psycology - brain structure and function
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
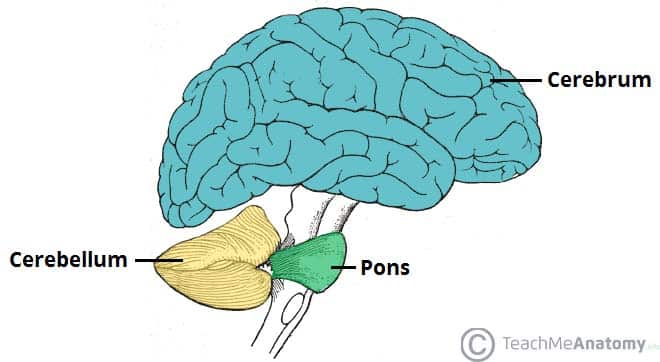
cerebrum
largest part of the brain
divided into two hemispheres (cerebral hemispheres")
areas in cerebrum control muscle functions, speech, thought, emotions, reading, writing
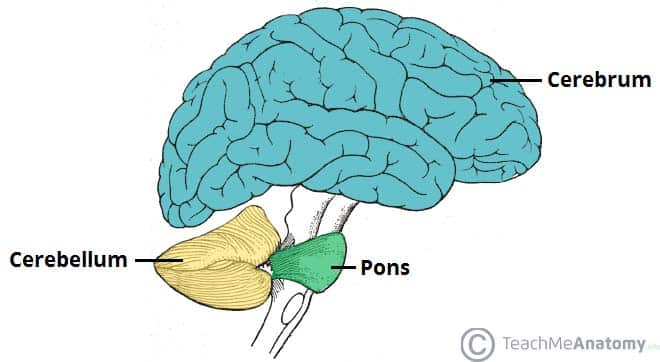
cerebral cortex
wrinkled outer layer of brain
responsible for complex functions like thought, language, memory, perception
brains “gray matter”
contrains frontal, parietal, temporal, and occipital lobe
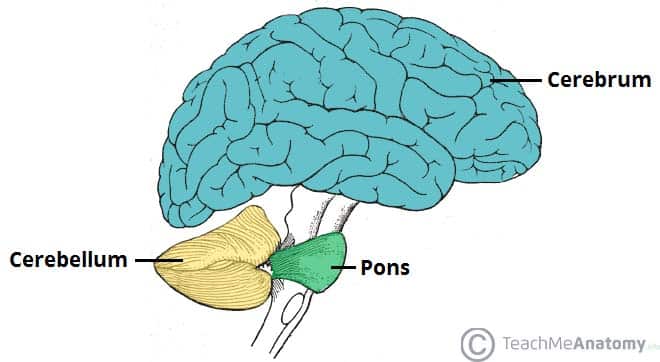
cerebellum
coordinates motor function and positional info from inner ear + muscles
helps maintain BALANCE
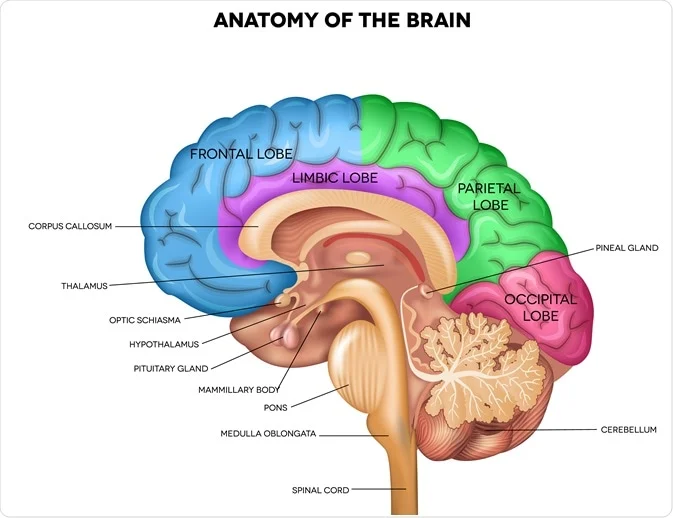
thalamus
relay station for sensory pathways carrying visual, auditory, taste, and somatosensory info to and from appropriate areas of cerebral cortex
exception of smell
doesn’t process the info but moves it to the correct parts
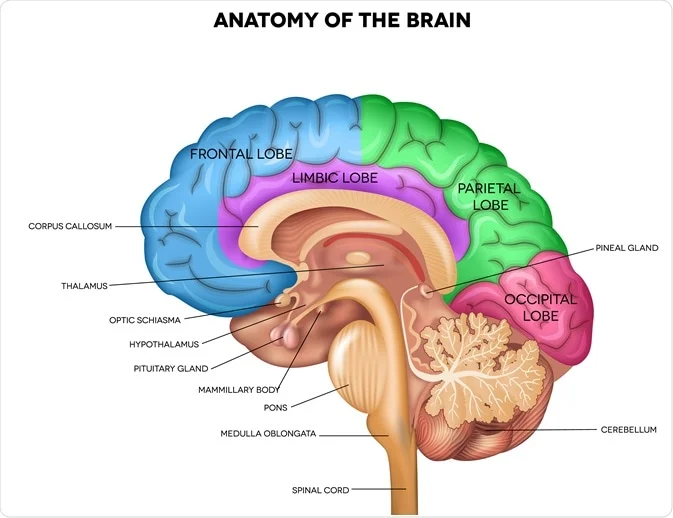
hypothalamus
controls autonomic functions and maintains homeostasis
monitors important states: hunger, thirst, temp, blood pH
also important in endocrine system by secretion of hormones that interact with hormones from pituitary gland
AKA controls pituitary gland
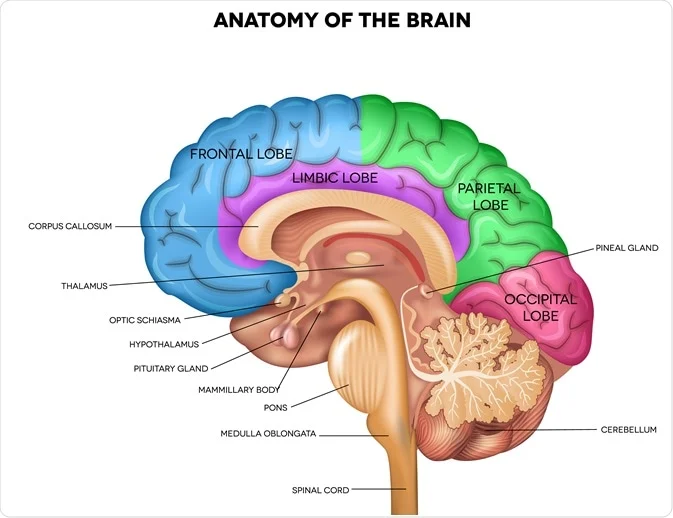
pituitary gland
important gland of endocrine system
releases hormones —> growth and reproductive
controlled by hypothalamus
corpus callosum
thick band of nerve fibers that connects the two hemispheres of the brain
plays crucial role in interhemispheric communication
allows information and signals to travel between left/right sides of brain
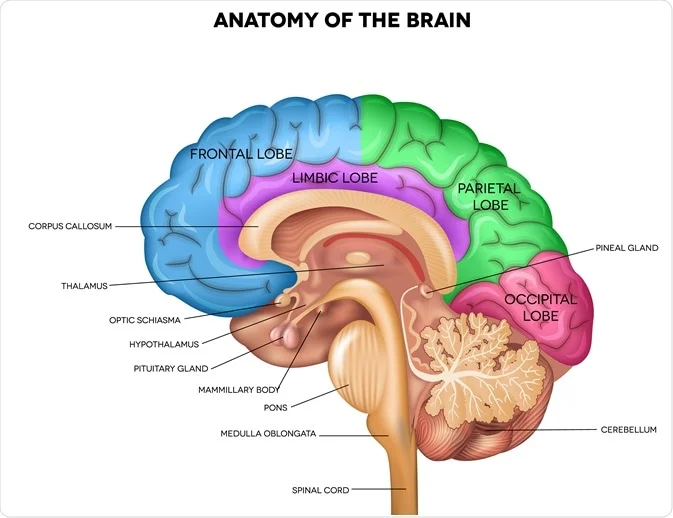
hippocampus
converts short term memories into long term memories
wraps around thalamus
declarative memory (not performative)
saves but doesn’t store memory —> stored all around brain
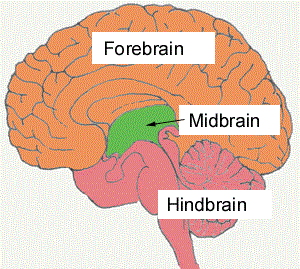
midbrain
plays crucial role in fundamental functions like vision, hearing, motor control, regulating alertness, sleep and waking, maintains muscle tone and posture through involuntary muscles
uppermost part of brainstem —> located between fore/hind brain
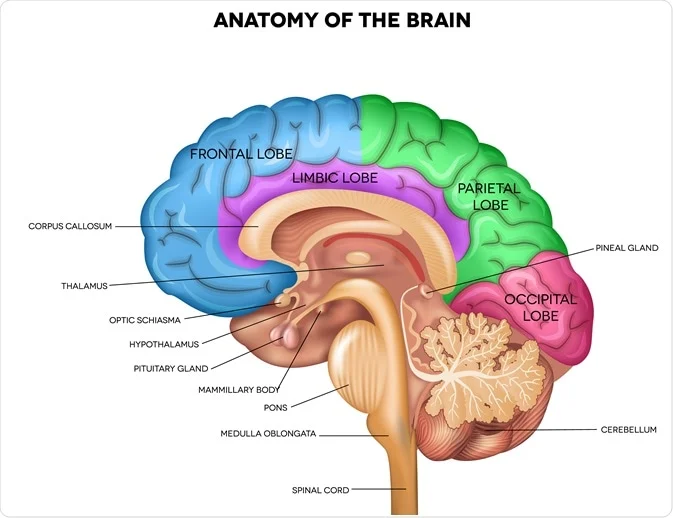
pons (bridge)
transmits messages between the cerebrum and the cerebellum
vital part of brainstem
plays crucial role in motor control, sensory processing, sleep, arousal, etc.
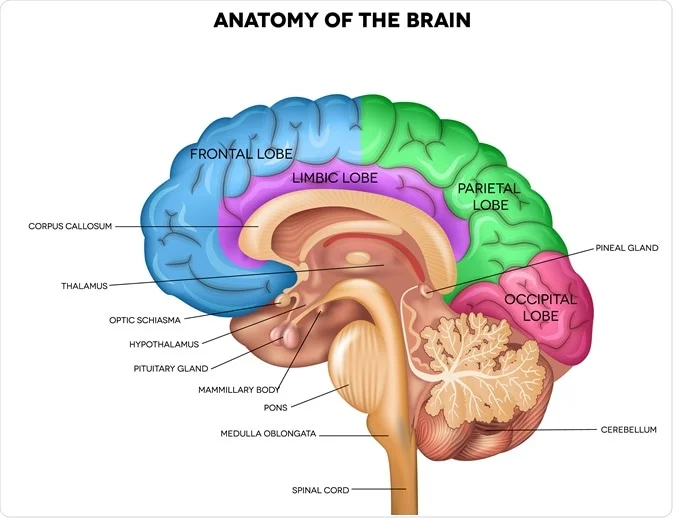
medulla (medulla oblongata)
regulates heart rhythm, blood flow, breathing rate, digestion, vomiting
located in brainstem at the bottom
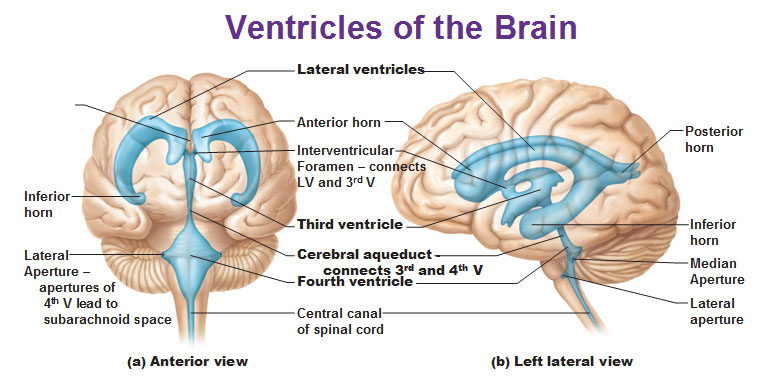
ventricles
series of interconnected cavities that are filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
protect, nourish, and remove wast products from the brain
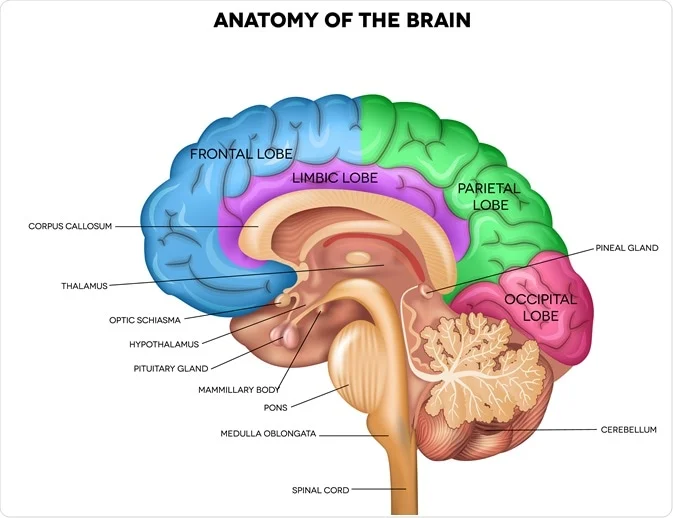
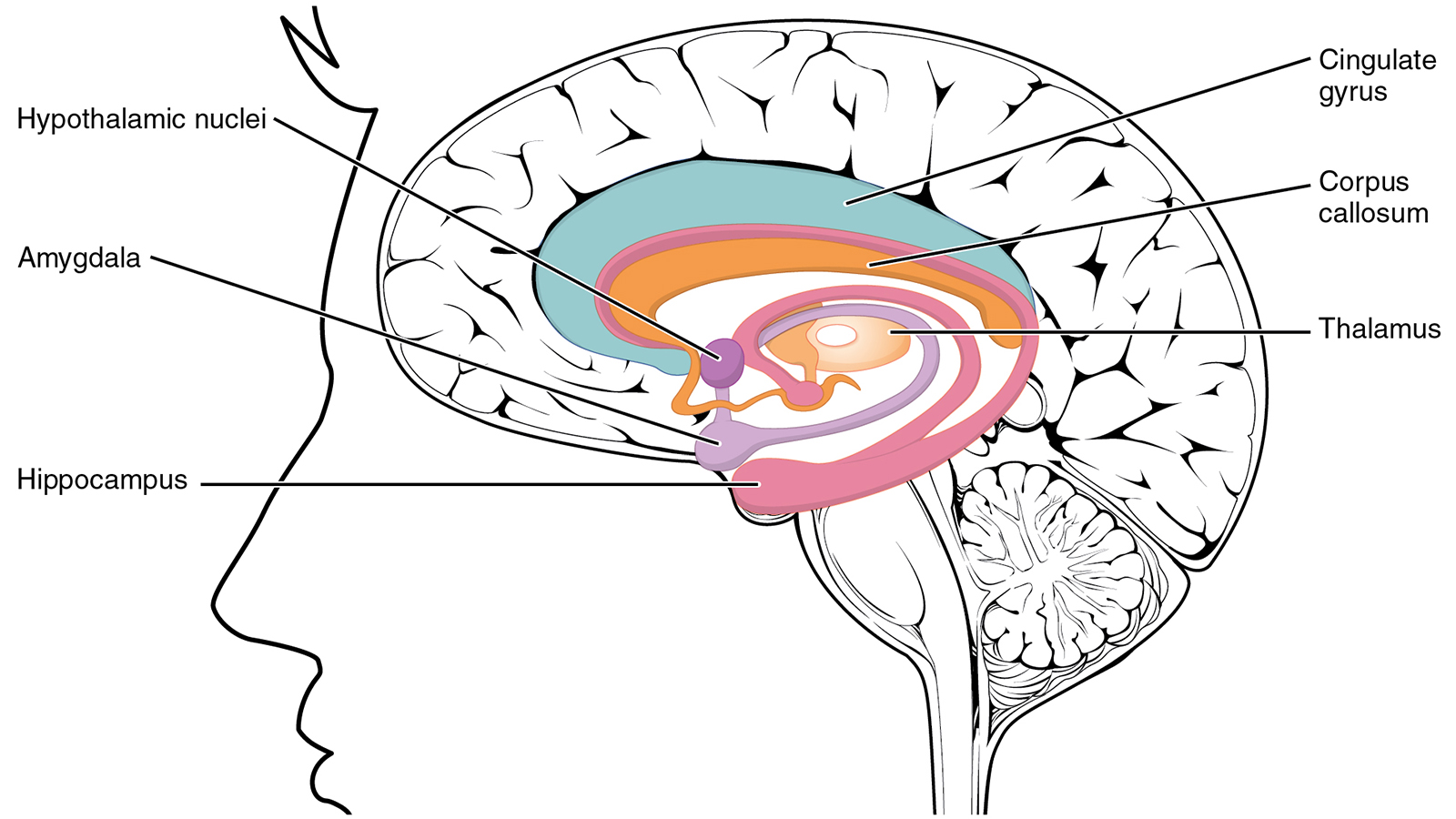
limbic system (AHH)
neural system that consists of the amygdala, hypothalamus, hippocampus, thalamus, and pituitary gland
associated with emotions and drives (hunger, thirst)
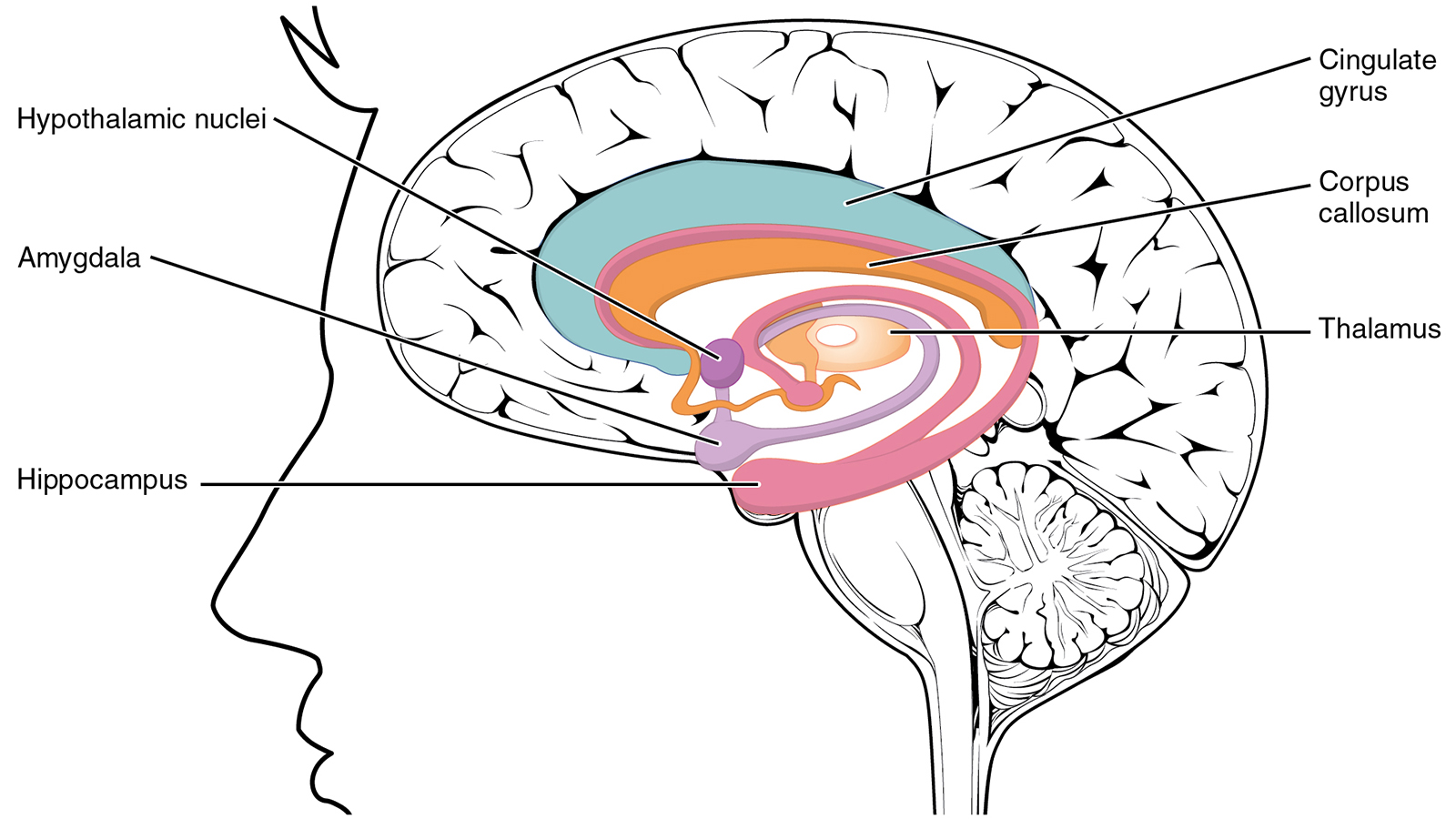
amygdala
emotional center of the brain
influences aggression and fear
coordinates fight or flight response (sympathetic)
teenagers use this a lot
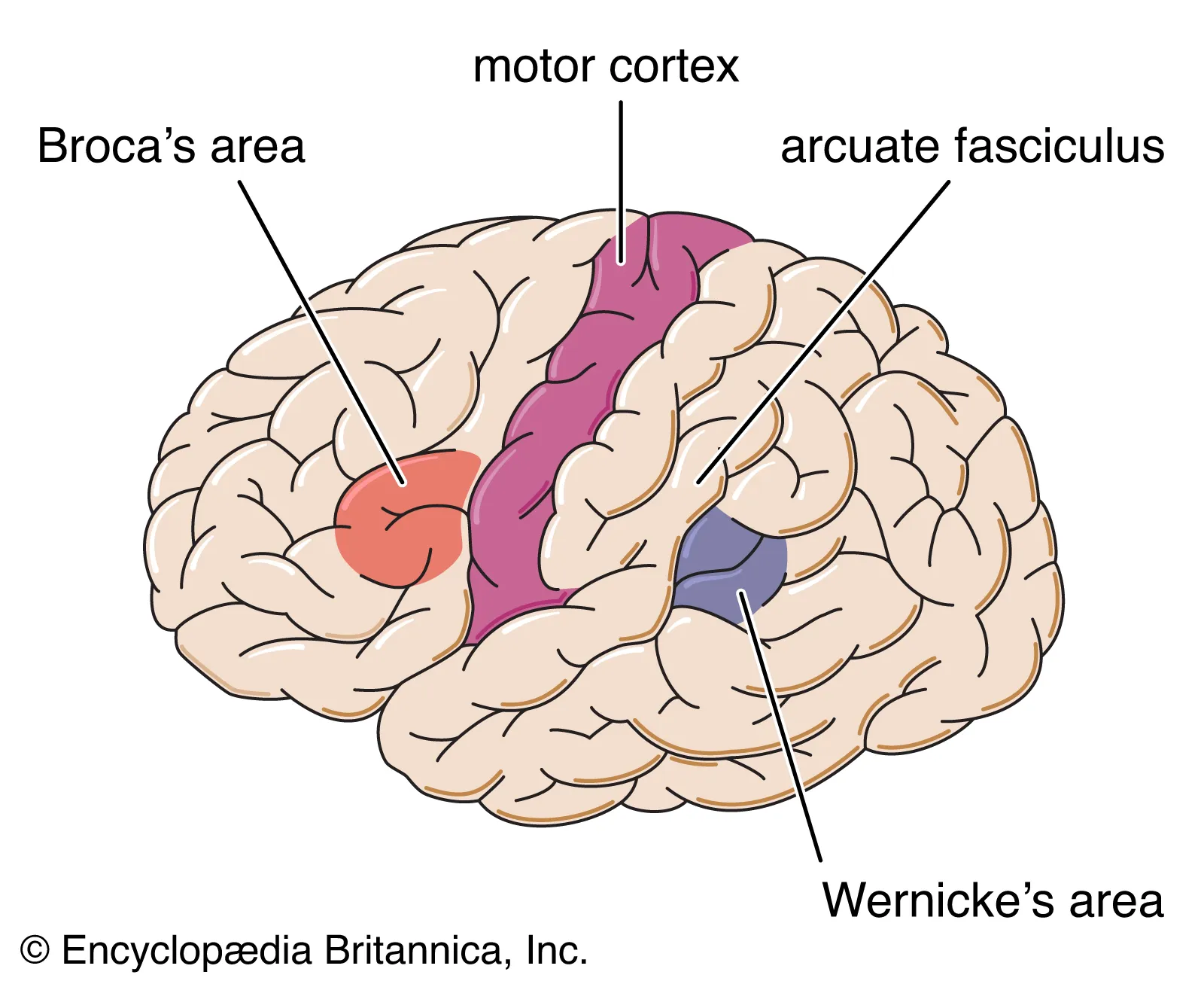
Broca’s area
important for speech production
located in left frontal lobe
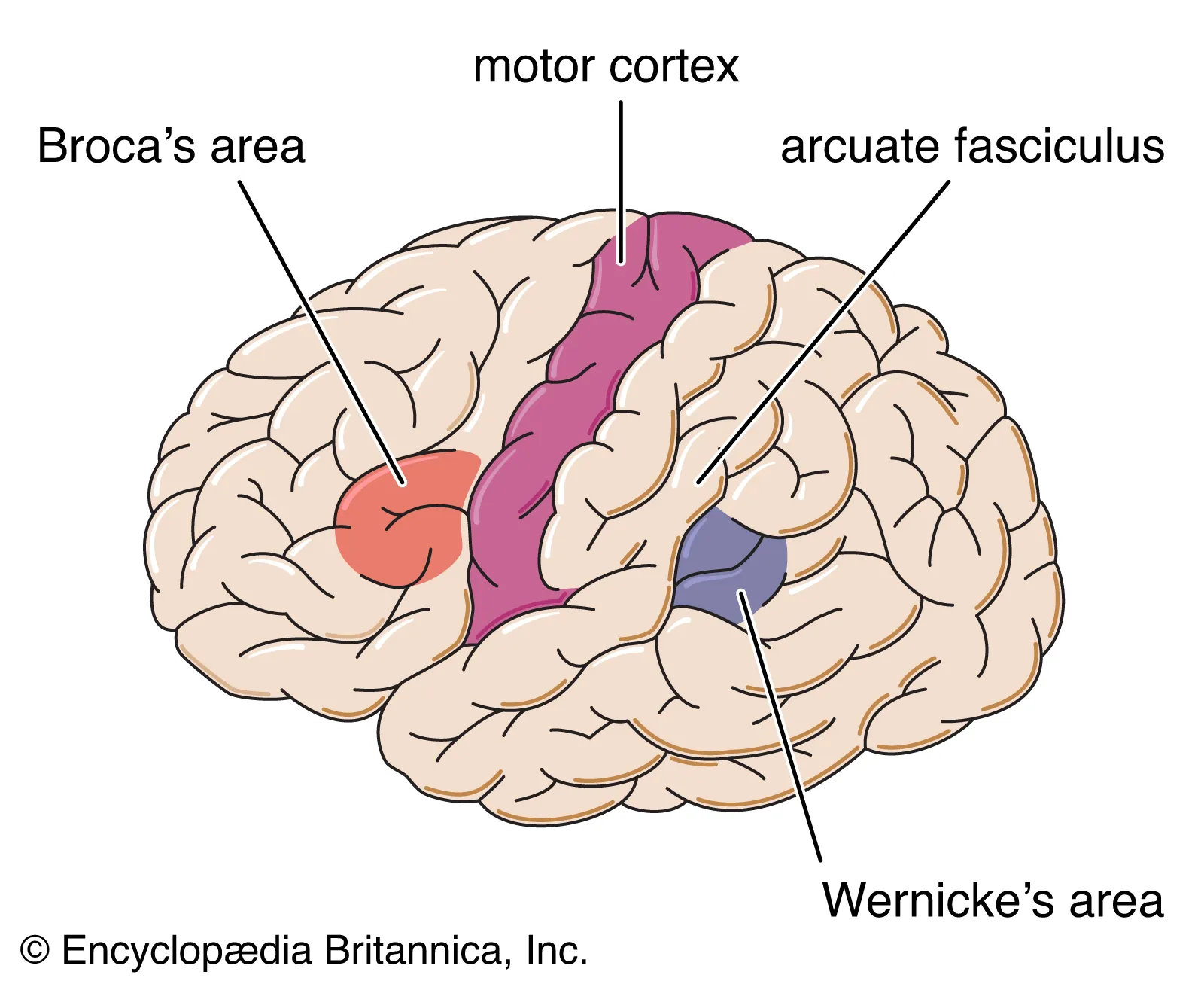
Wernicke’s Area
important in language comprehension
located in left temporal lobe
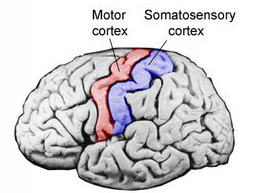
somatosensory cortex
processes sensory information from the skin, muscles, joins
plays crucial role in perceiving and interpreting sensation such as a touch, temperature, pain, and proprioception
located in parietal lob —> band
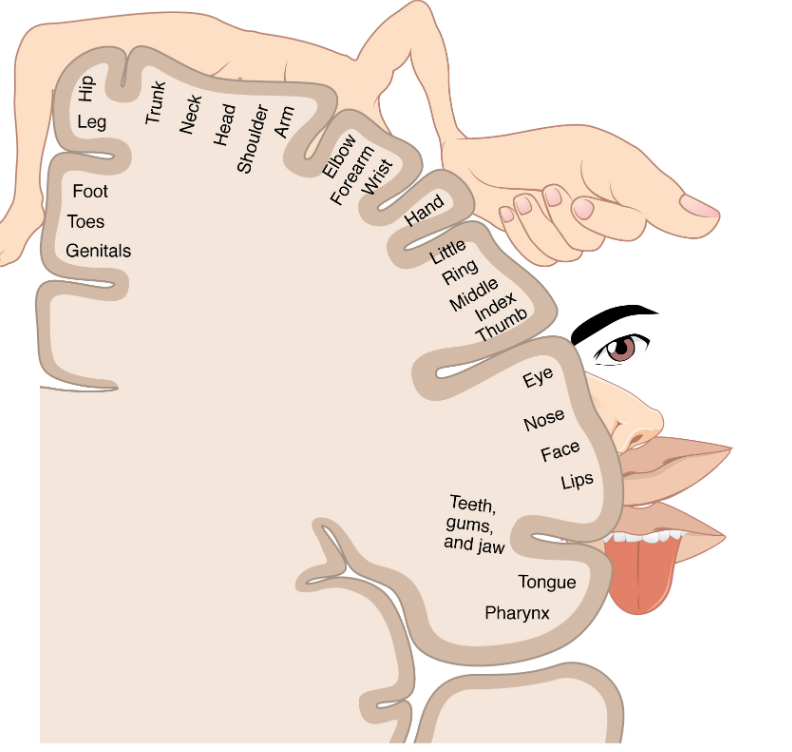
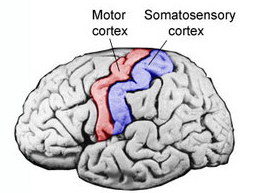
Motor cortex
plans, controls, and executes voluntary movements by sending signals to the body’s muscles
primary output area for movement commands and is essential for coordinated actions
different areas map to different body parts to enable precise muscle control
located in frontal lobe —> band
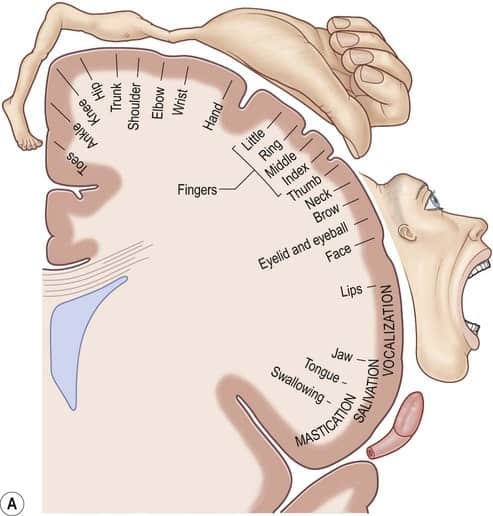
reticular formation
network of neurons in the brainstem responsible for arousal, alertness, attention, and regulating sleep-wake cycles
allows you to wake up, stay focused, filter sensory information, and respond to important stimuli (like name called)
inside pons, medulla
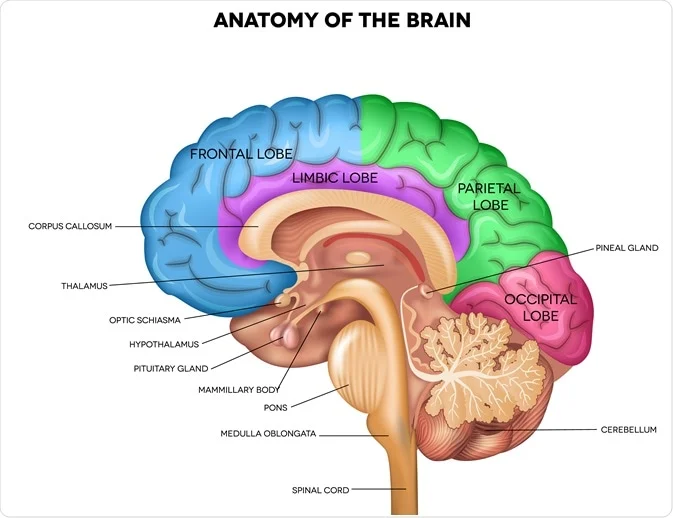
prefrontal cortex
plays crucial role in planning, decision making, impulse control, controlling emotions, attention critical thinking
located in front part of brain at skull
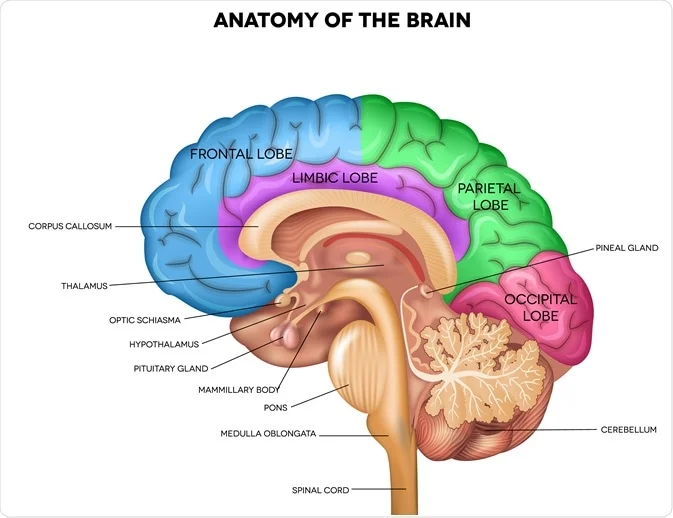
parietal lob
process somatosensory information (touch, pain), integrates sensory input, spatial awareness, navigation, attention
taste, temperature, touch
located at top and back of head
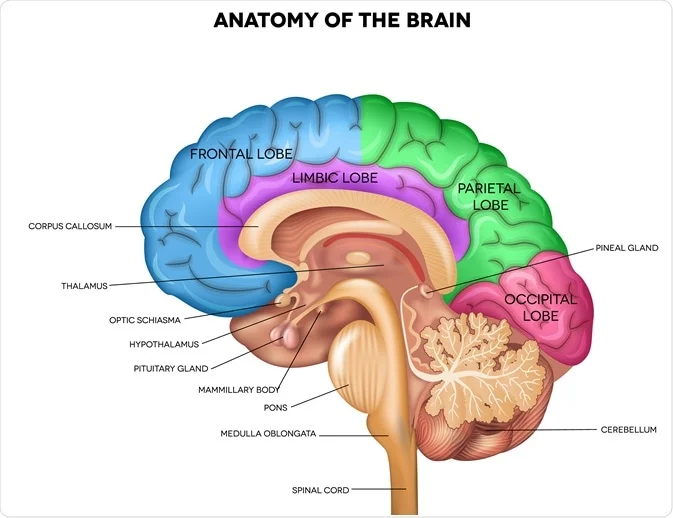
temporal lobe
important for hearing, selective listening, receives sensory info (sounds/speech), understanding speech
located on the lower part of head below ears
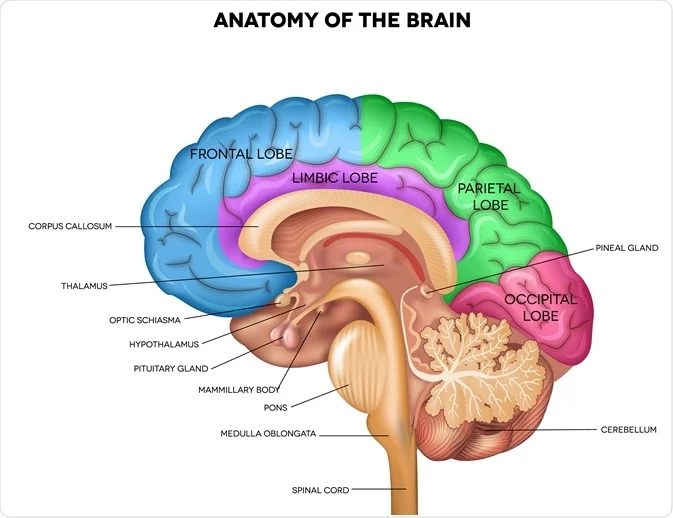
occipital lobe
plays a crucial role in visual processing
helps you understand what your eyes are seeing
lobes are fast to process rapid information
located at back and bottom of brian