9B1 - Cells (AQA Biology GCSE)
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
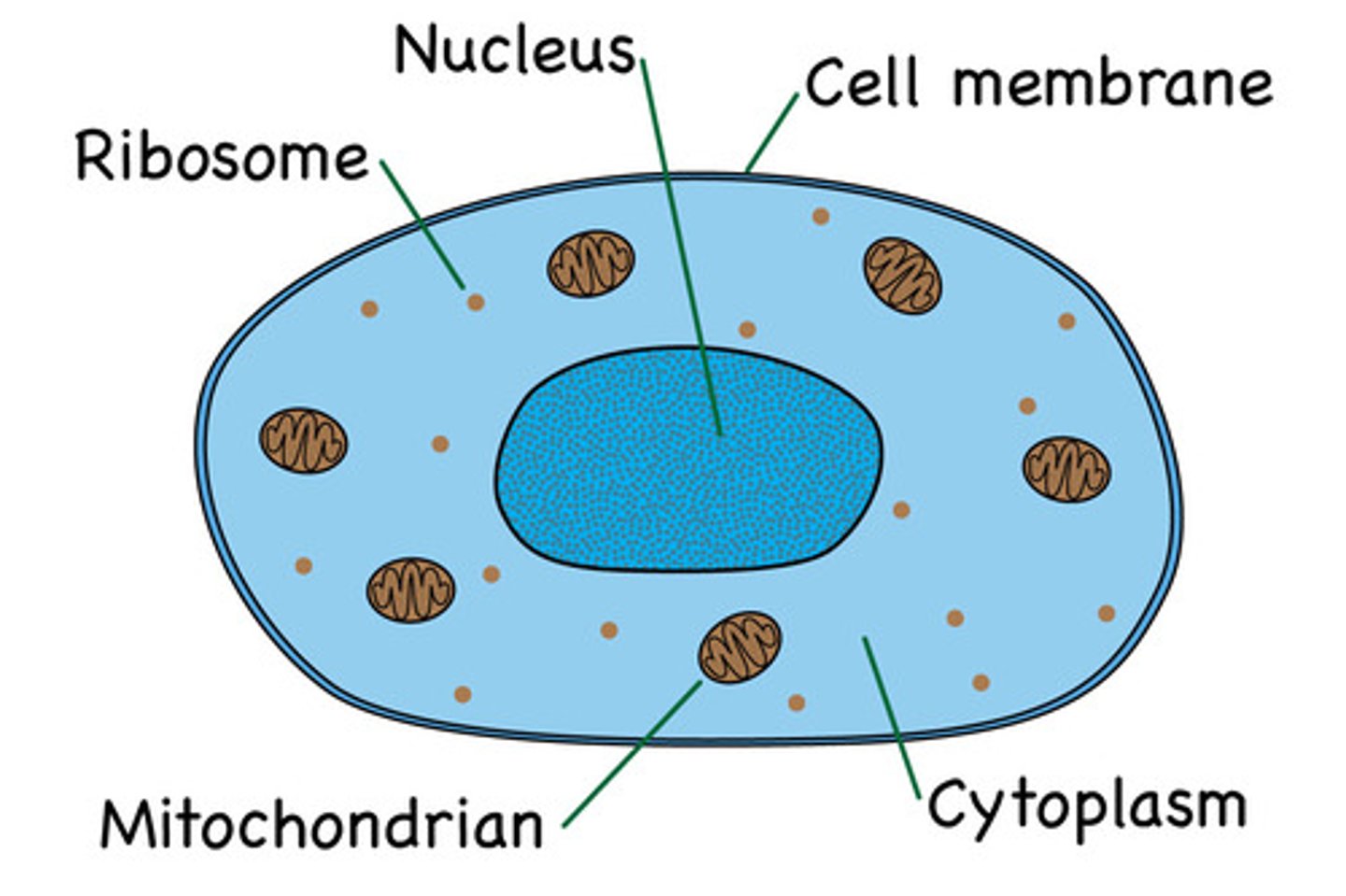
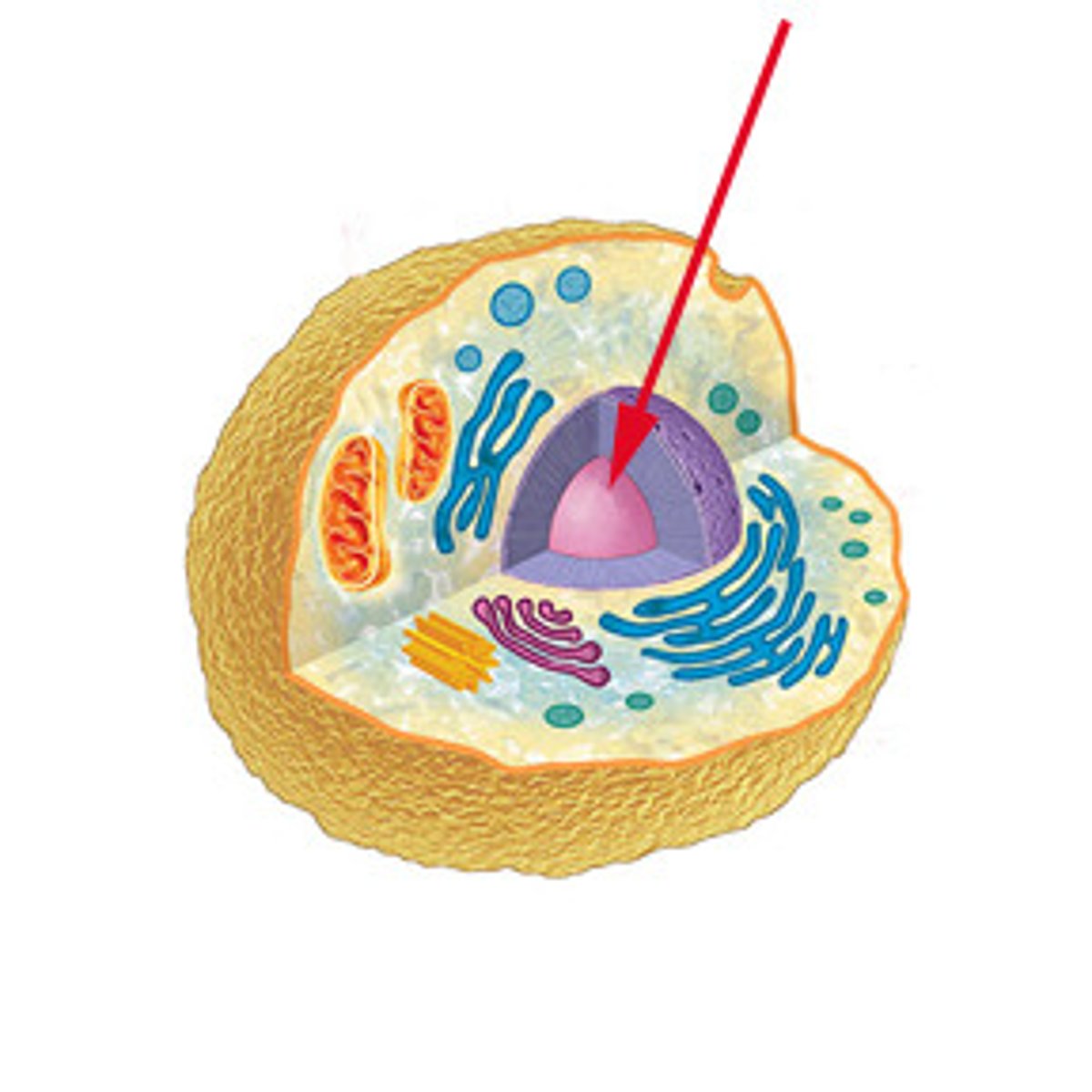
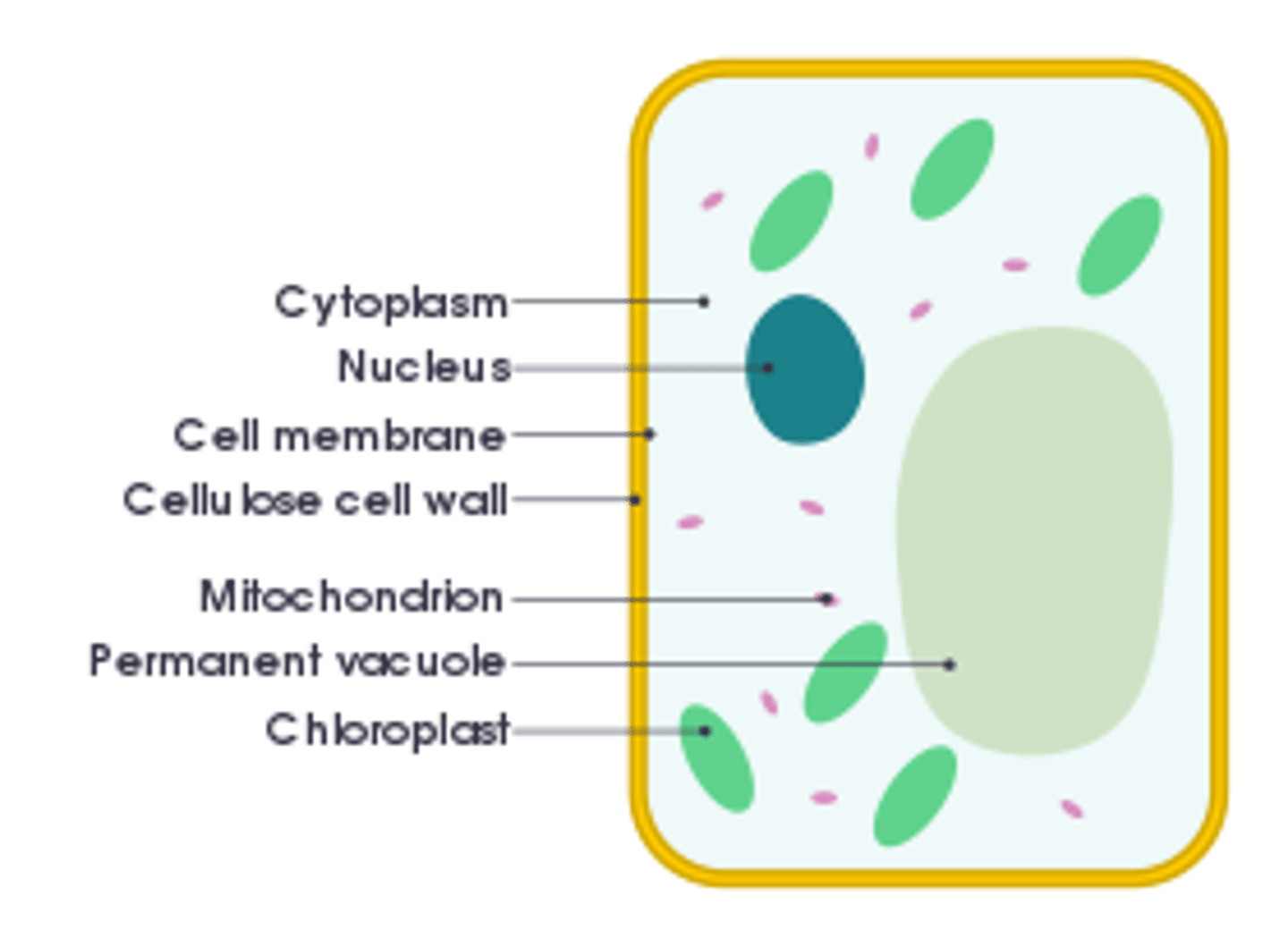
Nucleus
Control centre of the cell
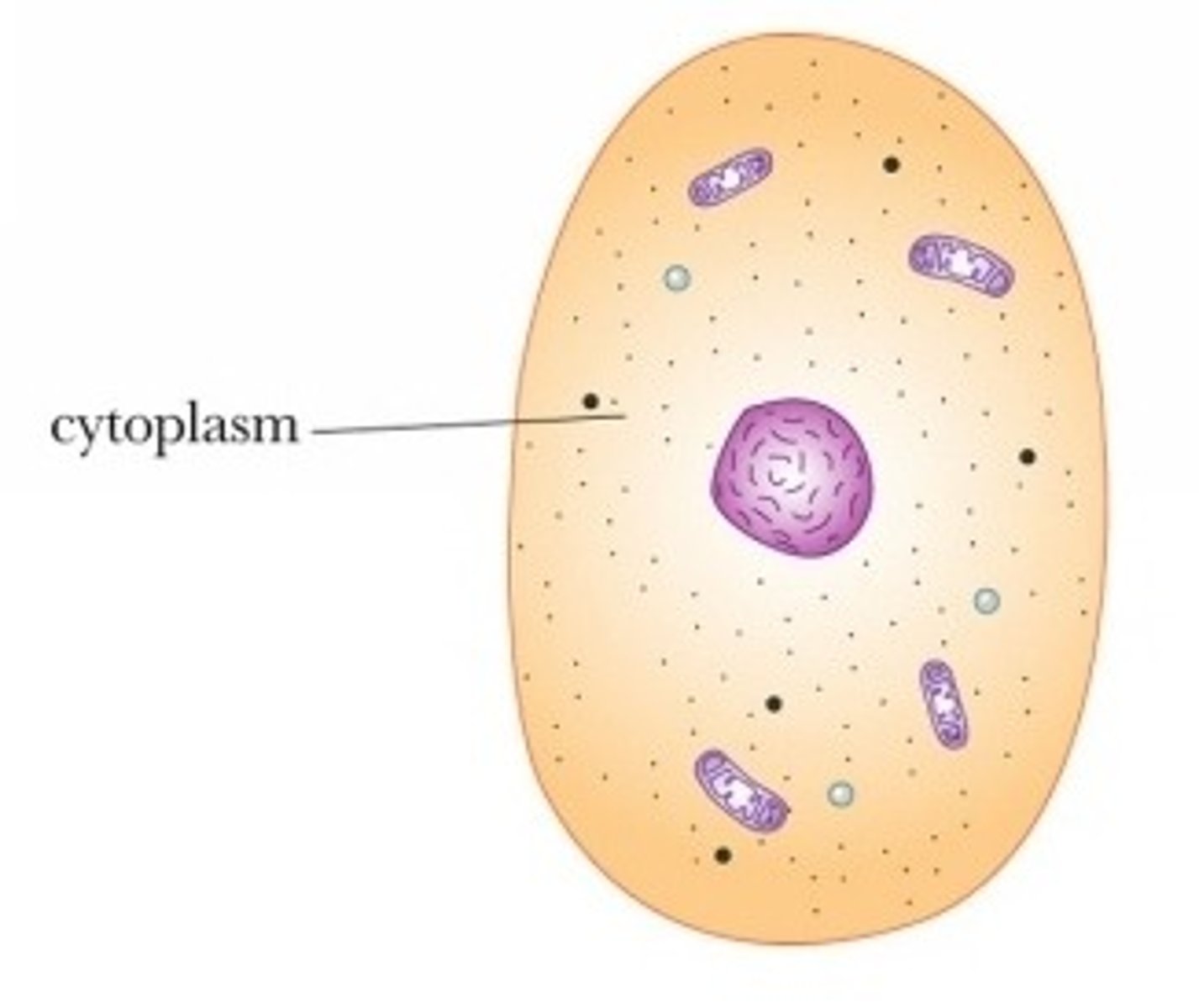
Cytoplasm
Jelly-like substance the cell organelles float in and where reactions occur
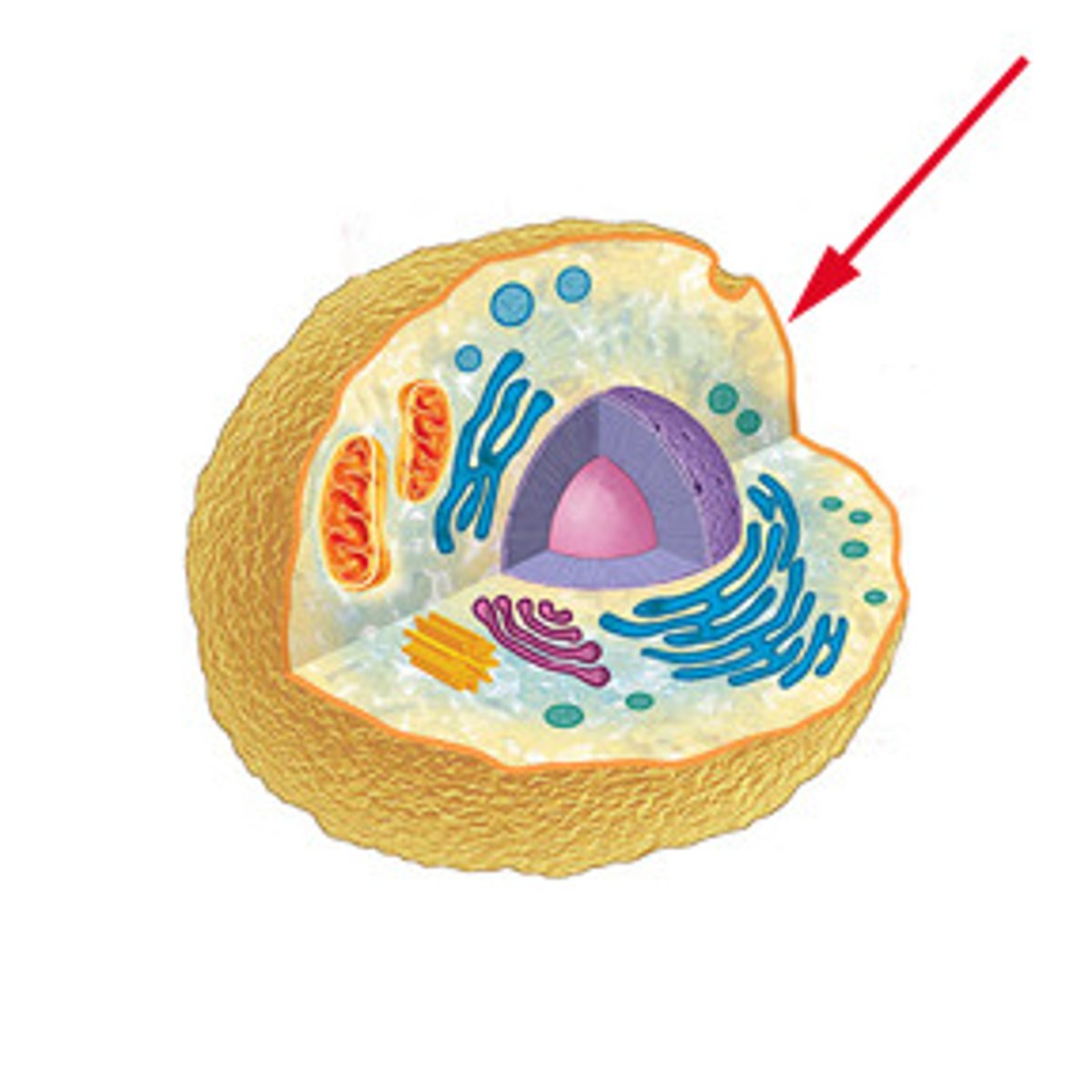
Cell membrane
A cell structure that controls which substances can enter or leave the cell.
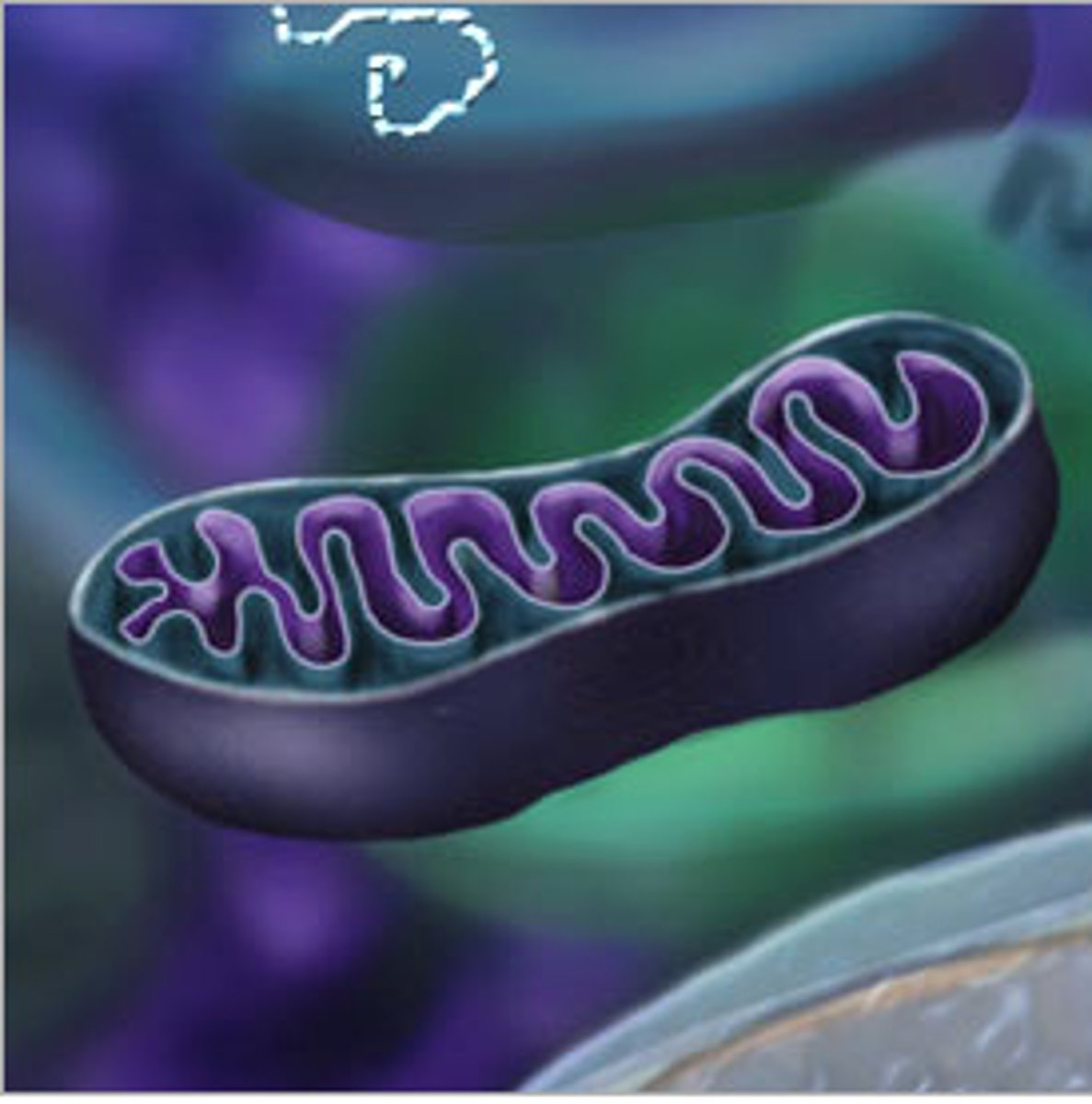
Mitochondria
Where respiration takes place
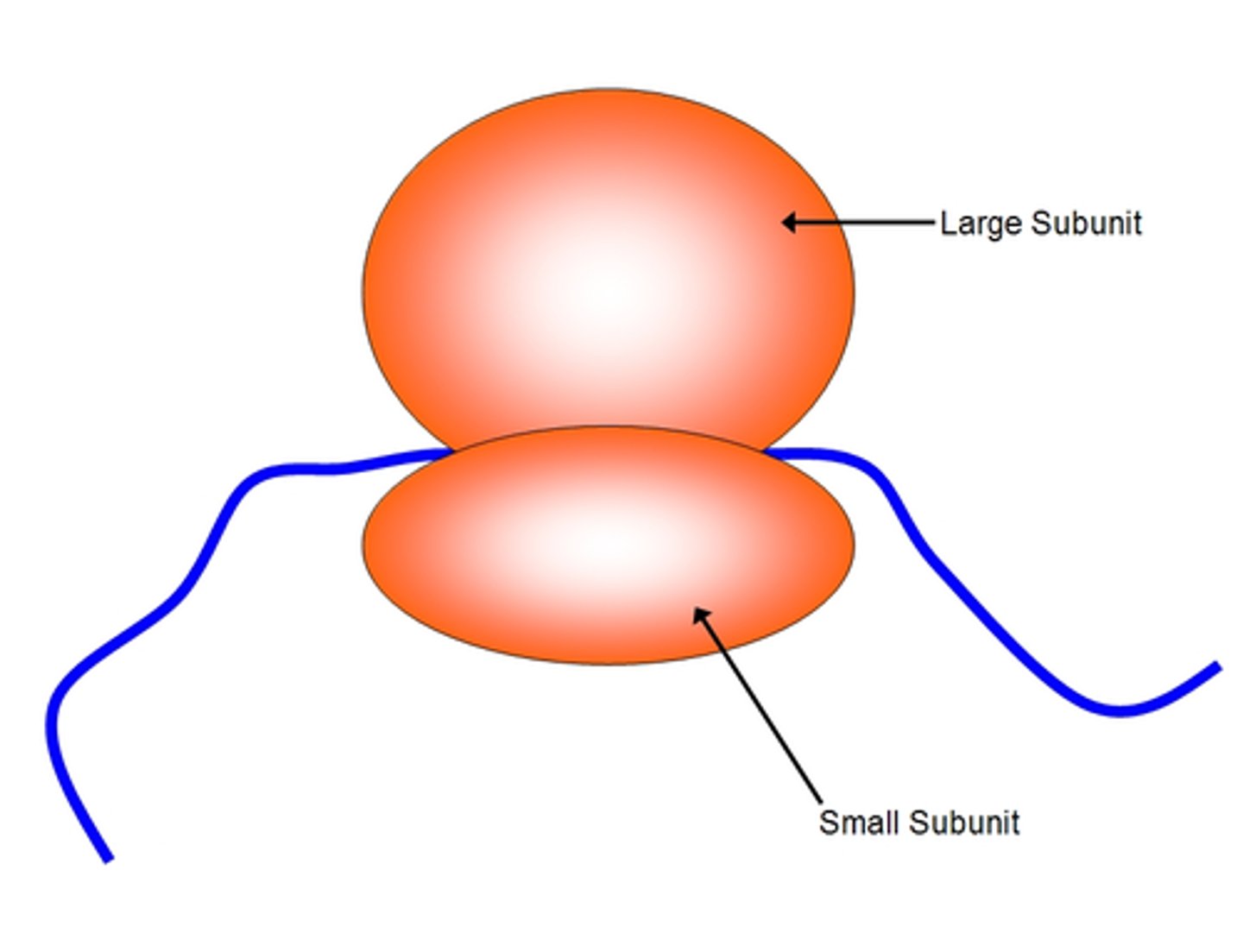
Ribosomes
Makes proteins
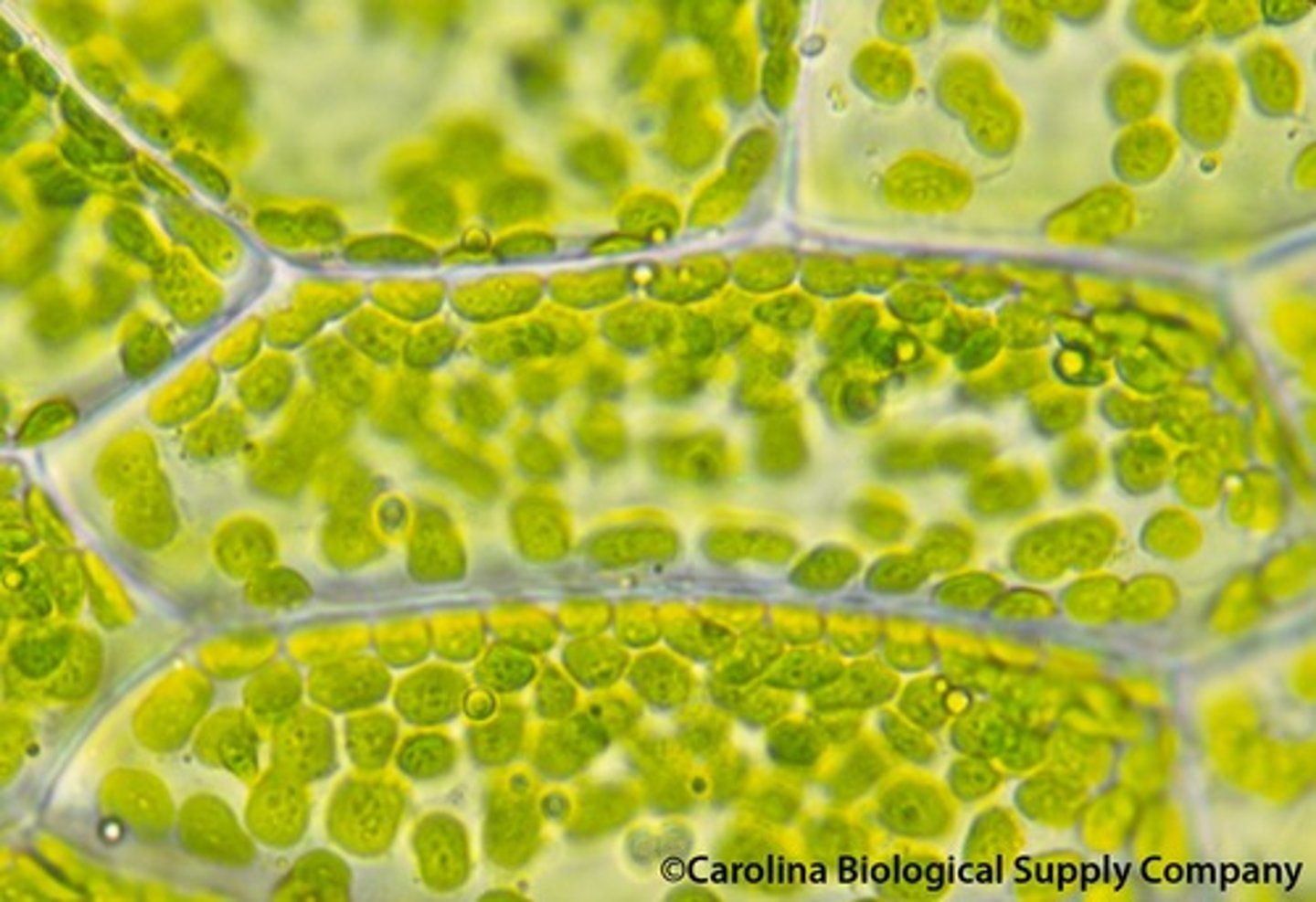
Chloroplast
An organelle found in plant and algae cells where photosynthesis occurs
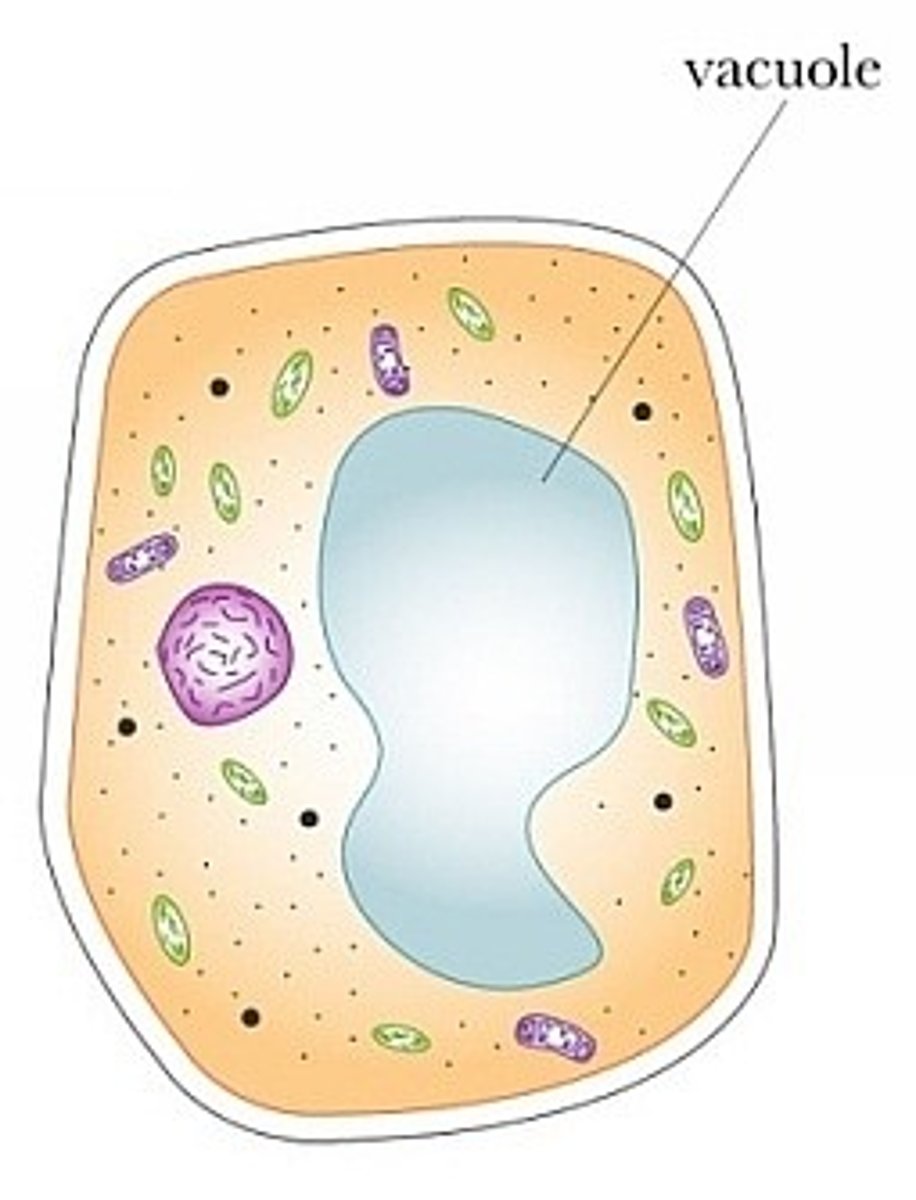
Vacuole
Plant cell organelle that stores cell sap
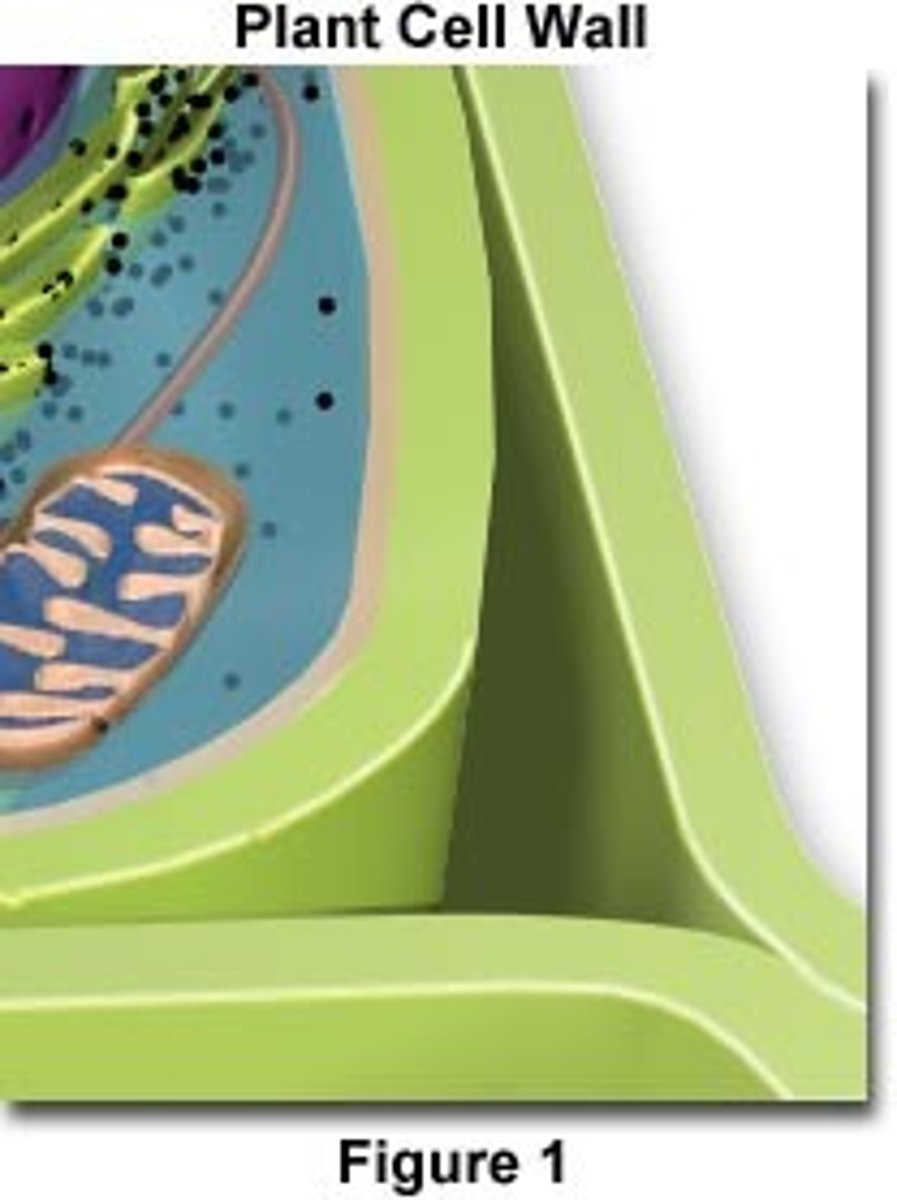
Plant cell wall
Strong, protective structure made from cellulose
Eukaryotic cells
Contain a nucleus and other organelles that are bound by membranes.
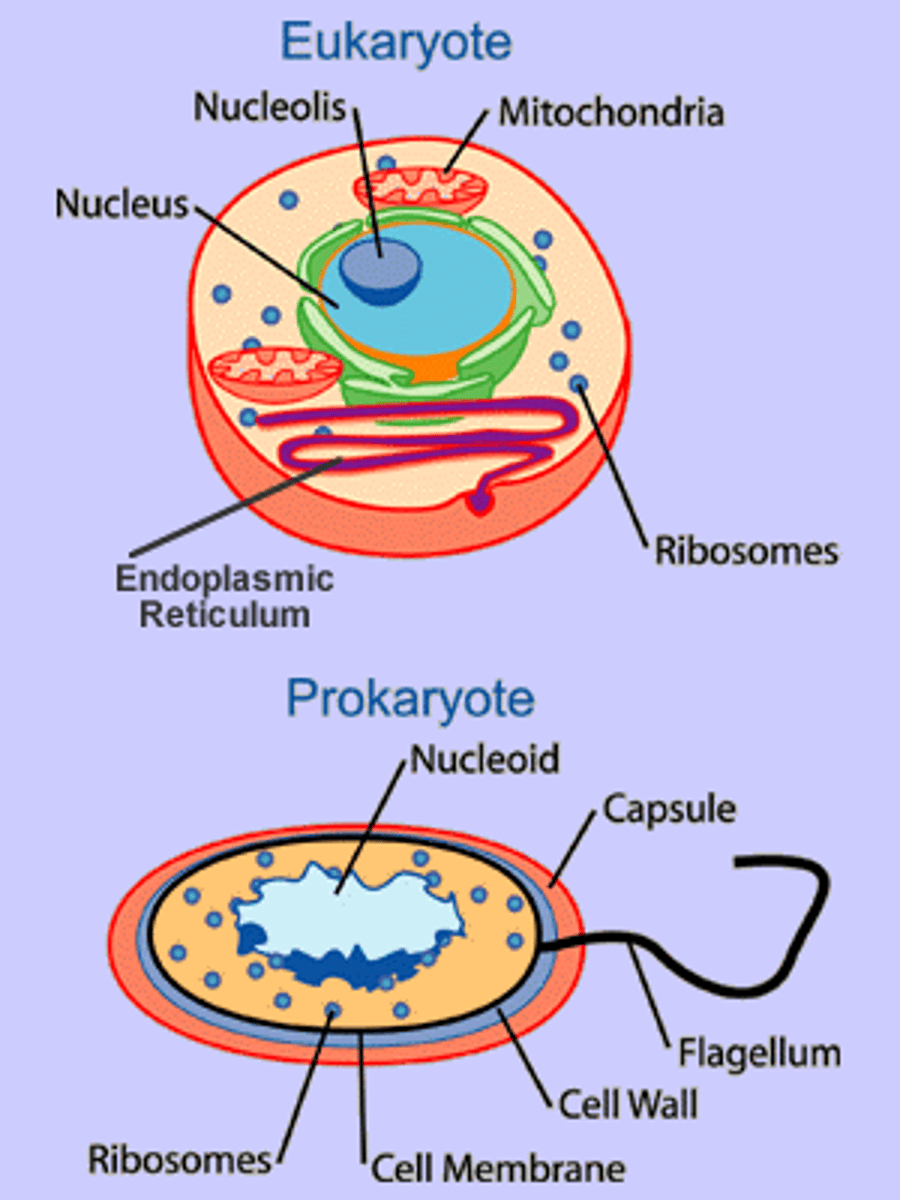
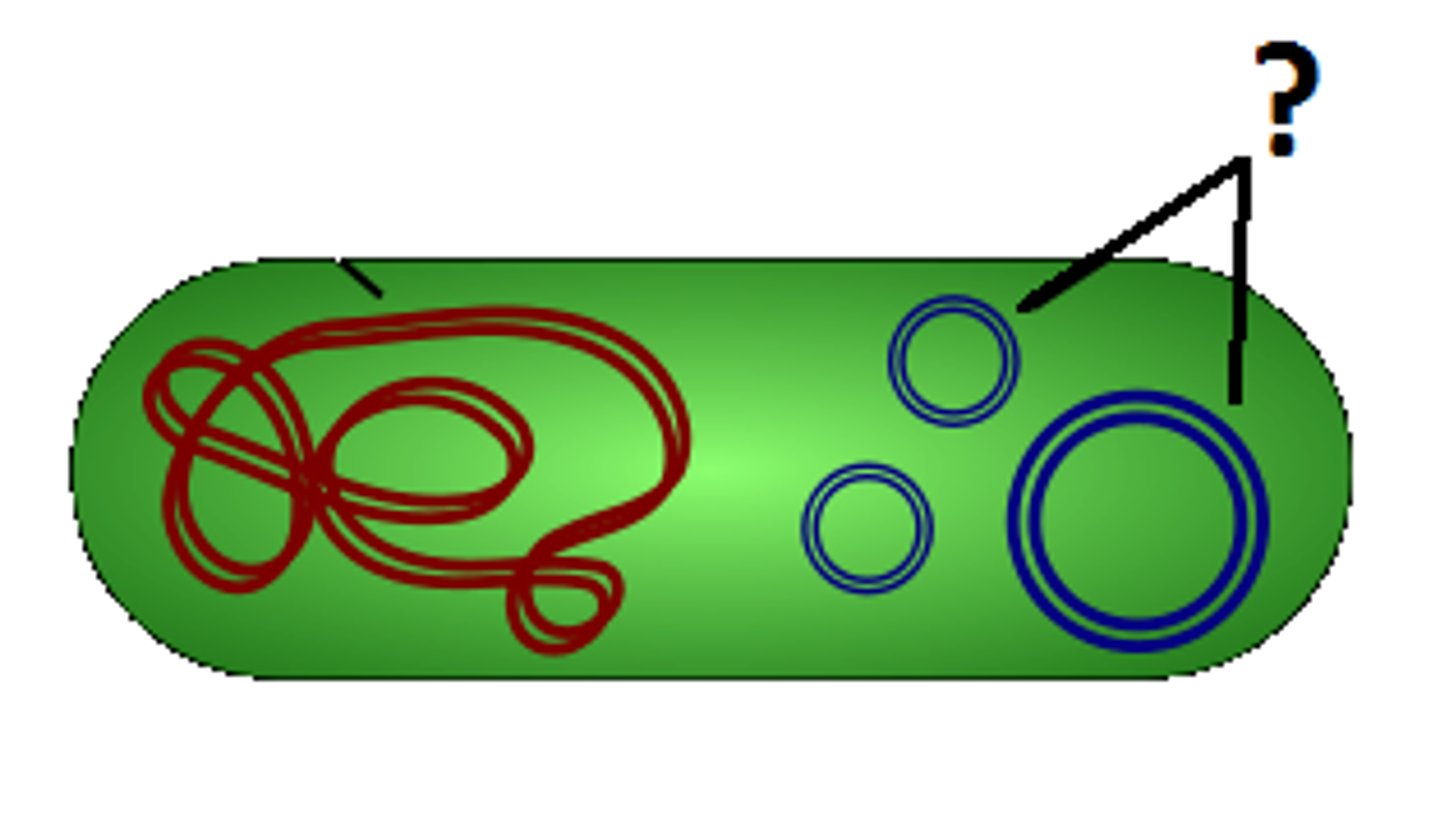
Prokaryotic cell
Cell that does not have a nucleus or other membrane-bound organelles.
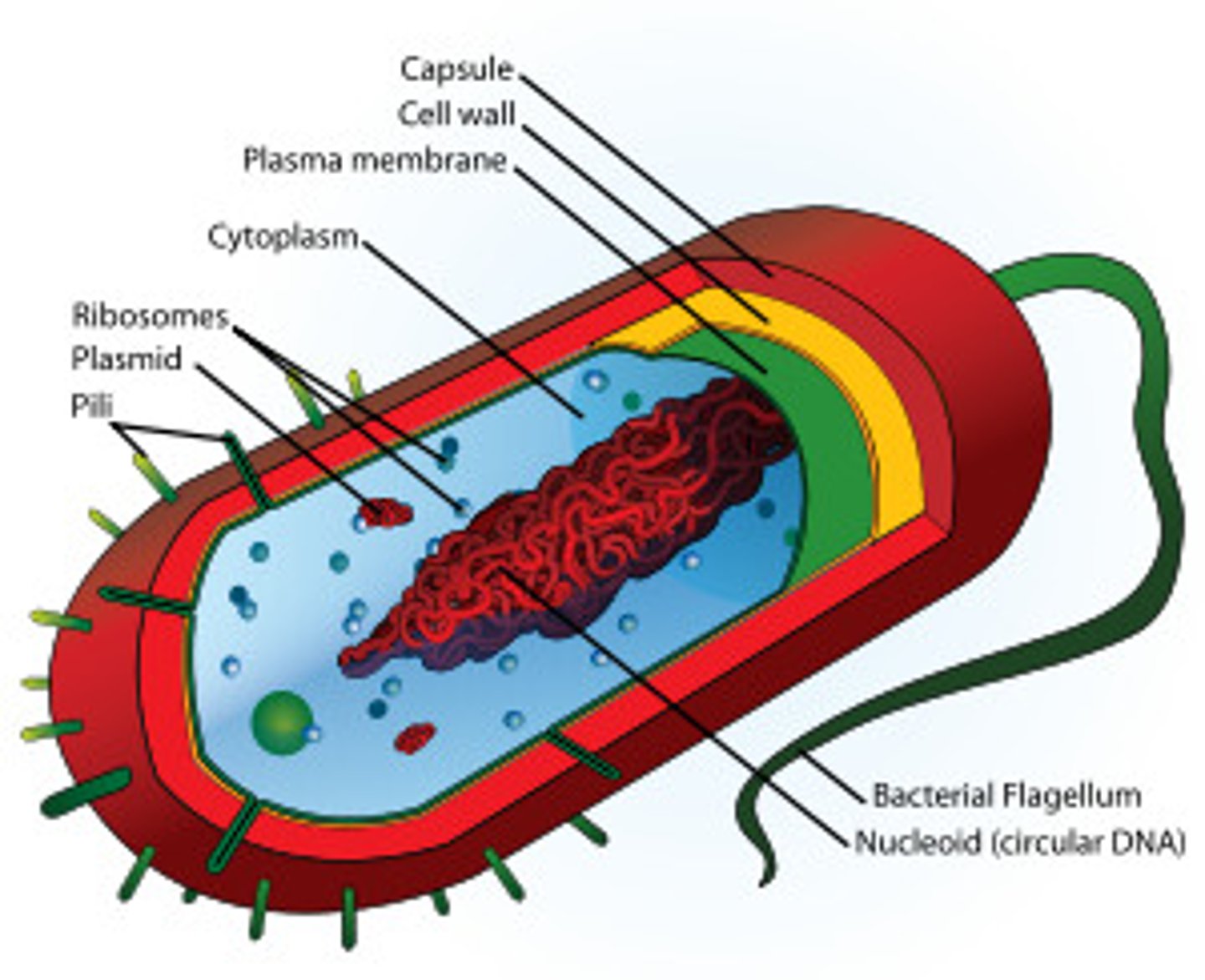
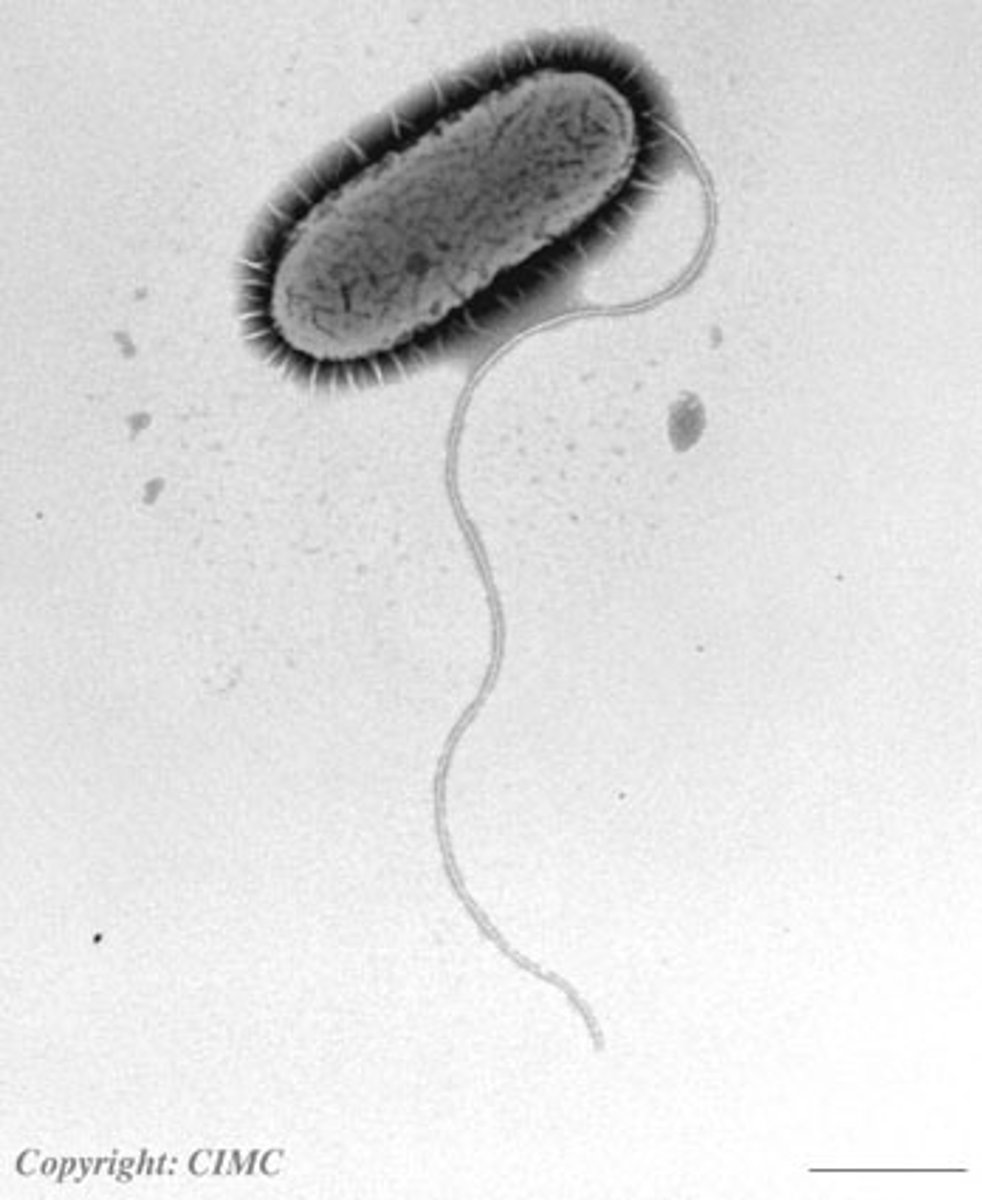
Flagellum
A long, hairlike structure that grows out of a cell and enables the cell to move.
Plasmid
Small, circular piece of DNA located in the cytoplasm of many bacteria
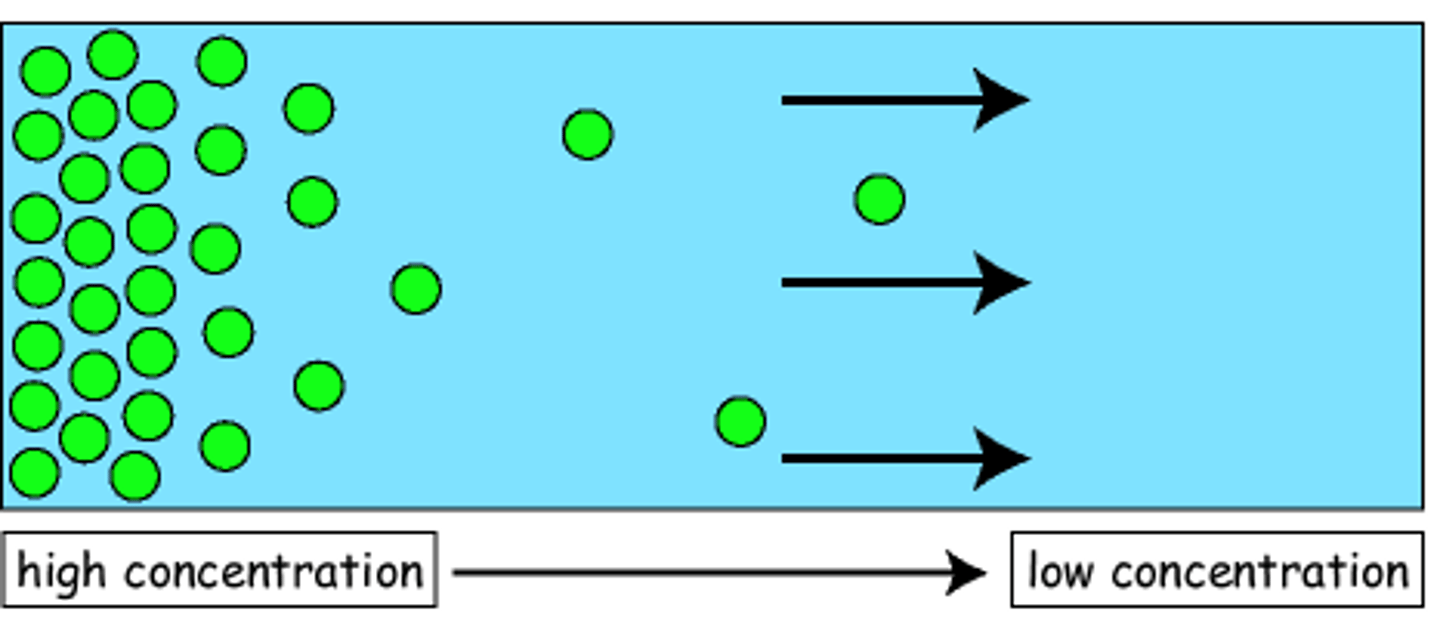
Diffusion
Movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration.
Organelle
A tiny cell structure that carries out a specific function within the cell
Cell
The basic unit of structure and function in living things
Tissue
A group of similar cells that perform the same function.
Organ
A collection of tissues that carry out a specialised function of the body
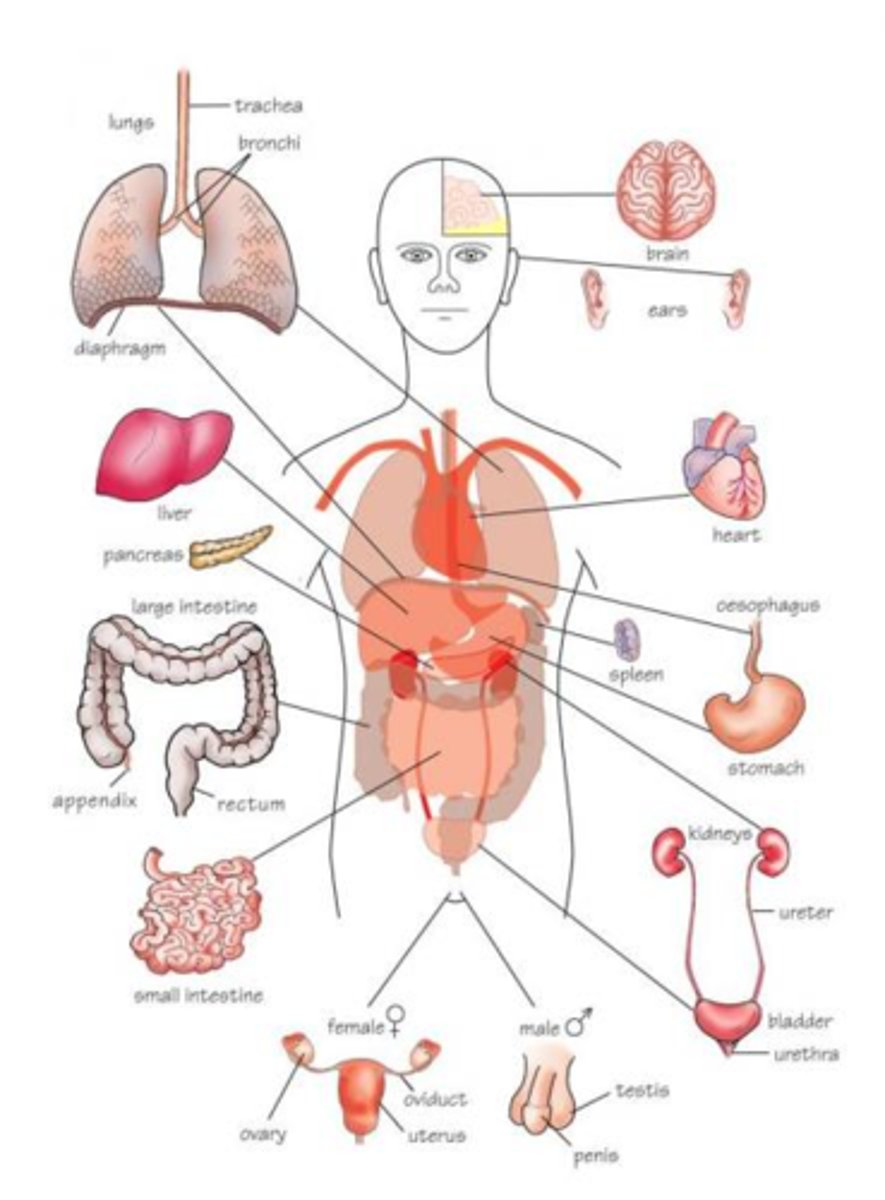
Organ System
Group of organs that work together to perform a specific function
Organism
A living thing
Magnification
An increase in the apparent size of an object

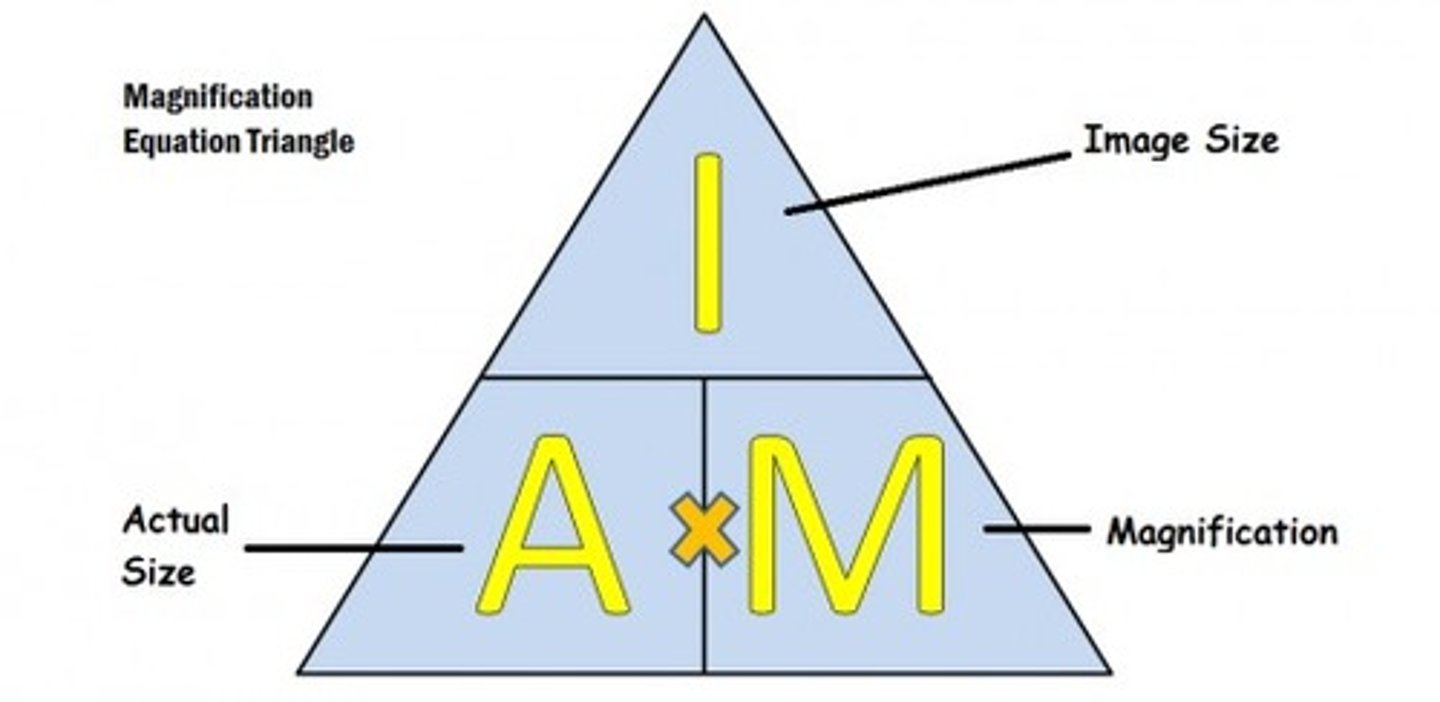
Magnification equation
Image size/actual size
Resolution
The ability to clearly distinguish the individual parts of an object
Eyepiece lens
Contains a lens that magnifies about 10x
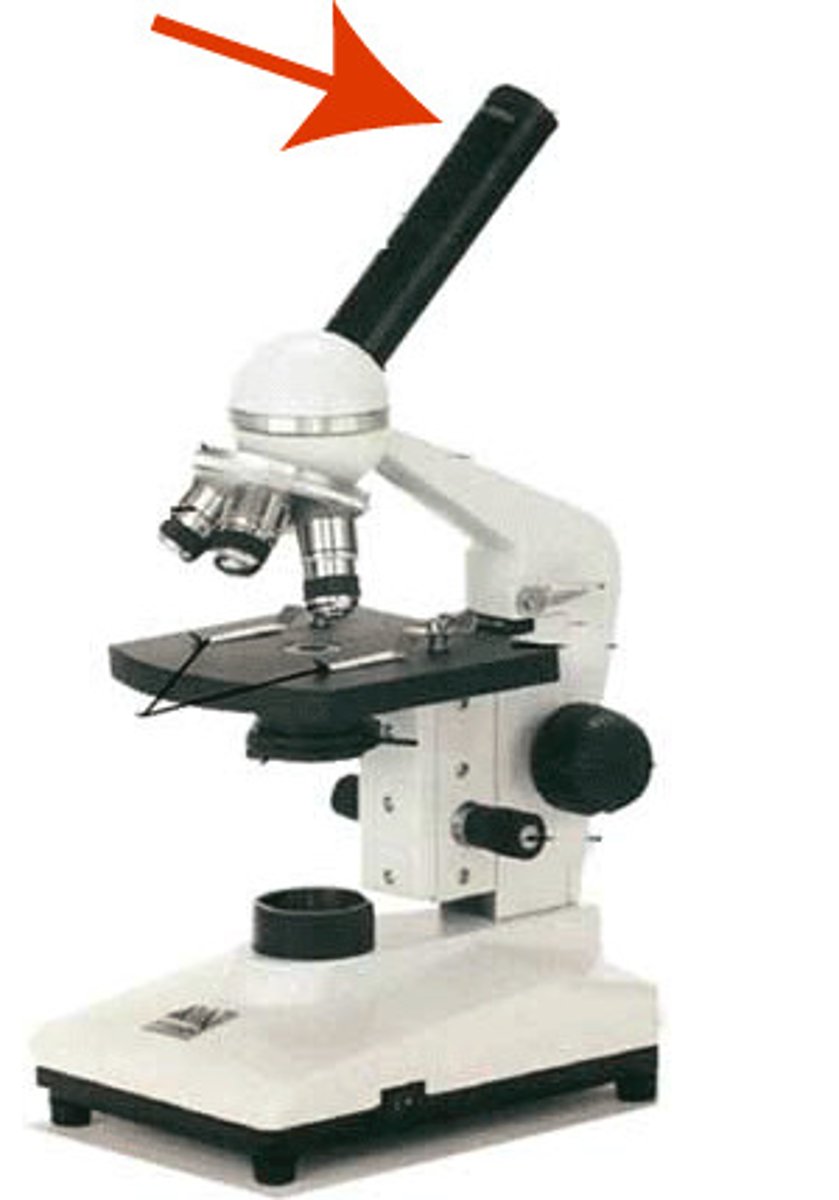
Objective lens
The lens on a light microscope that is closest to the stage.

Microscope stage
Supports the slide being viewed

Microscope staining
A method used to clearly show the organelles in a cell, usually done with an indicator like Iodine
Microscope specimen
Something viewed with a microscope
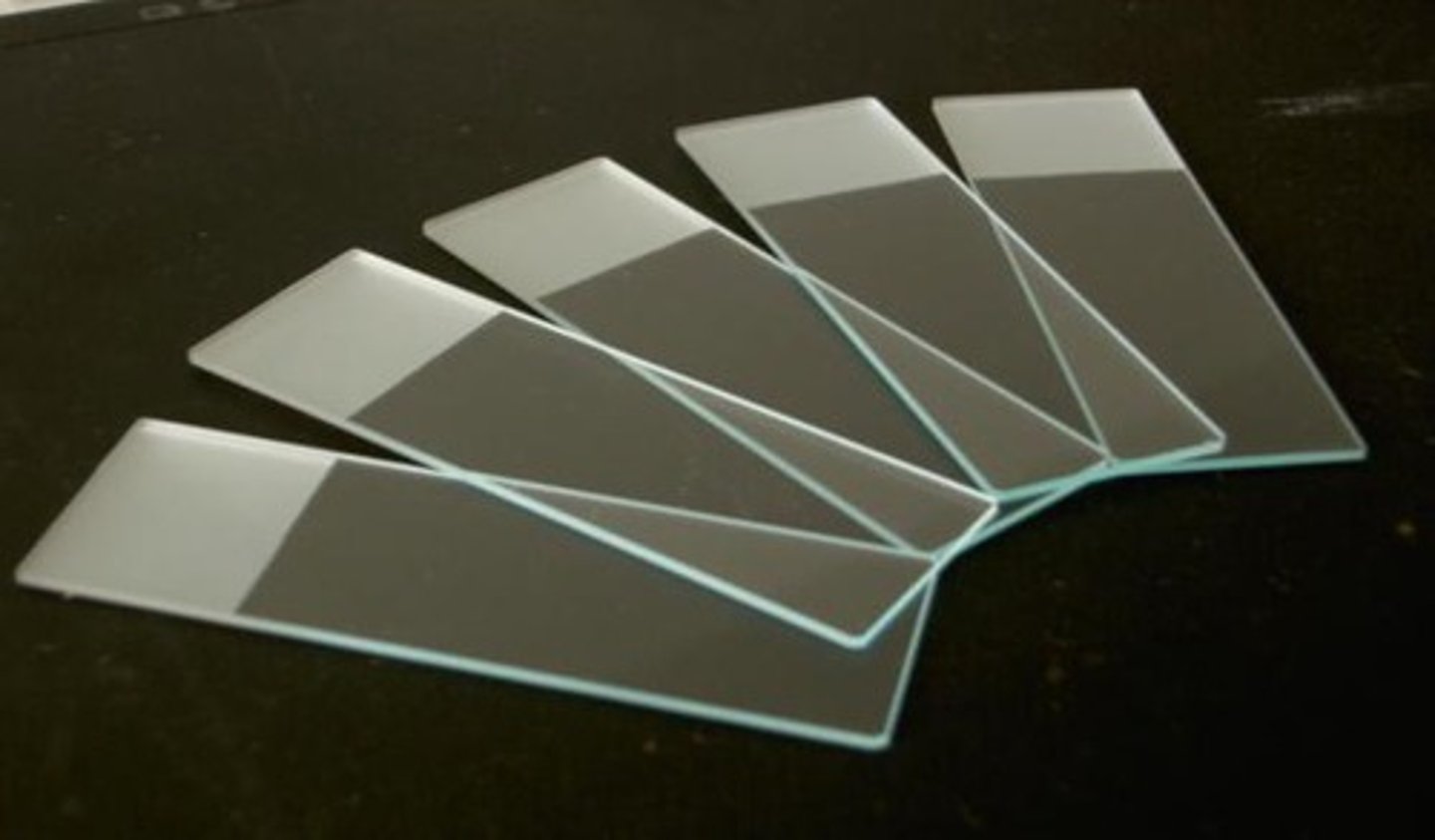
Light microscope
Light passes through one or more lenses to produce an enlarged image of a specimen

Electron microscope
Microscope that forms an image by focusing beams of electrons onto a specimen

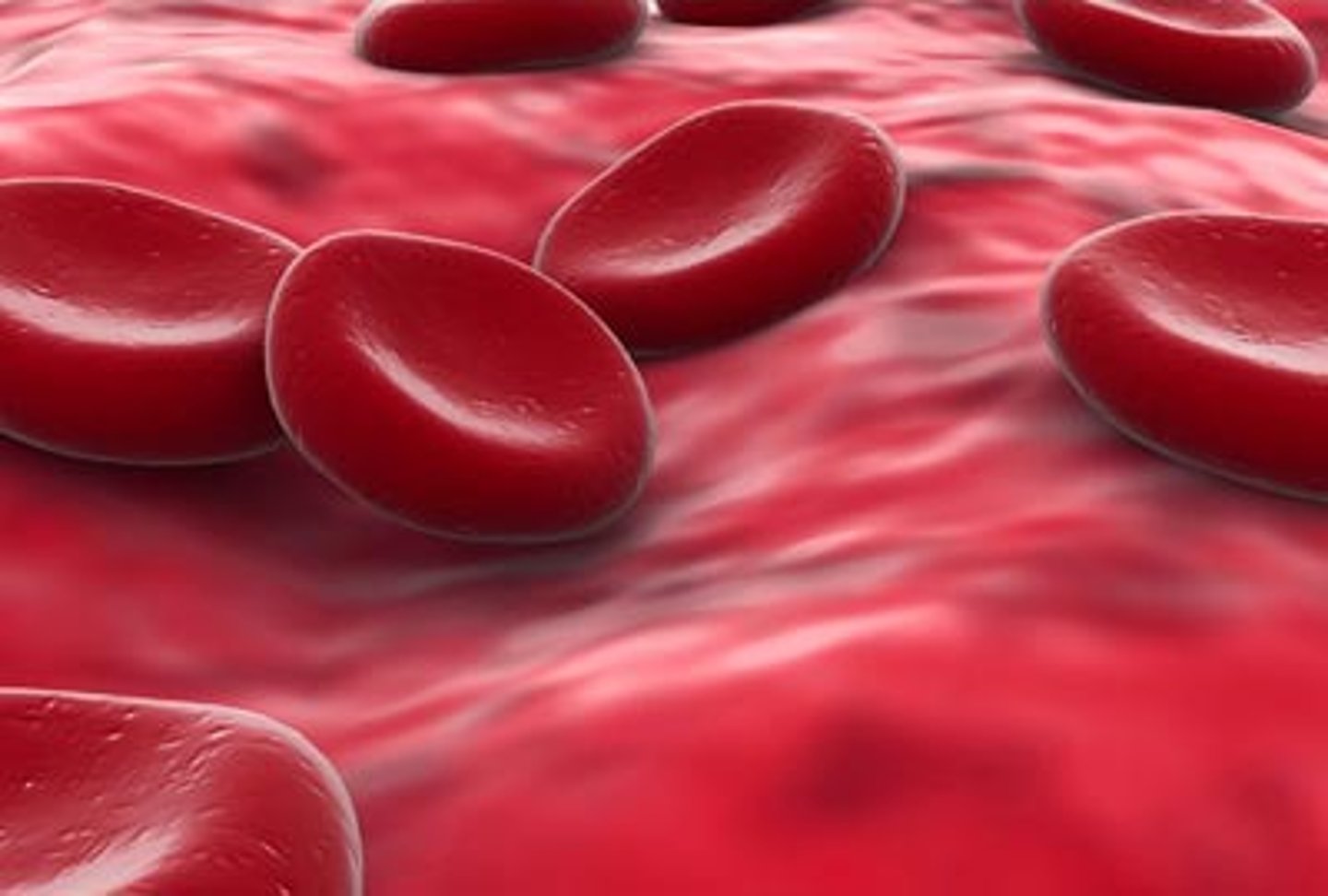
Red blood cells
Blood cells that carry oxygen from the lungs to the body cells.
Sperm Cell
Male reproductive cell
Root hair cell
Absorbs water and mineral ions from the soil.
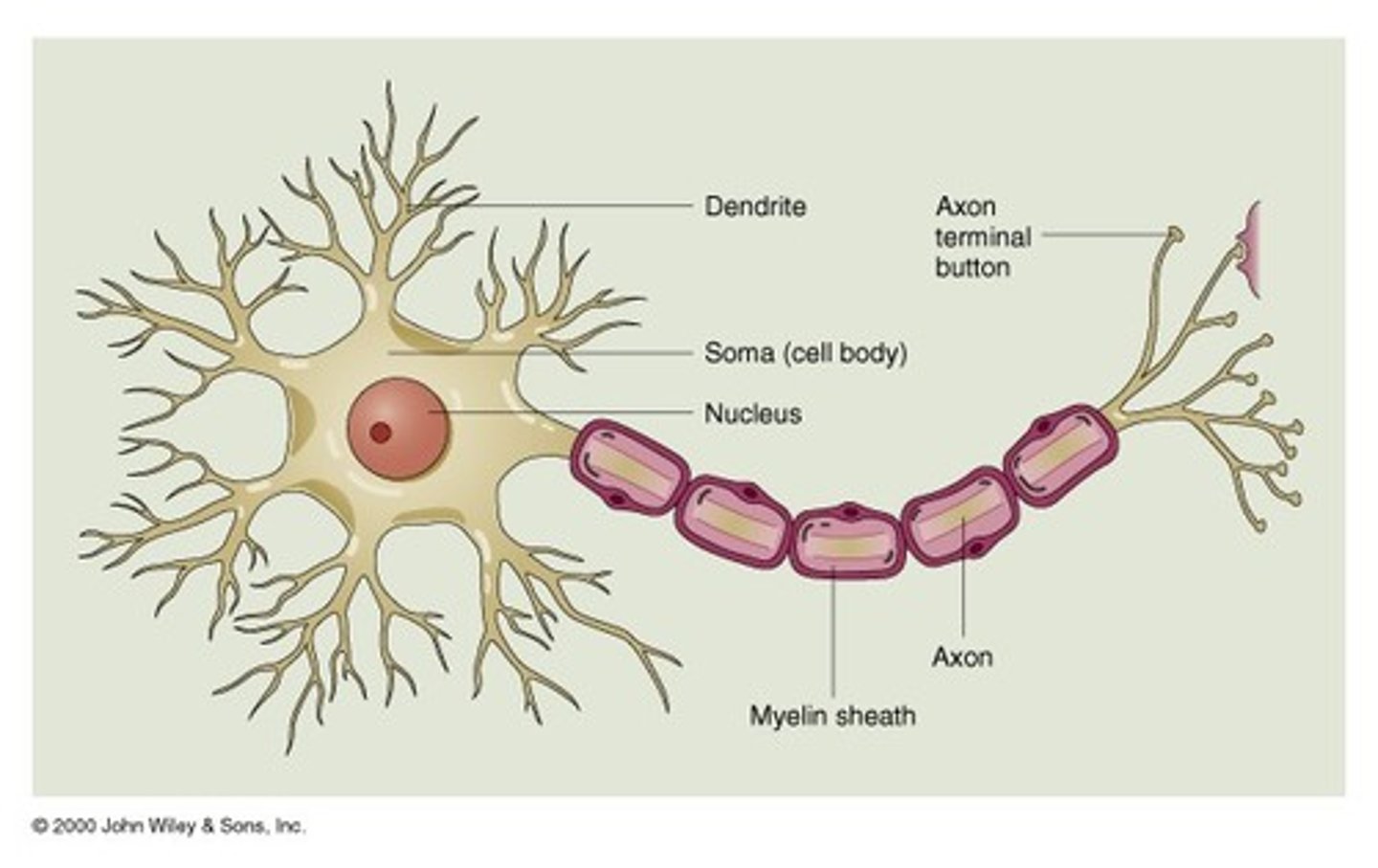
Nerve Cell
Carries electrical messages around the body
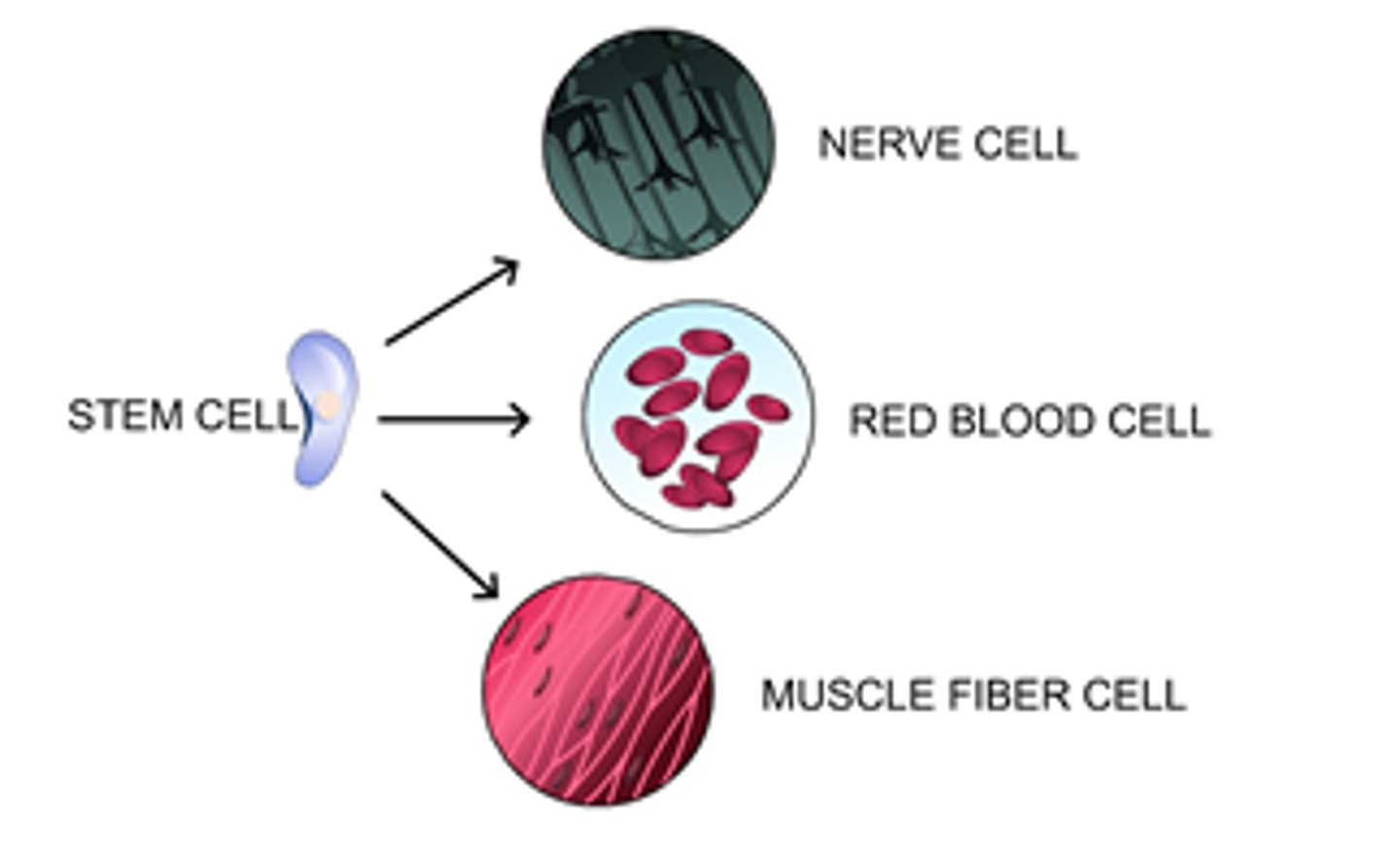
Cell differentiation
The process by which cells become different types of cells
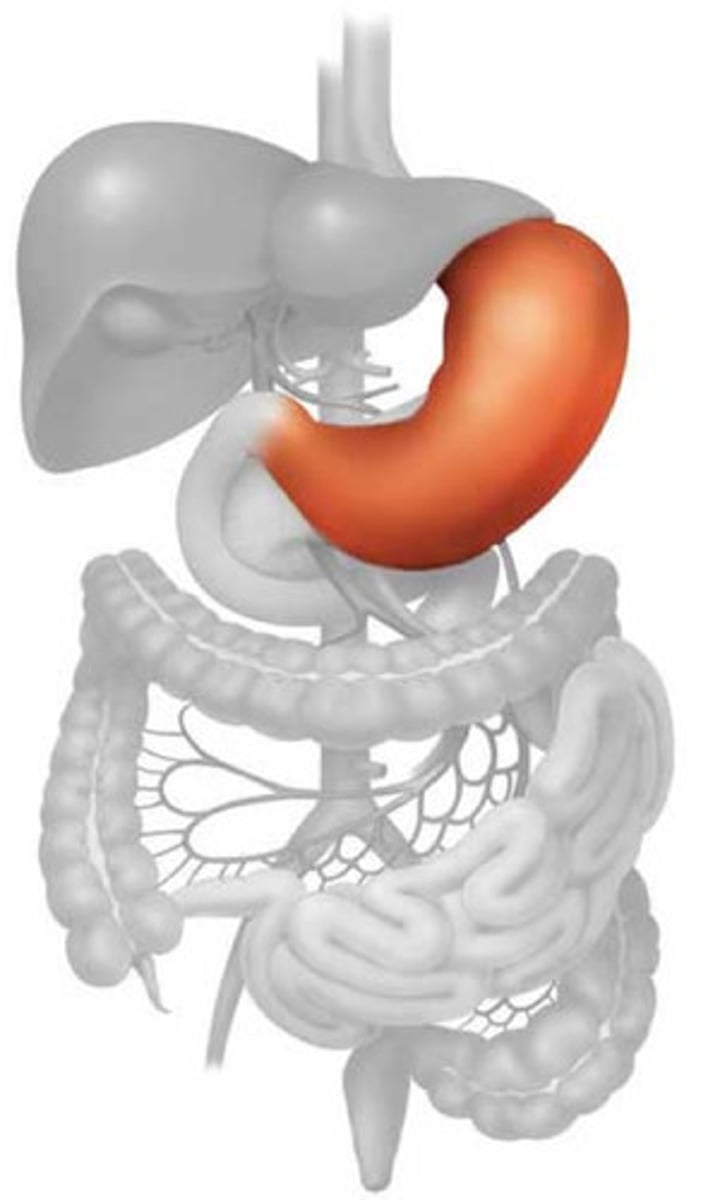
Stomach
Organ of the digestive system
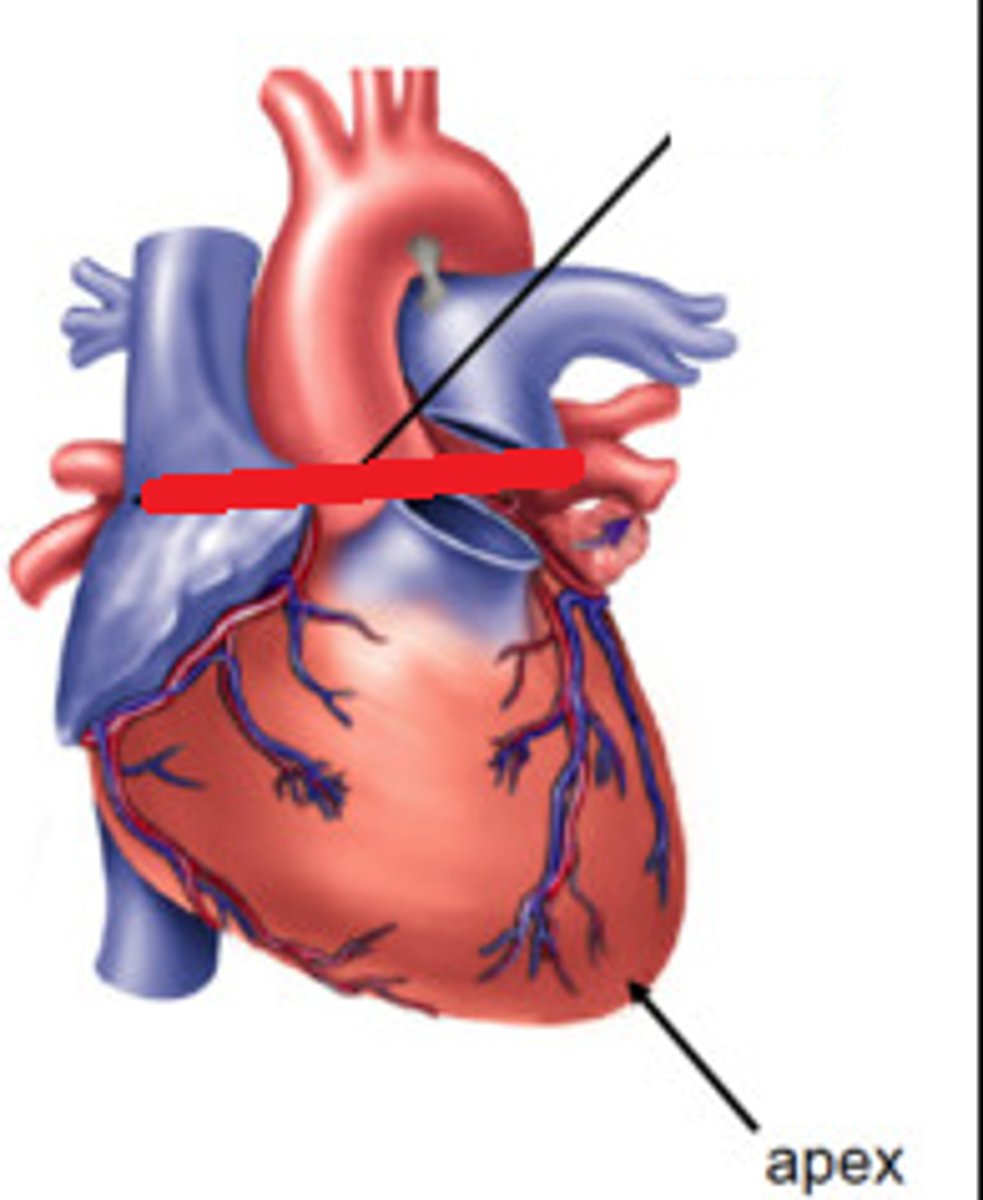
Heart
Organ that pumps blood throughout the body
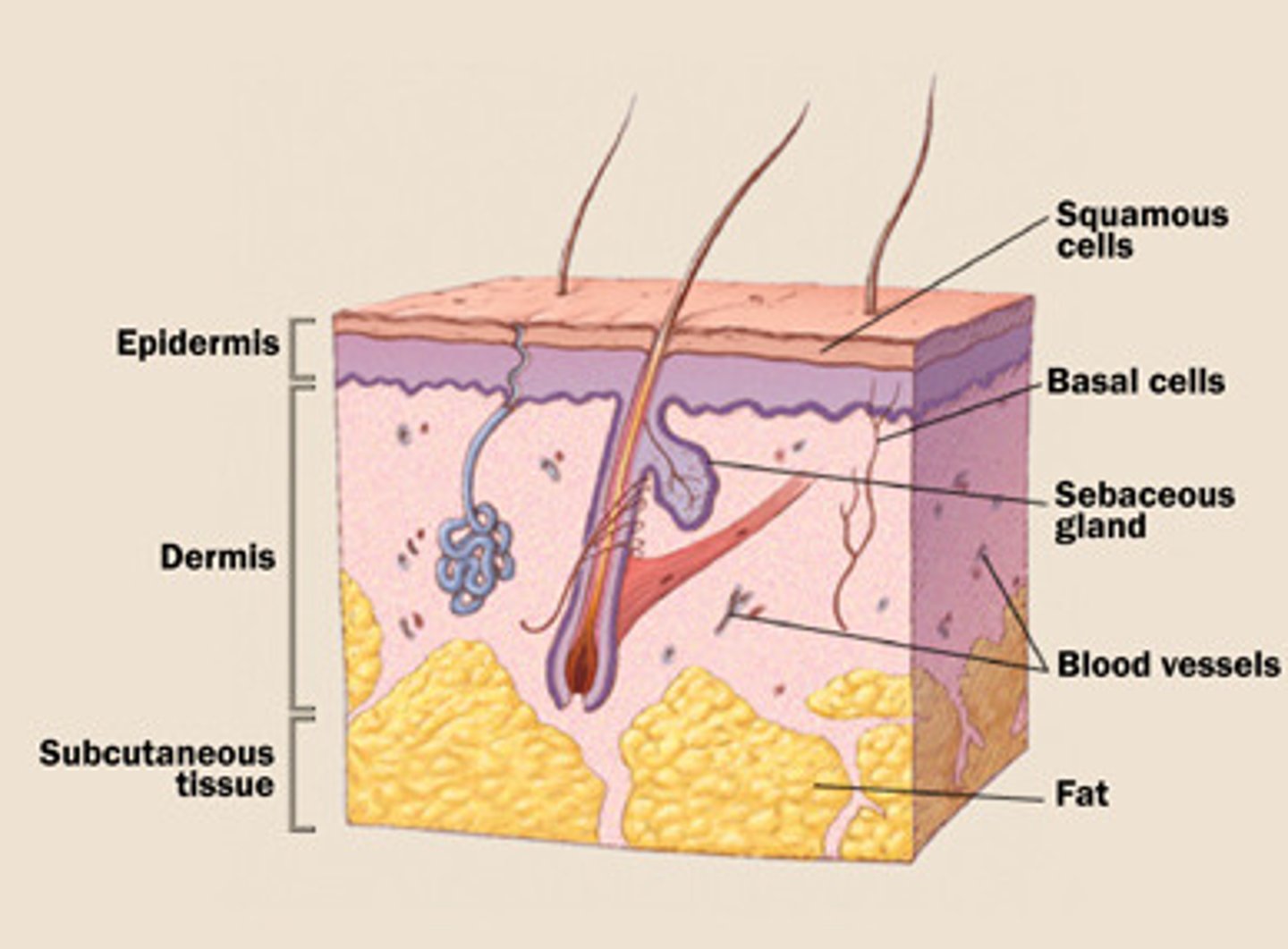
Skin
Largest organ of the body
Nervous System
Body system that sends messages
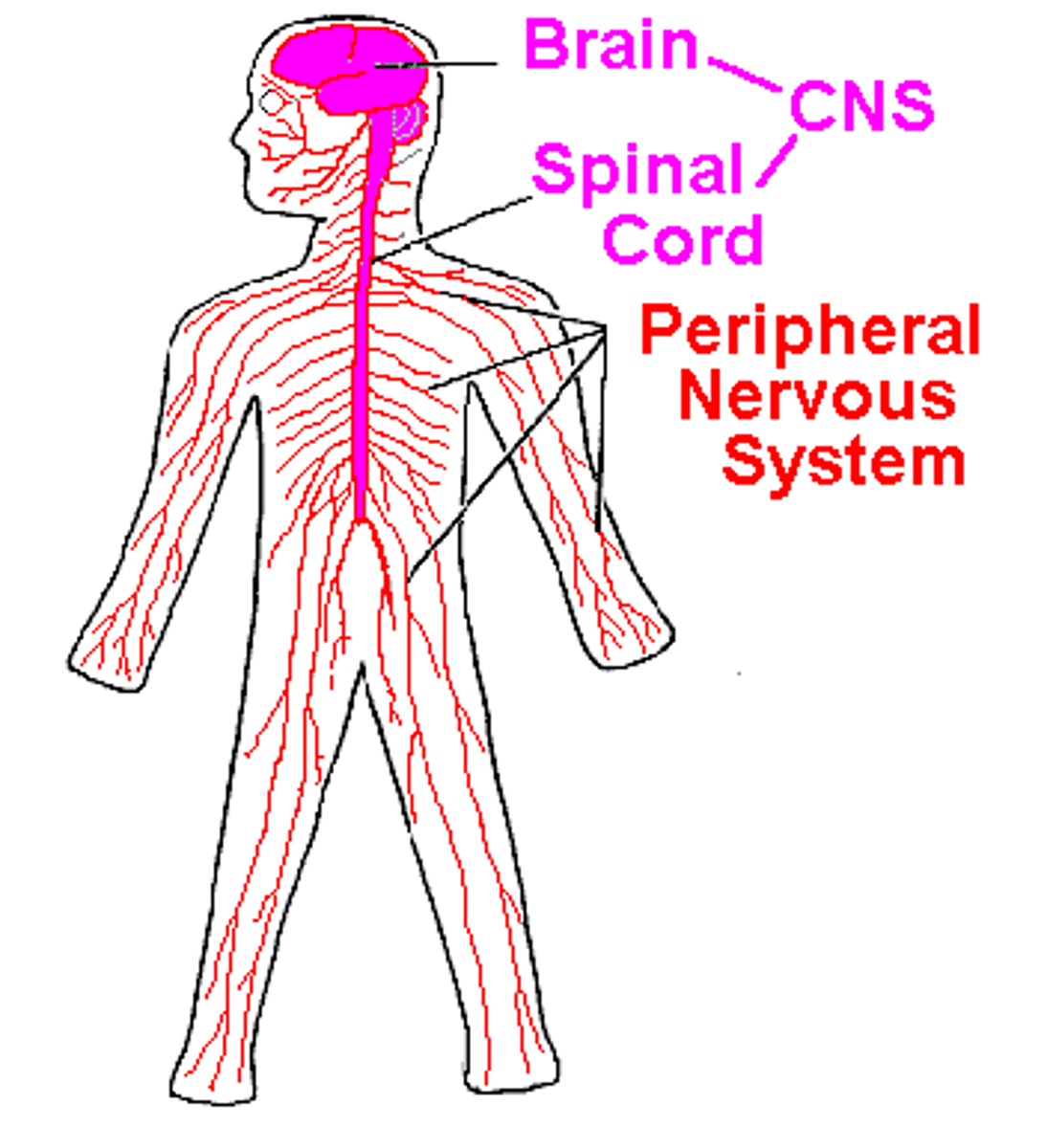
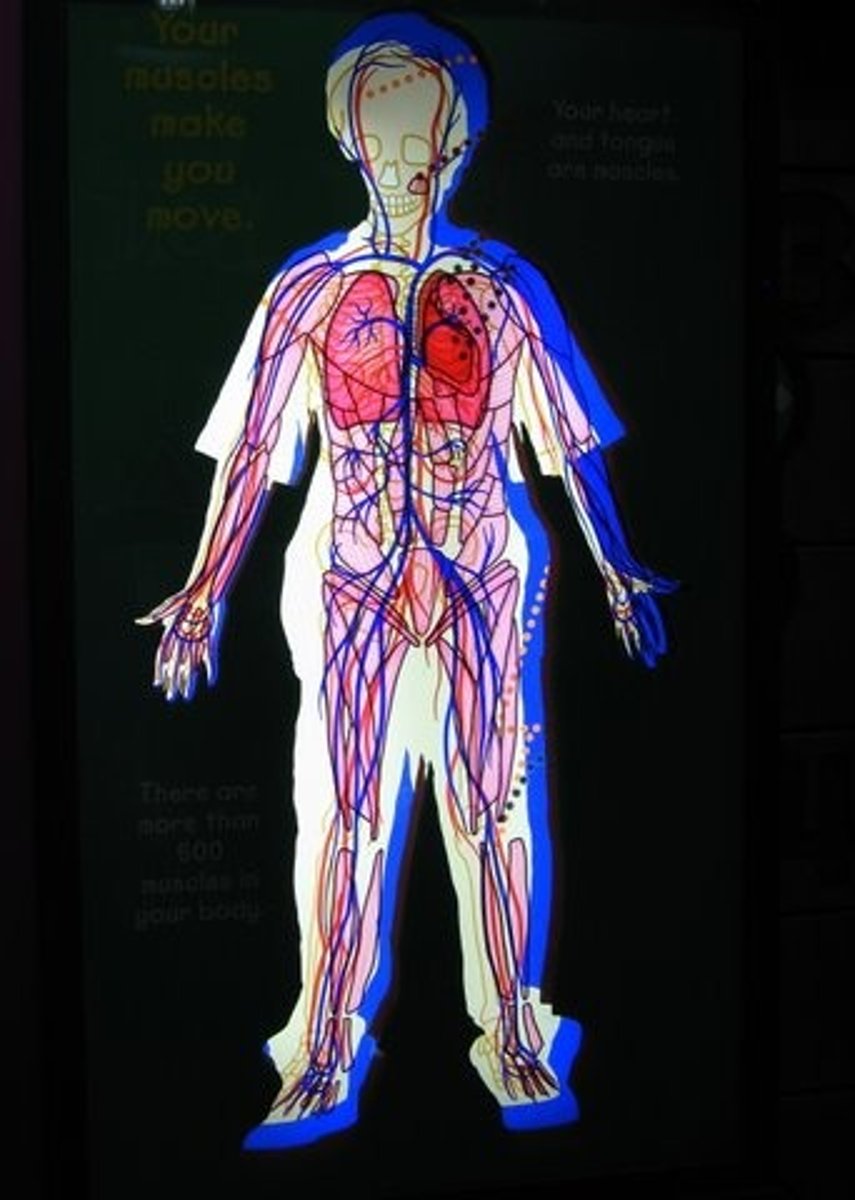
Circulatory system
Body system transporting oxygen and glucose
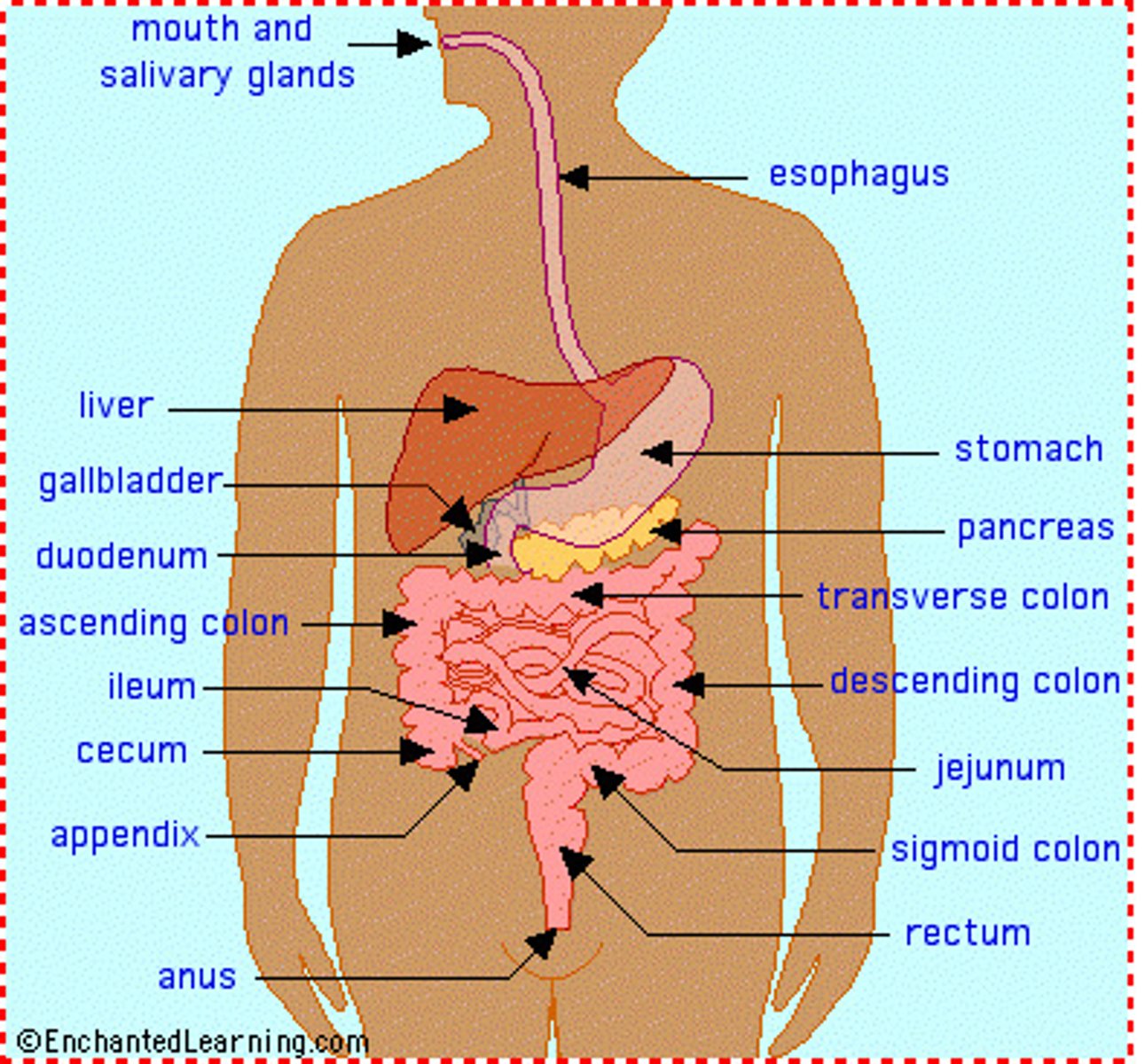
Digestive System
Group of organs that digest food
Leaf
A plant organ
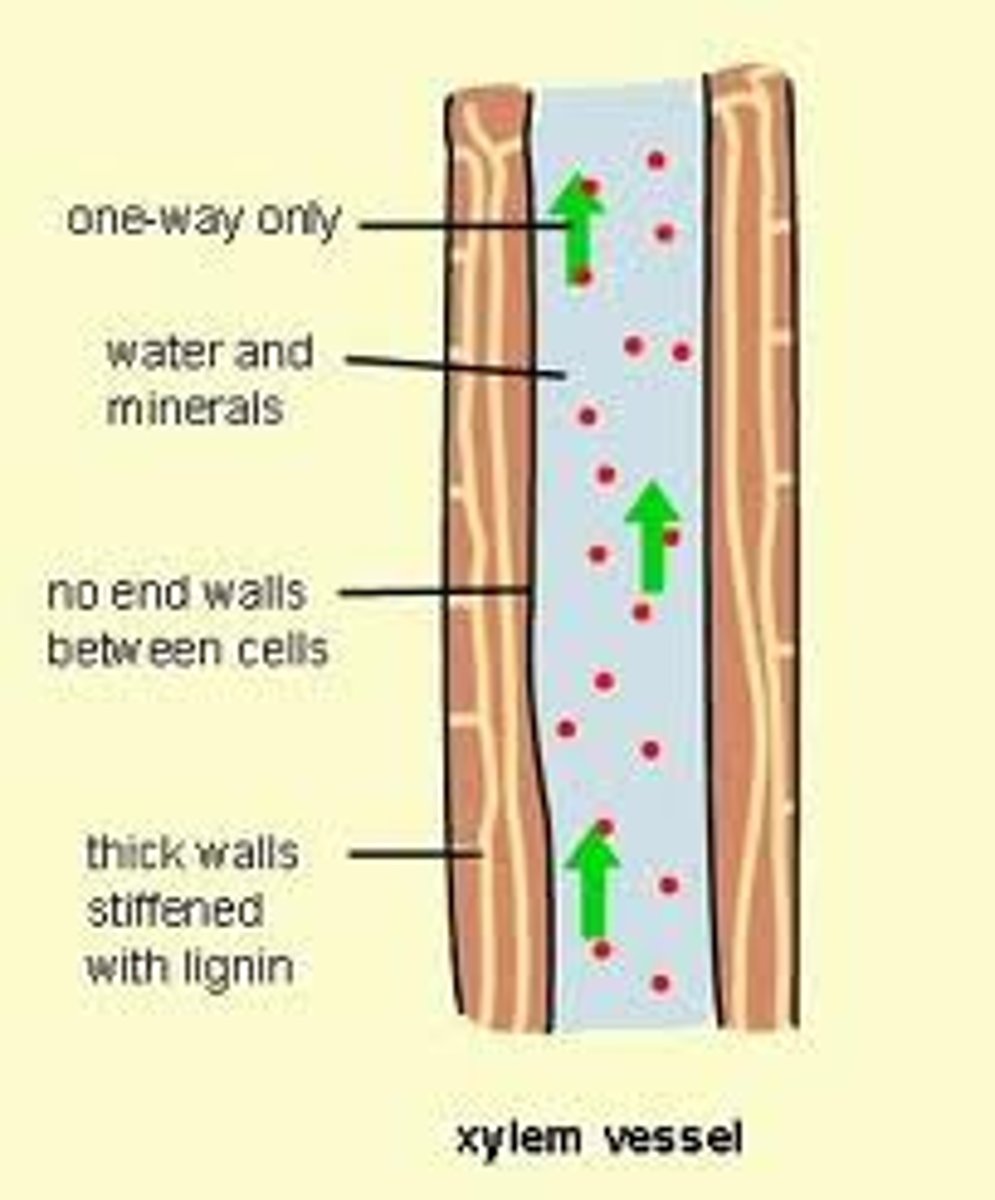
Xylem
A plant tissue carrying water
Phloem
A plant system carrying sugars
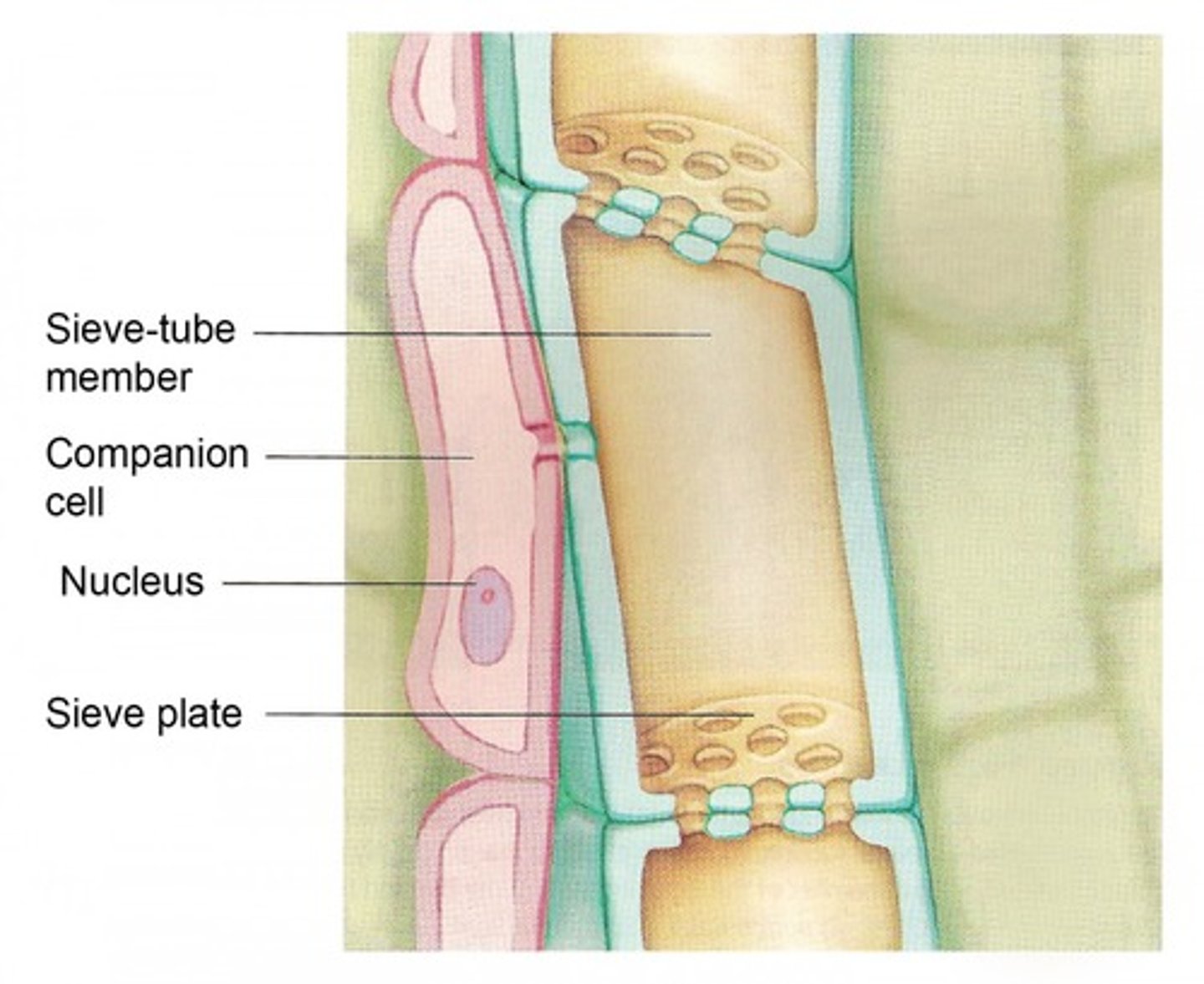
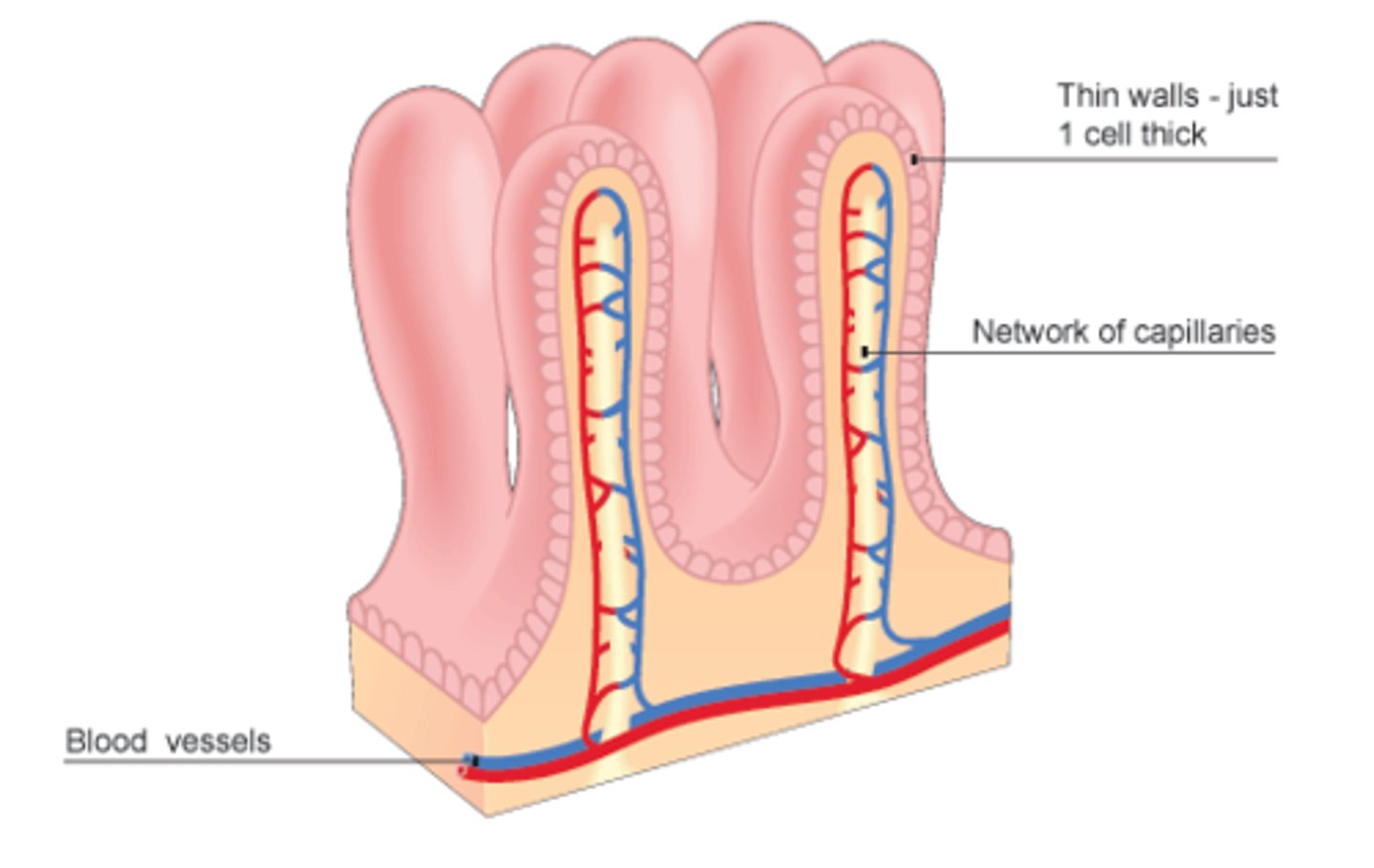
Exchange surfaces
Specially adapted surface where materials are exchanged
Alveoli
Air sacs in the lungs
Villi
Small fingerlike projections on the walls of the small intestines that increase surface area
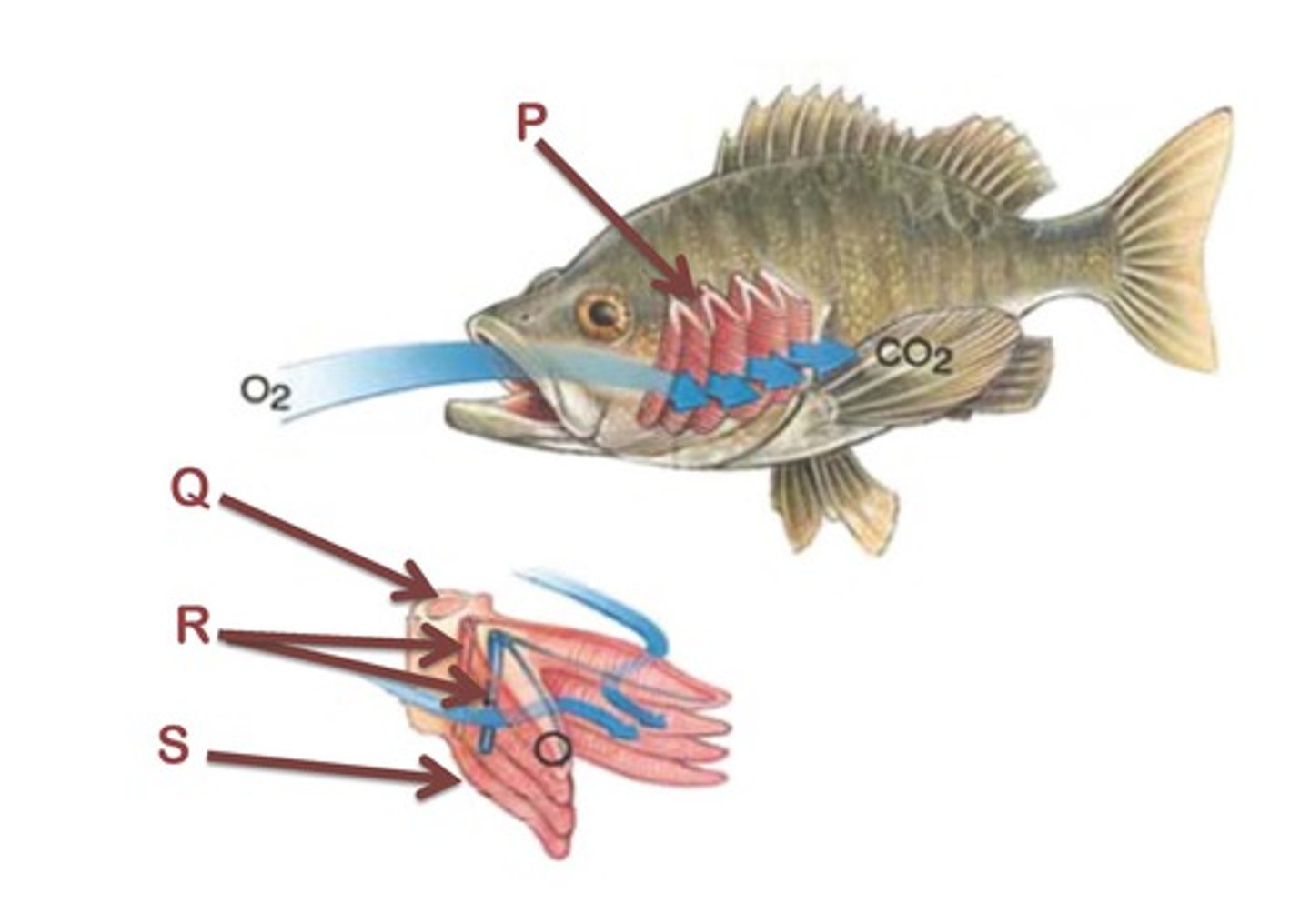
Gills in fish
Exchange surface for oxygen
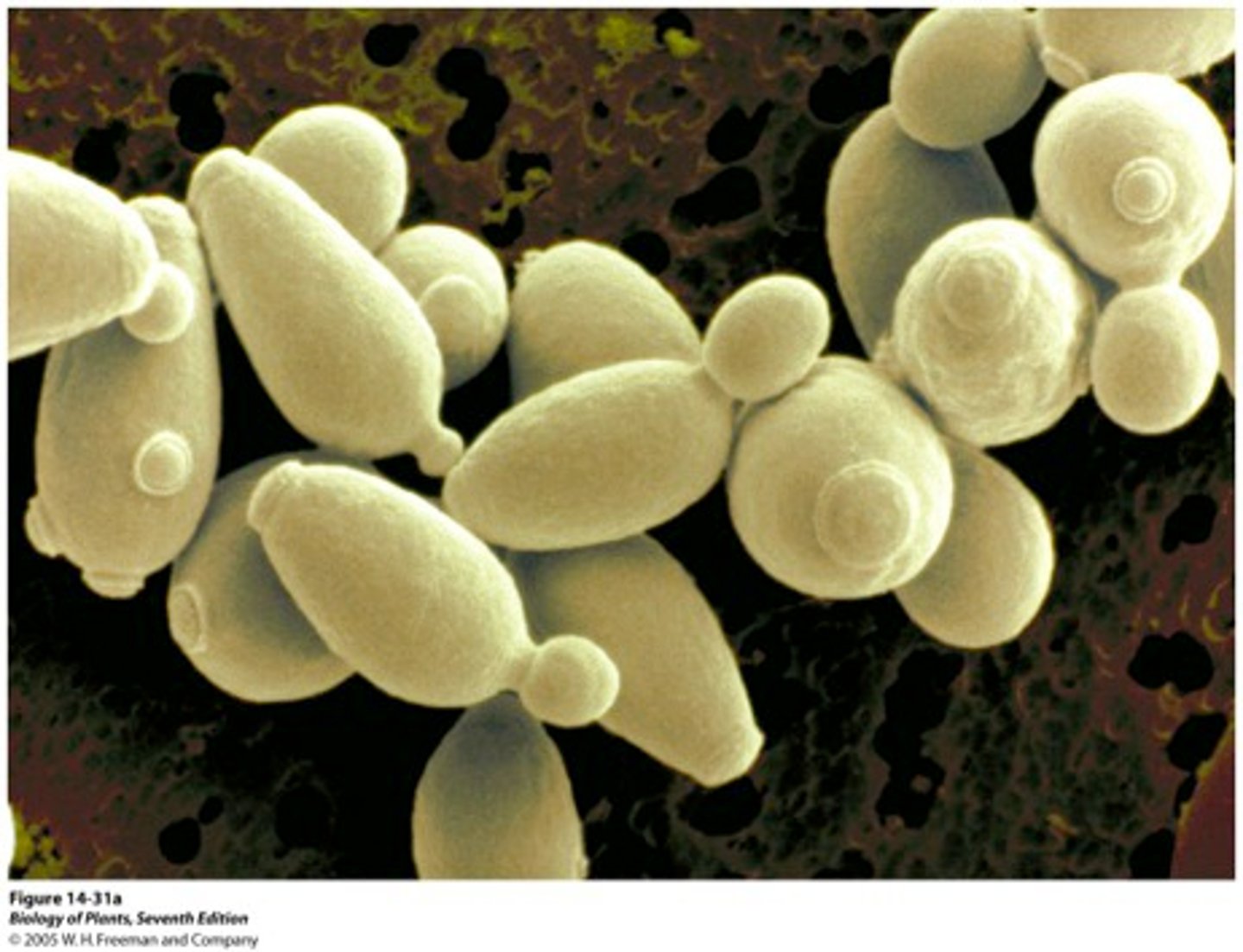
Yeast cells
a Eukaryotic cell with a cell wall but no chloroplasts
Plant cell
Contains a cell wall, chloroplast and large vacuole
Animal cell
Does not have a cell wall or chloroplast and a small vacuole