Chp. 16 Navigation incomplete
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
Pilotage
following land marks to track location
What are the four different time zones?
pacific, mountain, central, eastern
Universal coordinated time is referred to as
Zulu
True course is
True north measured by the actual meridian
True heading is
where the nose of your aircraft points
Varitation
Magnetic variation
caused by geographical differences
Magnetic deviation
the metals in the airplane disturb the magnetic compass
How to remember to subtract or add variation
“East is least (subtract) and west is best (add)”
Compass deviation card
How to convert minutes to hours and hours to minutes?
minutes to hours: divide minutes by 60 to find hours
hours to minutes: multiple hours by 60
How to calculate flight time?
D(NM)/GS = T
How to calculate the distance in flight?
GS x T = D
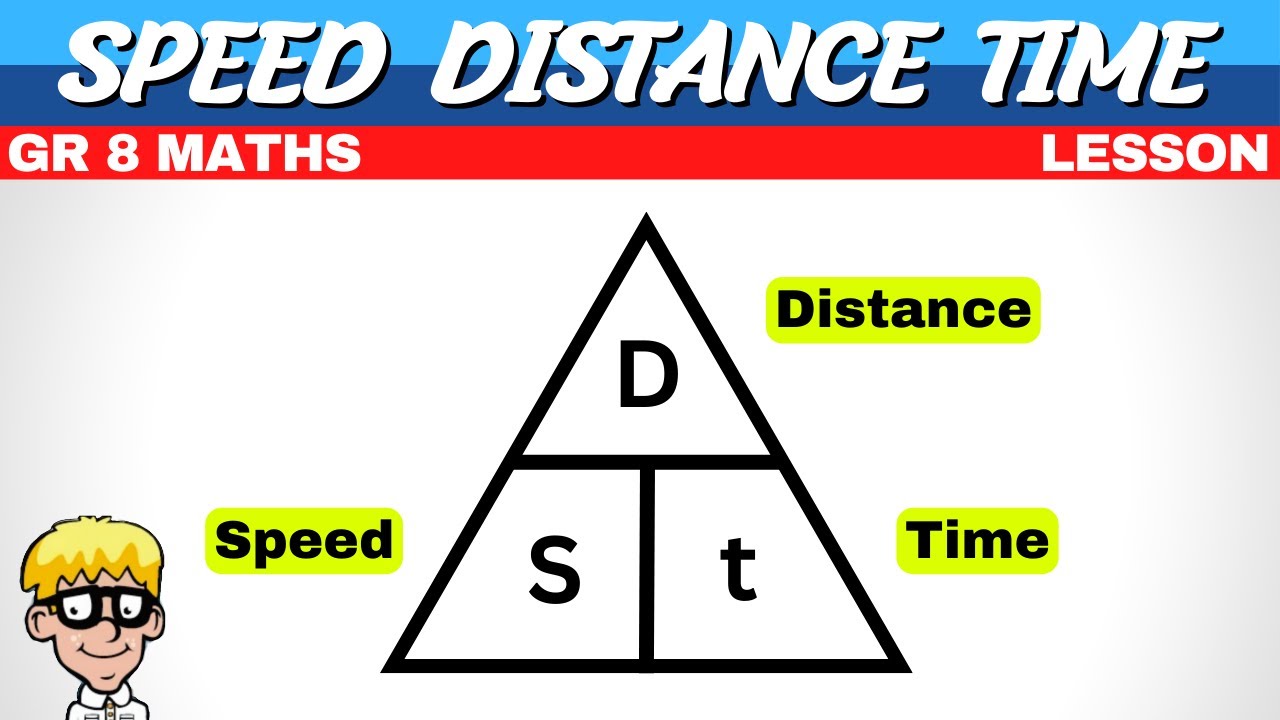
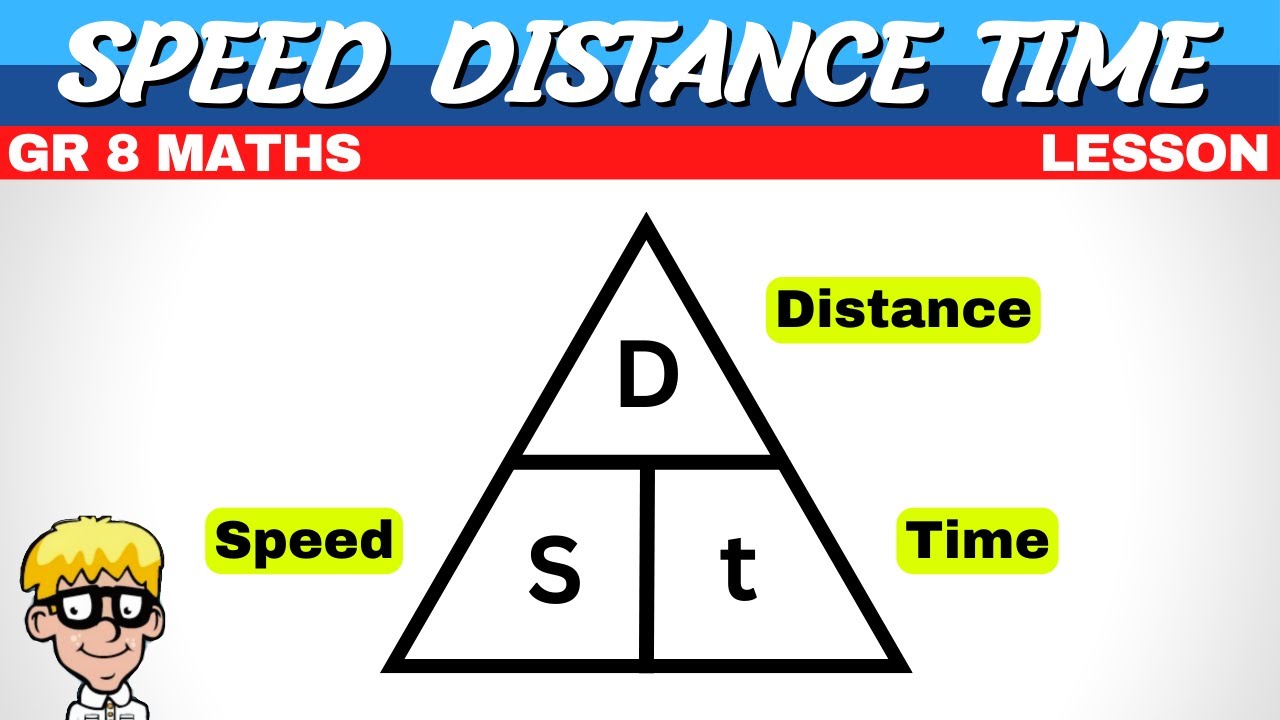
How to calculate for GS?
D/T = GS
Converting mph into knots
Isogenic lines
broken magenta lines that connect points of equal magnetic variation. (no vitiation between magnetic and true north)
magnetic variation pointing to the magnetic of the earth
true north where the actual north is located
What is the scale of 1 inch on the sectional map?
8SM or 6.87NM
Dead reckoning
using time, speed, and distance to have estimated times over checkpoint landmarks
What must you do in order to clear obstacles
Set altimeter to current local pressure to make sure you’ll clear
Magnetic North
where the lines of magnetic flux leave and enter the earth
Magnetic Variation
variable angular difference between true and magnetic north based on your location
Variations
Expressed in East and West depending if MN is east or west of TN
How to remember difference between variations
West is best(add) and East is least (subtract)
Formula for calculating West MN variation to TN
TC + W VAR = MC
Formula for calculating East MN variation to TN
TC - E VAR = MC
Earth is divided by
15degrees W variations
heading
direction airplane is pointing at
Course
path
True course
course relative to true north
Magnetic course
course relative to magnetic north
What heading do we use to fly?
Magnetic Heading
How to calculate true heading
TC ± WCA +TH
How to calculate magnetic heading
MC ± WCA = MH
How to calculate compass heading
MH ± DEV = CH
Very high frequency (VHF) Omnidirectional Range (VOR)
VOR system is present in three slightly different navigational aids (NAVAIDs): VOR, DME, VORTAC.
These systems provide magnetic bearing information to and from the station.
West is Best (TC + W VAR = MC)
East is Least (TC – E VAR = MC)
VFR at night what is the minimum additional fuel must you carry?
45 minutes
TAS on e6b
ref slide 34
Wind indicator to find ground speed
tail ends on the left you minus, tail ends up right add the wind angle degree
g = Gromit, ground speed
VORs are in reference to MN and are identified beginning with 001 which is 1 degree east. They are classified as T(Terminal0, L(low altitude), and H(high altitude) to show useable radius altitudes.
is a beam
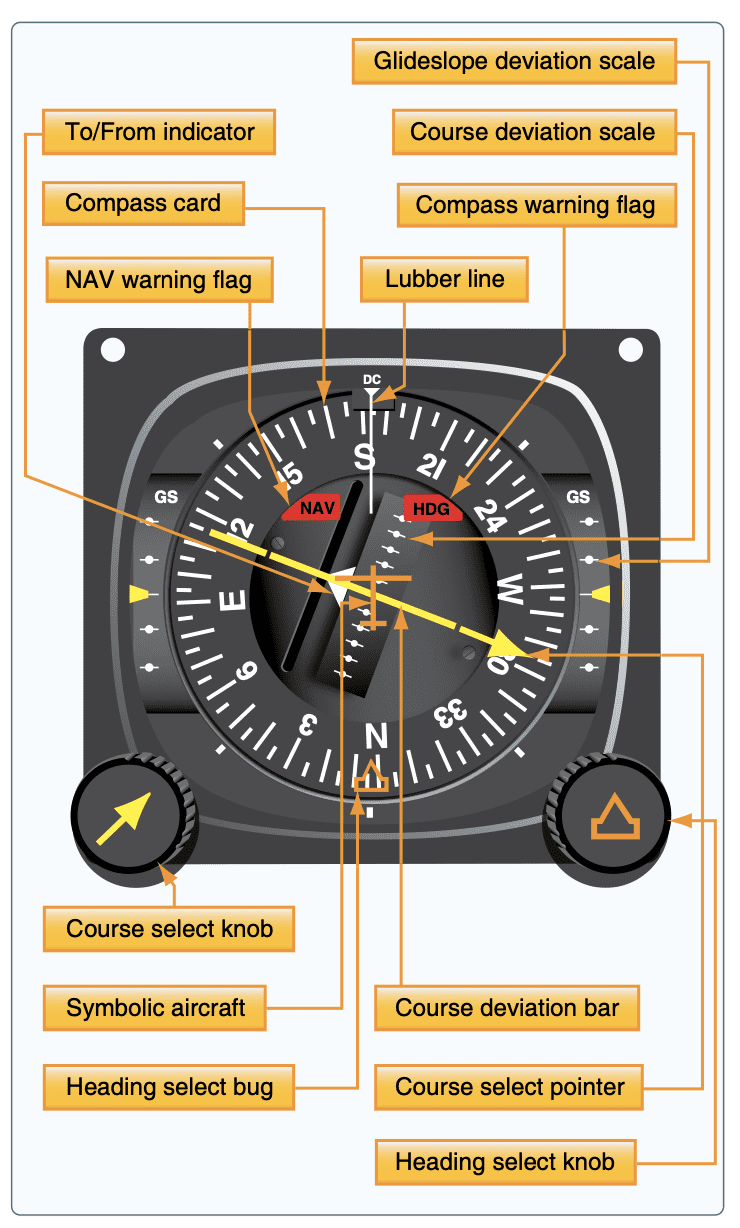
Horizontal situational indicator
Nav warning flag no reliable signal is being seen
HDG flag indicates there is an error with the compass card
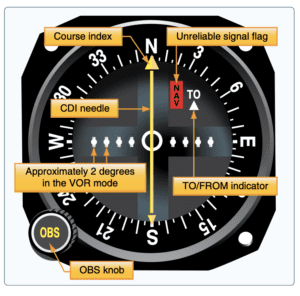
VOR indicator
OBS - omni bearing selector
CDI - course deviation indicator (white needle)
want to get the needle centered
if needle is left turn left
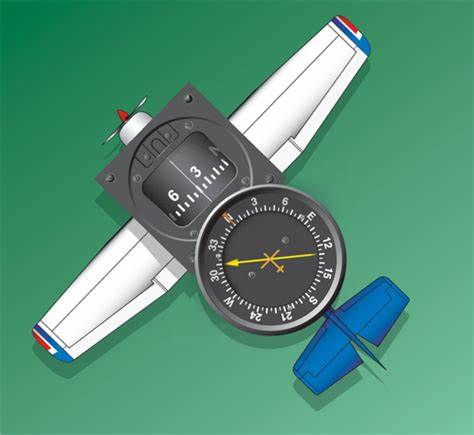

Automatic direction finder (ADF) tuned to nondirectional ground station known as (NDB). The one advantage of using this to navigate instead of a VOR is that VORs are based on frequency and NDB are based on the curvatures of the earth. This means NDB can be accessed at any altitude unlike VOR which is easily affected by electrical disturbances like lightening.
GPS and RAIM
RAIM - receiver autonomous integrity monitoring to determine if a satellite is receiving corrupted information. Without it, it is hard to understand if the GPS is accurate. Needs five satellites or four satellites and barometric altimeter (baro-aiding) to detect anomaly. Needs five satellites and baro-aiding or six satellites to detect where the anomaly is coming from.
There are two types. One that tells you there is not enough satellites and one that tells you a phase of the flight has a potential error.
Many VFR GPS are not equipped with RAIM which can result in the following issues:
If you cannot rename the waypoint or update the system
waypoint is blocked by aircraft positioning and unable to reach antenna
NAV
used to dial VOR
VOR will tell you what radial (degree) you’re on so that your NAVAID is on course (the beam). Very important that your to and from is set because they are each others reciprocal.
Make sure you’re flying the compass heading radical shown so that you can turn back on to the correct path if you’re off center
beam is perpendicular which would result in the VOR being confused and not indicating a to or from or you’re on top of the vor
To 0 is 180 and From is the direct course? ya i was right