Speech and Hearing Mechanisms Quiz 2
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
Coronal
Whole front and back of body, of or relating to the frontal plane that passes through the long axis of the body; cut in half vertically
Superior
Situated above or anterior or dorsal to another and especially a corresponding part
Sagittal
Of, relating to, situated in, or being the median plane of the body or any plane parallel to it
Transverse
Top and bottom cut in half horizontally
Lateral
Of or relating to the side
Anterior
Situated closest to the head or part most nearly corresponding to a head
Posterior
Situated behind
Inferior
From the bottom
Number of cervical vertebrae
7
Number of thoracic vertebrae
12
Number of lumbar vertebrae
5
Number of sacrum vertebrae
5
Number of coccyx vertebrae
4
Pelvic girdle structures
Sacrum, pubic bone, ischium, ilium
Pectoral girdle structures
Clavicles, scapula
Amount of ribs total
12
Amount of true ribs
7
Amount of false ribs
3
Amount of floating ribs
2
What is increased during thoracic expansion?
The volume of the thoracic cavity and lungs
What expands during thoracic expansion?
The chest cavity
Which muscles are involved with transverse movement?
The external intercostal muscles
Diaphragm - Inspiration or expiration?
Inspiration (Primary)
Diaphragm - Shape
Dome-shaped
Diaphragm - Function
Upon inhalation, contracts and flattens and the chest cavity enlarges.
Pectoralis minor - Shape
Fan-shaped minor
Pectoralis minor - Function
Moves the shoulder blade, or scapula, and the third through fifth ribs
Pectoralis minor - Inspiration or expiration?
Inspiration
Pectoralis major - Shape
Fan-shaped major
Pectoralis major - Function
Assists in drawing the sternum and ribs upward and increases transverse dimension of the rib cage
Pectoralis major - Inspiration or expiration?
Inspiration
Sternocleidomastoid - Function
Balances head and elevates sternum
Internal intercostals - Function
Fills spaces between ribs, connects ribs at opposite angles to external intercostals, pulls down from the pelvis through connection with abdominal muscles
Internal intercostals - Inspiration or expiration?
Expiration
Interchondral components - Description
The joints between the costal cartilages of the false ribs
Interchondral components - Function
Provide flexibility to the rib cage during respiration and help distribute mechanical forces across the chest
External intercostals - Function
Pull upward from the spine, skull, neck, and fixate upper ribs
External intercostals - Inspiration or expiration?
Inspiration
Transversus thoracis - Description
Flat muscle lying along inside front wall of the chest
Transversus thoracis - Fibers
Run obliquely
Transversus thoracis - Function
Assists in pulling the chest downward
Levator costarum - Description
Rib elevators, series of 12 small muscles
Levator costarum - Function
Pulls up on ribs
Levator costarum - Inspiration or expiration?
Inspiration
Rectus abdominus - Description
Large, vertical ribbon muscle
Rectus abdominus - Function
Downward pull on sternum provides powerful exhalatory force
Rectus abdominus - Inspiration or expiration?
Expiration
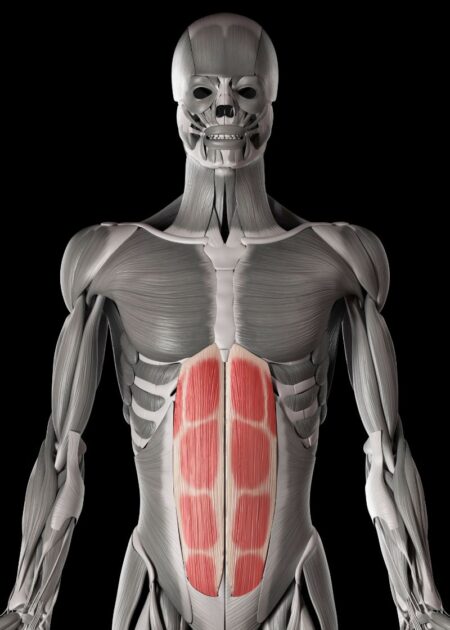
Rectus abdominis
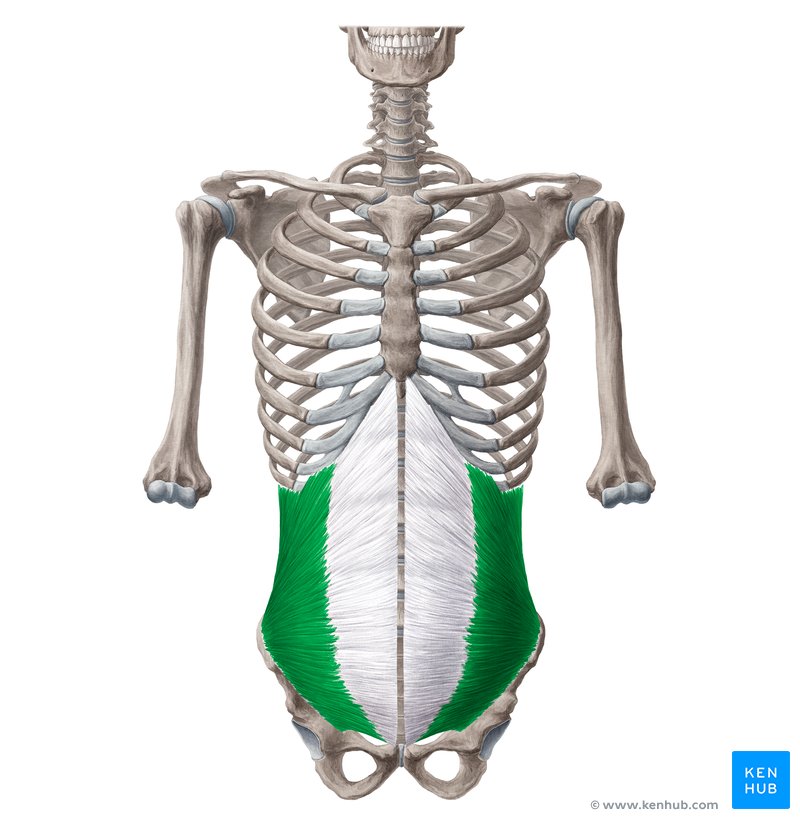
Internal oblique abdominis
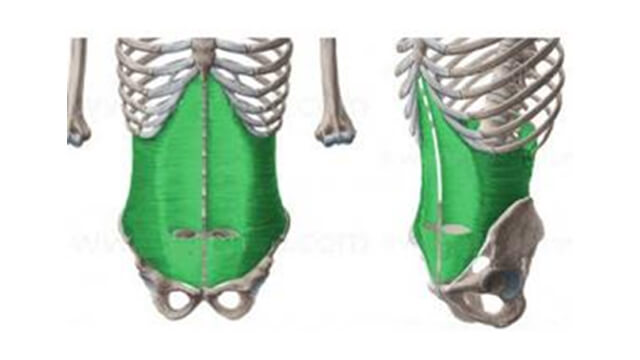
Transverse abdominis
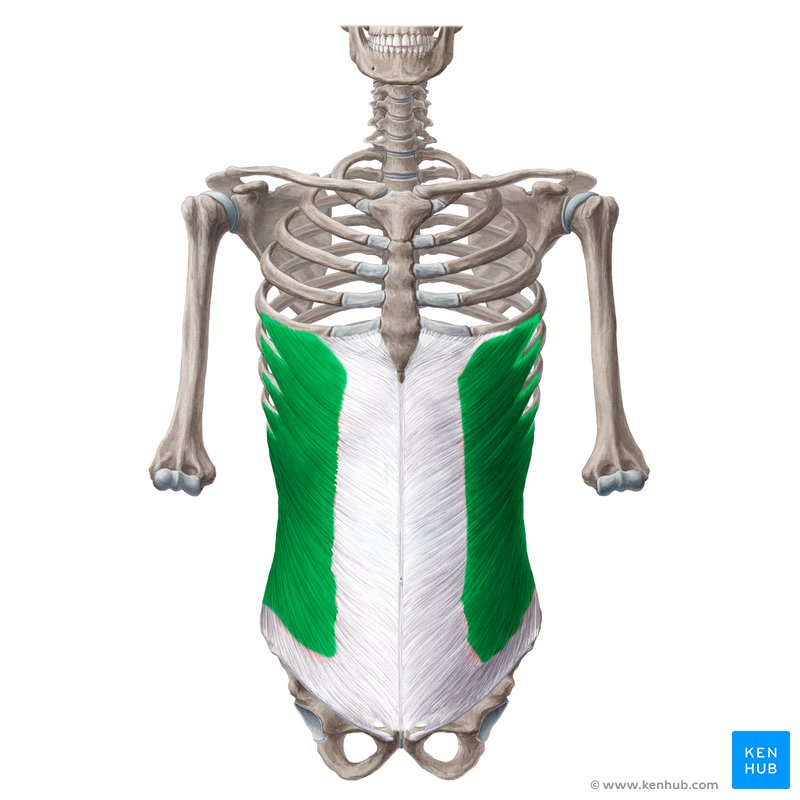
External oblique abdominis
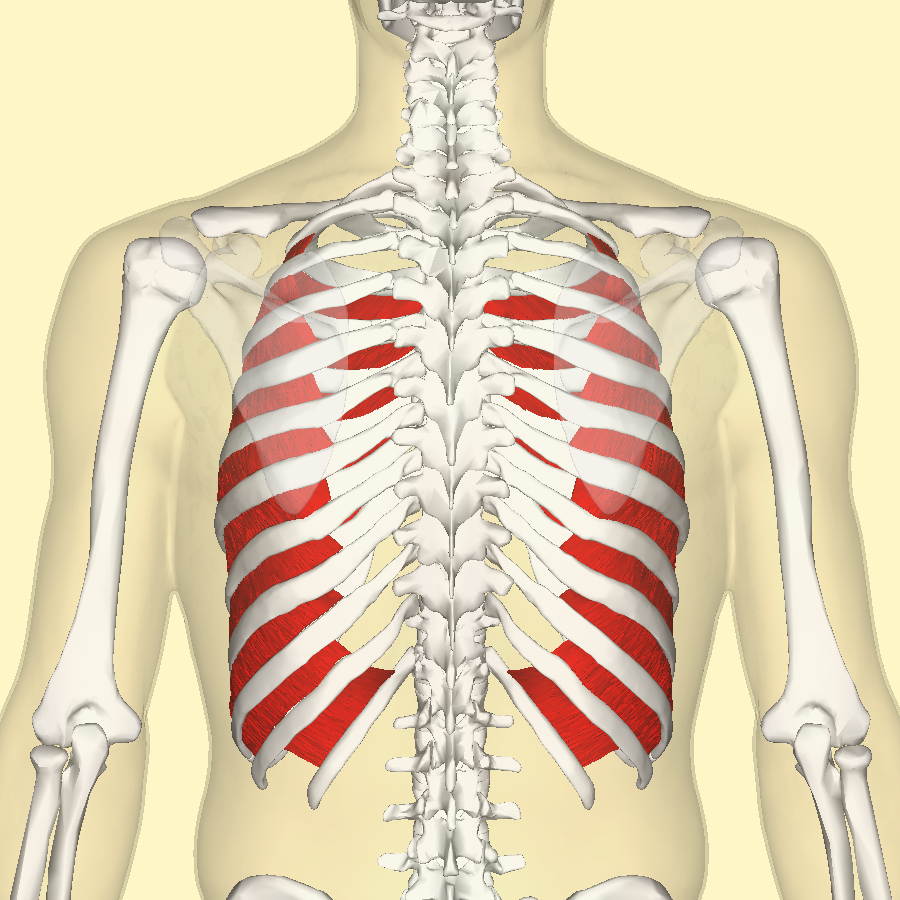
Internal intercostal
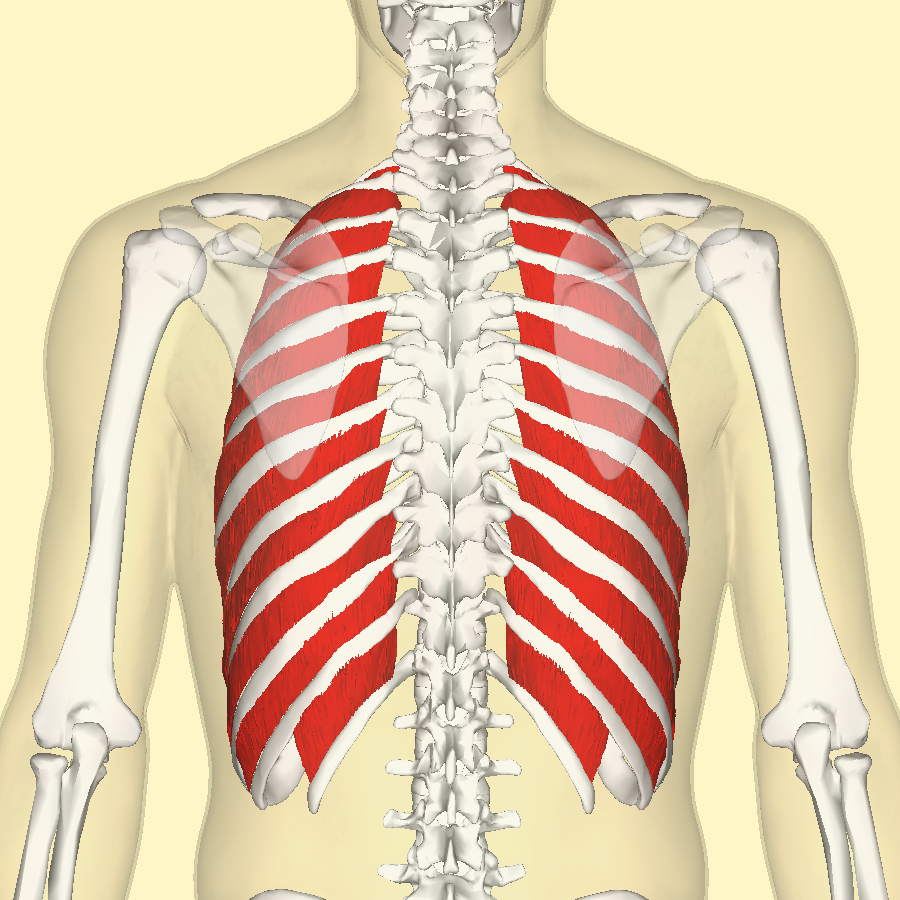
External intercostal
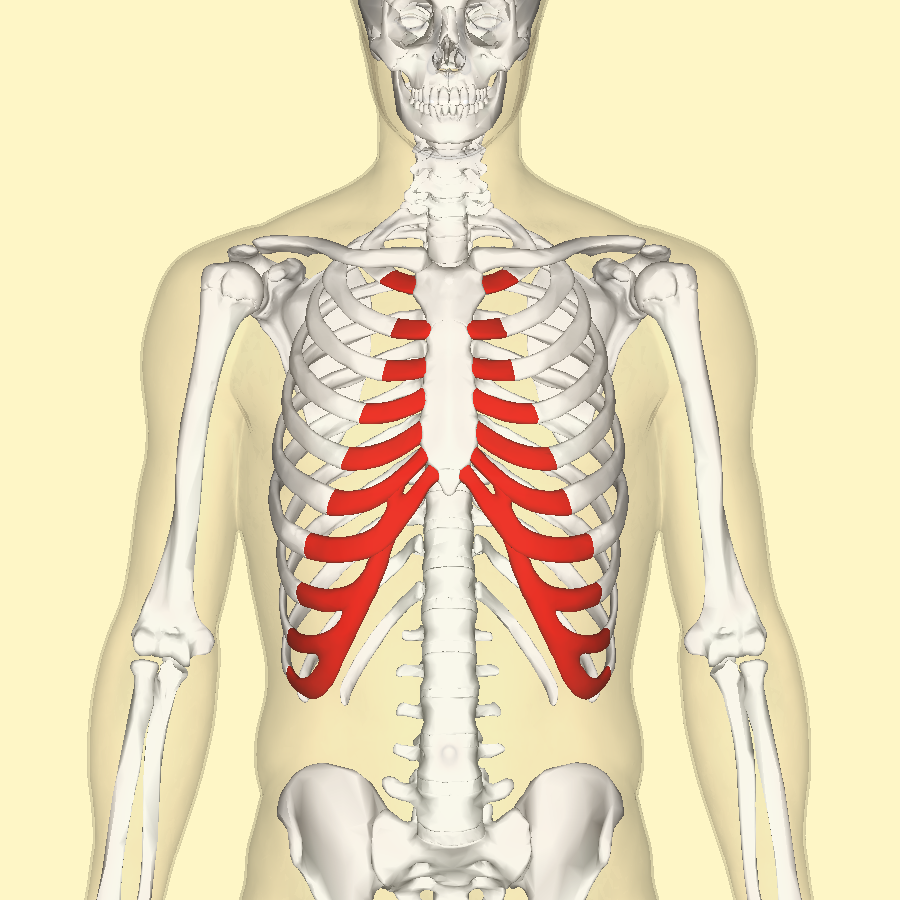
Costal cartilages/chondral portion of rib cage
Located at bottom of chart of diaphragm
Point of attachment to L4 and L5 vertebrae
Located at top middle of diaphragm
Sternal attachment of the diaphragm
Opening in middle of diaphragm
Esophageal hiatus
What’s the posterior-most attachment of the diaphragm?
Lumbar vertebrae, L4 and L5