Bio130
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/152
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
153 Terms
1
New cards
Nucleus
The structure that contains the chromosomes (DNA) in the center of the cell
area of transcription
area of transcription
2
New cards
Endoplasmic Reticulum
Irregular maze of spaces interconnected with membrane where cell exports are made(proteins)
very large in excretory cells.
very large in excretory cells.
3
New cards
Golgi apparatus
Processes and packages proteins and lipids meant for transport inside or outside of the cell. Stacks or membrane enclosed sacs.
4
New cards
Nucleolus
Produces and assembles ribosomes in the nucleus (rRNA gets transcribed and then assembly occurs)
5
New cards
Prokaryotic Cell
* Cell with no nucleus
* Single Celled
* Bacteria and Archaea
* No membrane-bound organelles
* Smaller
* Less DNA
* Ribosomes in cytosol
* Single Celled
* Bacteria and Archaea
* No membrane-bound organelles
* Smaller
* Less DNA
* Ribosomes in cytosol
6
New cards
Eukaryotic Cell
* Nuclei
* Single Celled OR Multi-cellular
* Plants, Fungi, Animals, Humans
* Several membrane-bound nucleus
* Larger and more Complex
* Single Celled OR Multi-cellular
* Plants, Fungi, Animals, Humans
* Several membrane-bound nucleus
* Larger and more Complex
7
New cards
Differences between DNA and RNA
Dna
* Double Stranded
* Has deoxyribose Sugar
* Is transcripted
* Synthesized from dNTPs
\
Rna
* Is Translated
* Single Stranded
* Has Ribose Sugar
* Synthesized from NTPs
* Double Stranded
* Has deoxyribose Sugar
* Is transcripted
* Synthesized from dNTPs
\
Rna
* Is Translated
* Single Stranded
* Has Ribose Sugar
* Synthesized from NTPs
8
New cards
Parts of Nucleotides
1) Nitrogenous Base
2) Pentose Sugar
3) Phosphate Group
2) Pentose Sugar
3) Phosphate Group
9
New cards
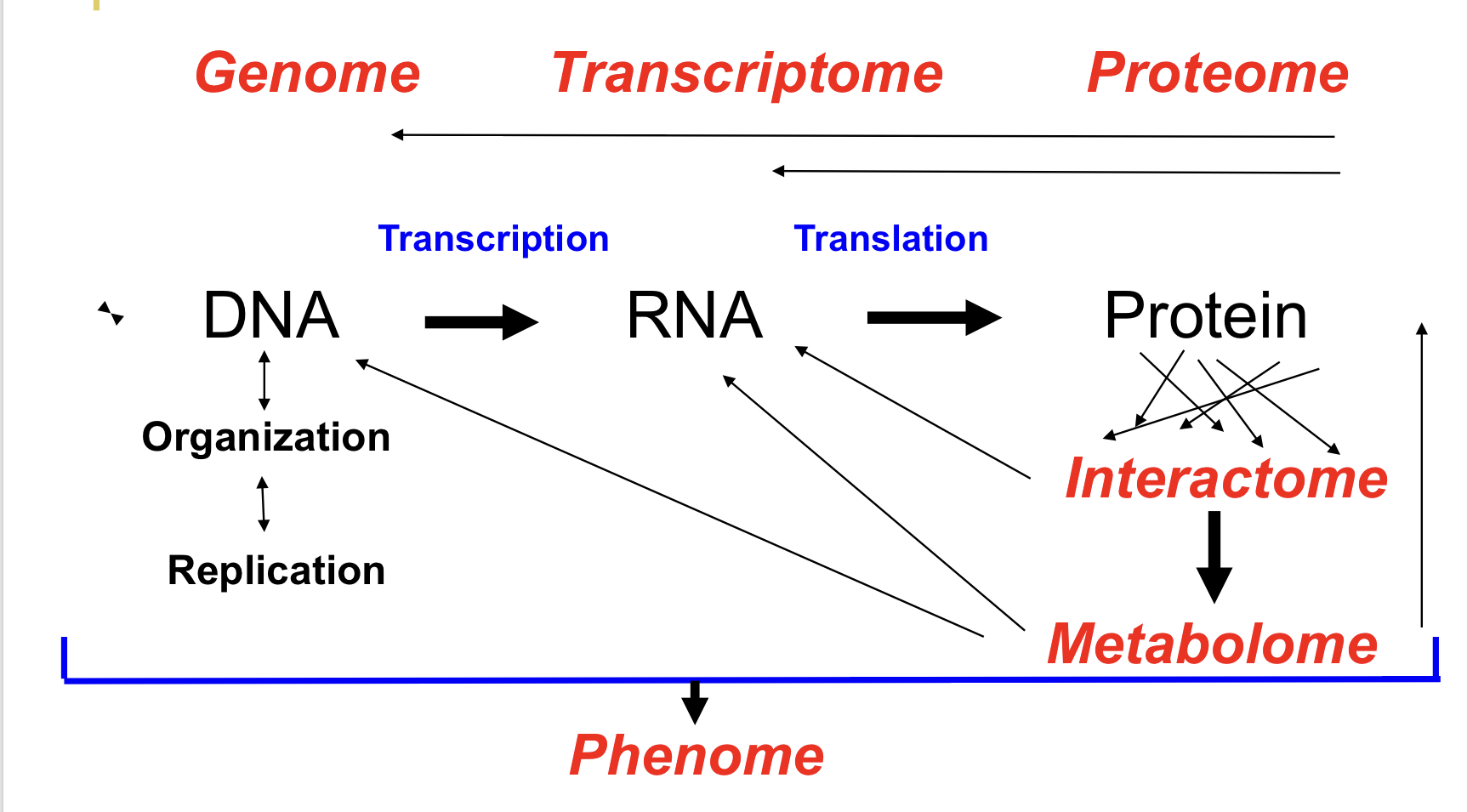
Central Dogma
Genetic information flows in 1 direction; from DNA to RNA to protein
\
\
10
New cards
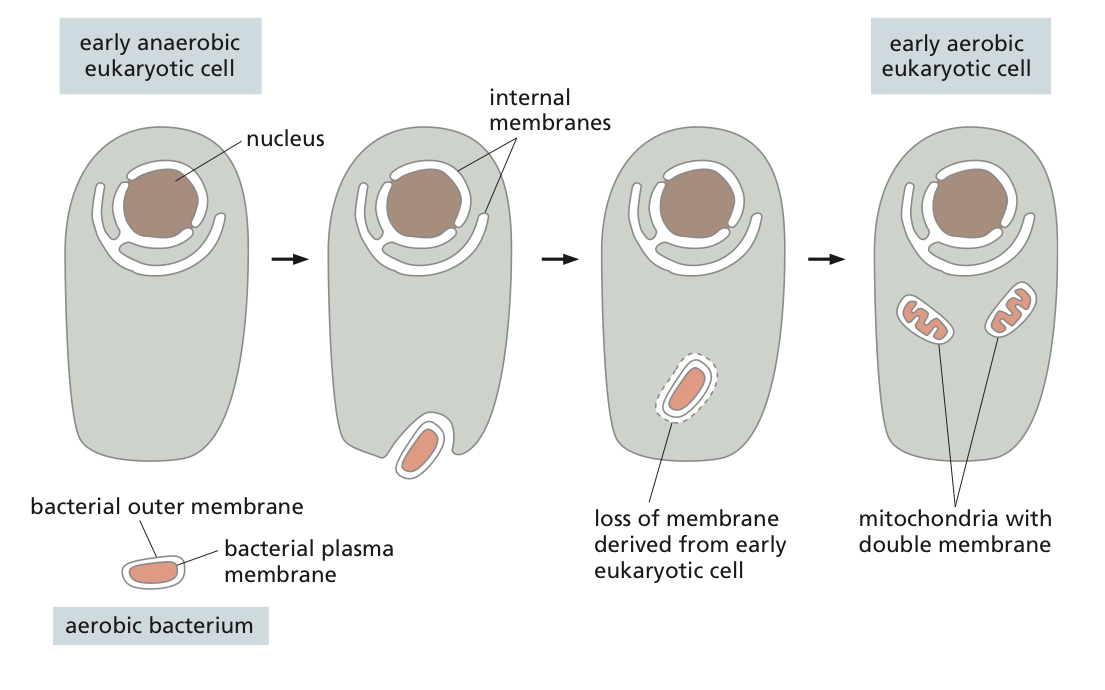
Origins of Mitochondria
resemble bacteria in many ways, and are thought to derive from bacteria that were engulfed by an anaerobic bacterium that later is an ancestor to present day Eukaryotic cells.
11
New cards
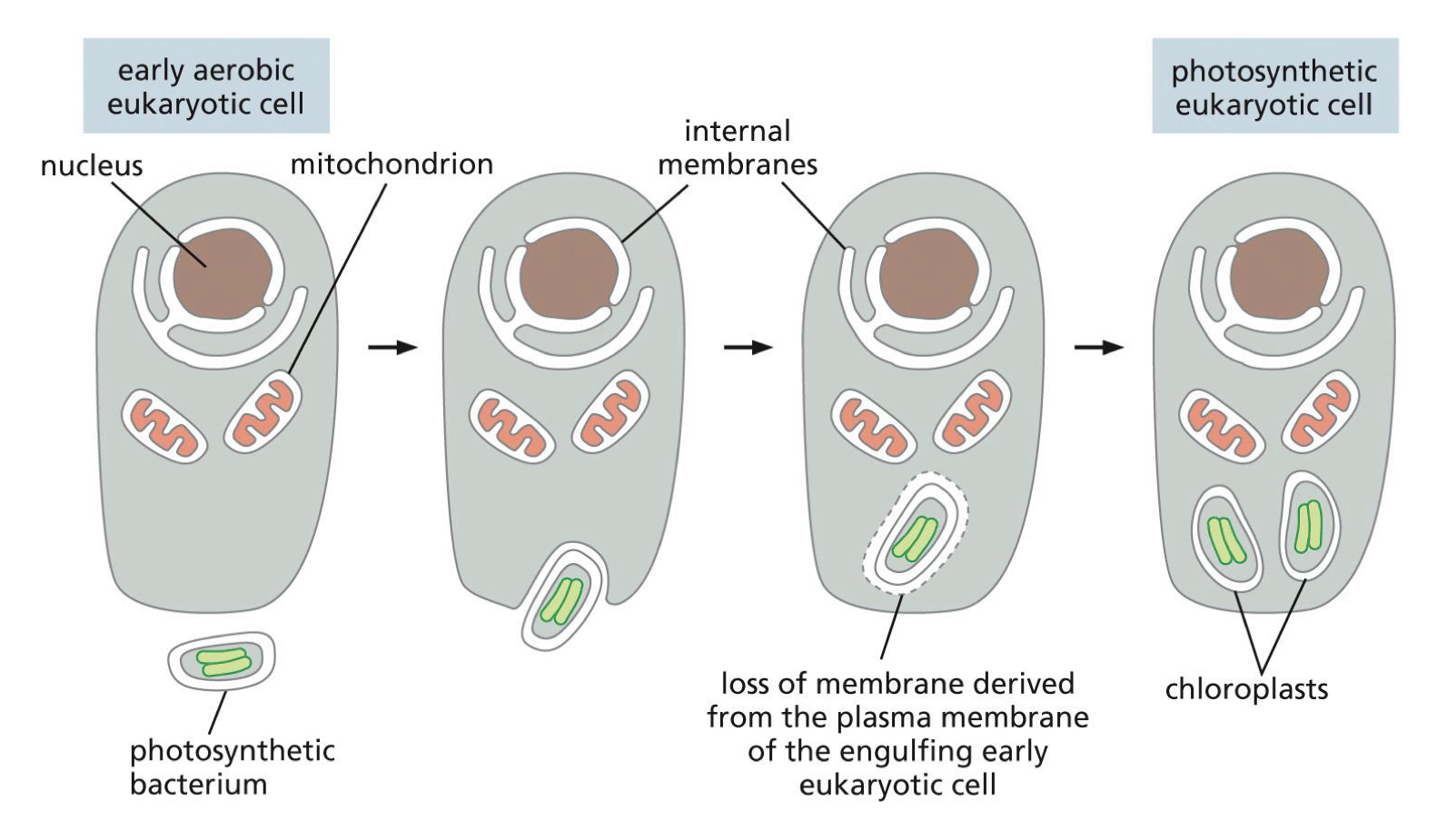
Origins of Chloroplast
Also contain their own DNA, and reproduce by dividing into two and are believed to have evolved from bacteria that were engulfed by an early aerobic eukaryote
\
Evolved later in time compared to mitochondria
\
Evolved later in time compared to mitochondria
12
New cards
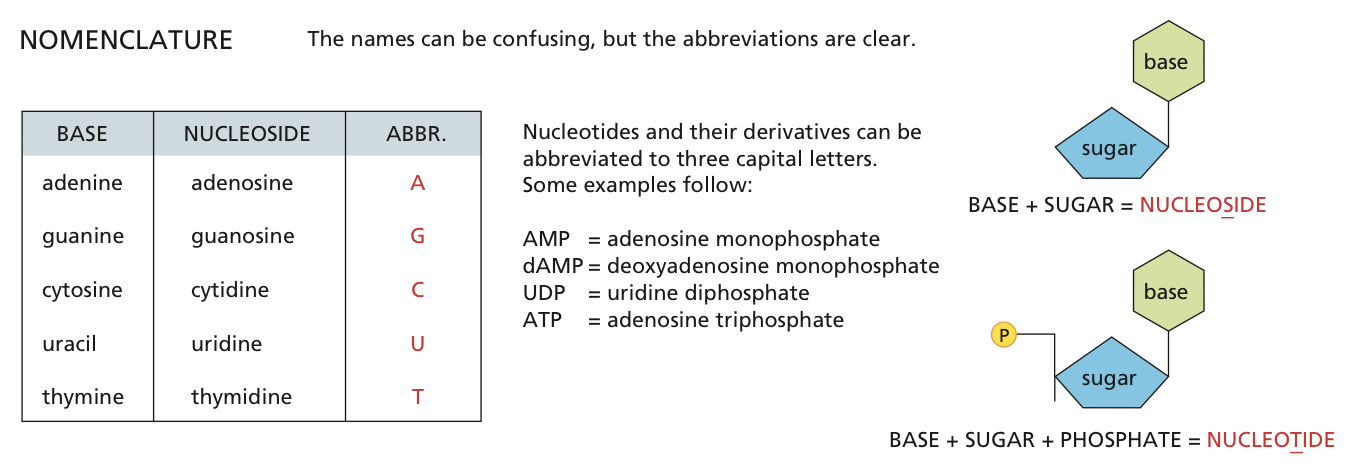
Nomenclature
\
13
New cards
Endosymbiont Hypothesis
1. Mitochondria and chloroplasts still have remnants of their own genomes and their genetic systems resemble that of modern day prokaryotes.
2. Mitochondria and chloroplasts have kept some of their own protein & DNA synthesis components and these resemble prokaryotes too.
14
New cards
Nucleoside
Contains base, and sugar ONLY (can also act as a chemical energy carrier ATP)
15
New cards
Nucleotide
Contains a base (varies), sugar (scaffold for base) AND phosphate group (backbone1,2,3)
Monomer/ subunit of Nucleic acid, order encodes genetic info based on base. Joined with phosphodiester bonds.
Monomer/ subunit of Nucleic acid, order encodes genetic info based on base. Joined with phosphodiester bonds.
16
New cards
Mouse, E-coli, FruitFly, Brewers Yeast, Zebra Fish
Model Organism Examples
* General attributes:
* rapid development with short life cycles
* small adult size
* readily available
* easily manipulated
* understandable genetics
* General attributes:
* rapid development with short life cycles
* small adult size
* readily available
* easily manipulated
* understandable genetics
17
New cards
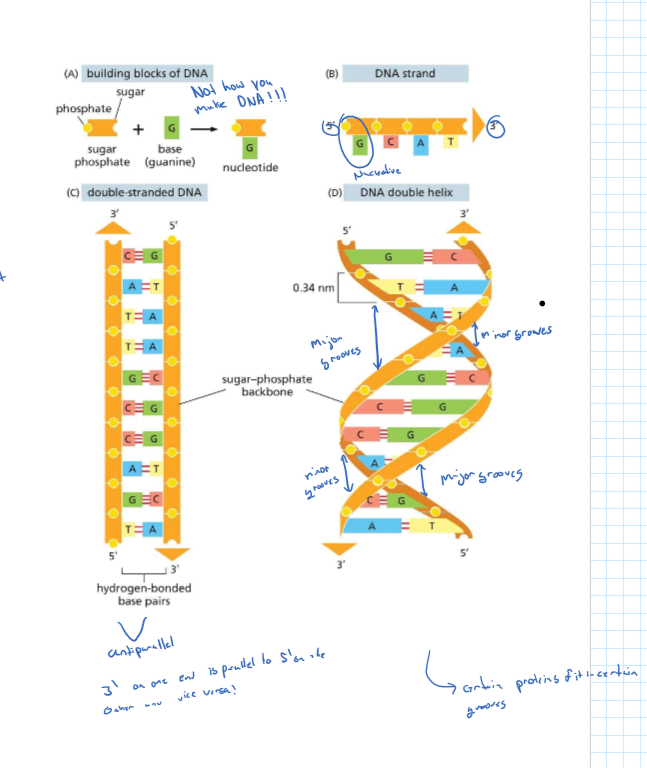
DNA structure
* 2 Chains of complementary nucleotide polymers running antiparallel
* strands held via hydrogen bonds between the bases of nucleotides (inside of helix)
* Double Helix (10 bases per twist)
* phosphodiester bonding between the phosphate group on the 5’ carbon and the hydroxyl on the 3’
* chemical polarity
* information encoded in the sequence of the nitrogen bases
* Major and minor groove (that proteins can interact with)
* deoxyribose sugar
* Bases (Thymine, Adenine (2 hbonds), cytosine, guanine(3hbonds))
* strands held via hydrogen bonds between the bases of nucleotides (inside of helix)
* Double Helix (10 bases per twist)
* phosphodiester bonding between the phosphate group on the 5’ carbon and the hydroxyl on the 3’
* chemical polarity
* information encoded in the sequence of the nitrogen bases
* Major and minor groove (that proteins can interact with)
* deoxyribose sugar
* Bases (Thymine, Adenine (2 hbonds), cytosine, guanine(3hbonds))
18
New cards
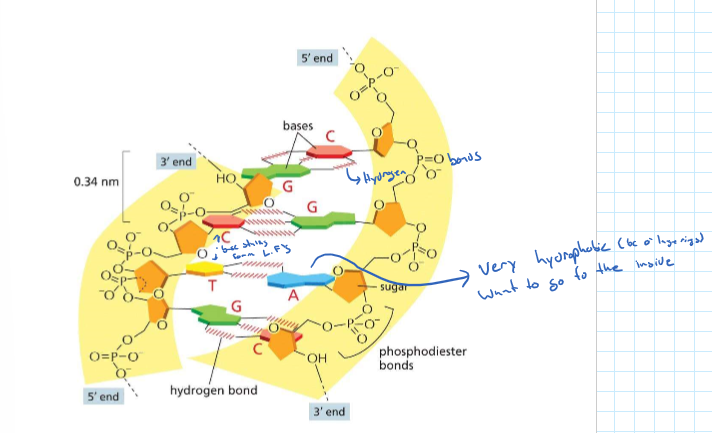
Molecular interactions
* Electrostatic attractions
* Hydrogen Bonds
* Van der Waals attractions
* Hydrophobic force
\
* Hydrogen Bonds
* Van der Waals attractions
* Hydrophobic force
\
19
New cards
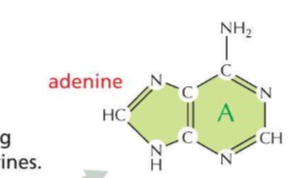
Purines
* “Al gore stinks PU”
* have two rings
* Adenine guanine
* have two rings
* Adenine guanine
20
New cards
Pyrimidines
* have one ring
* “U C the Pyamids
* bases: U, C, T
\
* “U C the Pyamids
* bases: U, C, T
\
21
New cards
Lysosomes
* Irregular shape
* where intracellular digestion occurs
* releases nutrients into the cytosol
* breaks unwanted molecules for recycling or excreting from cell
* where intracellular digestion occurs
* releases nutrients into the cytosol
* breaks unwanted molecules for recycling or excreting from cell
22
New cards
Cytoskeleton
* filament often anchored at one end of the membrane or radiating out from a side next to the nucleus
* thinnest filament: actin
* thickest: microtubules
* separates chromosome pairs and pulls them to their respective poles during mitosis
* even found in bacteria for use in division
* thinnest filament: actin
* thickest: microtubules
* separates chromosome pairs and pulls them to their respective poles during mitosis
* even found in bacteria for use in division
23
New cards
Mitochondria
* found in all eukaryotes
* double membrane
* inner membrane folded into inward-facing folds
* contain their own DNA and reproduce via division
* generate energy for the cell from the oxidation of food molecules to produce ATP
* double membrane
* inner membrane folded into inward-facing folds
* contain their own DNA and reproduce via division
* generate energy for the cell from the oxidation of food molecules to produce ATP
24
New cards
Transport vesicle
tiny membrane sacs that move materials (such as proteins and molecules) throughout the cell.
transport vesicles move cell proteins to the Golgi apparatus
transport vesicles move cell proteins to the Golgi apparatus
25
New cards
Peroxisomes
* found in eukaryotic cells
* organelle enclosed by a single membrane
* contains enzymes that degrade lipids and destroy toxins.
* organelle enclosed by a single membrane
* contains enzymes that degrade lipids and destroy toxins.
26
New cards
Nuclear envelope
* found in eukaryotic cells
* two lipid bilayer membranes: inner nuclear membrane and outer nuclear membrane
* separates contents of the nucleus from the cytoplasm
* structural framework of the nucleus
* two lipid bilayer membranes: inner nuclear membrane and outer nuclear membrane
* separates contents of the nucleus from the cytoplasm
* structural framework of the nucleus
27
New cards
Cytosol
* intra-cellular fluid (liquid found inside the cell)
* solution of water, proteins, and metabolites
* allows organelles, proteins, and other cell structures to float
* solution of water, proteins, and metabolites
* allows organelles, proteins, and other cell structures to float
28
New cards
Differences between Animal and plant cells
* animal cell:
* no cell wall
* no chloroplast
* contains a centrosome and lysosomes
* plant cell
* contains cell wall
* contains chloroplast
* no centrosome nor lysosomes
* no cell wall
* no chloroplast
* contains a centrosome and lysosomes
* plant cell
* contains cell wall
* contains chloroplast
* no centrosome nor lysosomes
29
New cards
endocytosis
* process by which cells absorb external material by engulfing it with the cell membrane
* includes two processes
* pinocytosis (“cell drinking”): soluble materials are ingested by the cells and incorporated into vesicles for digestion
* phagocytosis (“cell eating”): particulate materials are ingested by the cell. plays a role in the elimination of foreign substances.
* includes two processes
* pinocytosis (“cell drinking”): soluble materials are ingested by the cells and incorporated into vesicles for digestion
* phagocytosis (“cell eating”): particulate materials are ingested by the cell. plays a role in the elimination of foreign substances.
30
New cards
exocytosis
* process where molecules are transported out of a eukaryotic cell
* involves the fusion of secretory vesicles with the plasma membrane
* releases vesicle content, and incorporates new proteins and lipids into the plasma membrane
* involves the fusion of secretory vesicles with the plasma membrane
* releases vesicle content, and incorporates new proteins and lipids into the plasma membrane
31
New cards
RNA structure
* typically single stranded
* contains ribose as its pentose sugar
* contains the pyrimidine uracil instead of thymine
* polynucleotide composed of covalently linked ribonucleotide subunits
* contains ribose as its pentose sugar
* contains the pyrimidine uracil instead of thymine
* polynucleotide composed of covalently linked ribonucleotide subunits
32
New cards
proteome
All the proteins in a living cell or organism
33
New cards
Genome
All the DNA sequences in a living cell or organism
34
New cards
Cell Theory
the cell is the basic organizational unit of life
all organisms are composed of one or more cells
cells arise from preexisting cells.
all organisms are composed of one or more cells
cells arise from preexisting cells.
35
New cards
Transcriptome
all the RNA sequences in a living cell or organism
36
New cards
Interactome
all protein-protein interactions in a cell or organism
37
New cards
metabolome
all the small the small molecule metabolites in a cell or organism
38
New cards
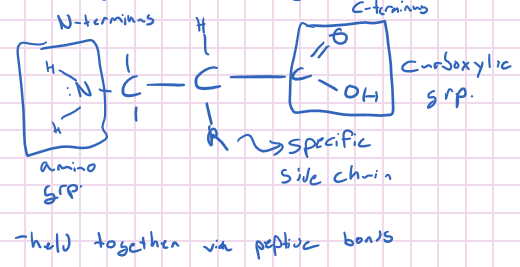
Amino Acids
* consist of an alpha carbon that’s attached to an amino group(N-terminus) and a carboxylic group (C-terminus)
* each amino acid has a unique side chair that is attached to the alpha carbon (called the R group)
* They’re the monomers of peptides and polypeptides
* There are 20 unique ones
* there are d an l forms (they’re optical isomers)
* each amino acid has a unique side chair that is attached to the alpha carbon (called the R group)
* They’re the monomers of peptides and polypeptides
* There are 20 unique ones
* there are d an l forms (they’re optical isomers)
39
New cards
Proteins
* long polymers of amino acids linked by peptide bonds and they are always written with the N-terminus on the left side
40
New cards
Peptides
* shorter polymers of amino acids, usually fewer than 50 amino acids long
41
New cards
Amino Acid Families
* acidic
* basic
* uncharged polar
* nonpolar
R group determines type
* basic
* uncharged polar
* nonpolar
R group determines type
42
New cards
Amino acids and the Genetic Code
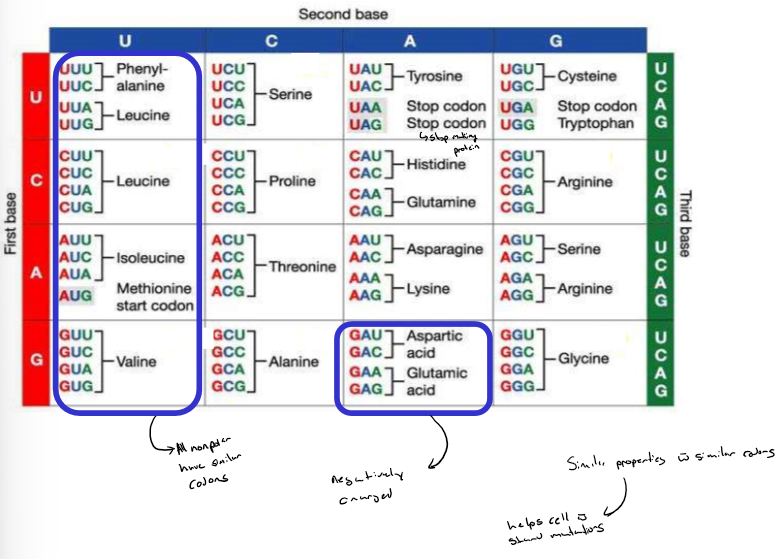
43
New cards
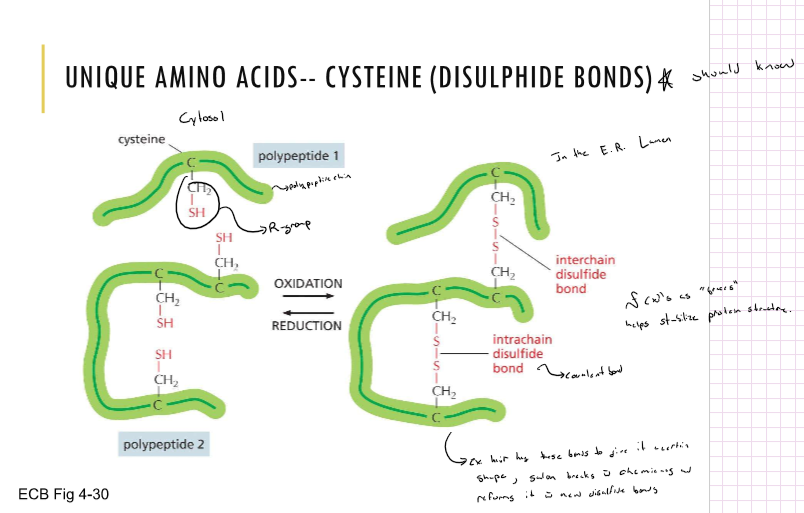
Disulfide bonds
* helps stabilizes protein structure acts almost as “braces”
* there are interchain and intrachain disulfide bonds
\
* there are interchain and intrachain disulfide bonds
\
44
New cards
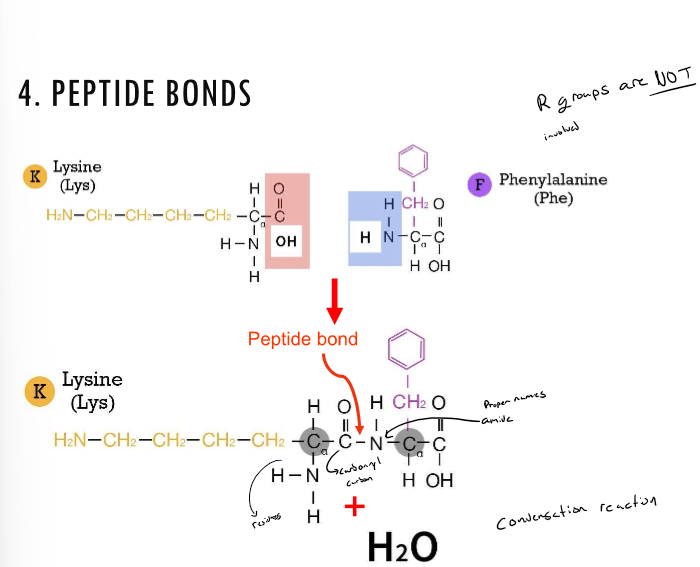
Peptides bonds
* hold together amino acids in their polymers
* forms between the carboxylic group of the amino acid and the amino group R GROUPS ARE NOT INVOLVED
* is a condensation reaction as it produces water upon formation
* the amino group is then referred to as an amide and the carboxylic group is now a carbonyl.
* The former amino acids are now referred to as residues
* forms between the carboxylic group of the amino acid and the amino group R GROUPS ARE NOT INVOLVED
* is a condensation reaction as it produces water upon formation
* the amino group is then referred to as an amide and the carboxylic group is now a carbonyl.
* The former amino acids are now referred to as residues
45
New cards
Backbone atoms of the polypeptide
all the protein atoms except the side chains
46
New cards
chaperone proteins
* They’re proteins that assist with protein folding
* bind to them and guide them to fold in the most energetically favored path or provide an isolated chamber where they can fold undisturbed
\
* bind to them and guide them to fold in the most energetically favored path or provide an isolated chamber where they can fold undisturbed
\
47
New cards
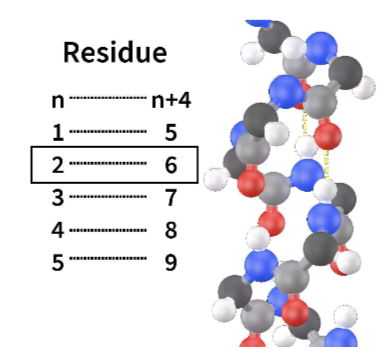
Alpha helix
* common secondary structure of proteins
* forms via hydrogen bonds between N-H and C = O groups in the BACKBONE (R groups are not involved and just stick out)
* Bonds form between the n and the n + 4 residue (e.g. 1 and 5, 2 and 6)
* it’s a regular right-handed helix
* typically found when there are many similar subunits arranged right next to each other
* forms via hydrogen bonds between N-H and C = O groups in the BACKBONE (R groups are not involved and just stick out)
* Bonds form between the n and the n + 4 residue (e.g. 1 and 5, 2 and 6)
* it’s a regular right-handed helix
* typically found when there are many similar subunits arranged right next to each other
48
New cards
ATP
* Adenosine Triphosphate
* principle carrier of energy in cells
* composed of adenine, ribose, and three phosphate groups
* principle carrier of energy in cells
* composed of adenine, ribose, and three phosphate groups
49
New cards
phosphodiester bond
* the linkage between the 3' carbon atom of one sugar molecule and the 5' carbon atom of another
* hold together nucleotide subunits within a DNA strand
* hold together nucleotide subunits within a DNA strand
50
New cards
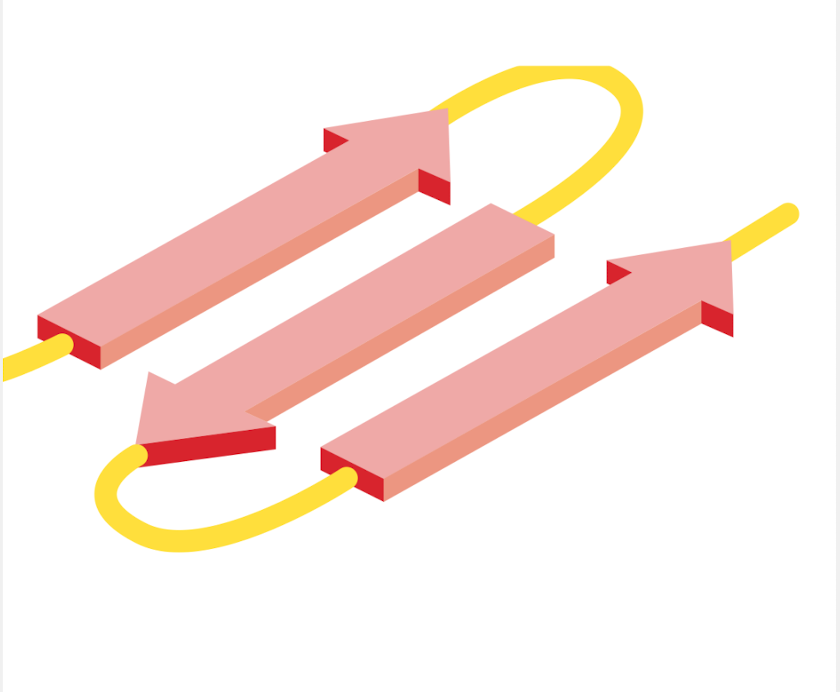
Beta Sheet
Folding pattern found in many proteins where neighbouring regions of the polypeptide chain associate side-by-side with each other through h-bonds to give a flat rigid structure
The H-bonding occurs between the carbonyl oxygen of 1 a.a and amide hydrogen of a.a in neighbouring strand
R groups are not involved in the structure but are projected up and down
Usually contain 4-5 beta strands
Can either be anti-parallel or parallel (longer but requires extra sequences)
The H-bonding occurs between the carbonyl oxygen of 1 a.a and amide hydrogen of a.a in neighbouring strand
R groups are not involved in the structure but are projected up and down
Usually contain 4-5 beta strands
Can either be anti-parallel or parallel (longer but requires extra sequences)
51
New cards
Protein Structure
Primary (aa sequence)
\
Secondary (local folding) - ex. alpha helix, beta sheet
\
Tertiary (long-range folding) - ex. 3D structure
\
Quaternary (multimeric organization) - ex. more than 1 polypeptide chain (Not all proteins experience this)
\
Secondary (local folding) - ex. alpha helix, beta sheet
\
Tertiary (long-range folding) - ex. 3D structure
\
Quaternary (multimeric organization) - ex. more than 1 polypeptide chain (Not all proteins experience this)
52
New cards
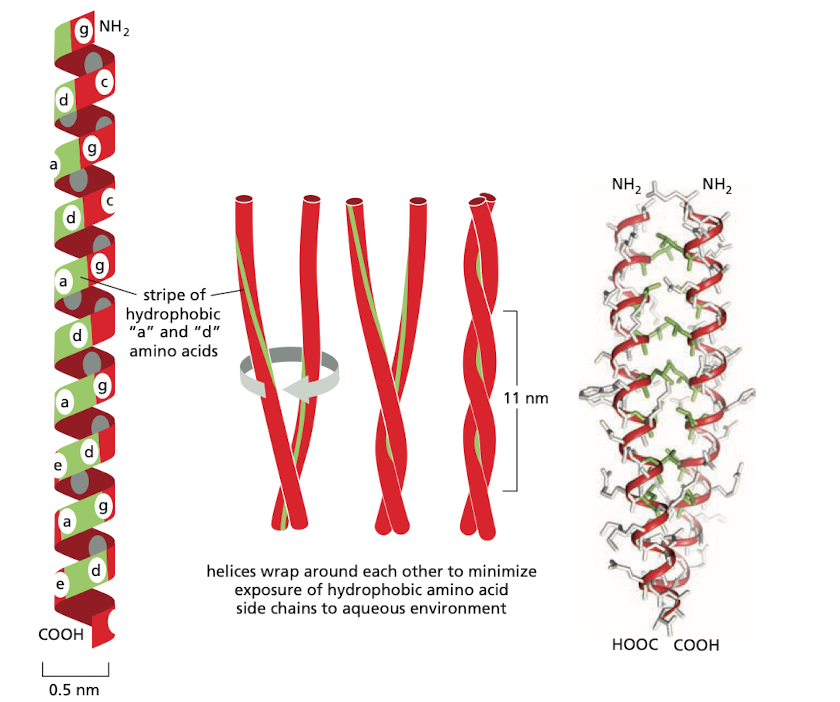
Coiled Coil
Two or more alpha helices twist repeatedly around each other
They wrap around each other to minimize exposure of hydrophobic amino acid side chains to aqueous environment
Amphipathic - contains both hydrophobic (side-groups) and hydrophilic (interior groups) parts
They wrap around each other to minimize exposure of hydrophobic amino acid side chains to aqueous environment
Amphipathic - contains both hydrophobic (side-groups) and hydrophilic (interior groups) parts
53
New cards
Protein Domains
Any segment of a polypeptide chain that can fold independently into its own compact stable structure
This portion of protein often functions in a semi-independent manner within the protein
Eukaryotic proteins often have 2 or more domains connected by intrinsically disordered sequences to allow for flexibility within the protein
This portion of protein often functions in a semi-independent manner within the protein
Eukaryotic proteins often have 2 or more domains connected by intrinsically disordered sequences to allow for flexibility within the protein
54
New cards
Protein Families
A group of proteins with common evolutionary origin
Fold similarly and have similar function
Most proteins belong to families with similar structural domains
Fold similarly and have similar function
Most proteins belong to families with similar structural domains
55
New cards
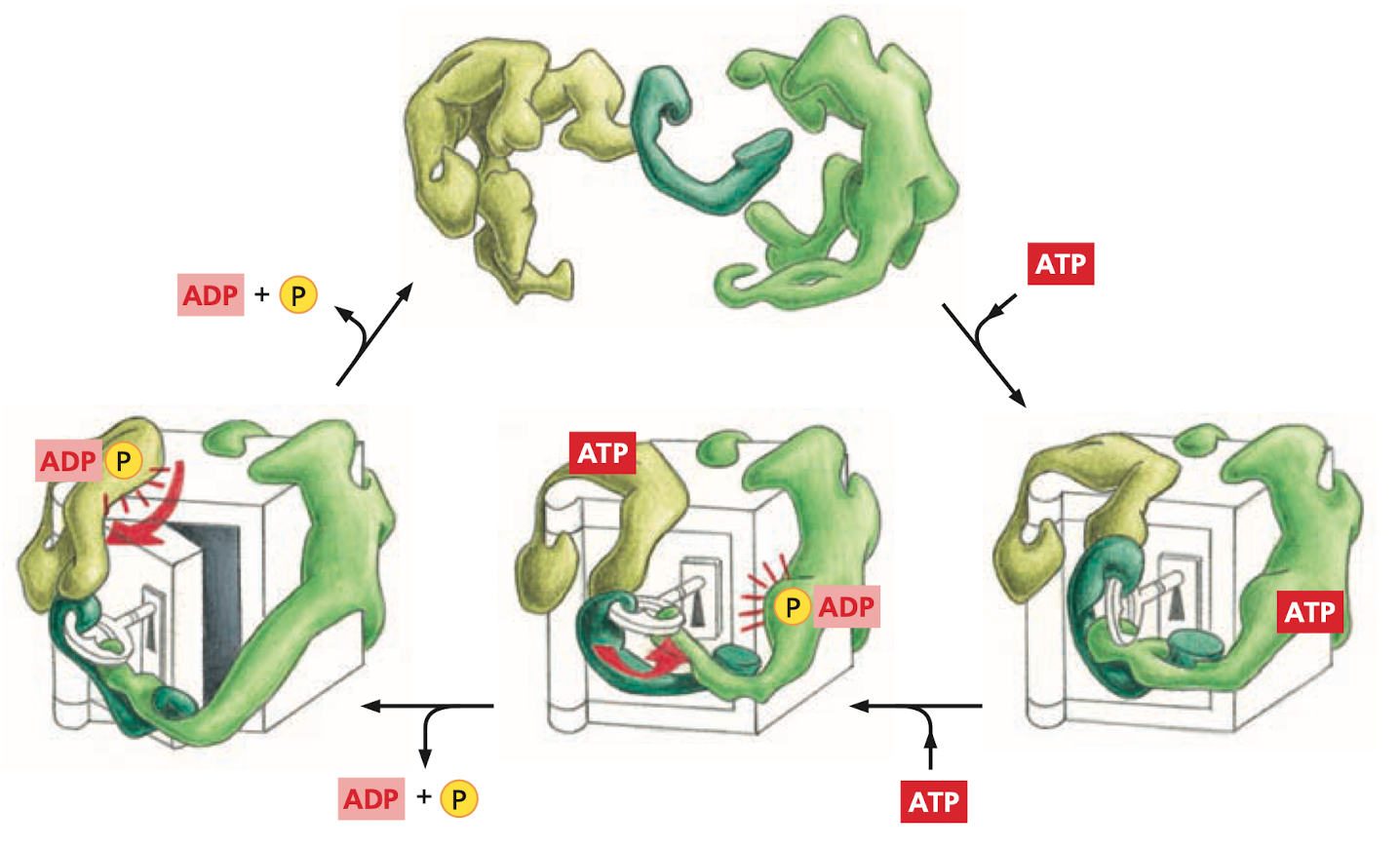
Protein Machines
“Machines” made up of individual proteins that collaborate to perform a more complex function
56
New cards
Tertiary structure
proteins will generally fold into the conformation that is the **most energetically favoured**
Proteins will fold into the shape dictated by their amino acid sequence, but chaperone proteins help make the process more efficient and reliable in living cells
Proteins will fold into the shape dictated by their amino acid sequence, but chaperone proteins help make the process more efficient and reliable in living cells
57
New cards
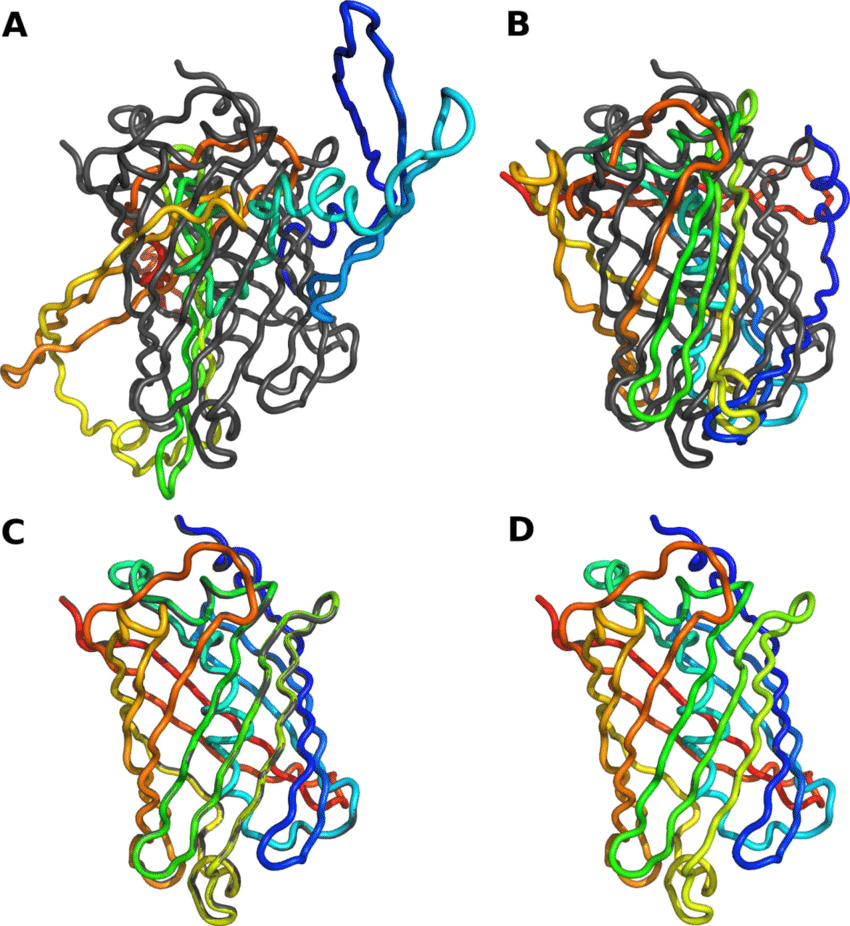
Backbone Model
→ Protein Model
* Shows overall organization
* Straightforward string-like model
* Shows overall organization
* Straightforward string-like model
58
New cards
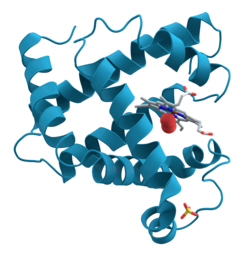
Ribbon Model
→ Protein Model
* Shows Polypeptide bonds
* emphasizes its most conspicuous folding patterns
* Shows Polypeptide bonds
* emphasizes its most conspicuous folding patterns
59
New cards
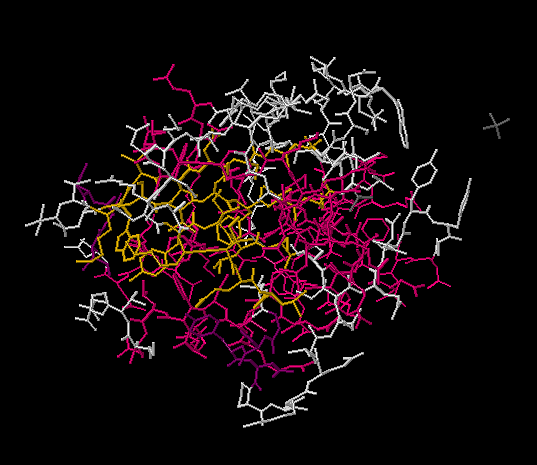
Wire Model
→ Protein Model
* Shows positions of all amino acid side chains
* useful to predict which A.A’s responsible for activity
* Shows positions of all amino acid side chains
* useful to predict which A.A’s responsible for activity
60
New cards
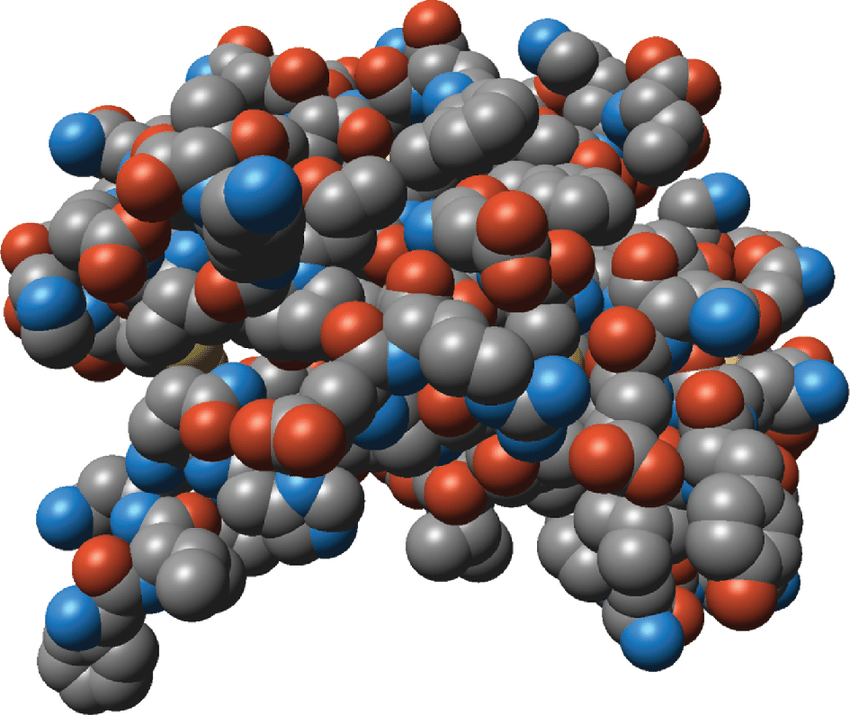
Space-Filling Model
→ Protein Model
* Contoured map of proteins surface
* Shows what amino acids are exposed on surface
* Shows how protein might look like to a smaller molecule
* Contoured map of proteins surface
* Shows what amino acids are exposed on surface
* Shows how protein might look like to a smaller molecule
61
New cards
Prion
misfolded protein
62
New cards
Biological Function Protein Requirements
* Well-Behaved
* Well Defined 3D conformations
* Stable
* Well Defined 3D conformations
* Stable
63
New cards
Dimer
2 Identical folded polypeptide chains form a symmetrical complex of two protein subunits
* held together by two identical binding sites
* held together by two identical binding sites
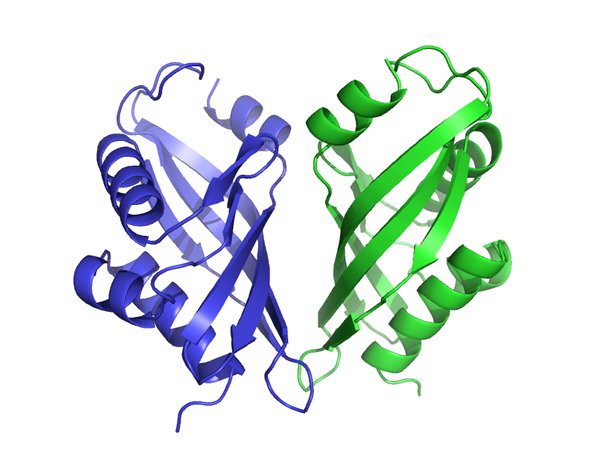
64
New cards
Acidic Side Chains
Aspartic Acid and Glutamic Acid
65
New cards
Mass Spectrometry
determines amino acid sequence of proteins that have been isolated from organisms for which the full genome sequence is known. Determines mass of every peptide fragment.
66
New cards
Electrophoresis
Mixture of proteins loaded onto polymer gel and subjected to an electric field. Size and net charge of polypeptides causes them to move through gel at different rates.
67
New cards
F.I.S.H
* Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization
* Diagnostic technique
* DNA probes are used to mark the locations of their respective nucleotide sequences
* The probes are labeled with different chemical groups that can be detected with fluorescent antibodies specific for those groups
* Diagnostic technique
* DNA probes are used to mark the locations of their respective nucleotide sequences
* The probes are labeled with different chemical groups that can be detected with fluorescent antibodies specific for those groups
68
New cards
Chromosome painting
Similar to F.I.S.H, chromosome painting uses multiple probs to mark specific sequences in chromosomes and “paints” them in a fluorescent dye
69
New cards
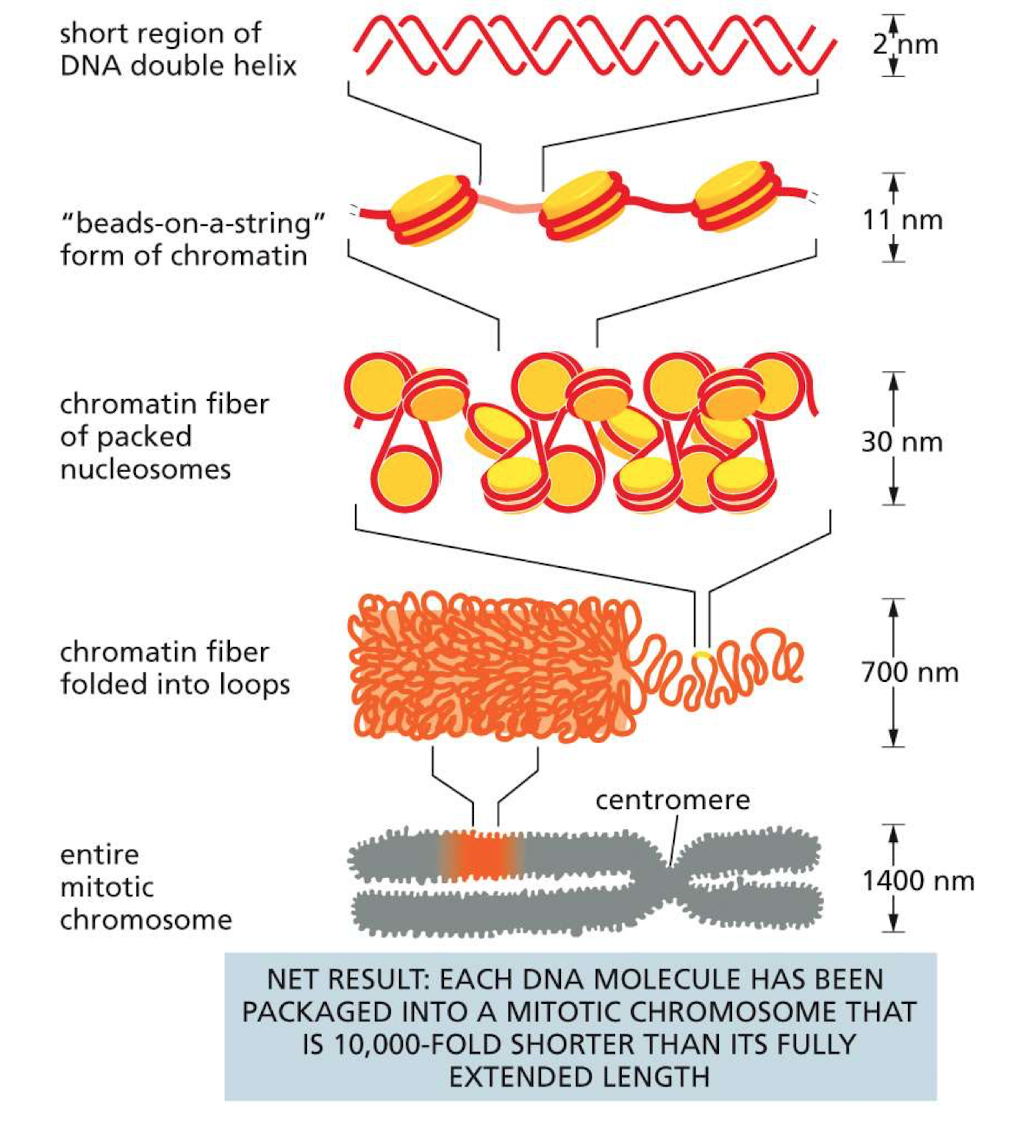
Chromatin levels of organization
The process starts with assembly of a nucleosome, which is formed when eight separate histone protein subunits attach to the DNA molecule.
\
Multiple nucleosomes are coiled together and these then stack on top of each other. The end result is a fiber of packed nucleosomes known as chromatin.
\
This fiber, which at this point is condensed to a thickness of 30 nanometers is then looped and further packaged using other proteins. The multiple folding allows 6 feet of DNA to fit into the nucleus of each cell of our body
The end result is that DNA are tightly packed into the familiar structures we can see through a microscope: chromosomes.
\
Multiple nucleosomes are coiled together and these then stack on top of each other. The end result is a fiber of packed nucleosomes known as chromatin.
\
This fiber, which at this point is condensed to a thickness of 30 nanometers is then looped and further packaged using other proteins. The multiple folding allows 6 feet of DNA to fit into the nucleus of each cell of our body
The end result is that DNA are tightly packed into the familiar structures we can see through a microscope: chromosomes.
70
New cards
Nucleosome
Basic structural unit of a eukaryotic chromosome composed of short length of DNA wrapped around an octameric core of histone proteins; includes a nucleosomal core particle (DNA plus histone protein) along with a segment of linker DNA that ties the core particles together
* Octamer: H2A H2B H3 and H4
* linker histone H1
* Octamer: H2A H2B H3 and H4
* linker histone H1
71
New cards
Histones
Small group of abundant, highly conserved proteins rich in lysine and arginine around which DNA wraps to form nucleosomes, structures that represent the most fundamental level of chromatin packing
72
New cards
Non-histone proteins
Chromatin in human chromosomes are folded into loops by special nonhistone chromosomal proteins that bind to specific DNA sequences, creating a clamp at the base of each loop
73
New cards
Chromatin packaging and re-modelling
Chromatin remodeling complexes and histone modifying enzymes are examples of proteins that make changes to chromatin structure and alter access to DNA for replication or transcription.
74
New cards
Heterochromatin
Highly condensed chromatin of an interphase chromosome; generally gene-poor and transcriptionally inactive
75
New cards
Euchromatin
Relatively non-condensed chromatin that exists within an interphase cell. Prevalent in gene-rich areas, its less compact structure allows access for proteins involved in transcription
76
New cards
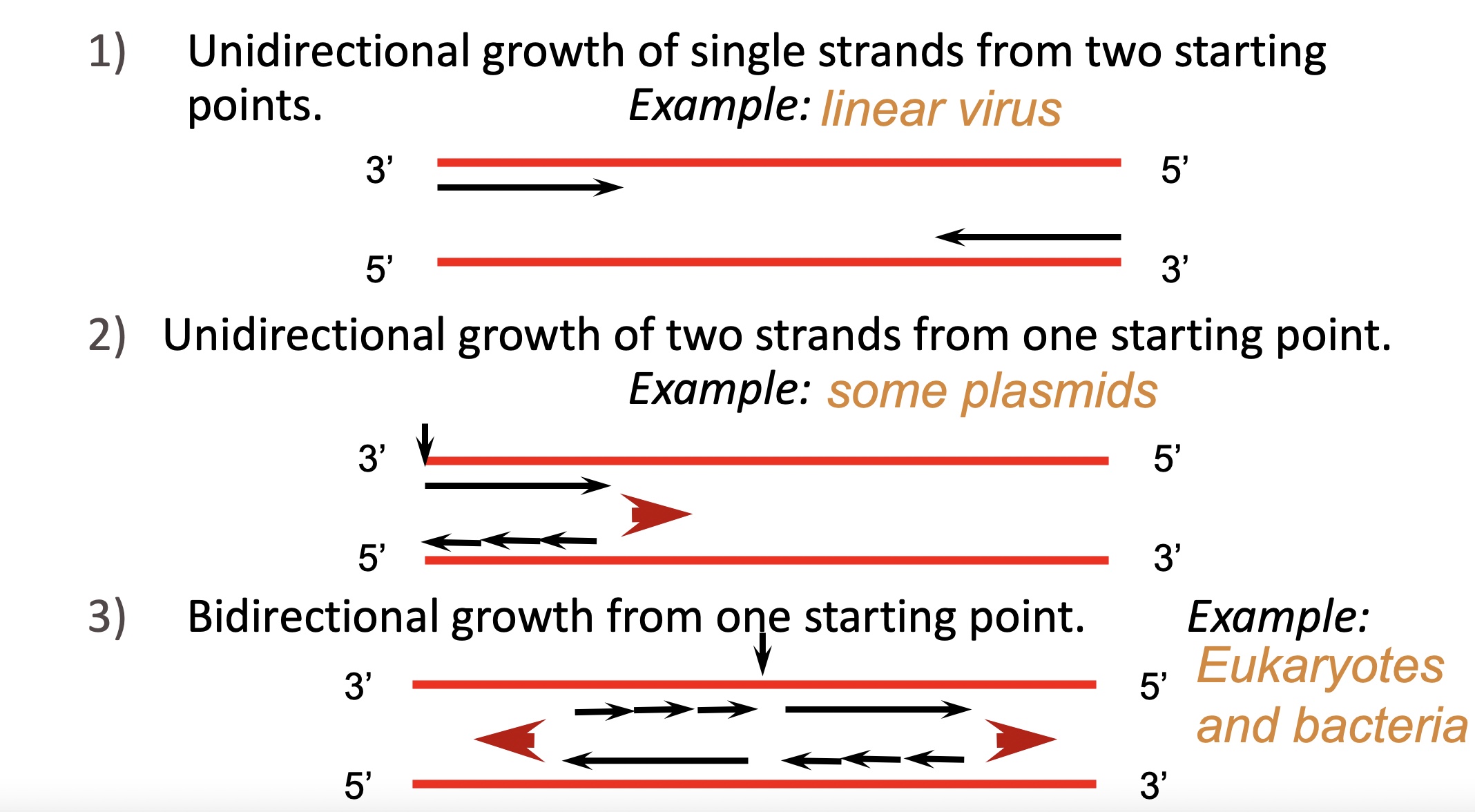
Direction of DNA replication
* DNA is always synthesized in the 5'-to-3' direction
* Unidirectional growth of a single strand from two points
* Unidirectional growth of two strands from one point
* Bidirectional growth from one point
* Unidirectional growth of a single strand from two points
* Unidirectional growth of two strands from one point
* Bidirectional growth from one point
77
New cards
Characteristics of sequences in replication origins
* easy to open, A-T rich
* Recognized by the binding of initiating proteins
* Recognized by the binding of initiating proteins
78
New cards
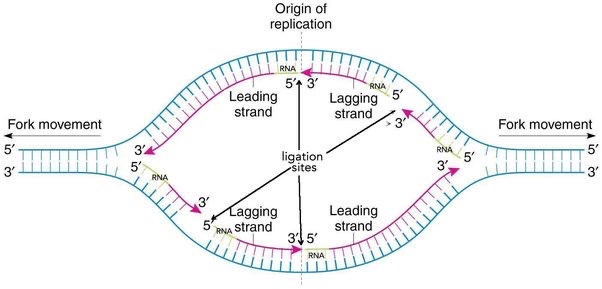
Replication bubble
* Structure formed by the separation of two DNA strands by the helicase enzymes
* Specialized proteins bind to the origin site, and open up the DNA
* Replication forks are formed and continue to move in opposite directions as replication proceeds.
* Specialized proteins bind to the origin site, and open up the DNA
* Replication forks are formed and continue to move in opposite directions as replication proceeds.
79
New cards
Origin of replication
* a particular sequence in a genome where replication is initiated.
* Single on in Bacteria Multiple eukaryotes
* Single on in Bacteria Multiple eukaryotes
80
New cards
DNA replication in Bacteria
* A bacterial genome has a single origin of replication (unique to circular genomes) forming one replication fork
* Supercoiled DNA is unwound by DNA gyrase
* Helicase separates the DNA strands by breaking the hydrogen bonds between the nitrogenous base pairs.
* Supercoiled DNA is unwound by DNA gyrase
* Helicase separates the DNA strands by breaking the hydrogen bonds between the nitrogenous base pairs.
81
New cards
DNA replication fork
* Y shaped function (though it can curve to improve efficiency of the DNA polymerase (brings them in proximity to each other)
* two per replication origin going in different directions
* asymmetrical with a leading strand synthesized continuously and a lagging strand made discontinuously.
* two per replication origin going in different directions
* asymmetrical with a leading strand synthesized continuously and a lagging strand made discontinuously.
82
New cards
Nucleosome core particle
* consists of DNA wound around a core of histone proteins
* each one contains a complex of eight histone proteins
* two molecules each of H2A, H2B, H3, and H4
* double stranded DNA wounds around the protein complex
* DNA is 147 nucleotide pairs long
* each one contains a complex of eight histone proteins
* two molecules each of H2A, H2B, H3, and H4
* double stranded DNA wounds around the protein complex
* DNA is 147 nucleotide pairs long
83
New cards
Chromatin
* single, long, linear DNA molecule associated with proteins
* Dynamic
* tightly packaged but DNA still remains accessible for transcription, replication and repair
* Dynamic
* tightly packaged but DNA still remains accessible for transcription, replication and repair
84
New cards
Retrotransposons
* DNA sequences that are made into RNA
85
New cards
Initiator Proteins for replication in E.Coli
* Binds to origin
* helps helicase bind
* requires ATP
* helps helicase bind
* requires ATP
86
New cards
DNA-only transposon
* Sequences that only exist as DNA
87
New cards
Mobile Genetic elements
* Regions of DNA that make copies and inserts themselves back into the sequence
88
New cards
Simple elements
* simple sequences that are often repeated example: AG 30 - 100 times
89
New cards
segment duplications
* 1000’s - 200,000’s of base pairs and duplicated
90
New cards
Introns
* transcribed but spliced out of the RNA (not translated)
91
New cards
protein-coding exons
* sequences transcribed and translated (made into proteins)
* Wilk Wilk have untranslated regions
* Wilk Wilk have untranslated regions
92
New cards
non-repetitive DNA that is in neither introns nor exons
* A Unique Sequence that makes up about 30% of the Human Genome
* promoters (help determine how much RNA is transcribed and which cells transcribe the RNA)
* promoters (help determine how much RNA is transcribed and which cells transcribe the RNA)
93
New cards
Packaging of DNA in the Cell
DNA is condensed through folding and twisting about 1000 fold and is complexed with proteins.
* Forms the prokaryotic nucleoid
* In eukaryotic cells, this DNA is packed into chromosomes to save space in nucleus
* Forms the prokaryotic nucleoid
* In eukaryotic cells, this DNA is packed into chromosomes to save space in nucleus
94
New cards
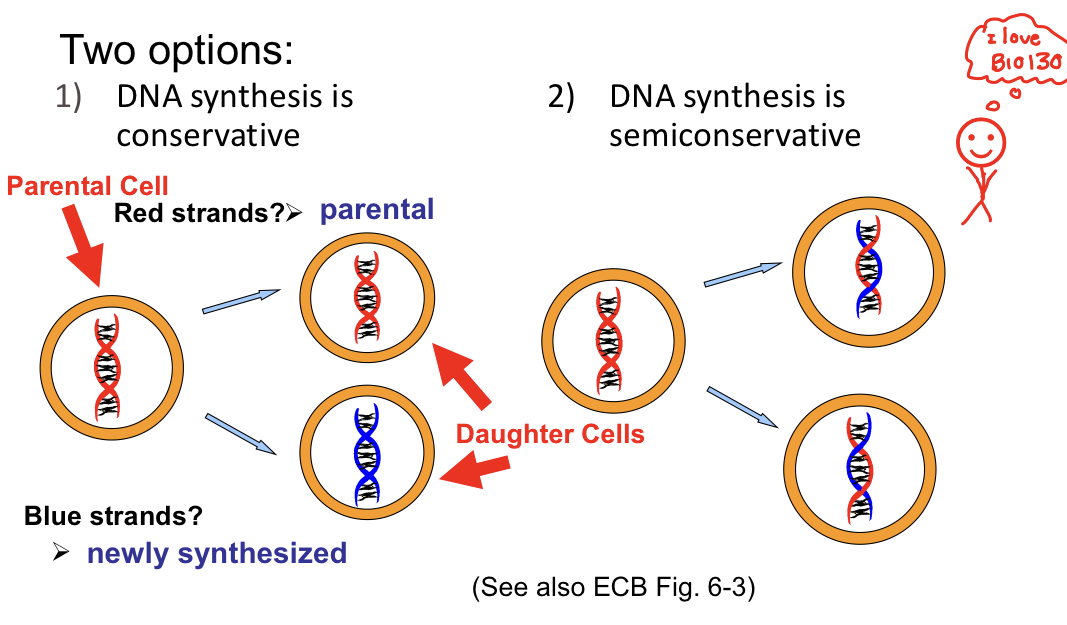
Conservative versus semiconservative DNA
Conservative
* Parental Cell makes one pure daughter cell and one newly synthesized daughter cell
SemiConservative
* Parental Cell makes two daughter cells that are both half newly synthesized and half parental strand
* Parental Cell makes one pure daughter cell and one newly synthesized daughter cell
SemiConservative
* Parental Cell makes two daughter cells that are both half newly synthesized and half parental strand
95
New cards
Interphase
Long period of the cell cycle between one mitosis and the next. Includes G1, S Phase, and G2 phase
96
New cards
Correlation of genome size
Genome Size does NOT equal size of animal
97
New cards
Re-orientation of chromatin in expressed DNA
Condensed into chromosomal territory - homologous chromosomes detected by hybridization techniques and a specially marked gene that can be on or off.
98
New cards
Non-Packaged State
Small prokaryotic genome would occupy a considerable portion of cell volume in this state
99
New cards
The Human Genome
* only 1.5 % codes for a protein
* 50% of genes are repetitive DNA
* 50% repeated sequences
* 50% Unique sequences
* 3 billion base pair per genome
* one genome from one parent and one genome from another parent
* \~19,000 protein-coding genes spread across 23 pairs of chromosomes
* 50% of genes are repetitive DNA
* 50% repeated sequences
* 50% Unique sequences
* 3 billion base pair per genome
* one genome from one parent and one genome from another parent
* \~19,000 protein-coding genes spread across 23 pairs of chromosomes
100
New cards
Binding of initiator Proteins
Binds to specific DNA sequences called replication origins, prying open the DNA strands breaking the h-bonds present (AT rich segment, not a lot of h-bonding present in that region)
\
A group of proteins (helicases) are attracted to the short segments of unzipped regions to carry out DNA replication. These proteins form a replication machine, in which each protein carries out a specific function.
\
A group of proteins (helicases) are attracted to the short segments of unzipped regions to carry out DNA replication. These proteins form a replication machine, in which each protein carries out a specific function.