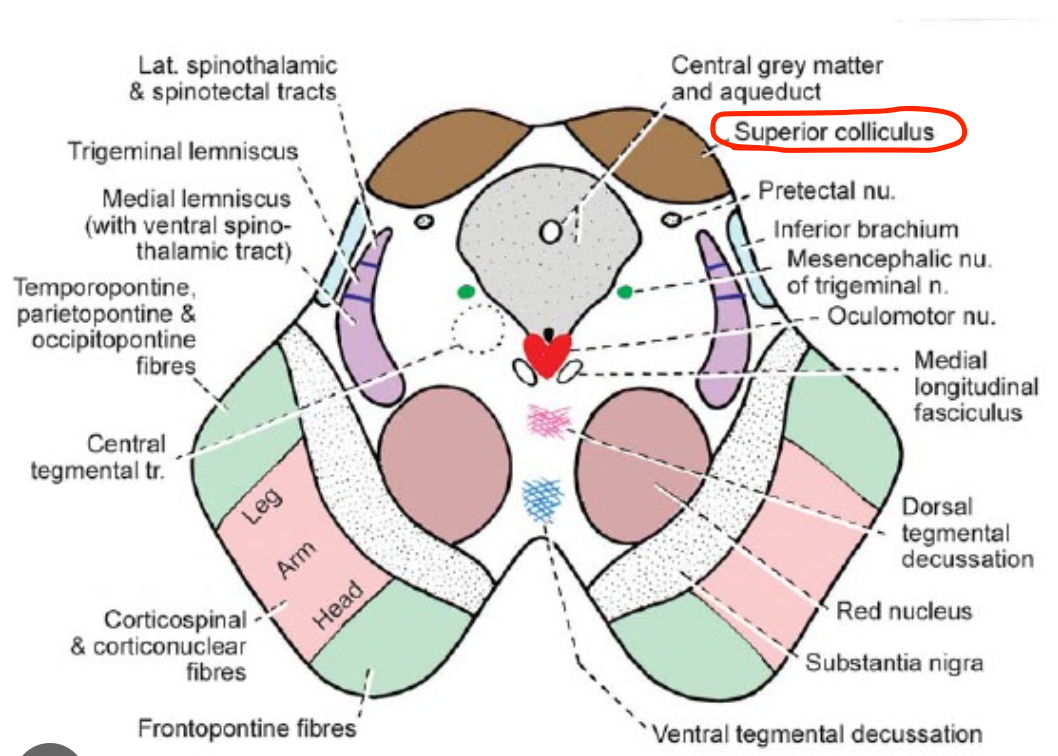
Superior colliculus nucleus
Located in the midbrain (tectum);
mediates visual reflexes and eye–head coordination;
origin of the tectospinal tract
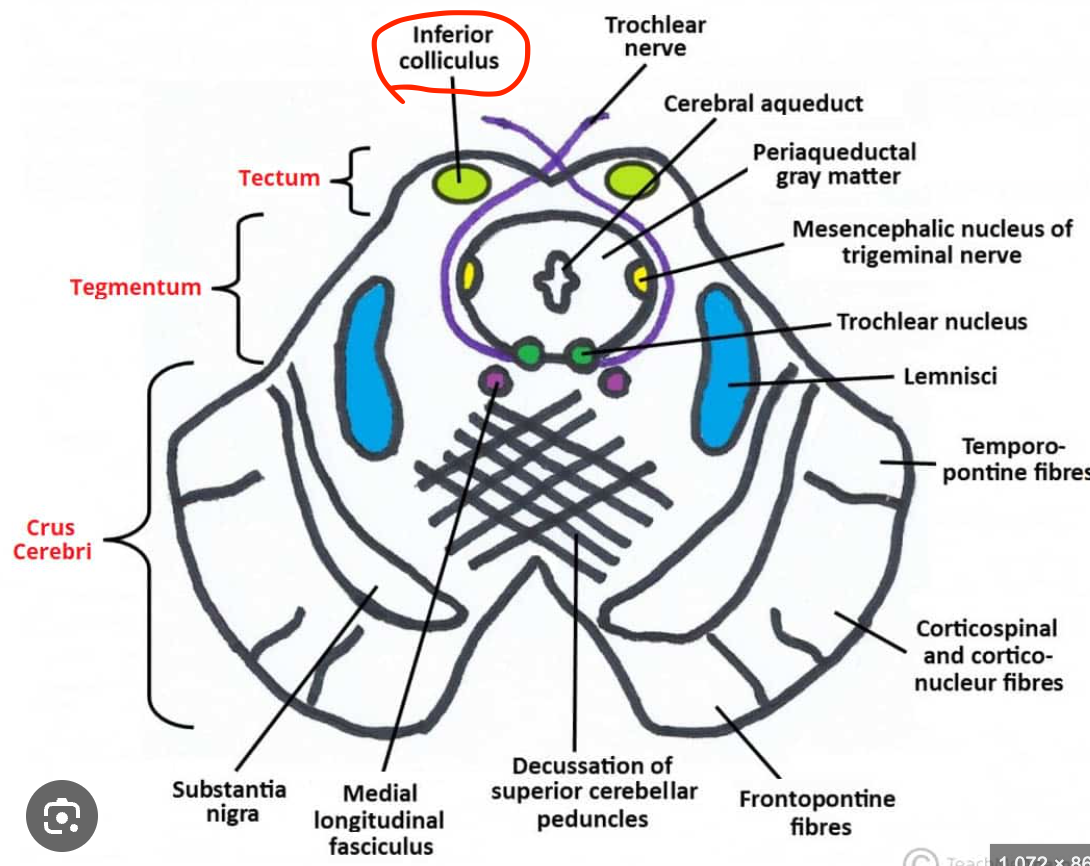
Inferior colliculus nucleus
Located in the midbrain (tectum);
processes auditory reflexes and sound localization;
projects to the medial geniculate body
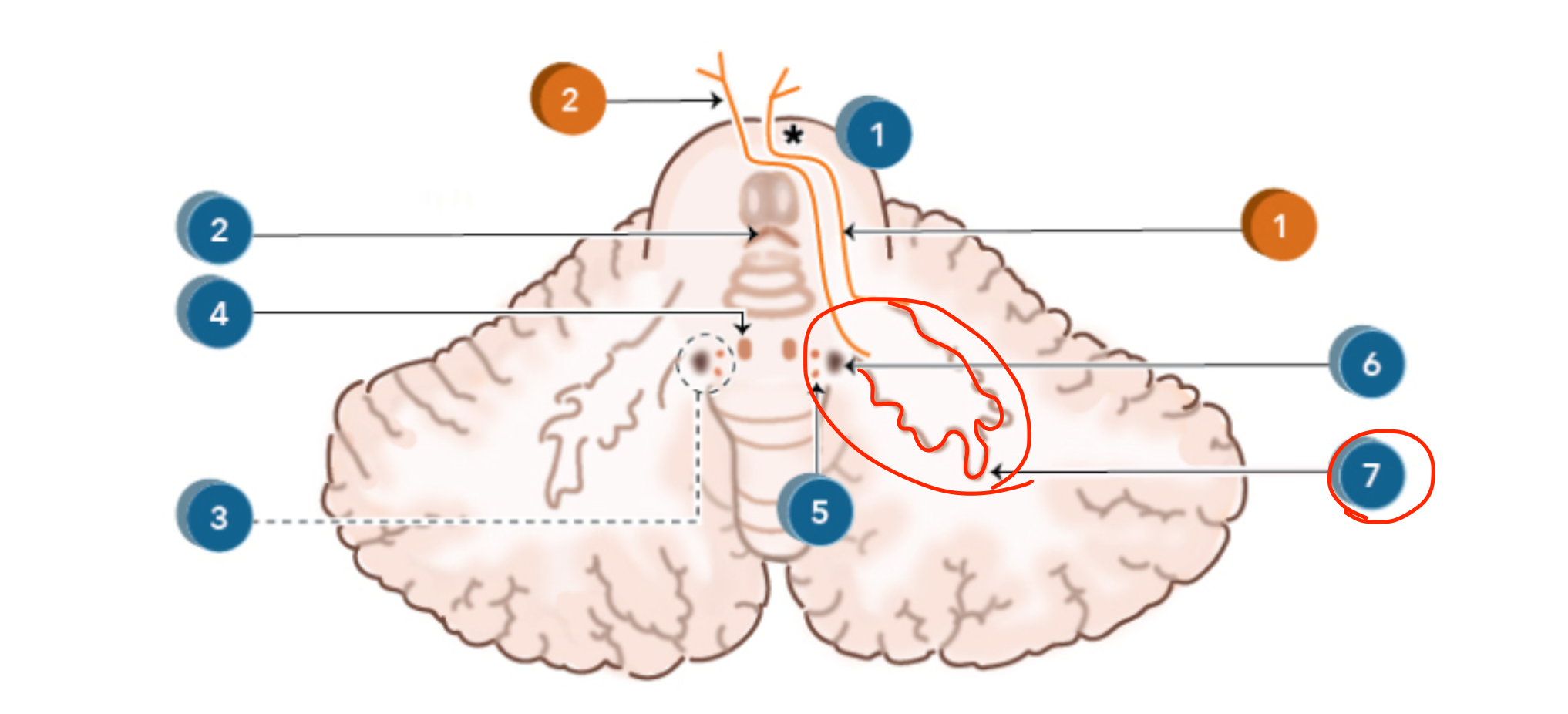
Dentate nucleus
Located in the lateral cerebellar hemisphere;
coordinates planning, initiation, and precise control of voluntary movements;
projects via the dentatothalamic and dentatorubral tracts
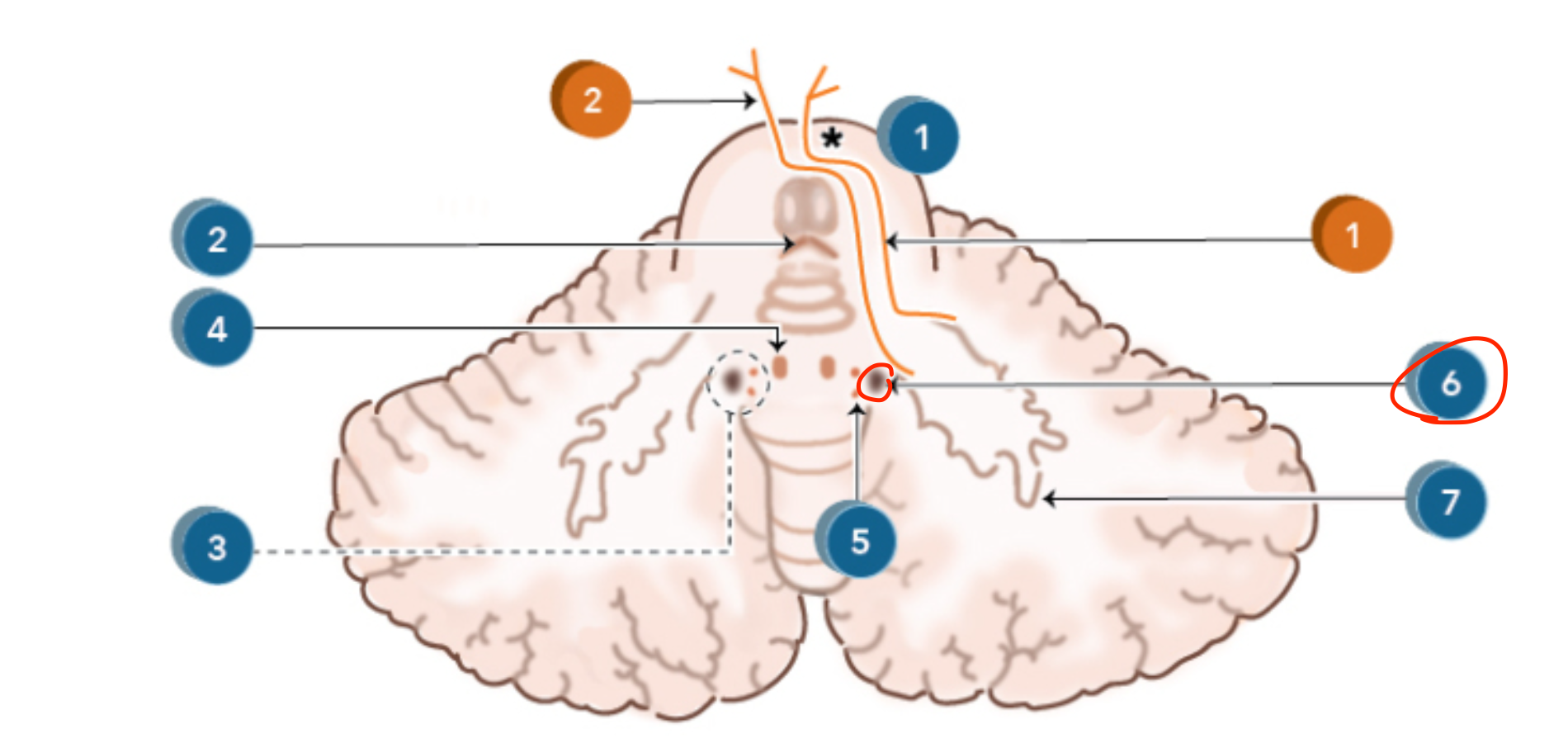
Emboliform nucleus
Located in the intermediate cerebellar hemisphere;
regulates limb movements and muscle tone;
sends output through the interposed nuclei pathways to the red nucleus
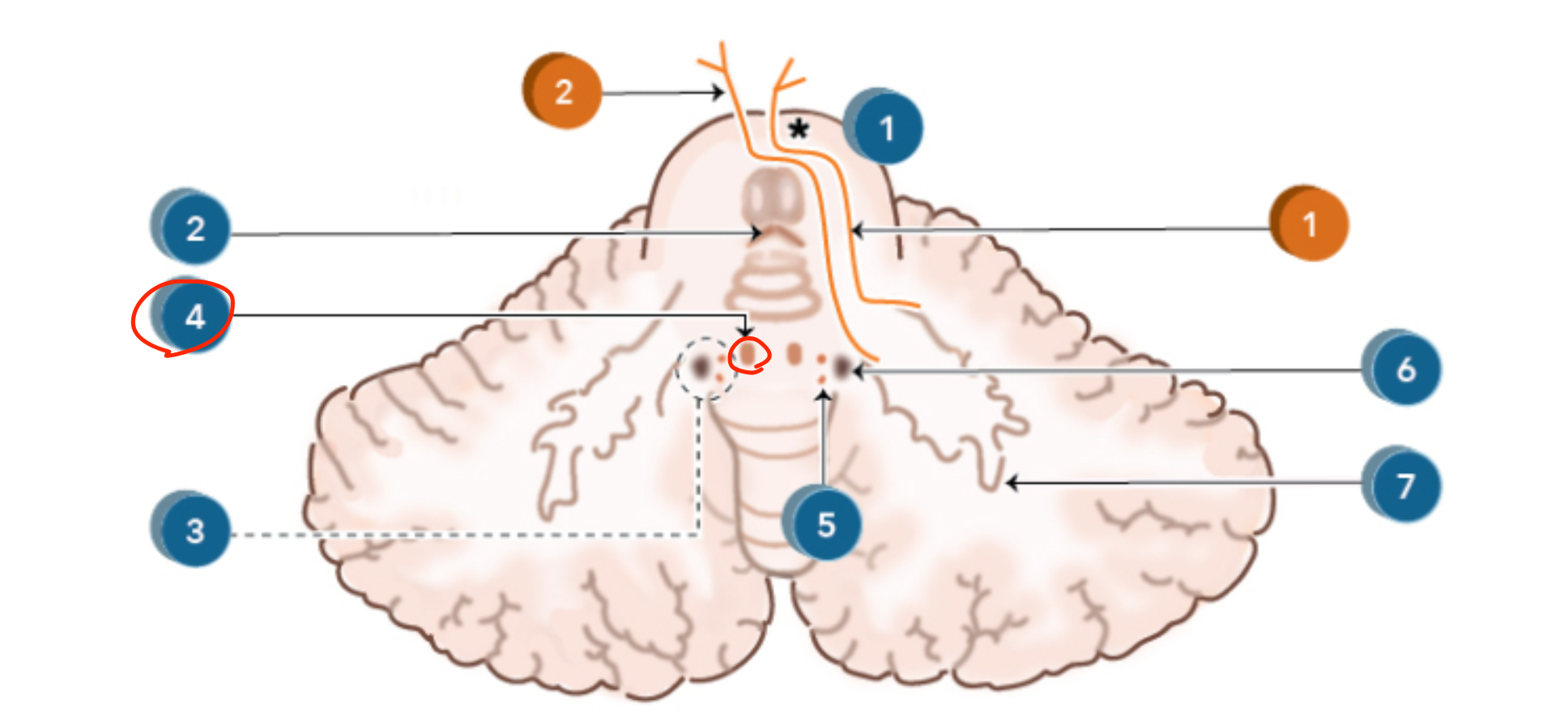
Globose nucleus
Located medial to the emboliform nucleus in the intermediate zone;
controls proximal limb movements;
connects to the red nucleus via the cerebellorubral tract
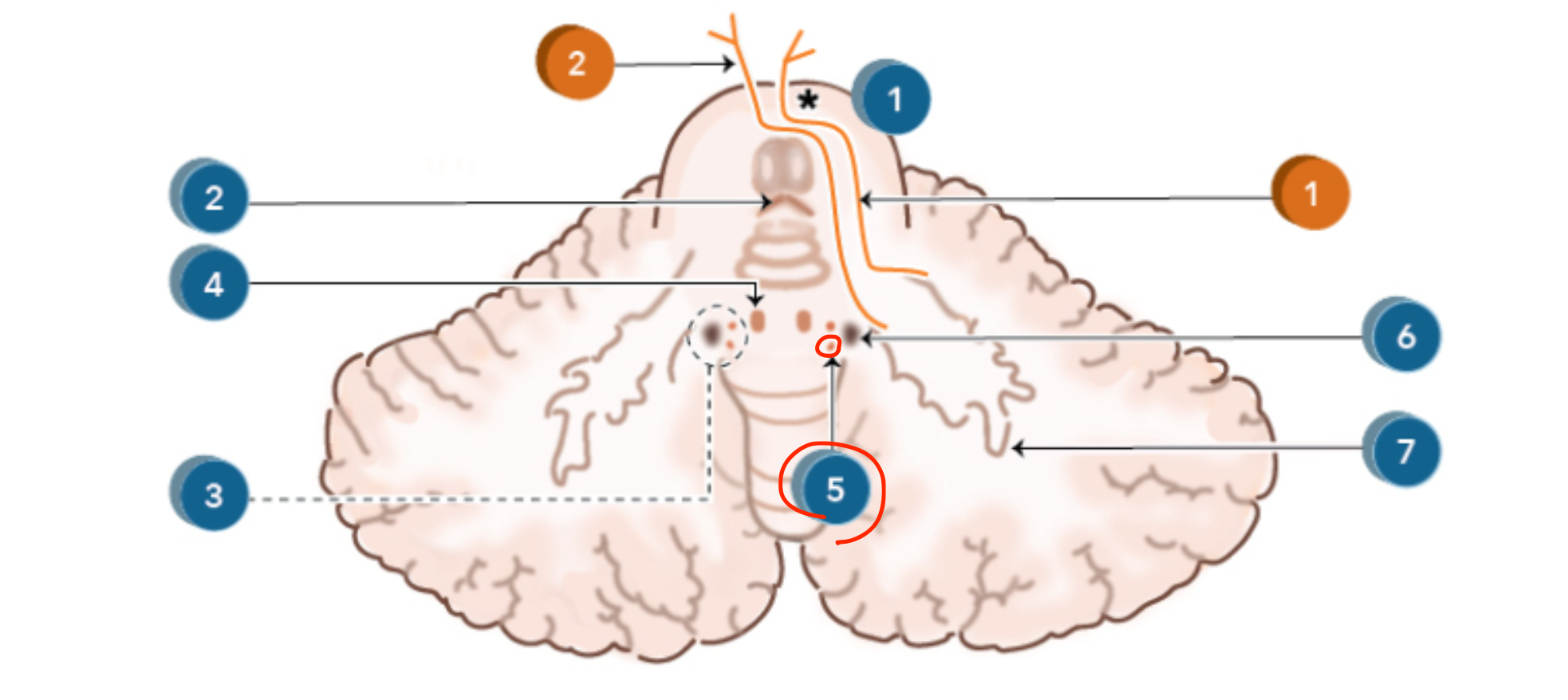
Fastigial nucleus
Located in the vermis (medial cerebellum);
maintains posture, balance, and eye movements;
connects via vestibulocerebellar and reticulocerebellar tracts
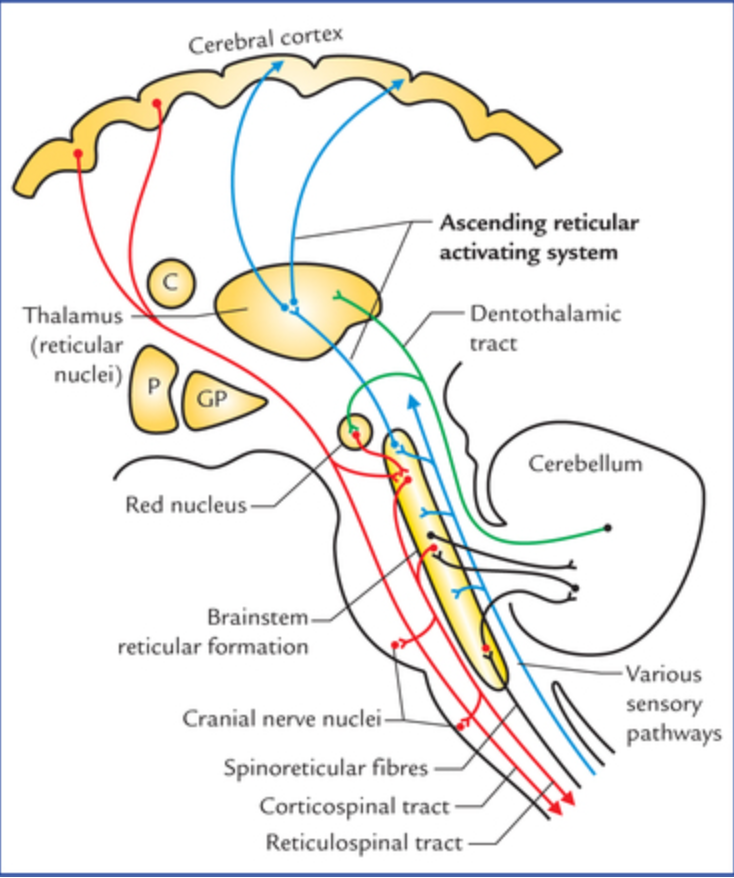
Reticular formation nuclei
Located throughout the brainstem;
regulate arousal, pain, and autonomic functions;
connected via reticulospinal and reticulocerebellar tracts
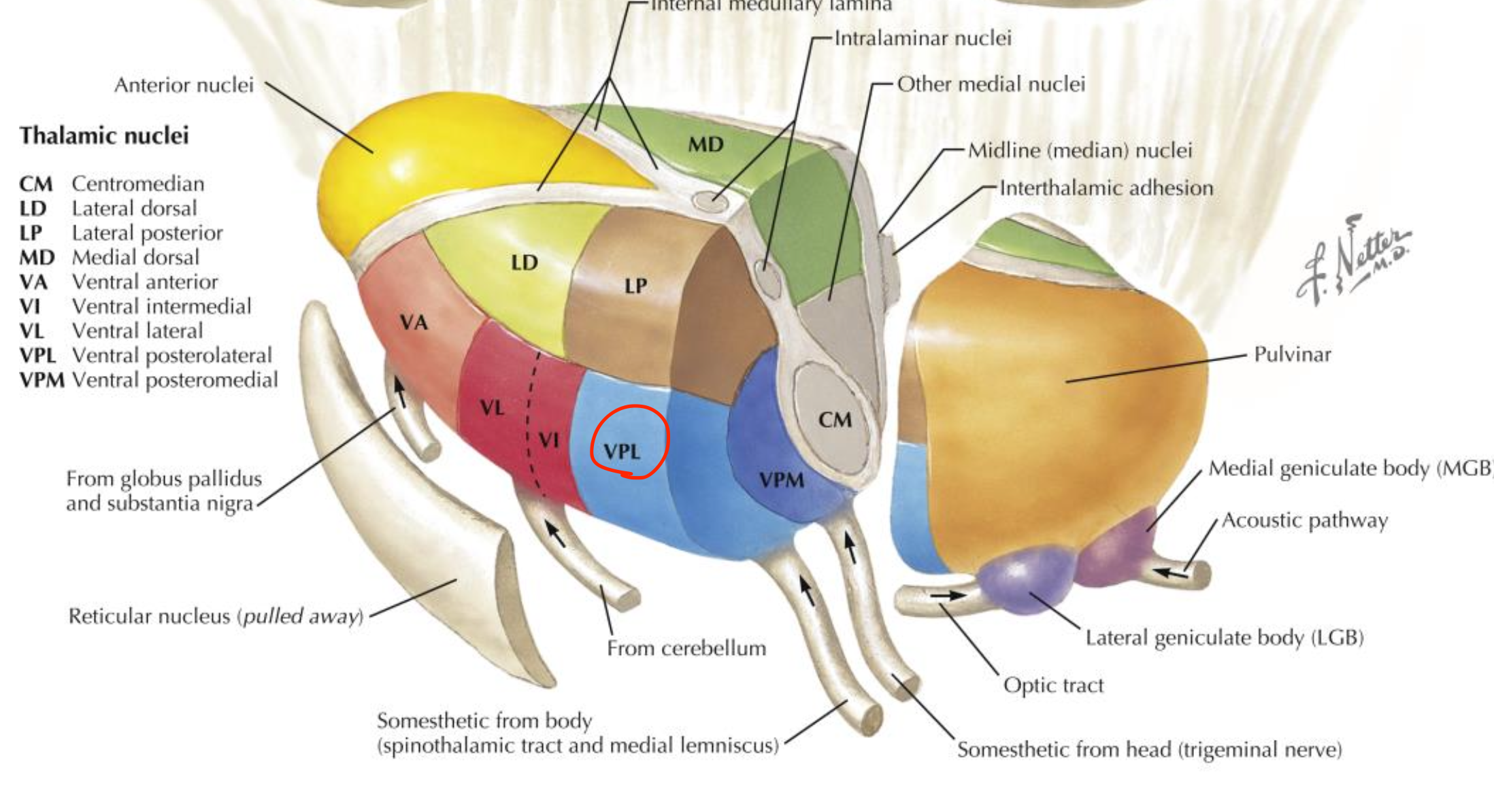
Ventral posterior lateral nucleus (VPL)
Located in the thalamus (lateral group);
relays sensory input from the body to the somatosensory cortex;
receives spinothalamic and medial lemniscus fibers
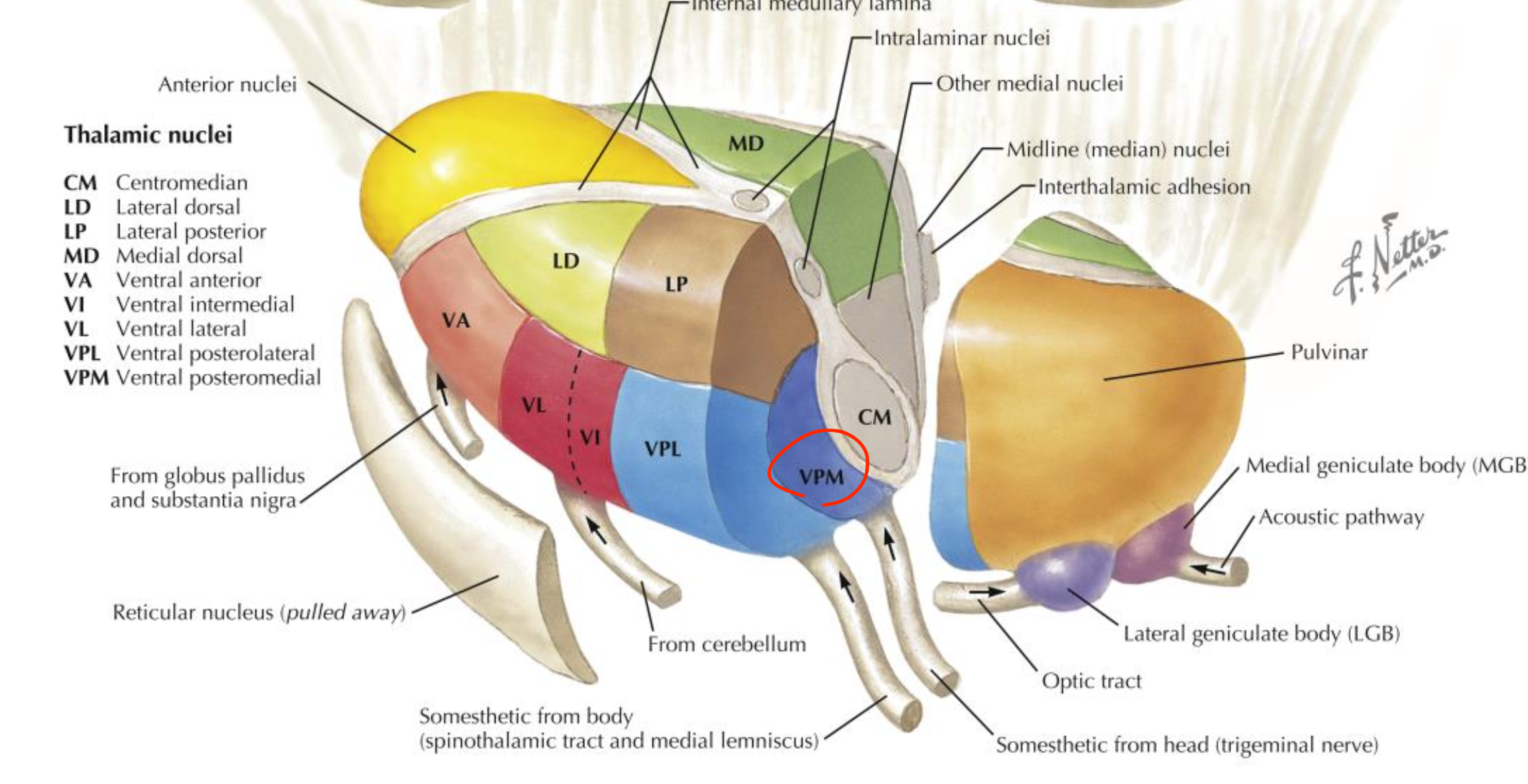
Ventral posterior medial nucleus (VPM)
Located in the thalamus (lateral group);
relays sensory input from the face to the somatosensory cortex;
receives trigeminal lemniscus fibers
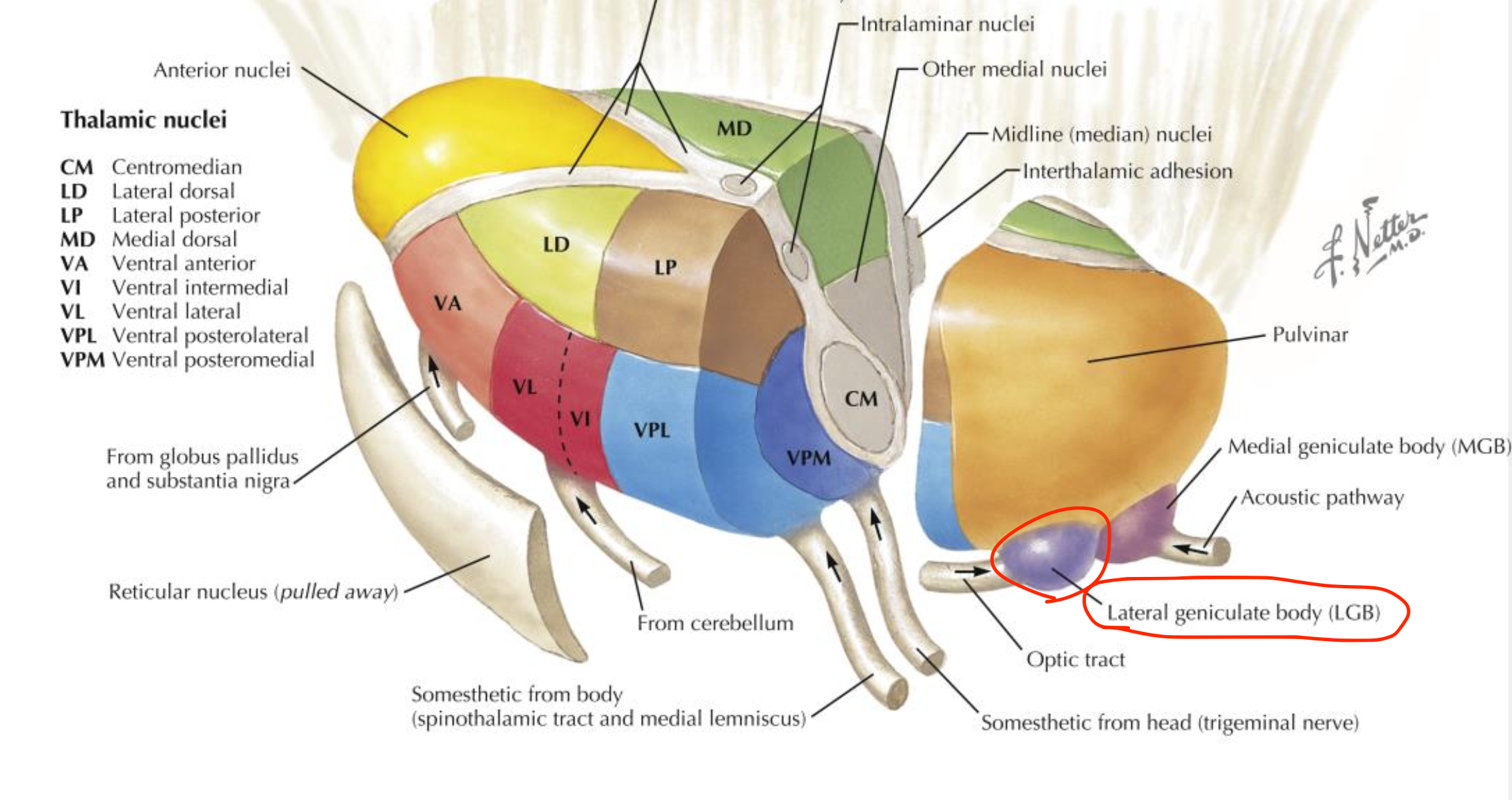
Lateral geniculate body (LGB)
Located in the thalamus (metathalamus);
visual relay nucleus;
receives optic tract and projects to the visual cortex
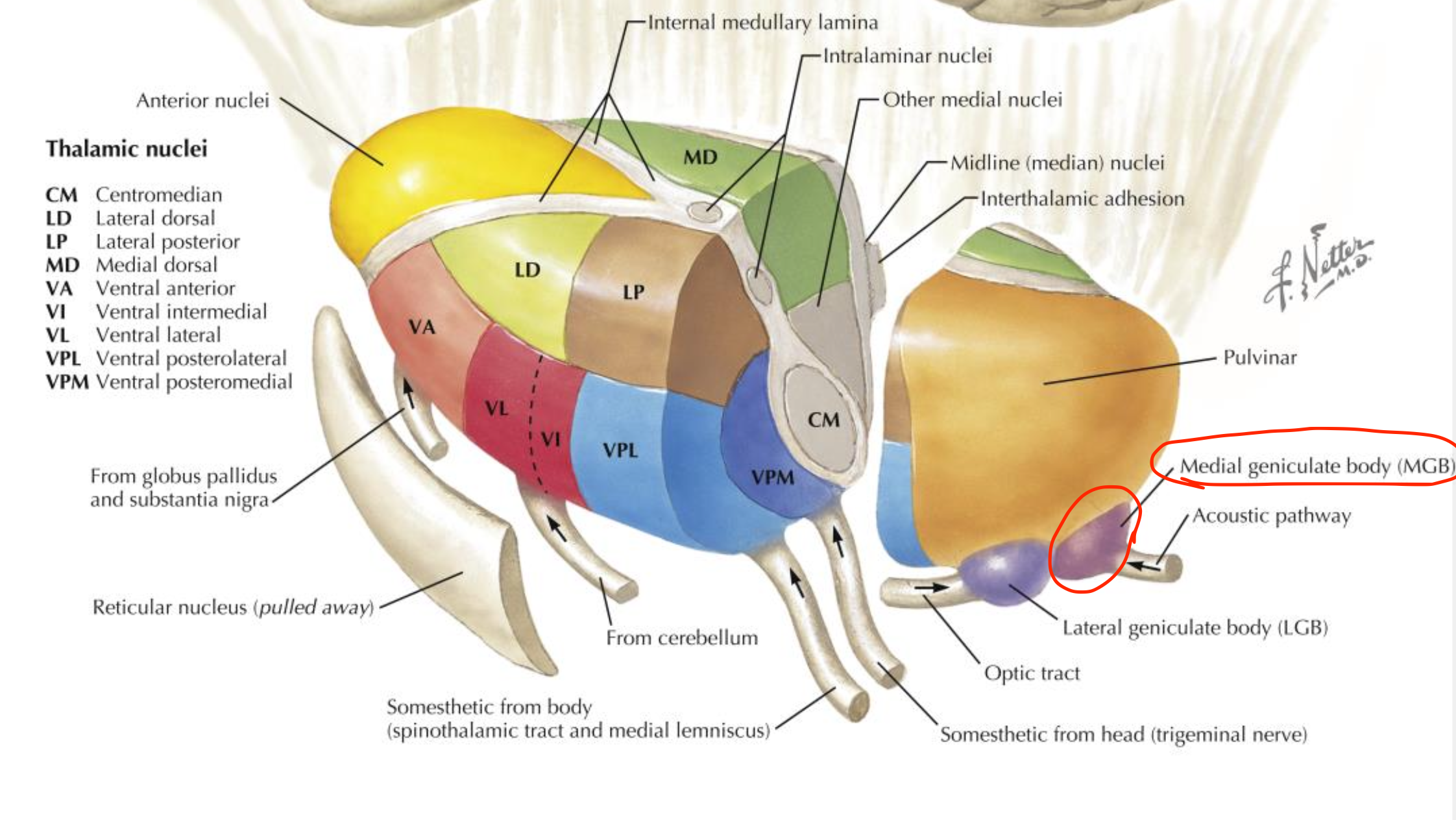
Medial geniculate body (MGB)
Located in the thalamus (metathalamus);
auditory relay nucleus;
receives inferior colliculus input and projects to the auditory cortex
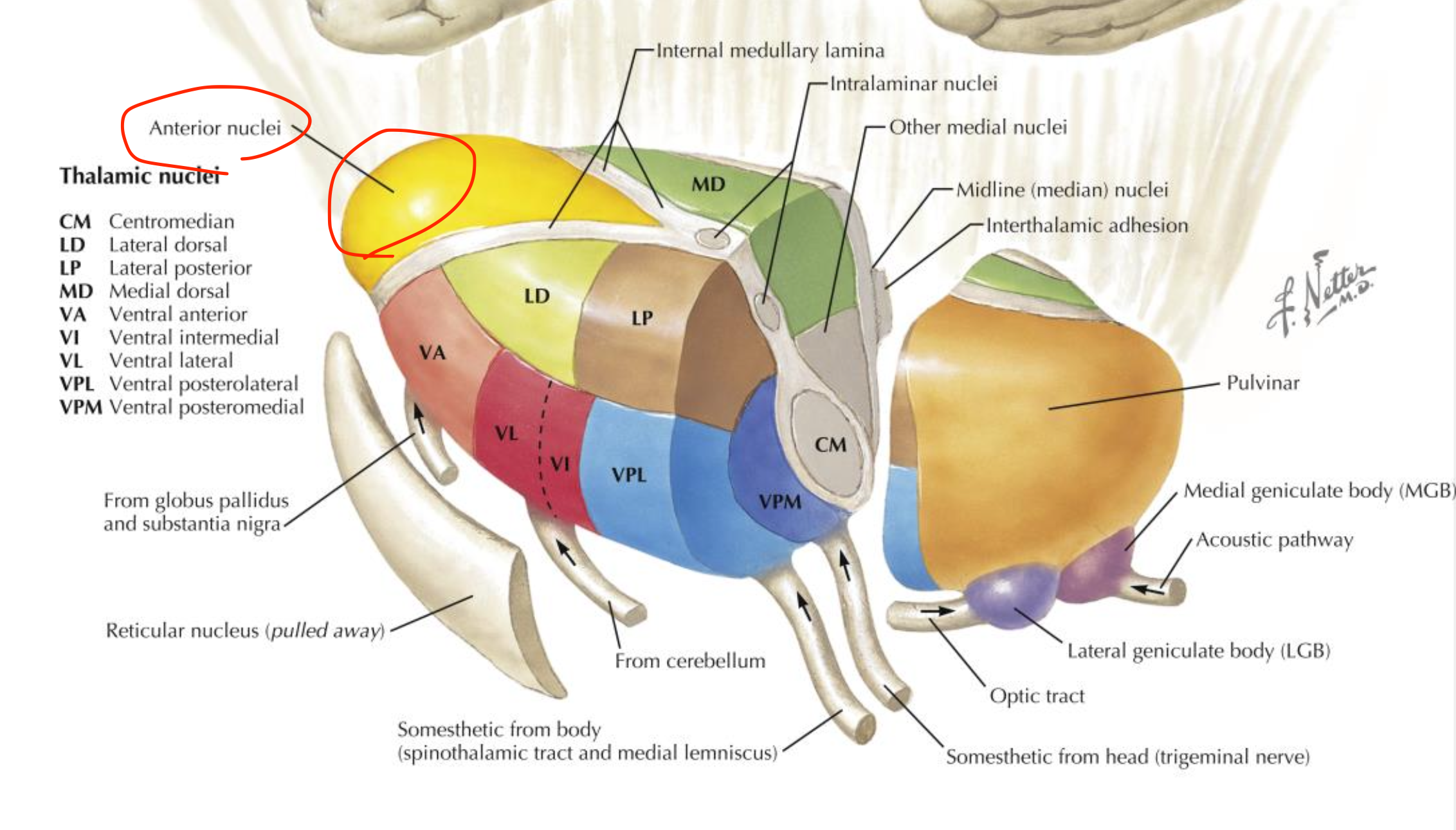
Anterior thalamic nuclei
Located in the thalamus (anterior group);
relay limbic information for emotion and memory;
connected via the mammillothalamic tract to the cingulate cortex
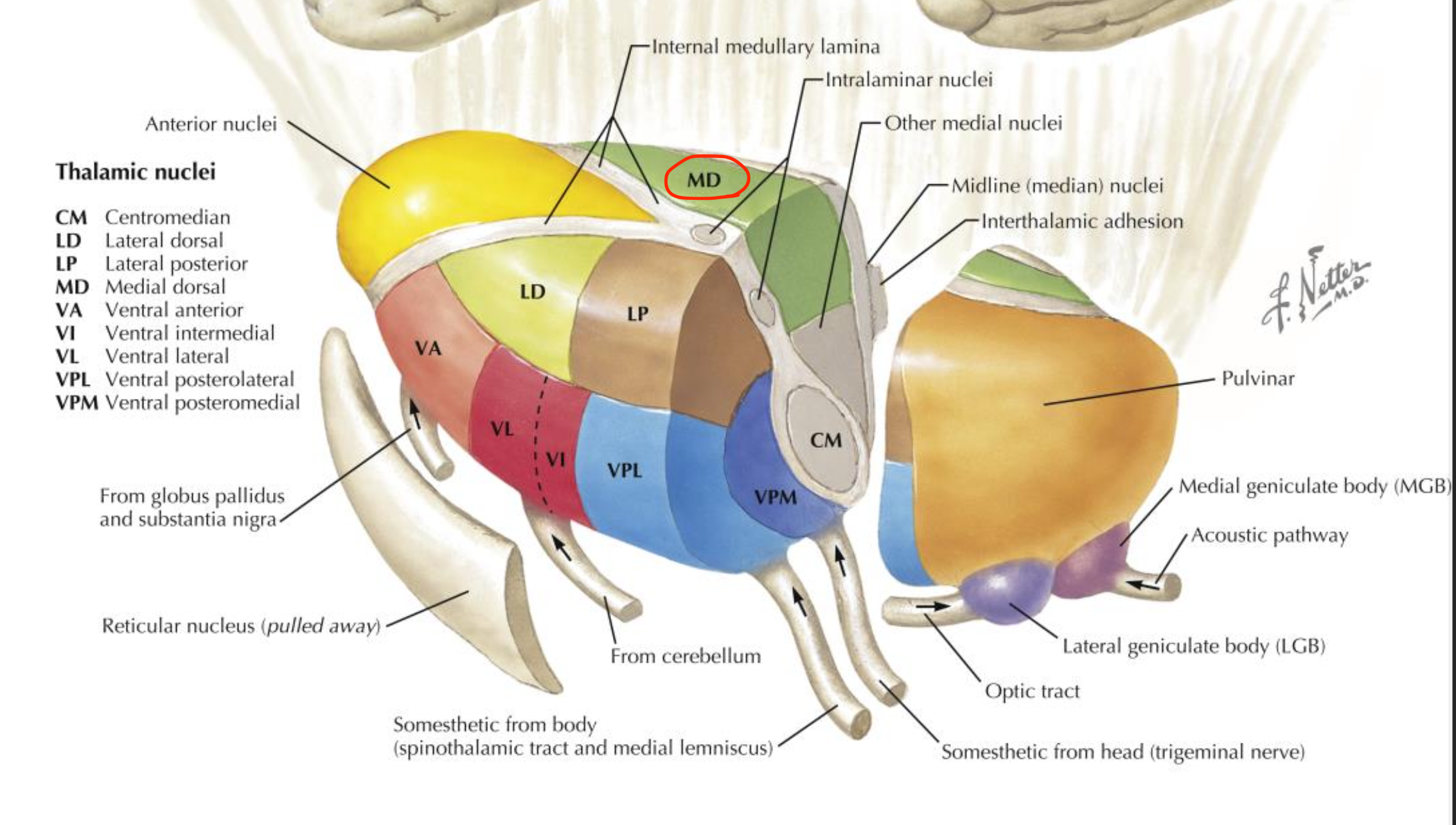
Mediodorsal thalamic nucleus
Located in the thalamus (medial group);
involved in emotion and cognition;
connects to frontal and cingulate cortices
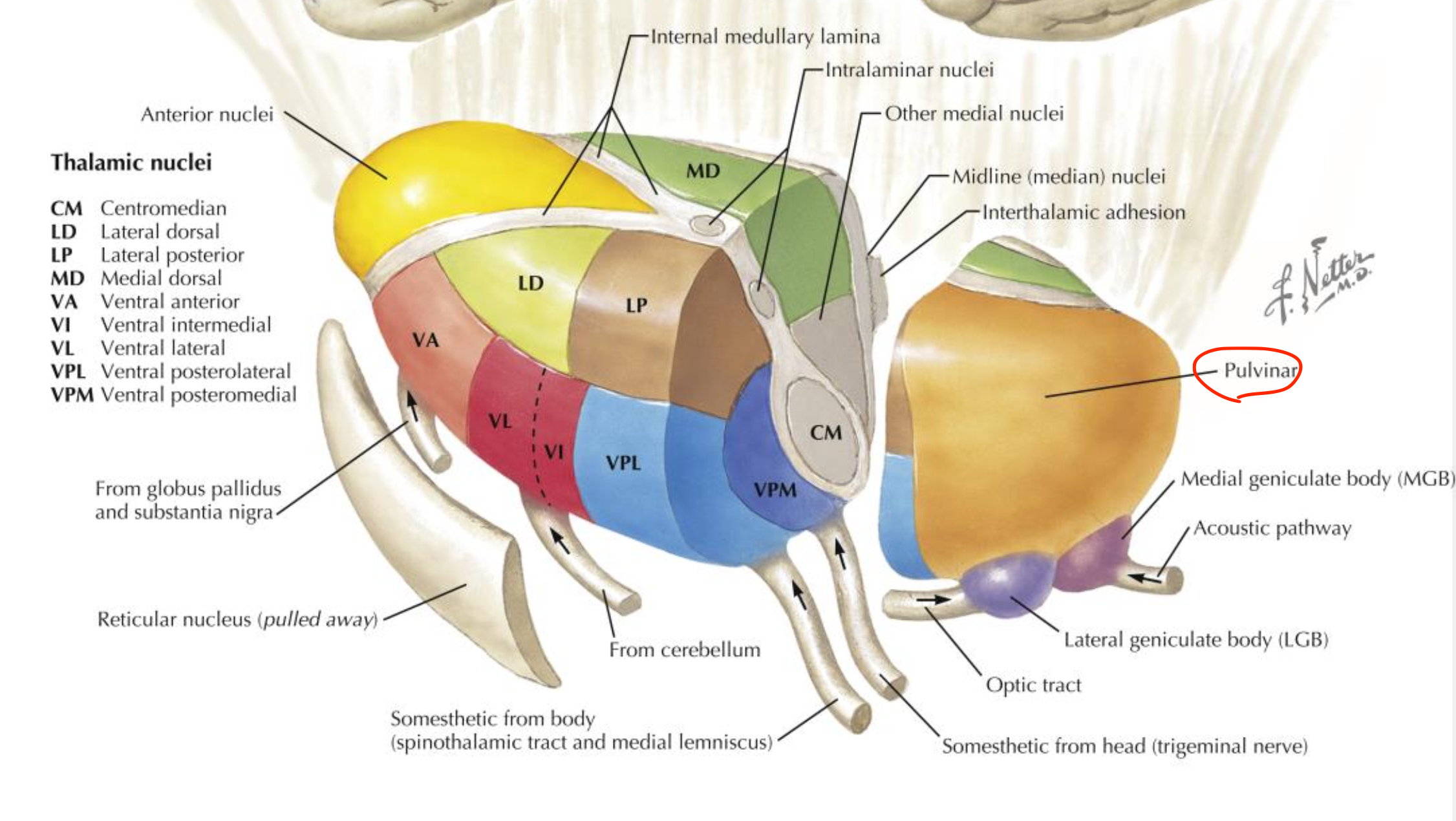
Pulvinar nucleus
Located in the thalamus (posterior-lateral group);
integrates sensory information and attention;
projects to the parietal cortex
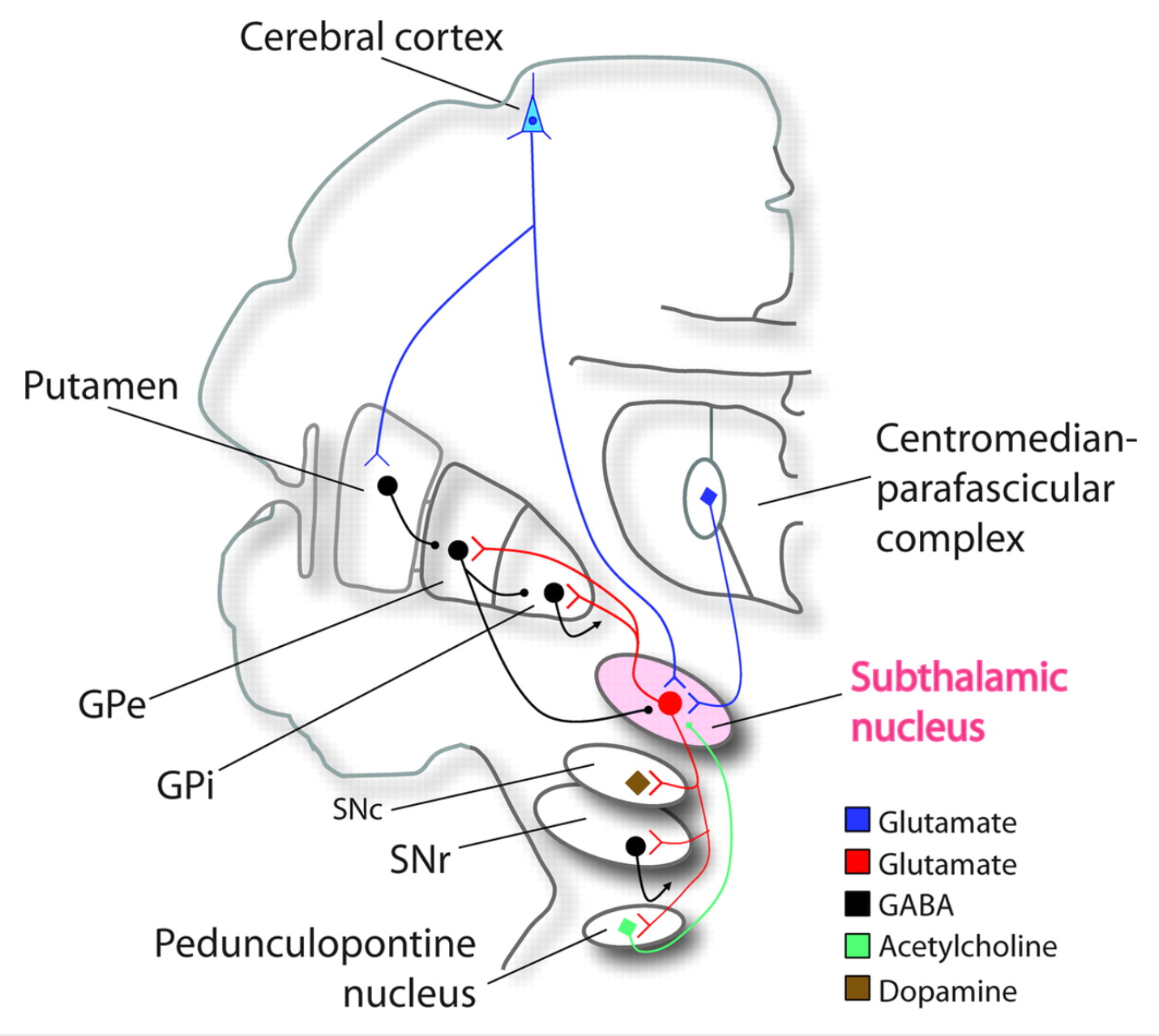
Subthalamic nucleus
Located in the subthalamus;
modulates motor activity of the basal ganglia;
connected to the globus pallidus via the subthalamic fasciculus
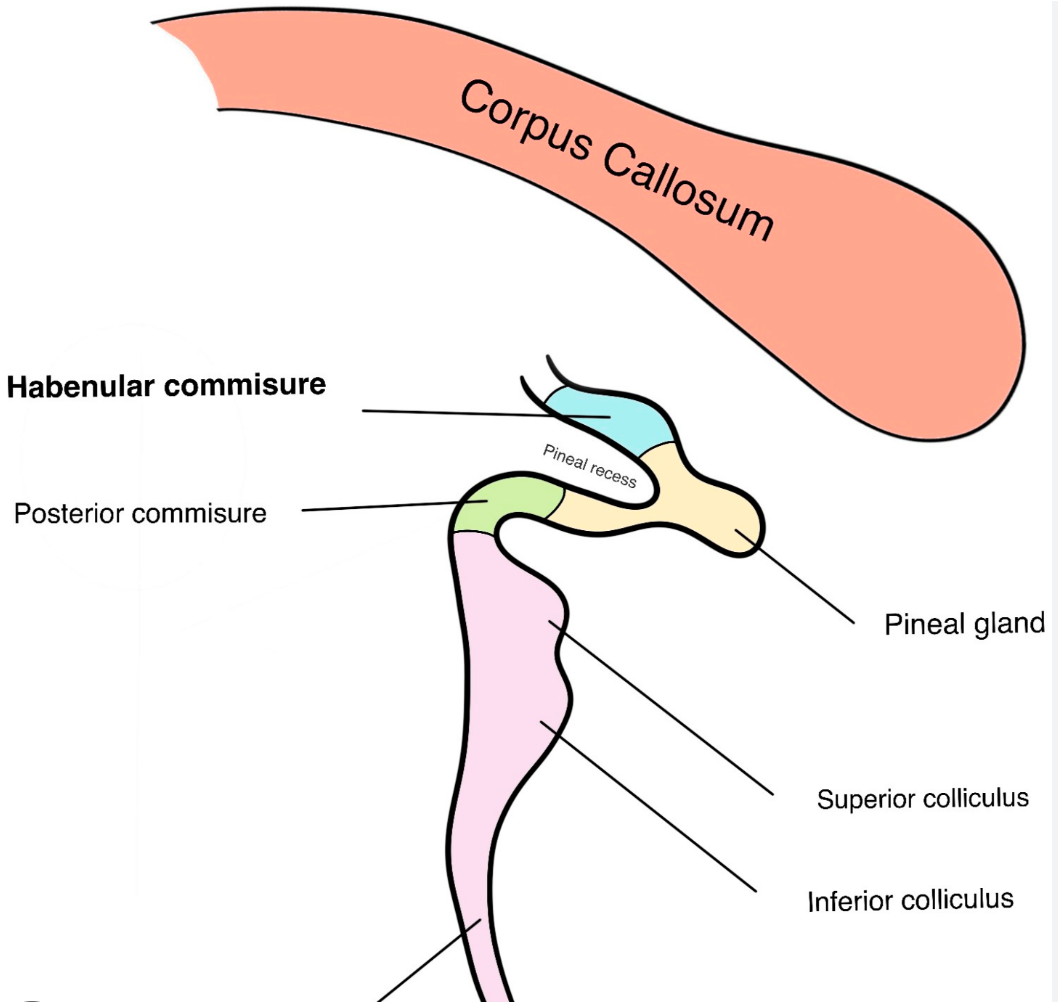
Habenular nuclei
Located in the epithalamus;
process reward and emotional responses;
connected via the habenulointerpeduncular tract
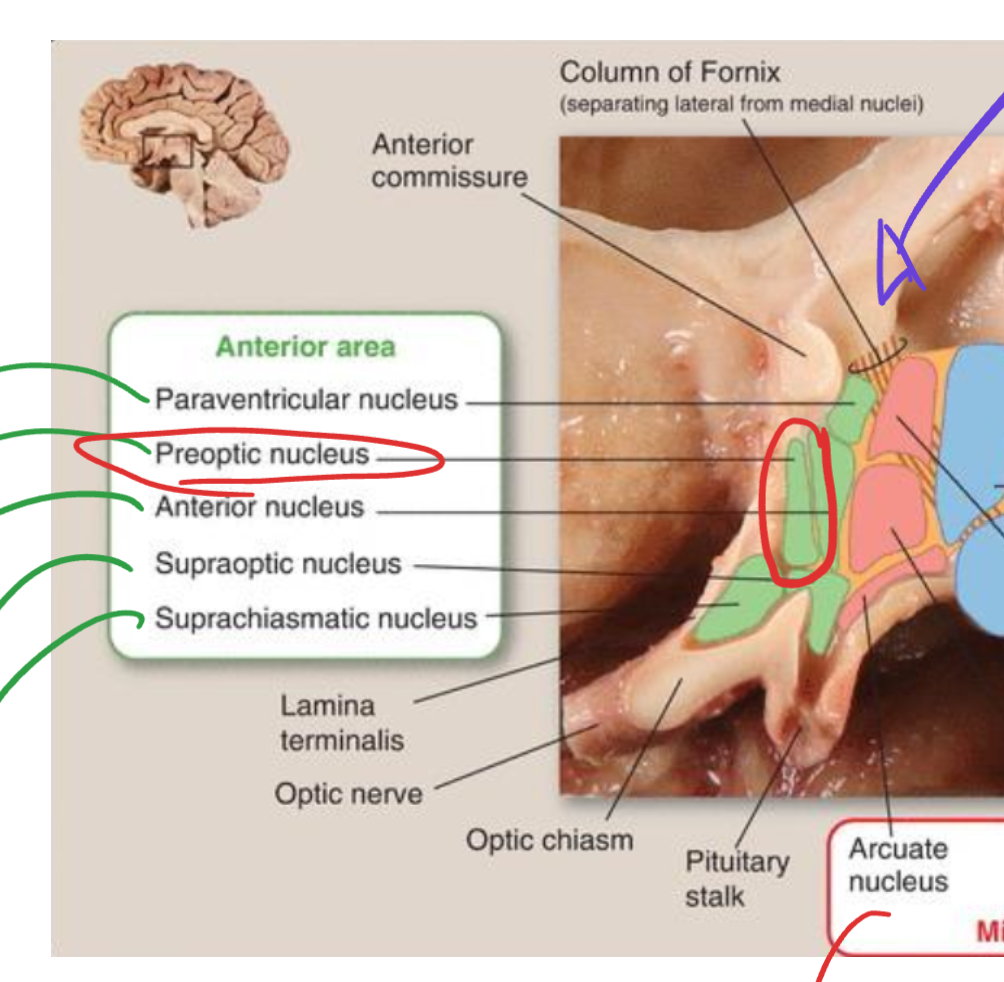
Preoptic nucleus
Located in the anterior hypothalamic area;
regulates body temperature by promoting heat loss through vasodilation and sweating;
part of the thermoregulatory center
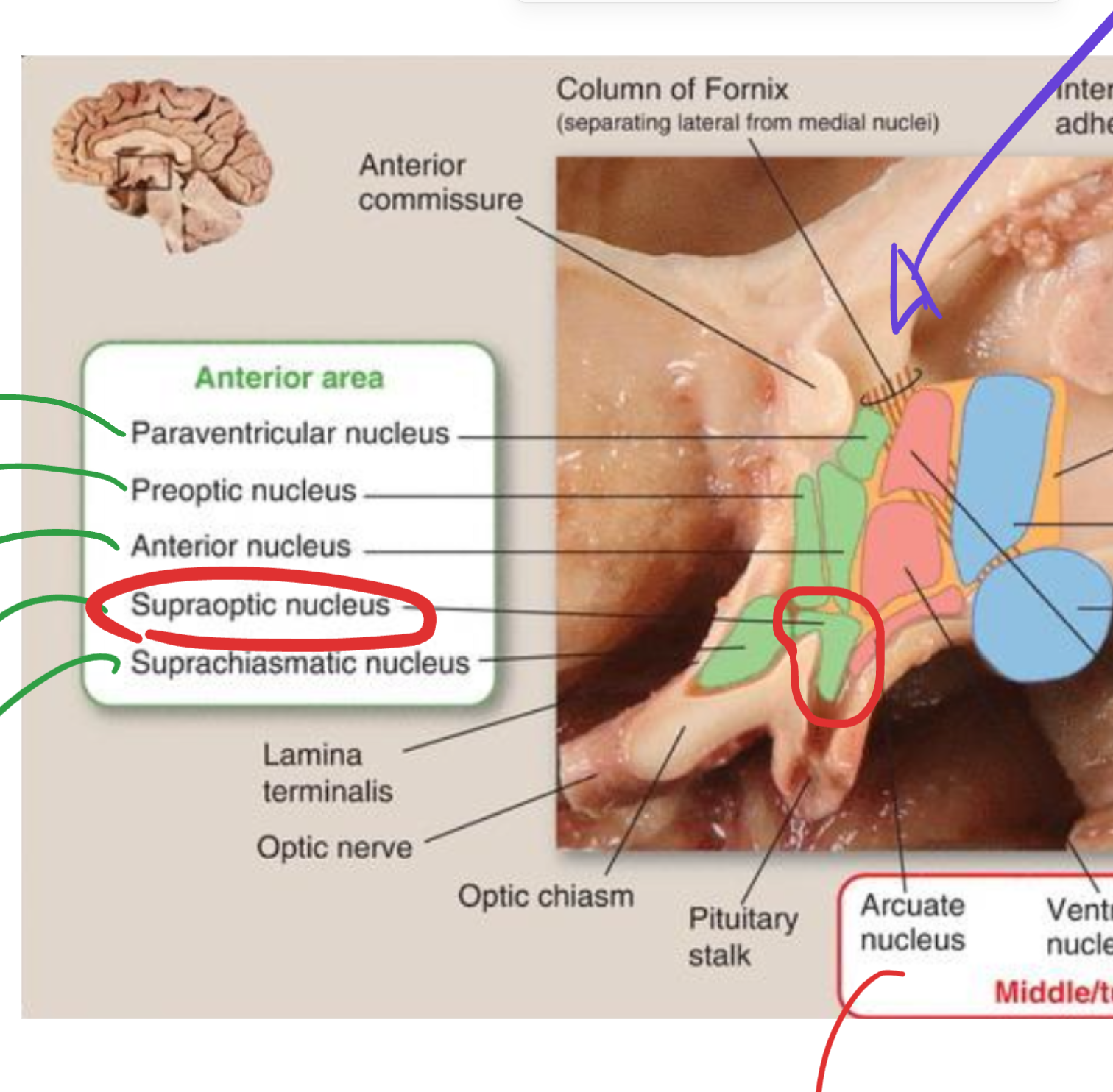
Supraoptic nucleus
Located in the hypothalamus (anterior region);
produces vasopressin (ADH);
sends axons through the hypothalamo-hypophyseal tract to the posterior pituitary
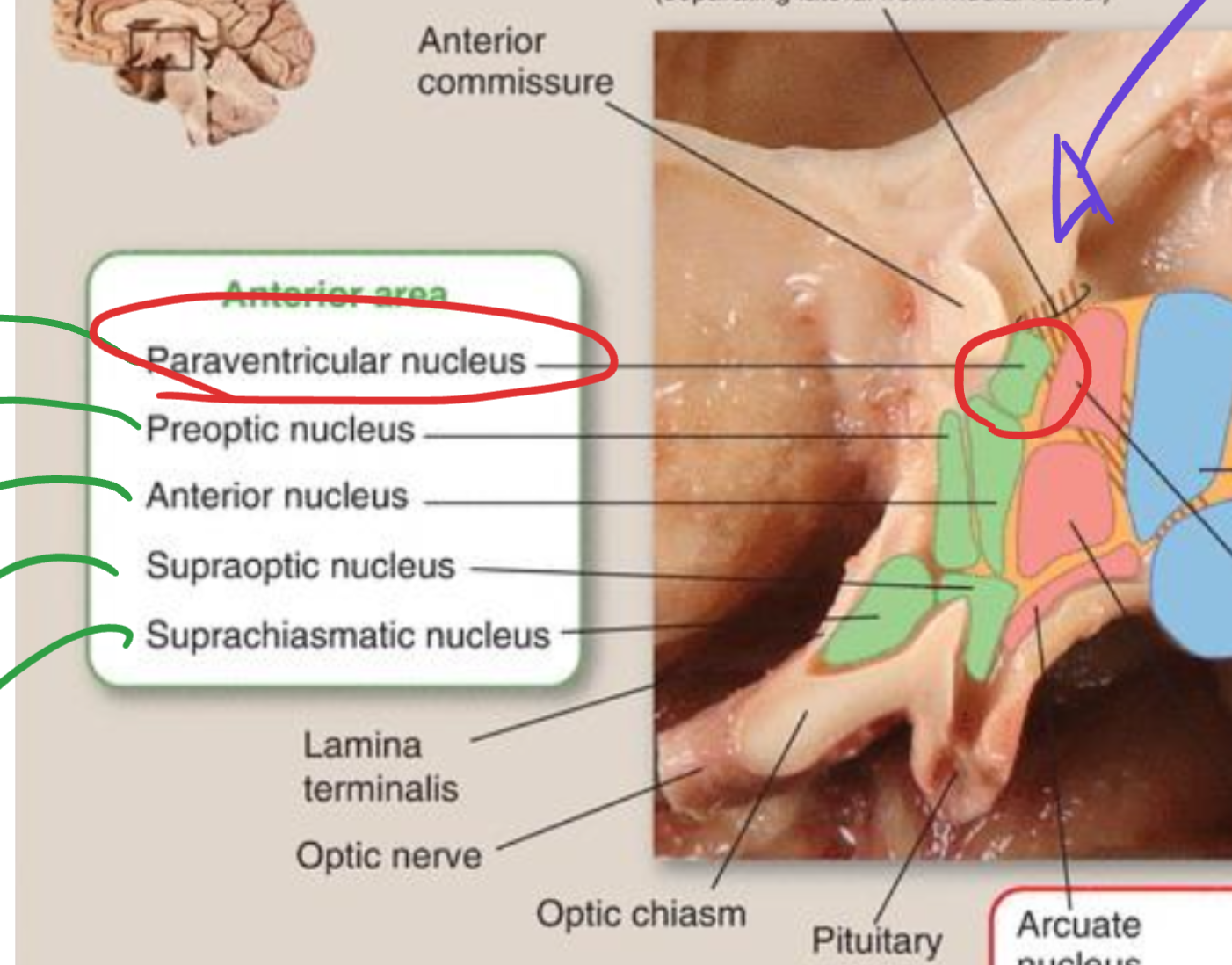
Paraventricular nucleus
Located in the hypothalamus (anterior region);
produces oxytocin and releasing hormones;
connected via the hypothalamo-hypophyseal tract
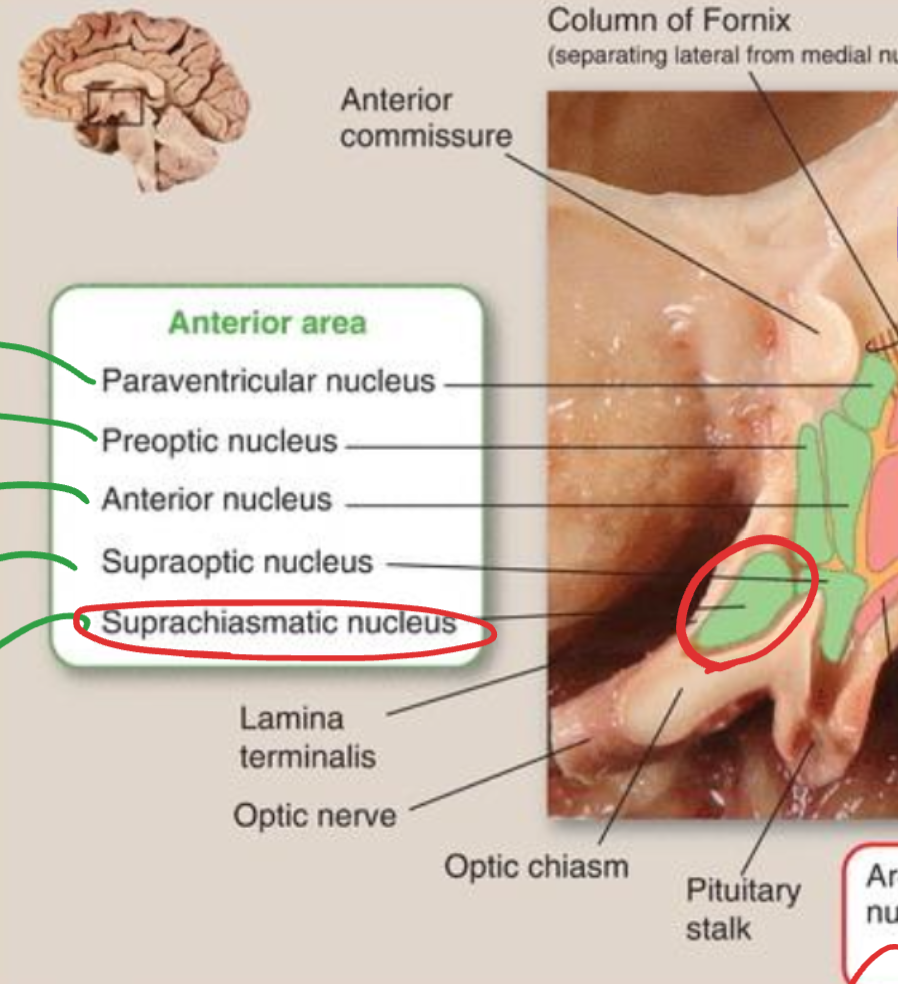
Suprachiasmatic nucleus
Located above the optic chiasm;
serves as the circadian rhythm pacemaker;
receives direct retinal input for synchronization of biological clocks
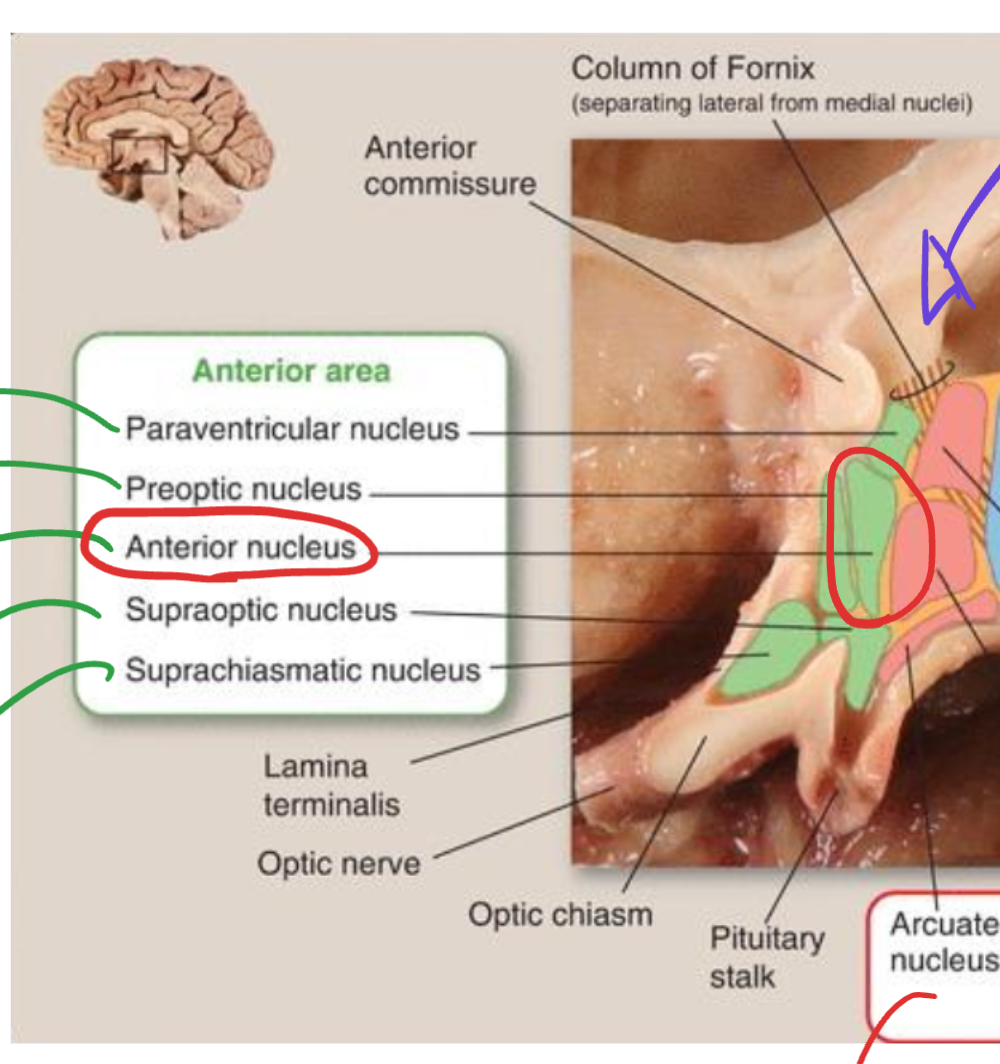
Anterior hypothalamic nucleus
Located anteriorly near the preoptic area;
promotes heat dissipation and activates parasympathetic responses during elevated body temperature
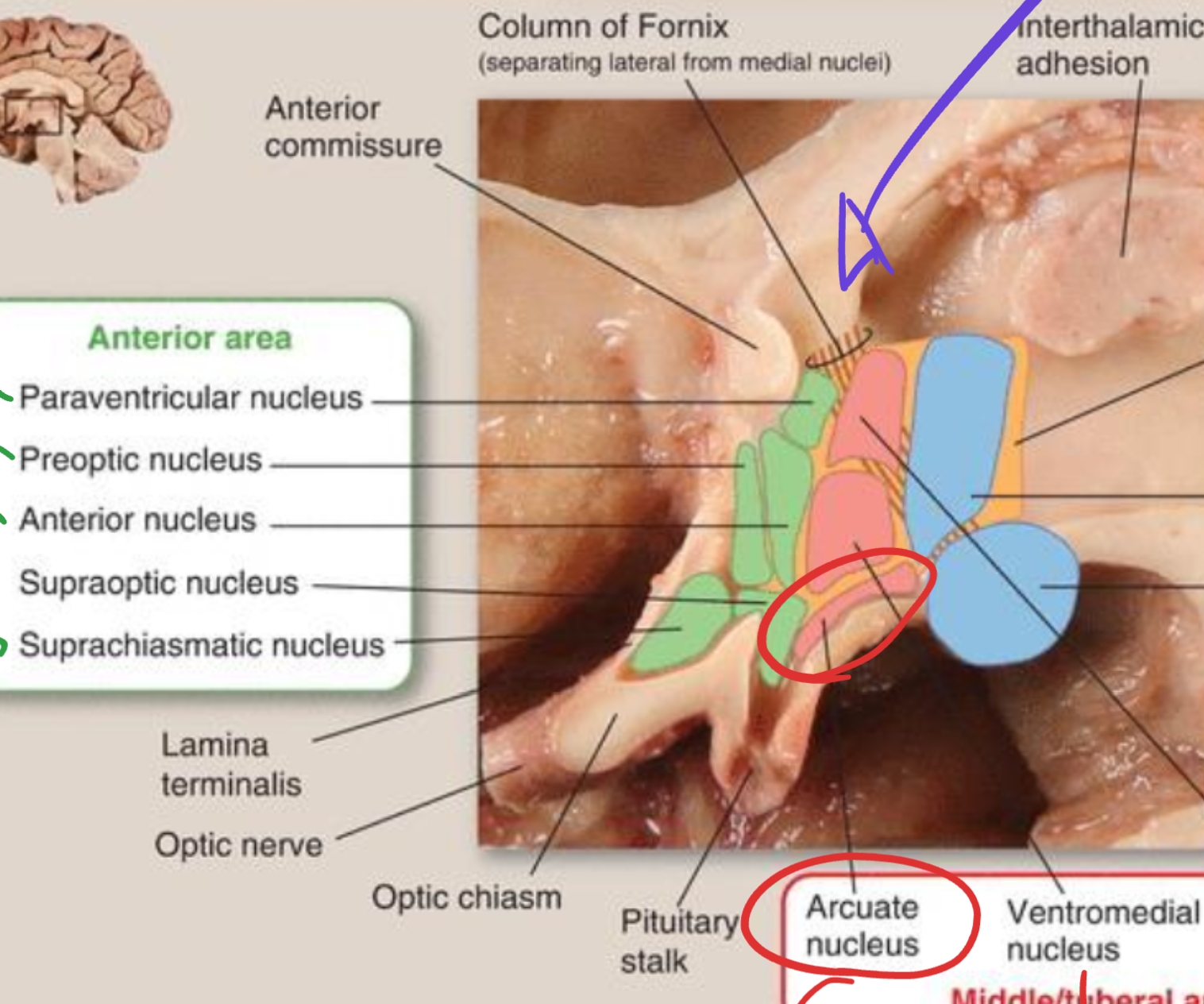
Arcuate nucleus
Located in the hypothalamus (tuberal region);
regulates pituitary hormone secretion;
projects through the tuberoinfundibular pathway
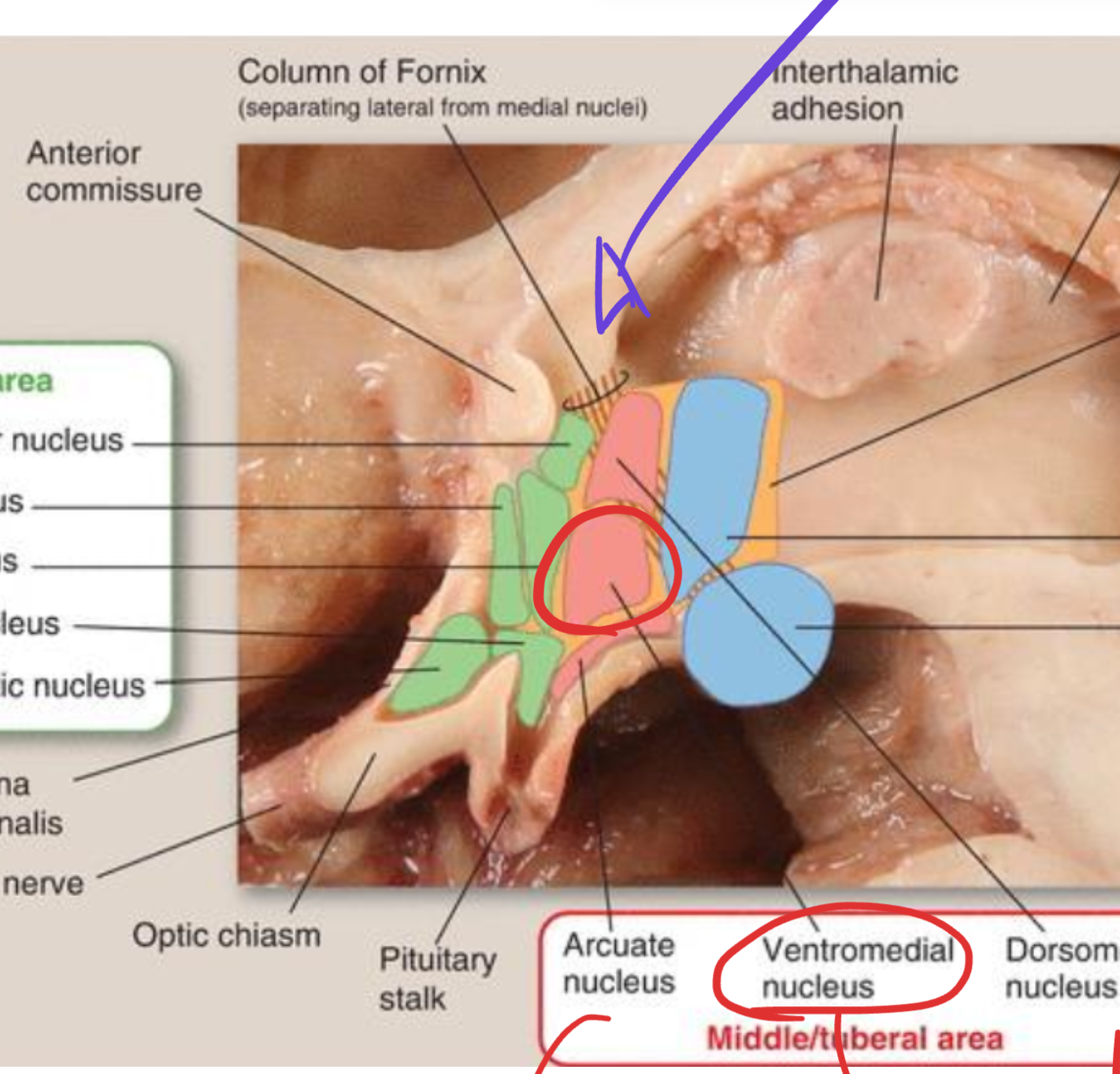
Ventromedial nucleus
Located in the hypothalamus (tuberal region);
acts as the satiety center inhibiting feeding;
connected via the medial forebrain bundle
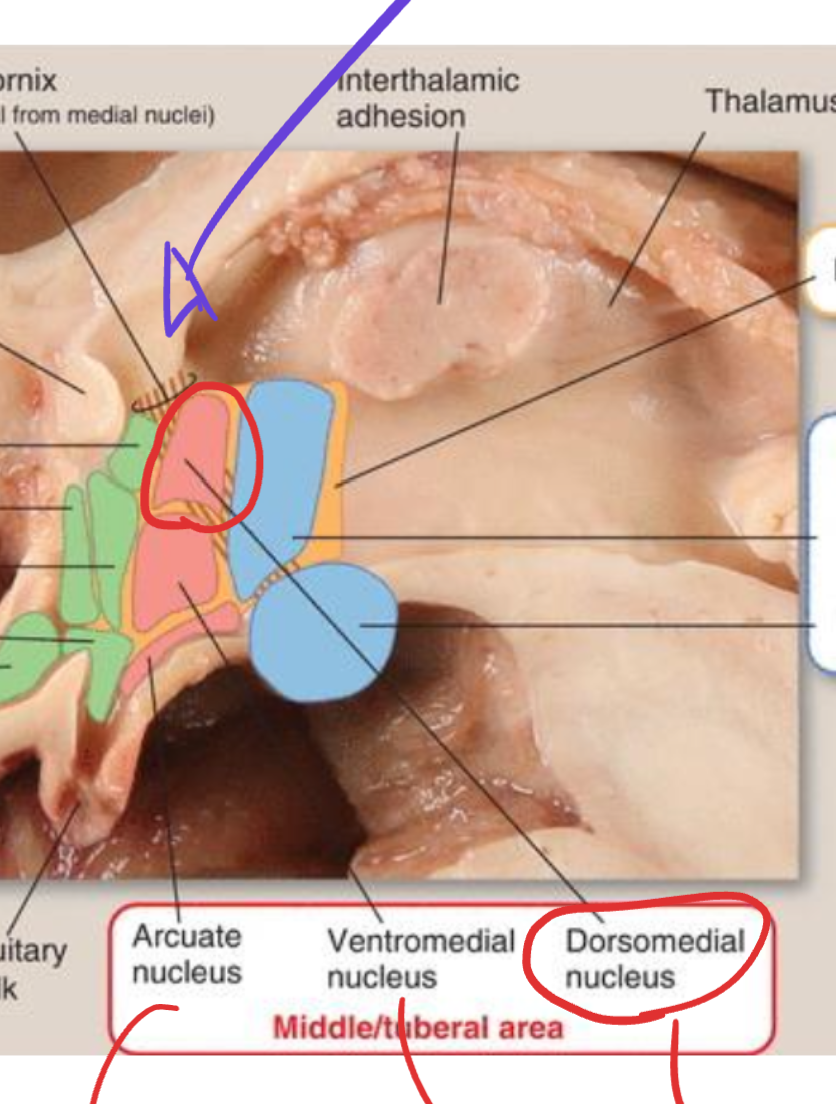
Dorsomedial nucleus
Located in the tuberal region;
integrates autonomic and emotional behavior;
influences circadian and feeding responses
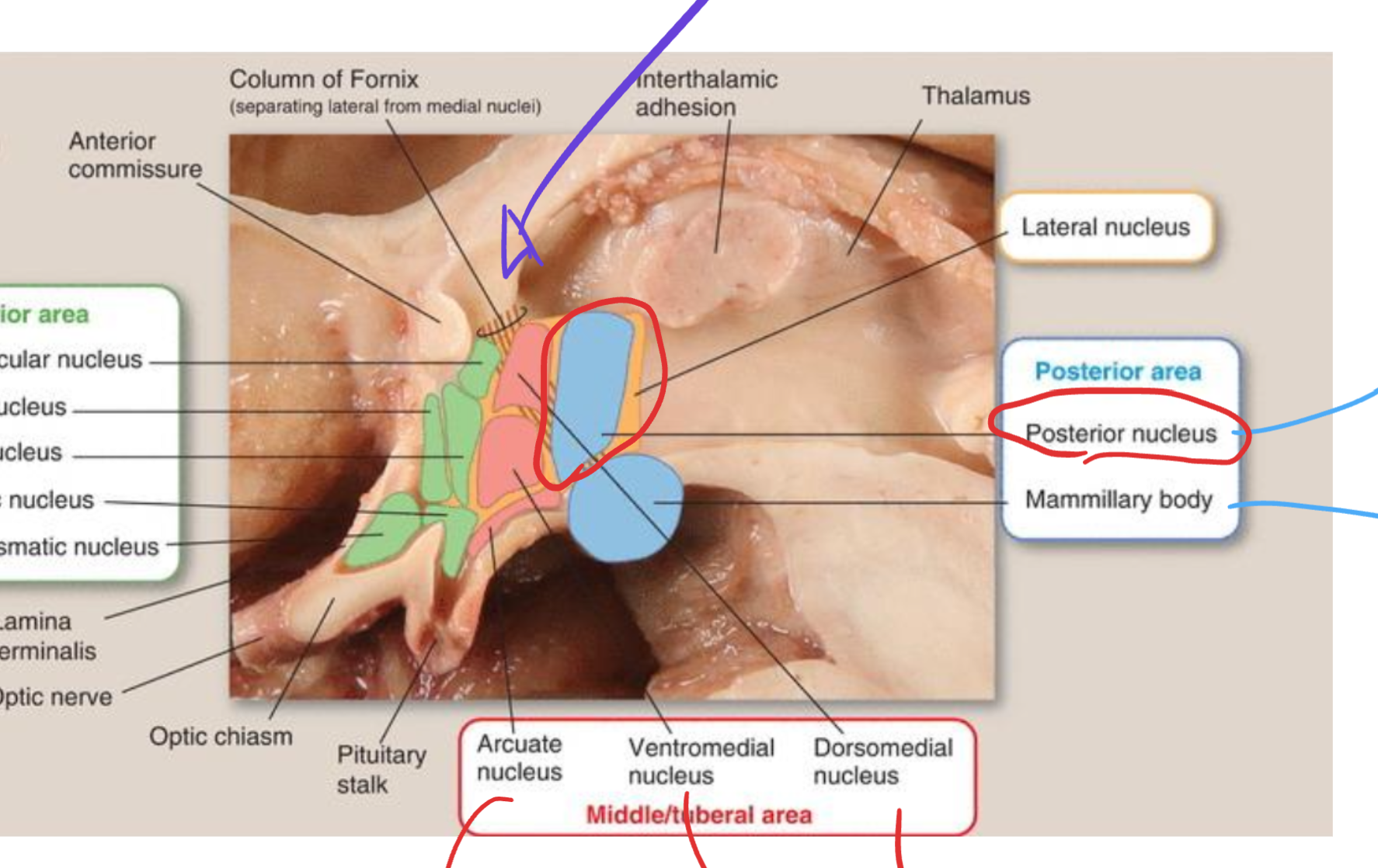
Posterior hypothalamic nucleus
Located in the posterior hypothalamic area;
promotes heat conservation and sympathetic activation during cold exposure;
associated with arousal and wakefulness
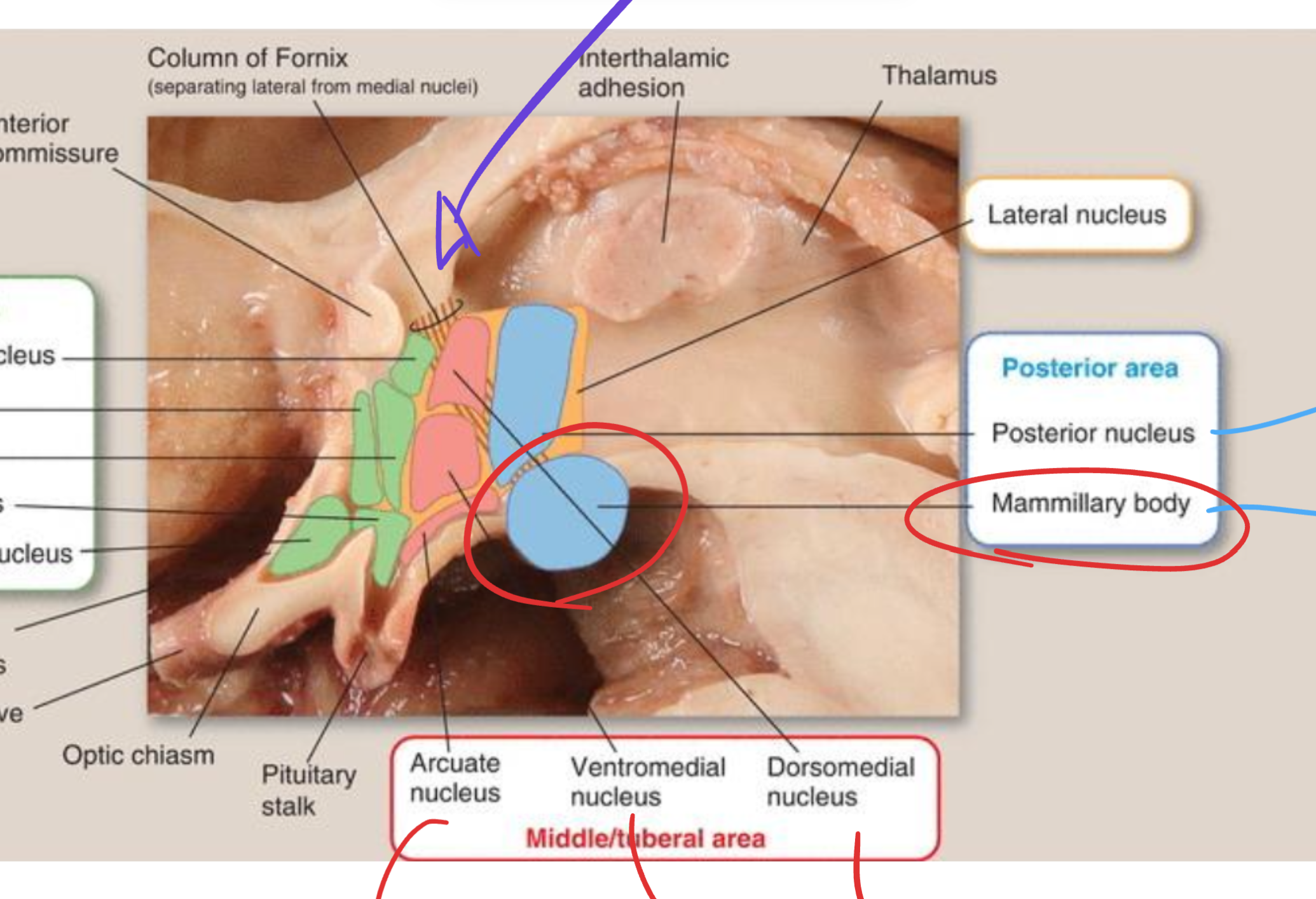
Mammillary nucleus
Located in the hypothalamus (posterior region);
involved in memory and limbic relay;
projects via the mammillothalamic tract to the anterior thalamus
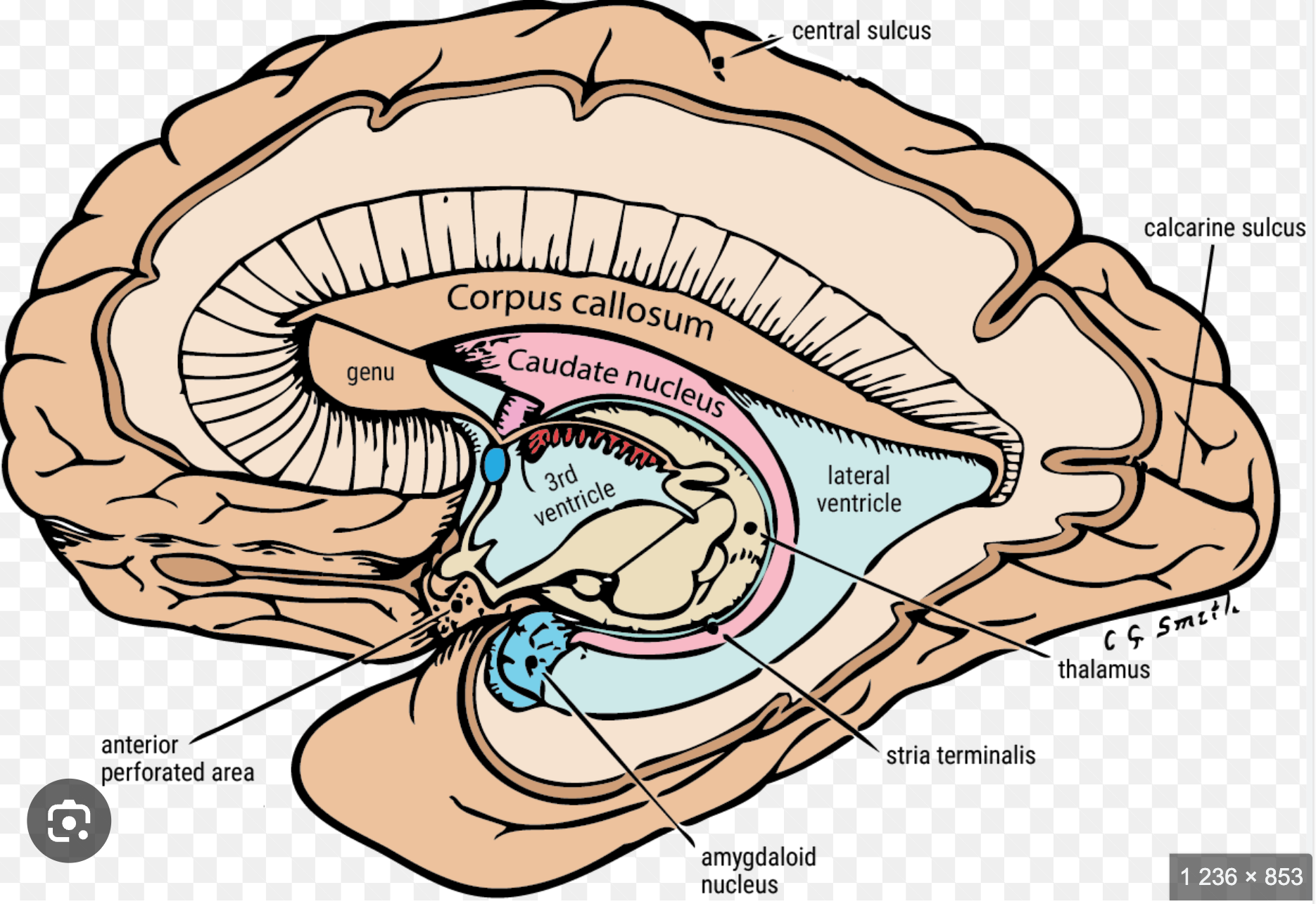
Caudate nucleus
Located in the telencephalon (basal nuclei);
controls movement and cognition;
receives corticostriatal and nigrostriatal inputs
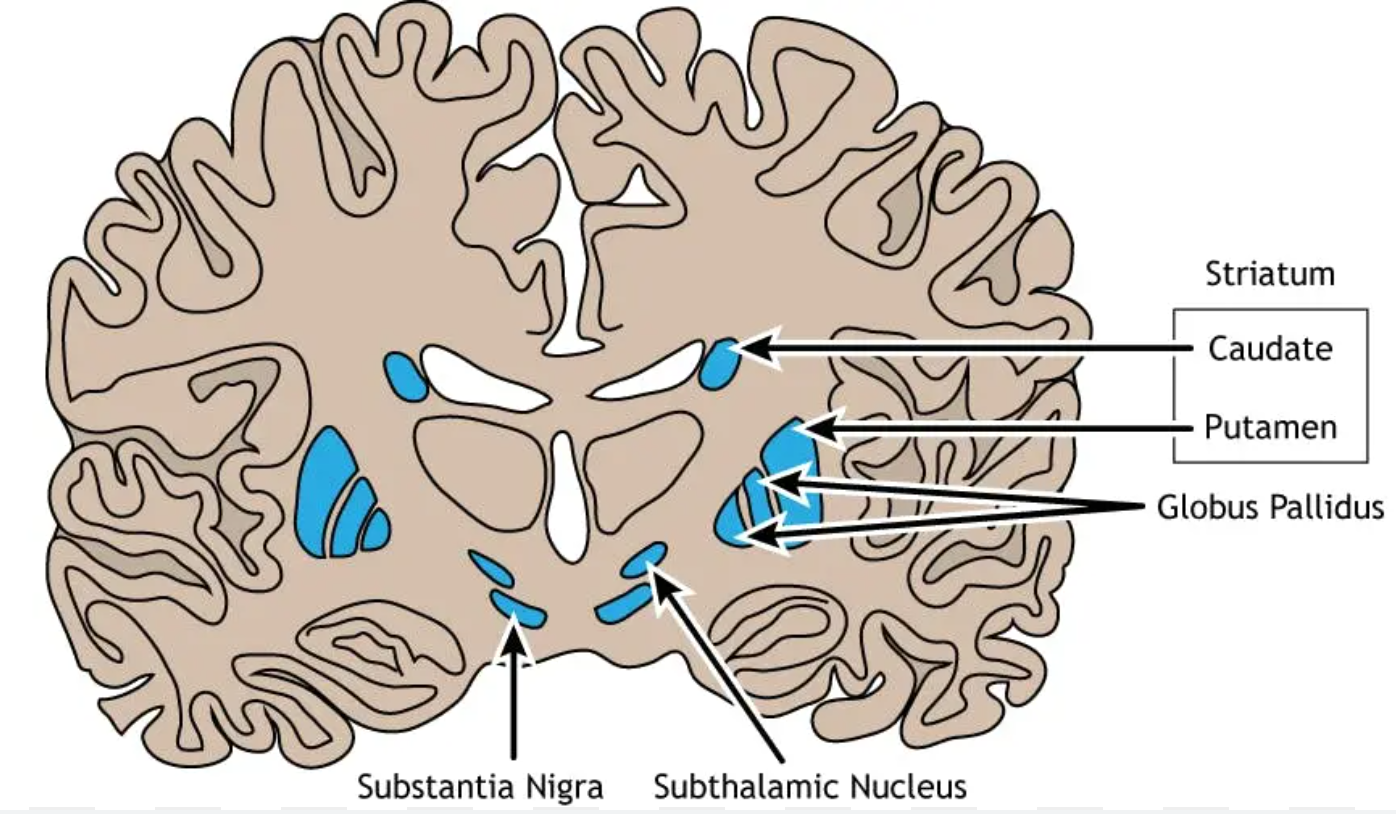
Putamen
Located in the telencephalon (basal nuclei);
regulates learned movement patterns;
receives corticostriatal fibers
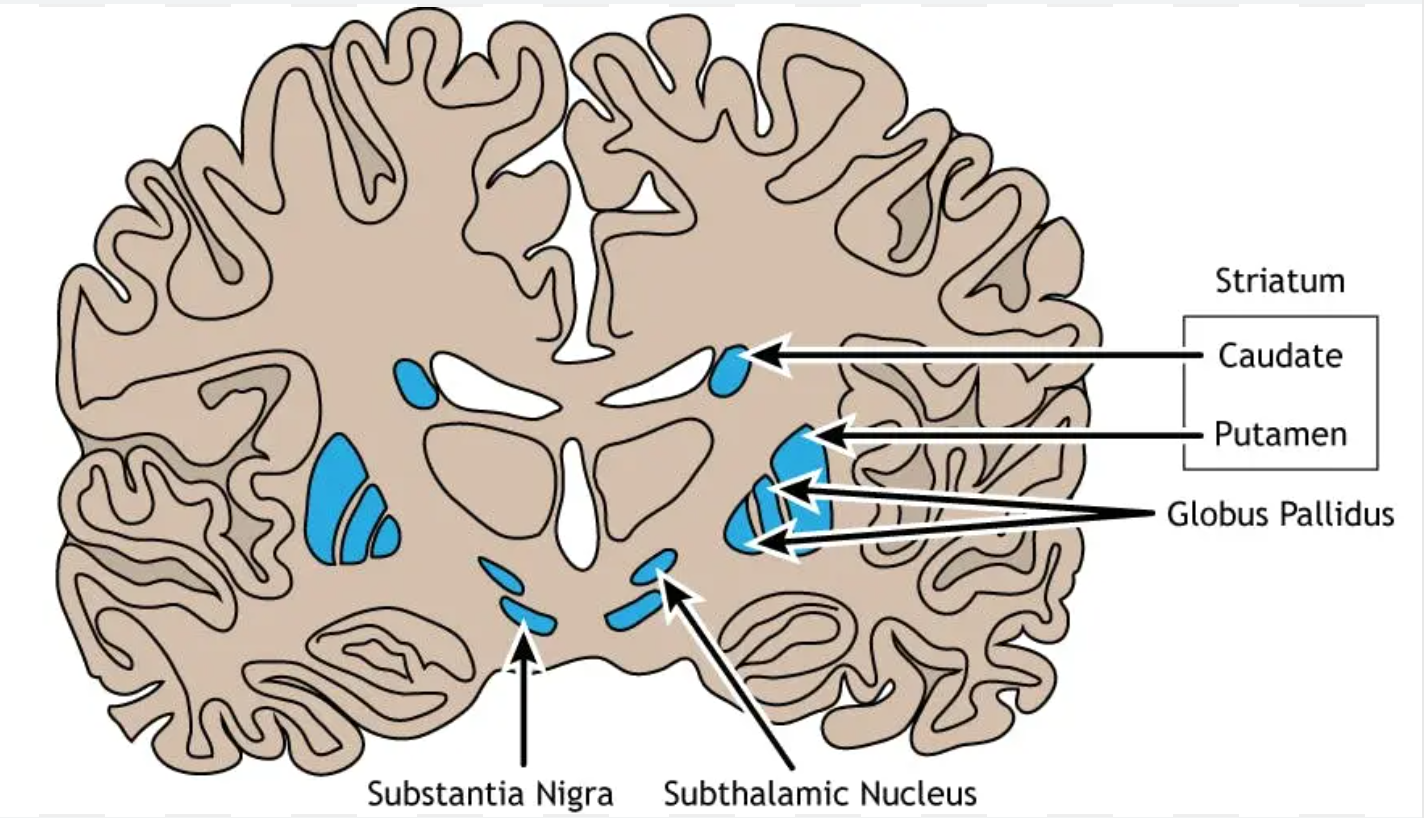
Globus pallidus
Located in the telencephalon (basal nuclei, internal and external segments);
regulates voluntary movement via pallidothalamic fibers to VA/VL thalamic nuclei
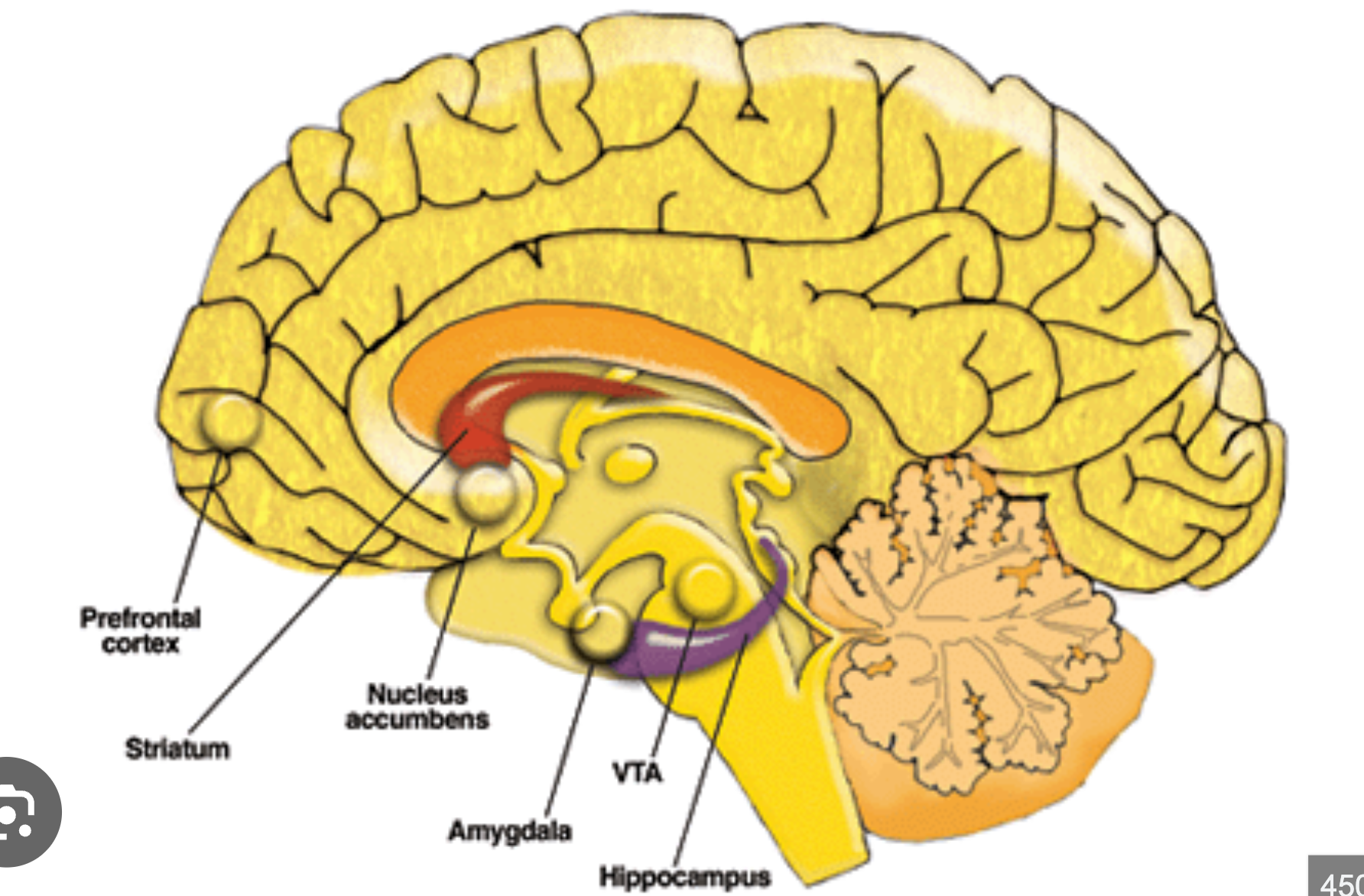
Nucleus accumbens
Located in the telencephalon (ventral striatum);
mediates reward, motivation, and reinforcement;
receives mesolimbic dopaminergic input
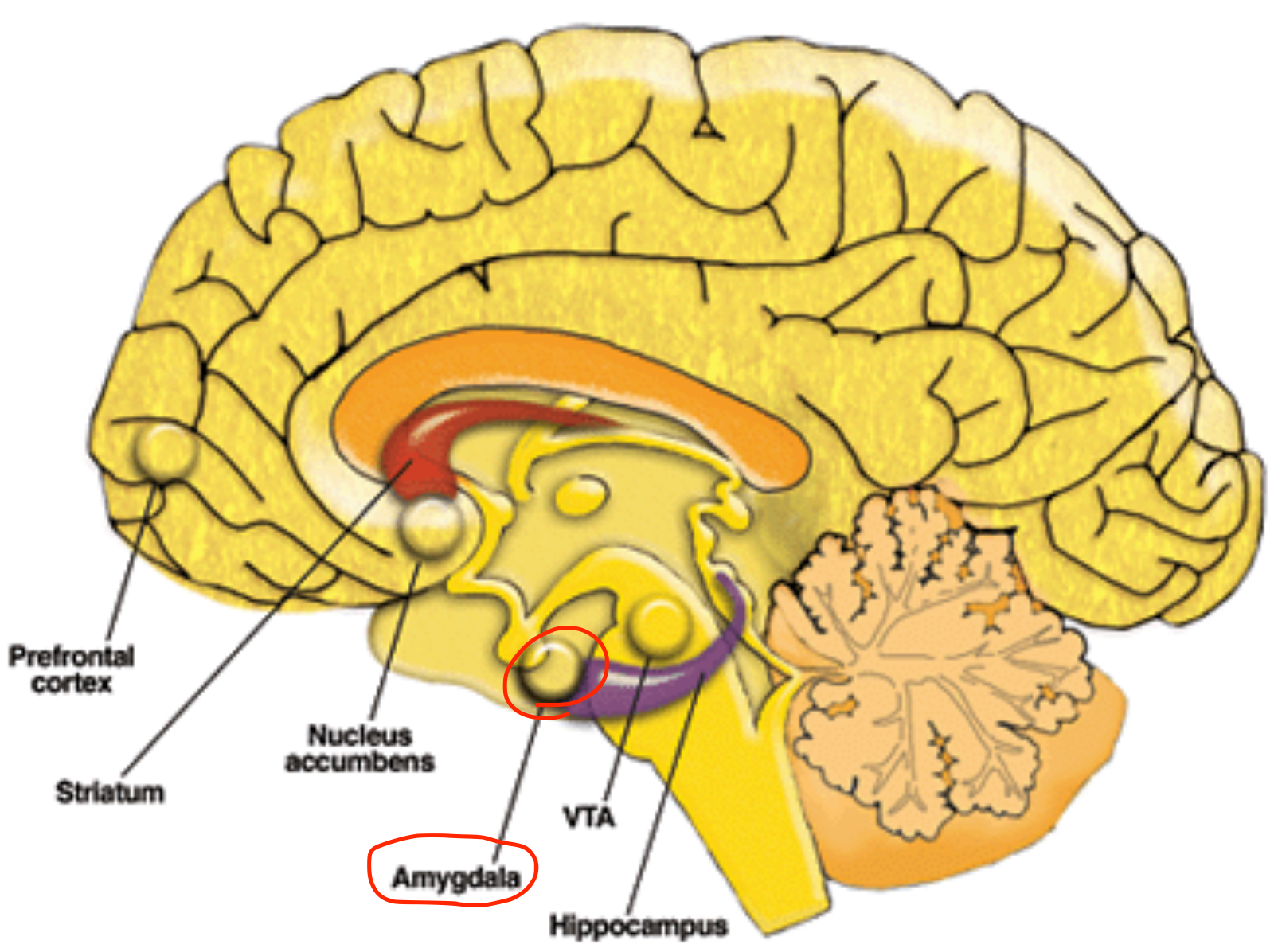
Amygdaloid nucleus
Located in the telencephalon (temporal lobe, limbic system);
controls emotion and behavior;
connected via stria terminalis and ventral amygdalofugal pathway
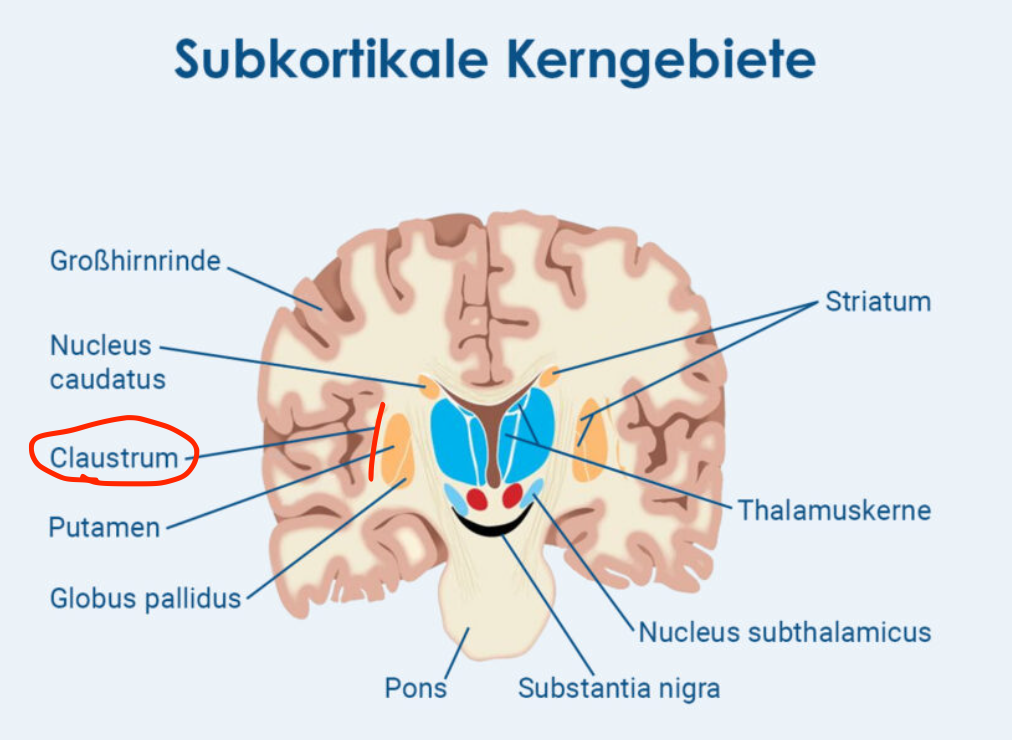
Claustrum
Located in the telencephalon (between insula and putamen);
integrates multisensory information;
connected with cortical association areas
Olfactory (I)
Nucleus: Olfactory bulb and tract
Location: Telencephalon (base of frontal lobe)
Function: Smell perception
Type: Sensory
Optic (II)
Nucleus: Lateral geniculate body
Location: Diencephalon (thalamus)
Function: Visual relay to occipital cortex
Type: Sensory
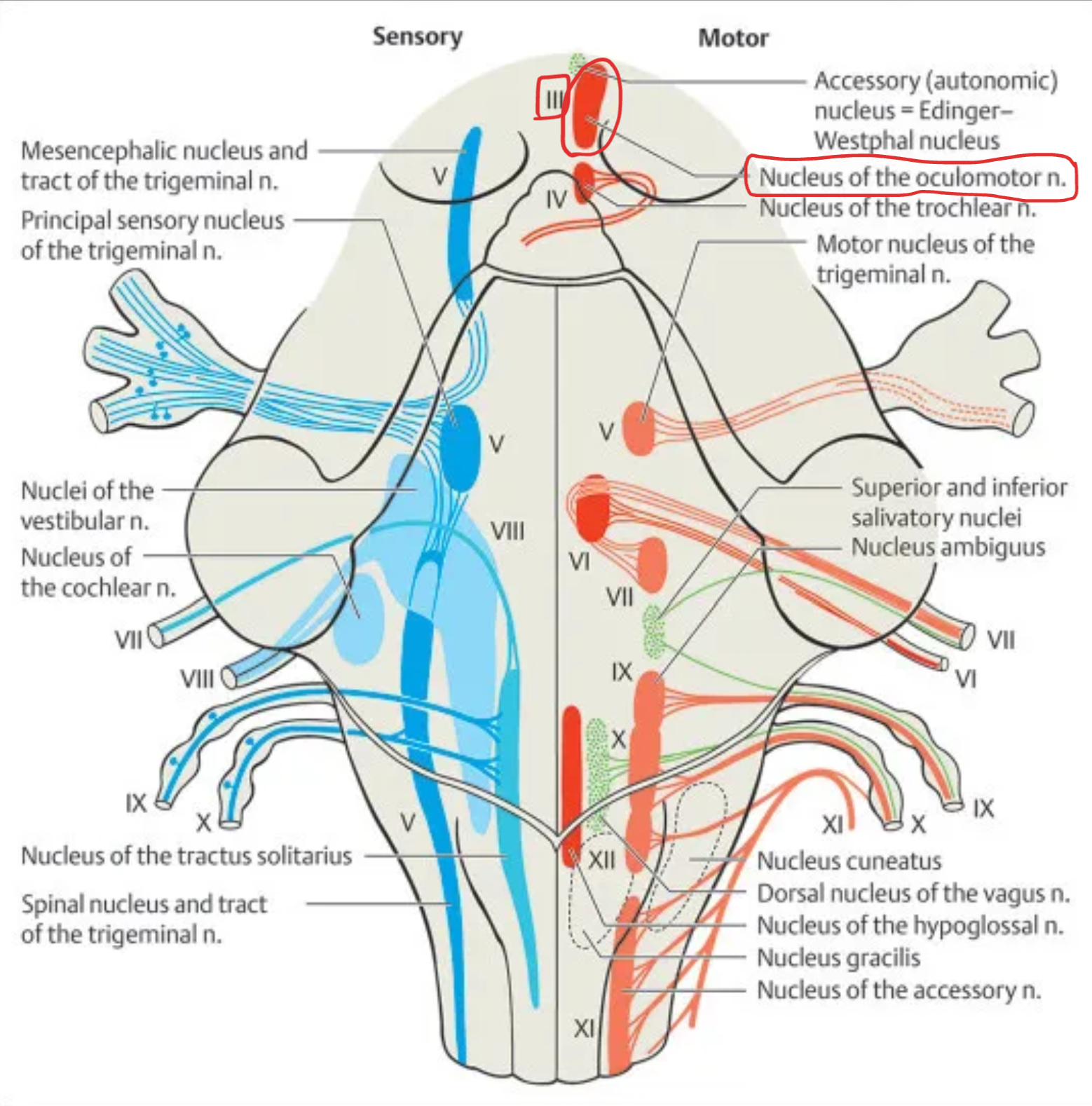
Oculomotor (III)
Nucleus: Oculomotor nucleus, Edinger–Westphal nucleus
Location: Midbrain at the level of superior colliculus
Function:
Oculomotor nucleus: motor control of extraocular muscles (SR, IR, MR, IO)
Edinger–Westphal nucleus: parasympathetic control for pupil constriction and lens accommodation
Type: Motor + Parasympathetic
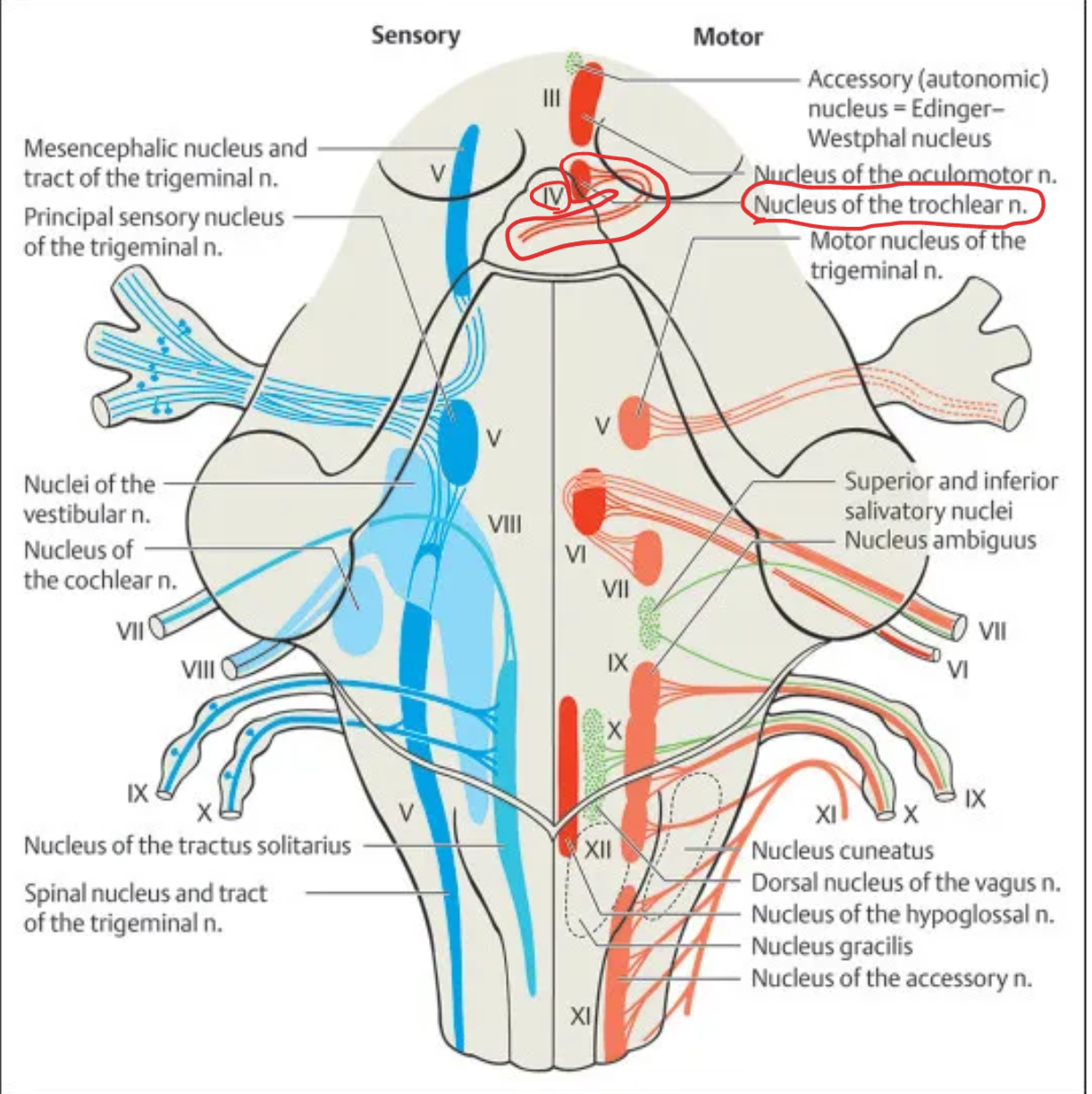
Trochlear (IV)
Nucleus: Trochlear nucleus
Location: Midbrain at the level of inferior colliculus (dorsal aspect)
Function: Innervates superior oblique muscle (eye depression and intorsion)
Type: Motor
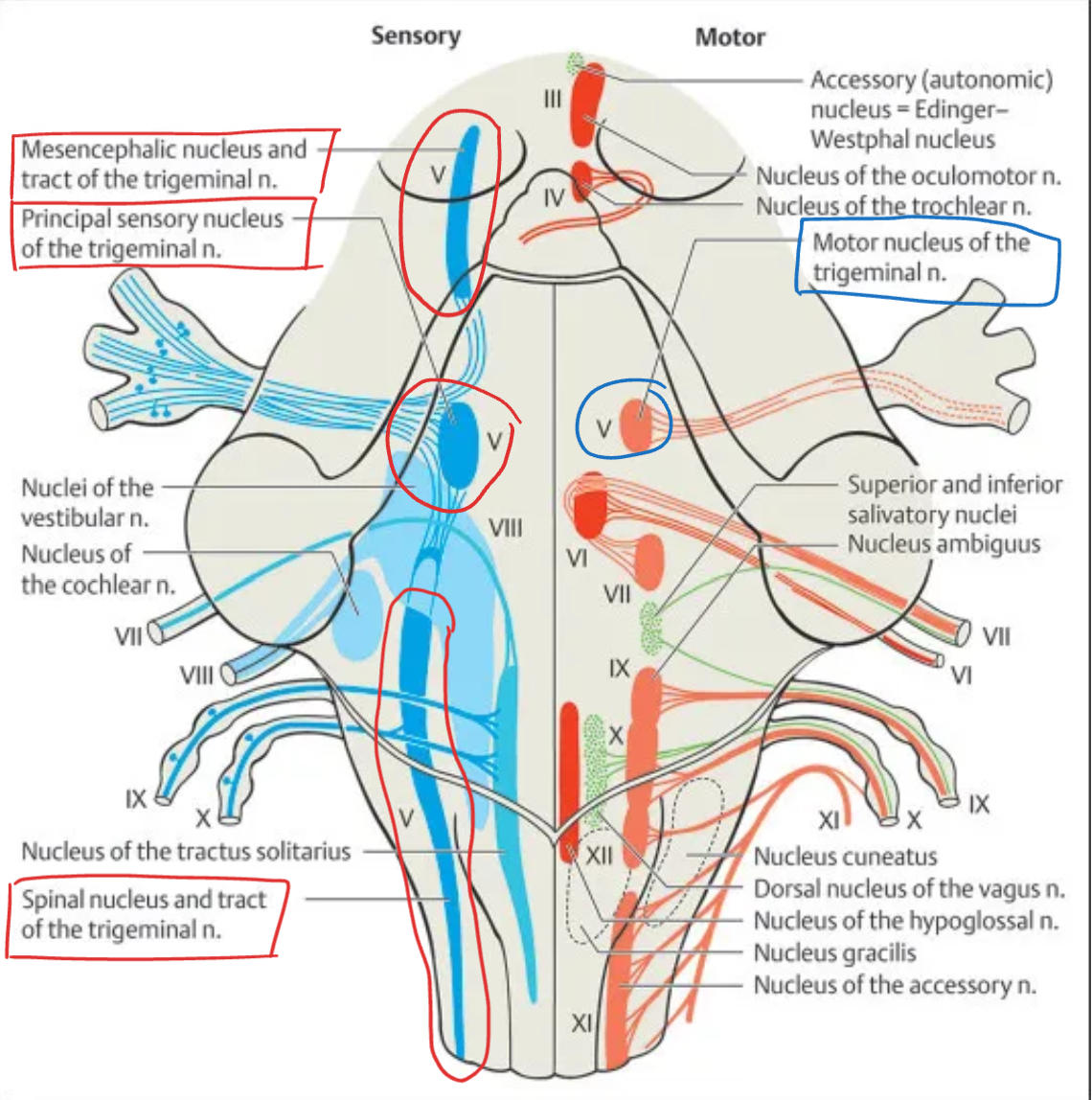
Trigeminal (V)
Nuclei:
Motor nucleus of V – controls muscles of mastication
Principal (chief) sensory nucleus – touch and pressure from face
Spinal nucleus of V – pain and temperature from face
Mesencephalic nucleus of V – proprioception from jaw muscles
Location: Pons and medulla (extends into midbrain)
Type: Sensory + Motor
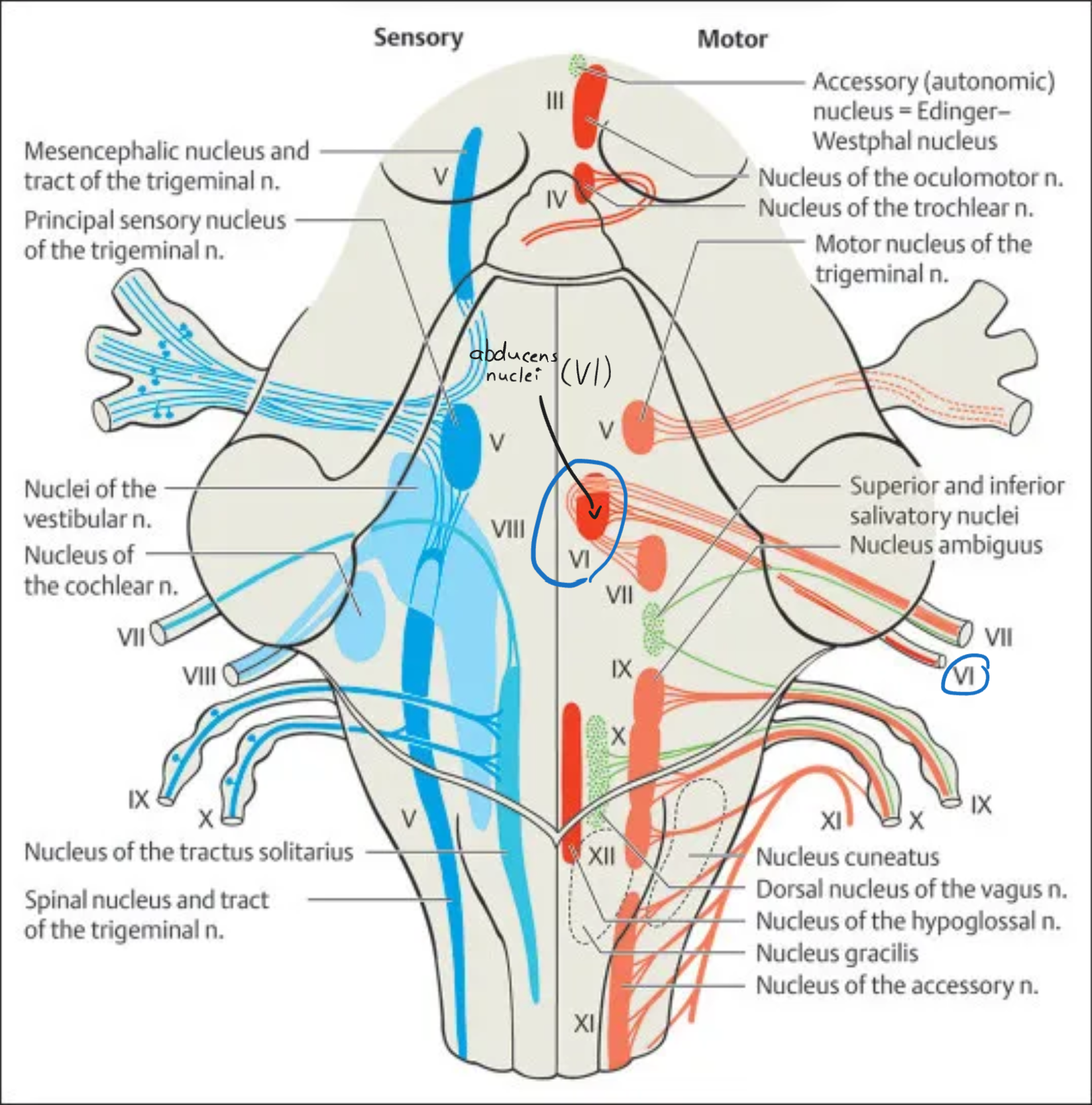
Abducens (VI)
Nucleus: Abducens nucleus
Location: Pons (floor of 4th ventricle)
Function: Innervates lateral rectus muscle for eye abduction
Type: Motor
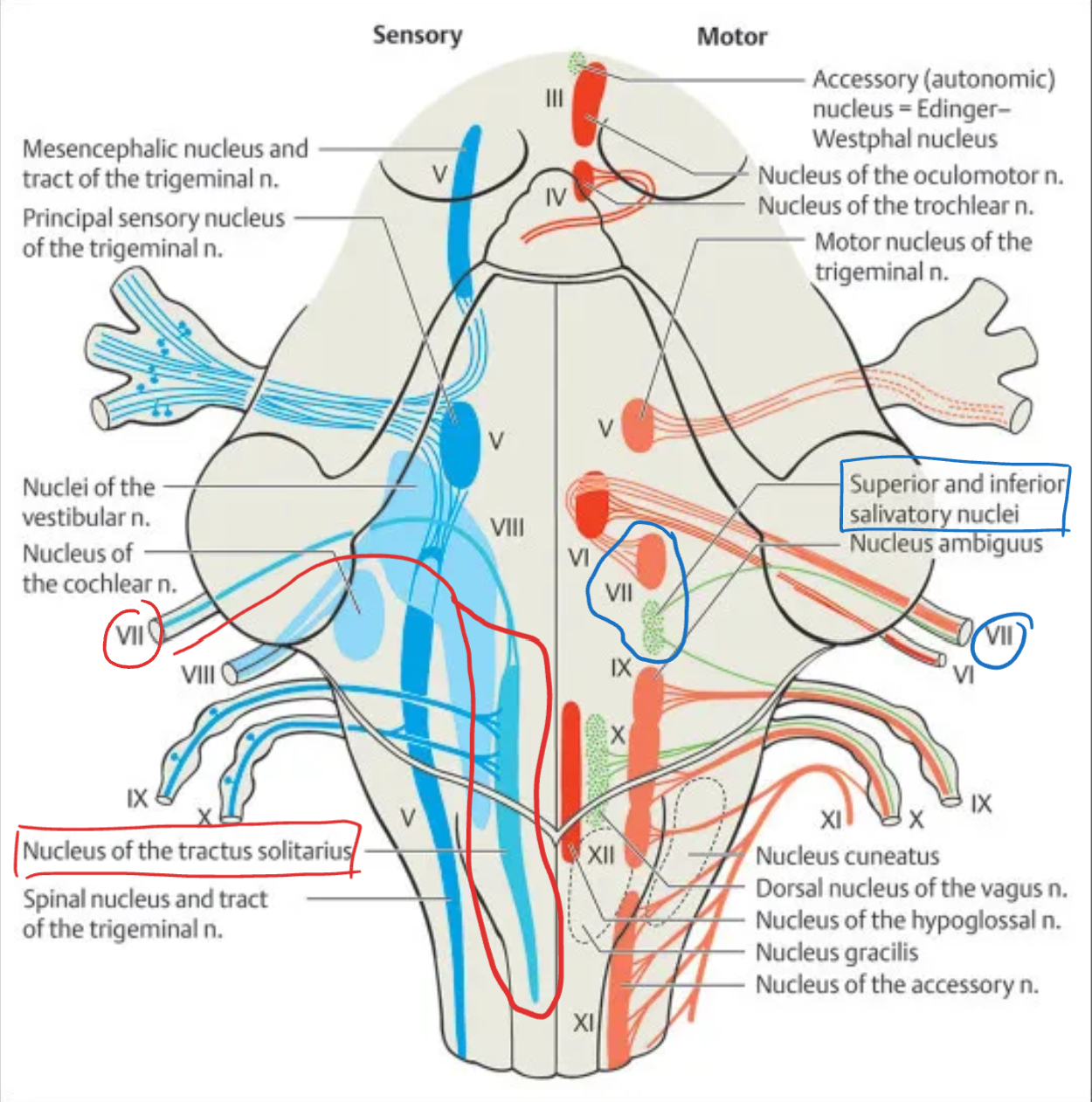
Facial (VII)
Nuclei:
Facial motor nucleus – muscles of facial expression
Superior salivatory nucleus – parasympathetic to submandibular, sublingual, lacrimal glands
Nucleus tractus solitarius (NTS, rostral part) – taste from anterior 2/3 of tongue
Location: Pons
Type: Motor + Sensory + Parasympathetic
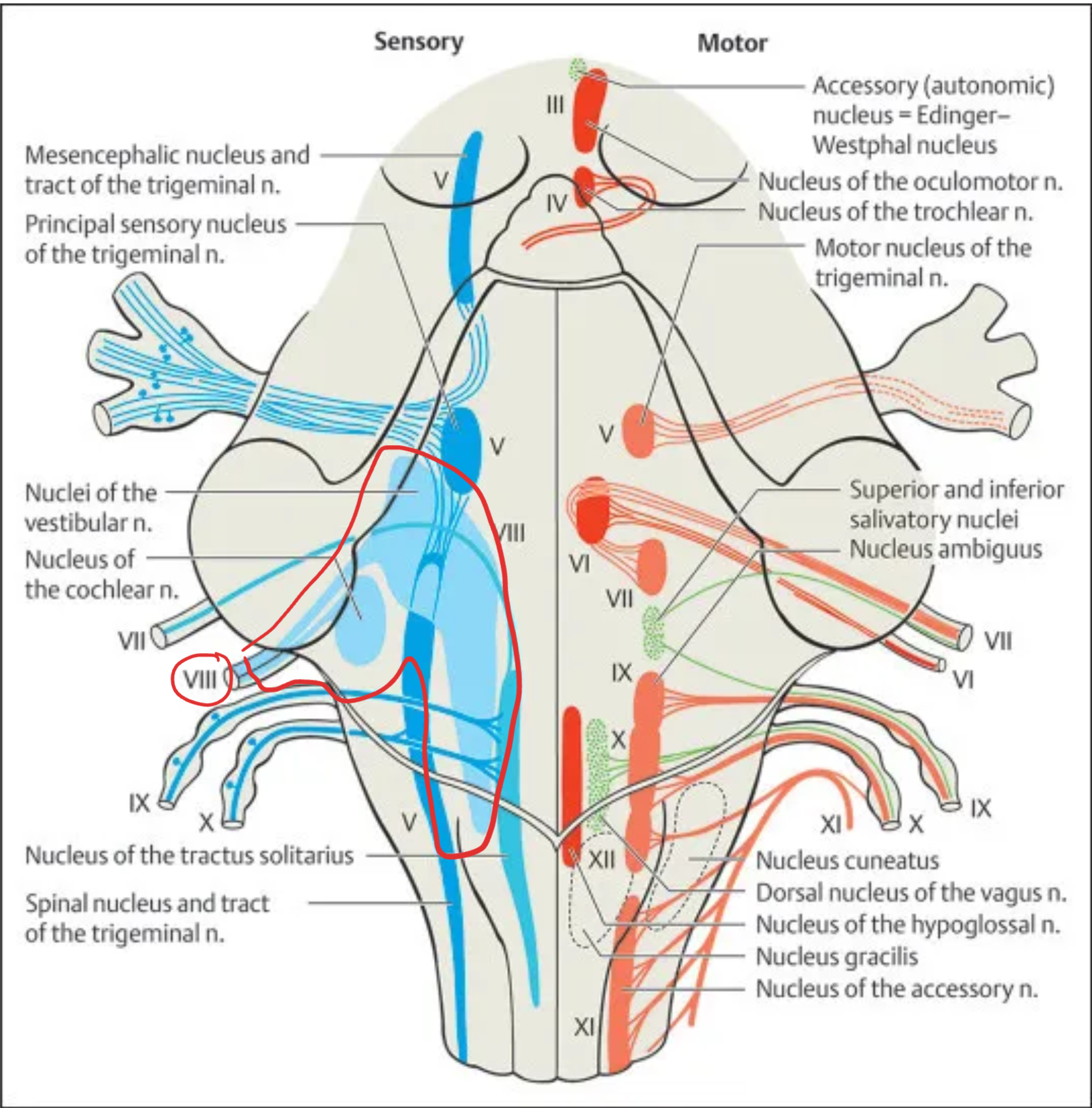
Vestibulocochlear (VIII)
Nuclei:
Vestibular nuclei (superior, inferior, medial, lateral) – balance and head position
Cochlear nuclei (anterior and posterior) – auditory information
Location: Pons–medulla junction
Type: Sensory
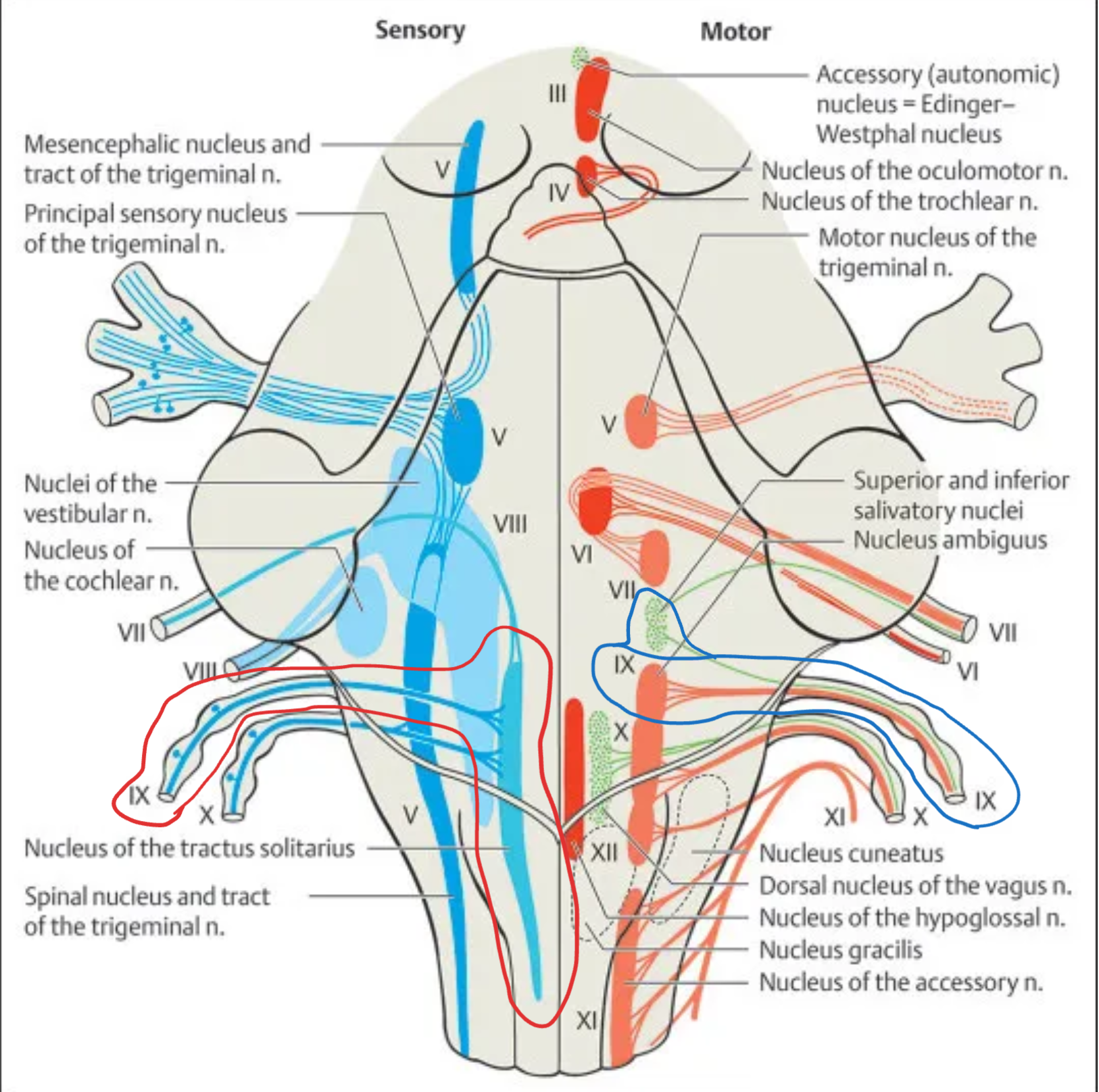
Glossopharyngeal (IX)
Nuclei:
Nucleus ambiguus – motor to stylopharyngeus muscle
Inferior salivatory nucleus – parasympathetic to parotid gland
Nucleus tractus solitarius (NTS, middle part) – taste and visceral sensation from posterior 1/3 of tongue
Spinal nucleus of V – pain and temperature from ear and pharynx
Location: Medulla oblongata
Type: Motor + Sensory + Parasympathetic
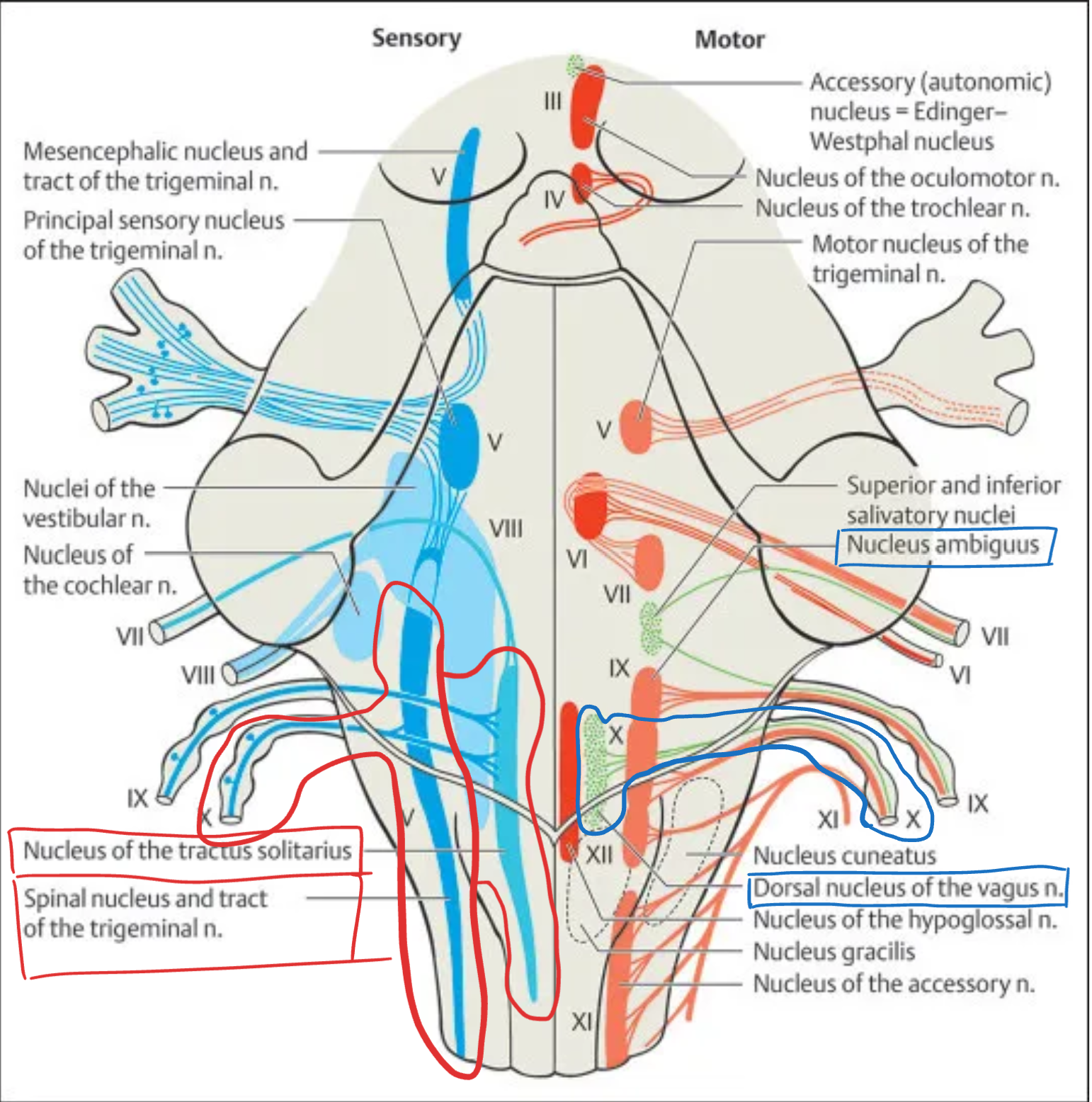
Vagus (X)
Nuclei:
Dorsal motor nucleus of vagus – parasympathetic control of thoracic and abdominal viscera
Nucleus ambiguus – motor to pharynx and larynx
Nucleus tractus solitarius (NTS, caudal part) – visceral sensory input
Spinal nucleus of V – somatic sensory from ear and meninges
Location: Medulla oblongata
Type: Motor + Sensory + Parasympathetic
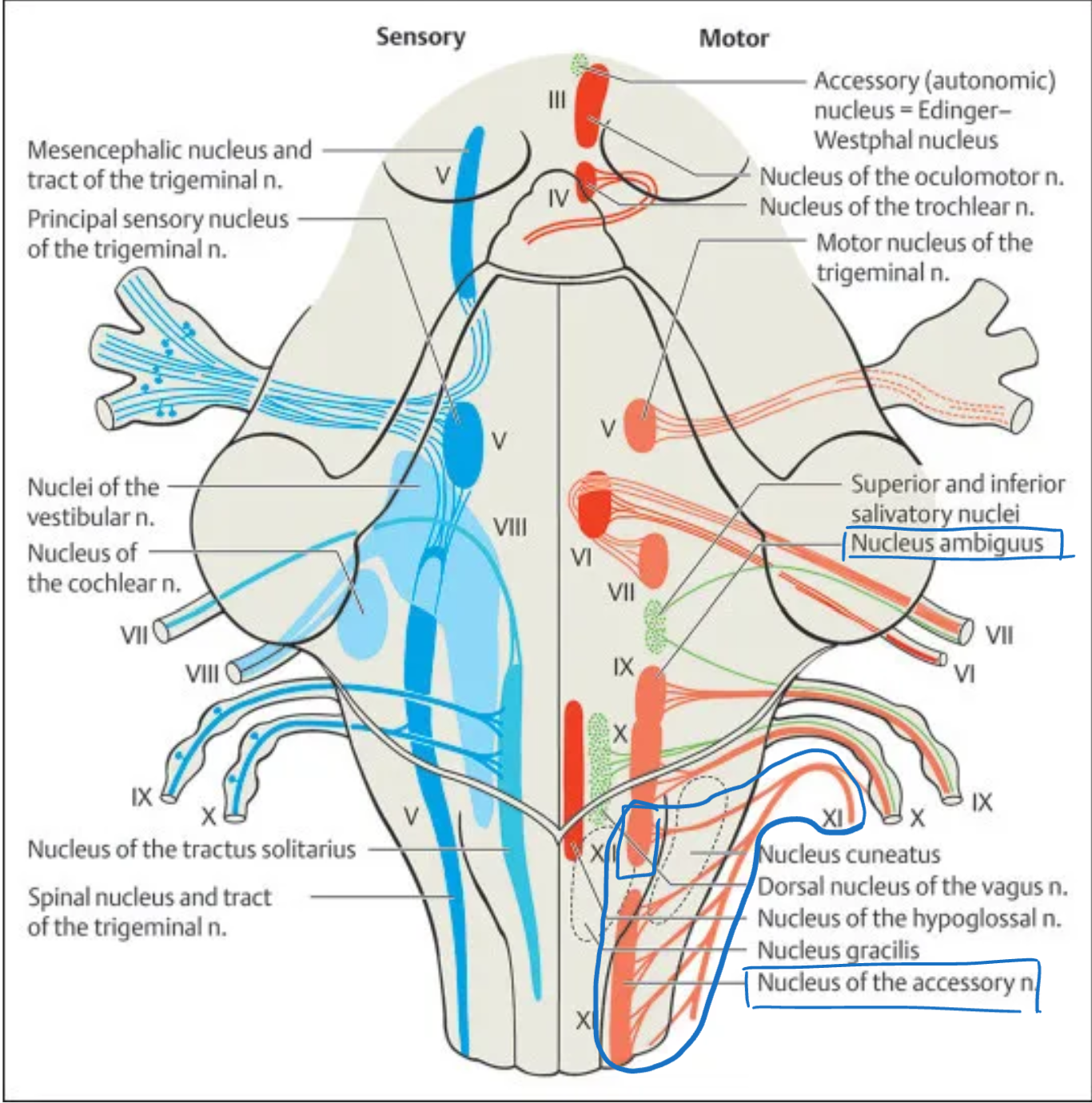
Accessory (XI)
Nucleus: Spinal accessory nucleus (C1–C5 ventral horn), cranial root from nucleus ambiguus
Location: Cervical spinal cord and medulla
Function: Sternocleidomastoid and trapezius control (spinal part); pharyngeal and laryngeal muscles (cranial part)
Type: Motor
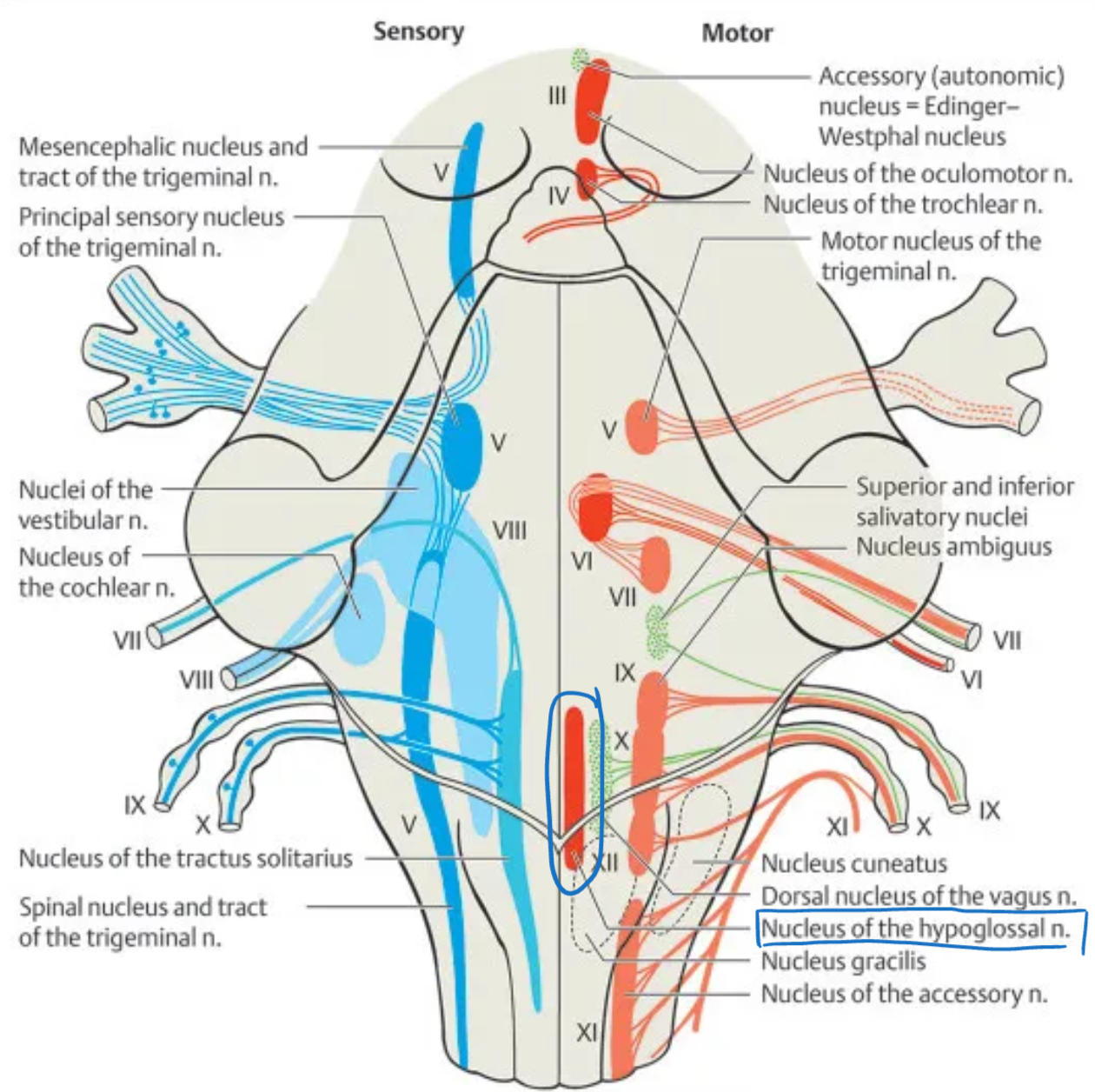
Hypoglossal (XII)
Nucleus: Hypoglossal nucleus
Location: Medulla oblongata (floor of 4th ventricle)
Function: Tongue muscle movement (intrinsic and extrinsic)
Type: Motor