Cellular respiration
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Living things need energy for
Chemical reactions and mechanical processes.
E.g.
synthesizing new protoplasms for growth and repair
transmit nerve impulses for any folow-up reaction
absorb food substances in the small intestine by activie transport
What is the origin of energy? How is it captured?
The sun. The energy is captured by plants through photosynthesis. Energy from the sun is converted into chemical energy, stored in food molecules.
Cellular respiration produces? and by?
Energy for all activities by releasing energy from glucose to produce ATP
respiration (define)
Process by which food molecules are broken down to release energy
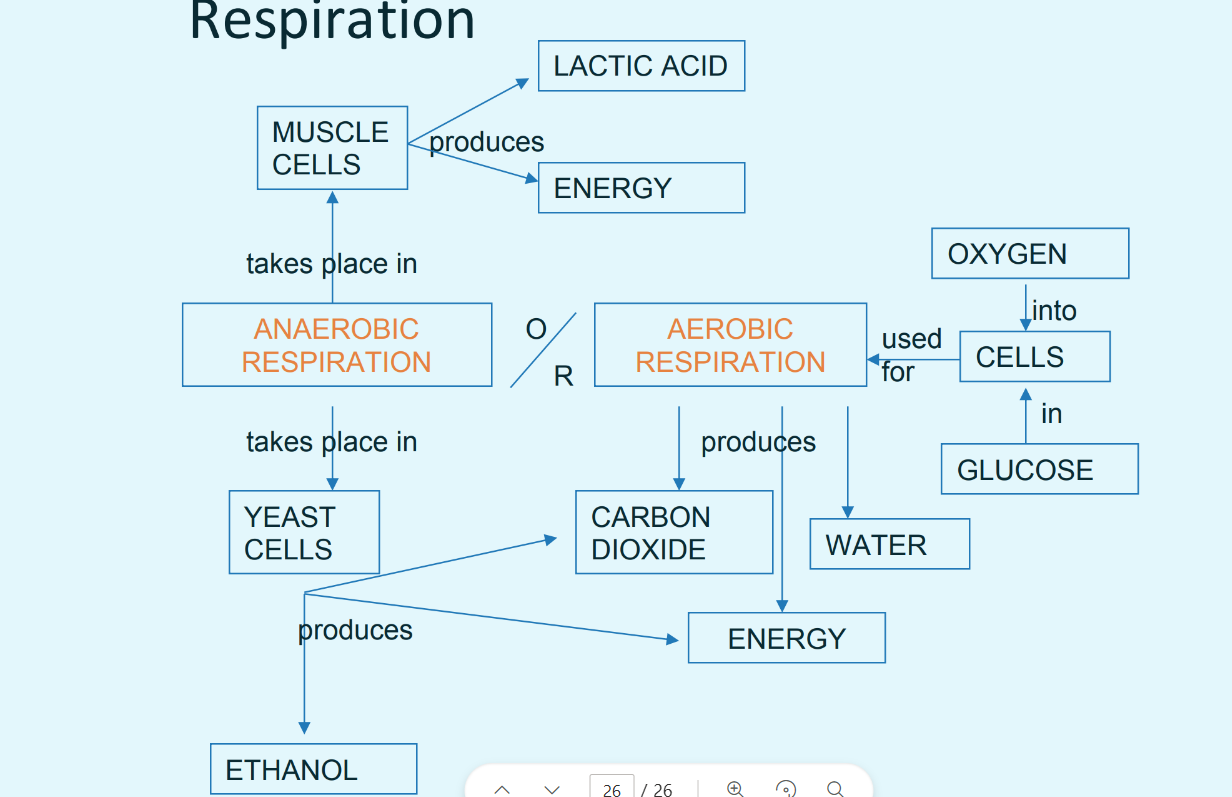
Types of cellular respiration
Aerobic respiration and Anaerobic respiration
Aerobic respiration is the? Define the process aswell. (when is it occured, and what does it produce?)
MAIN source of energy for living things that BREATHE OXYGEN
Process by which glucose is broken down fully in the PRESENCE of oxygen, releasing a LARGE amount of energy, with carbon-dioxide and water as by-products.
What is the chemical formula for aerobic respiration, and how much ATP does it produce?
Glucose + Oxygen —> Carbon dioxide, water and energy (large amount)
38 ATP per glucose molecule
When does anaerobic respiration occur?
Occurs when there is INSUFFICIENT or ABSENCE of oxygen
Produces 2 ATP per glucose molecule
Fermentation definition + main types
Fermentation is a type of anaerobic respiration and is definied as the process by which sugar is broken down to release energy in the absence of oxygen.
Lactic acid fermentation
Ethanol fermentation
What organism carries out ethanol fermentation? What is ethanol fermentation, where does it occur, and what is its chemical formula? How much ATP is produced?
Yeast carries out ethanol fermentation
Ethanol fermentation is where glucose is broken down in the cytoplasm to release energy in the form of ATP, with carbon dioxide and ethanol as by-products
2 ATP
Glucose —> carbon dioxide + ethanol + energy (small amount) (
(in bacteria) What organism carries out lactic fermentation? What is lactic fermentation, where does it occur, and what is its chemical formula? How much ATP is produced?
Some bacteria (e.g. Lactobacillus)
In the cytoplasm
2 ATP
Glucose —> lactic acid + energy (small amount) (
Why is lactic acid useful?
e.g.
Used to create foods like yoghurt and kimchi.
Enhance the flavour of the food
helps to preserve the food by creating an acidic environment that is less hospitable to pathogenic bacteria.
(In humans) Why do we rely on anaerobic respiration, and what are the effects of it, and why?
We rely on anaerobic respiration to provide QUICK bursts of energy during activities that require intense effort.
Bacteria can release the lactic acid as a waste product, but we cant. Lactic acid can build up in muscles and can cause muscle cramps and soreness, hence we cannot rely on anaerobic respiration for energy for extended periods of time.
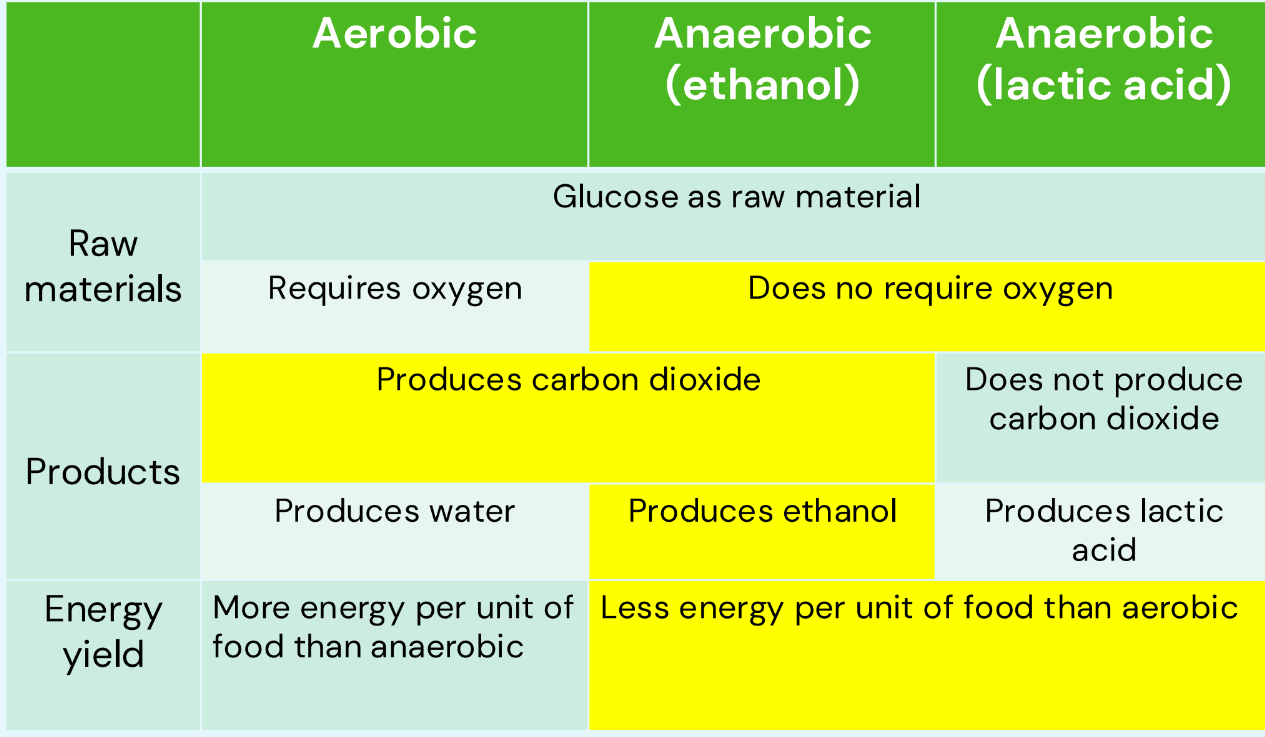
Aerobic respiration vs Anaerobic respiraton (energy yield, speed and what is needed)
Aerobic
slower
higher energy yield (38 ATP per glucose molecule)
Uses oxygen to release energy from glucose
Anaerobic
faster
lower energy ield (2 ATP per glucose molecule)
Doesnt use oxygen to release energy from glucose
What is the main source of carbohydrate for all respiration types?
Glucose is the main source of carbohydrate for most types of respiration.
But other carbohydrates can be used. (depends on organism)
We basically use sugars
How do we obtain glucose?
In humans, food is broken down into simpler substances in the digestive system like glucose. Glucose is then absorbed into the bloodstream via the small intestine and is transported by the blood to cells all over the body.
In plants, glucose is produced from photosynthesis.
How do we obtain oxygen?
In humans, oxygen is obtained from the air through breathing. Oxygen is then absorbed into the blood stream through the lungs (in mammals). The oxygen binds to red blood cells (due to a special part in them called haemoglobin) which are transported by the blood to cells all over the body.
In plants, oxygen diffuses from the air into the leaves through the stomata. (opening found on leaves)
Yeast vs bacteria (fermentation types)+ what does fermentation do (for ethanol)
Yeast carries out ethanol fermentation (Produces carbon dioxide which helps make bread rise)
Some bacteria carry out lactic acid fermentation
Why is ethanol useful?
E.g.
Ethanol can be used to produce alcohol,
used for its disinfectant properties
and used as an organic solvent.
It can also be used as biofuel in a 1:9 ratio of ethanol and petroleum. Renewable energy can be produced from plants like corn and potato
The fermentation of carbohydrates commonly results in?
Ethanol production (essental in breweries that produce alcohol)
What does methanol (home brewed beer) fermentation do and how is it formed
Methanol is poisonous and may cause death in extreme cases. It is caused when the carbohydrate source contains high levels of pectin.
How does swiss cheese form? (propionic acid) (chemical formulas and how)
Bacteria (PROPIONIBATERIUM) converts the lactic acid produced by lactobacillus to release propionic acid (nutty and sweet flavour), acetic acid and carbon dioxide that forms the ‘eyes’ of the cheese.
glucose( DERIVED FROM LACTOSE IN MILK OR IS ADDED TO THE MILK) is fermented by the lactic acid bacteria to produce lactic acid and release energy. The lactic acid lowers the pH of the mlk, helping to coagulate the milk proteins and form curds.
Glucose → Lactic Acid + energy
Lactic acid —> Propionic Acid + acetic Acid + carbon dioxide
Acetic acid (vinegar) how is it formed?
Bacteria (ACETOBACTER) converts ethanol to acetic acid and water
ALCOHOLIC FERMENTATION - sugars from a carbohydrate source are broken down by yeast under anaerobic conditions
Glucose —> Ethanol + carbon dioxide
Acetic acid production - in the presence of oxygen, acetic acid bacteria (acetobacter) oxidise ethanol into acetic acid, giving vinegar its sour taste.
Ethanol + oxygen —→ Acetic Acid + water
This makes it an aerobic respiration type!
recap (diff between types of respiration
mindmap