✅ [T] ELECTRICITY
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
Electricity
The science dealing with the physical phenomena arising from the existence and interaction of electric charges
Battery
A group of two or more cells connected together to produce electric current
Primary Batteries
Designed for one-time use only; Delivers electricity as soon as its parts are assembled, or put together, provided that it is connected to circuit
Secondary Batteries
Can be recharged multiple times by applying an external electrical current to reverse the chemical reactions that occur during discharge; Electricity from some external source must be passed through it before it can deliver an electric current
Generator
A machine that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy
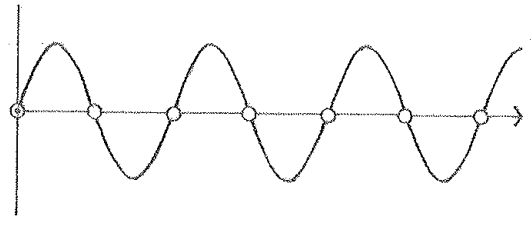
Alternating Current (AC)
An electric current that reverses direction at regular recurring intervals, having a magnitude that varies in a sinusoidal manner
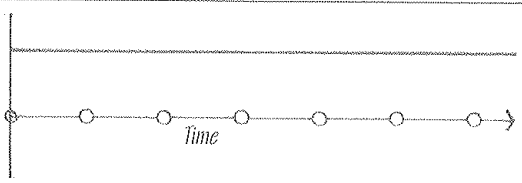
Direct Current (DC)
An electric current flowing in one direction only and having a magnitude that does not vary or varies only slightly
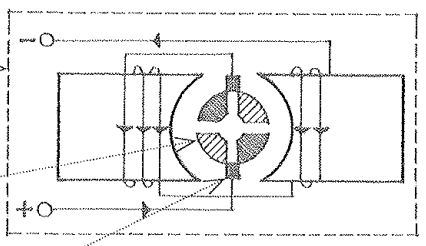
Alternator
A generator for producing alternating current
Power Plant
Facility designed to generate electricity by converting various forms of energy into electrical energy;
Natural Gas Power Plants
Plants use natural gas as fuel to generate electricity; Can be classified into combined-cycle or simple-cycle plants, depending on the type of technology used to convert gas into electricity
Geothermal Power Plant
Utilize heat from the Earth's interior to generate electricity; Extract heat from geothermal reservoirs or hot rock formations and use it to produce steam for electricity generation
Hydroelectric Power Plant
Harness the energy of flowing water to generate electricity; Involve the construction of dams and reservoirs to control water flow and drive turbines
Wind Power Plant
Use wind turbines to convert the kinetic energy of wind into electrical energy; Deployed in wind farms located in areas with high wind speeds
Nuclear Power Plant
Use nuclear fission reactions to generate heat, which is then used to produce steam to drive turbines connected to generators; Produce large amounts of electricity with minimal greenhouse gas emissions
Power
The product of potential difference and current in a direct-current circuit
Watt (W)
The SI unit of power, equal to one Joule per second or to the power represented by a current of one ampere flowing across a potential difference of one volt
Wattage
An amount of power, especially the power required to operate an electrical device or appliance
Kilowatt (kW)
A unit of power, equal to 1000 watts
Current
The rate of flow of electric charge in a circuit per unit time, measured in amperes
Ampere (A)
The basic SI unit of electric current, equivalent to a flow of one coulomb per second or to the steady current produced by one volt applied across a resistance of one ohm
Amperage
The strength of an electric current measured or expressed In amperes: analogous to the rate of water flow
Resitivity
The resistance per unit length of a substance with a unit cross-sectional area; Also called specific resistance
Conductivity
A measure of the ability of a substance to conduct electric current, equal to the reciprocal of the resistivity of the substance; Also called specific conductance
Voltage
Potential difference or electromotive force expressed in volts: analogous to pressure in water flow
Volt (V)
The SI unit of potential difference and electromotive force, defined as the difference of electric potential between two points of a conductor carrying a constant current of one ampere, when the power dissipated between the points is equal to one watt
Circuit
The complete path of an electric current, including the source of electric energy
Series
An arrangement of components in an electric circuit In which the same current flows through each component in turn without branching
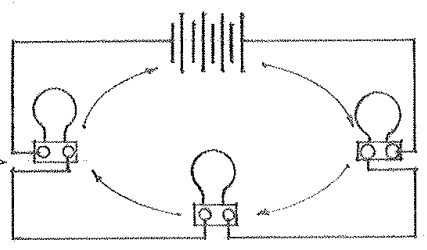
Parallel
An arrangement of components in an electric circuit in which all positive terminals are connected to one conductor and all negative terminals are connected to a second conductor, the same voltage being applied to each component
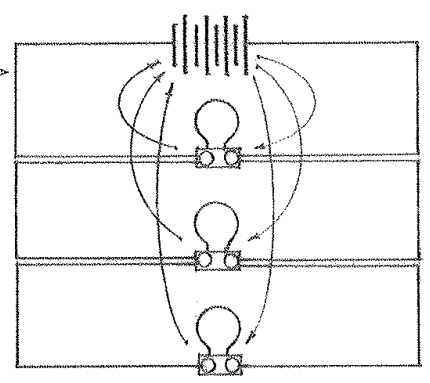
Transformer
An electric device consisting of two or more windings wound on the same core, which employs the principle of mutual induction to convert variations of alternating current in a primary circuit into variations of voltage and current in a secondary circuit
Phase
The fractional part of a period or cycle through which time has advanced, measured from a specified reference point and often expressed as an angle
Ground
A conducting connection between an electric circuit or device and the earth or other point of zero potential
Neutral
Not electrically charged
Dead
Not electrically connected to a source of voltage
Live
Electrically connected to a source of voltage, or electrically charged so as to have a potential different from that of earth, also hot
Short Circuit
An abnormal, usually accidental condition or low resistance between two points in an electrical circuit, resulting in a flow of excess current also called short
Shock
The muscular spasms caused by an electric current passing through the body
Circuit Breaker
A switch that automatically interrupts an electric circuit to prevent excess current from damaging apparatus in the circuit or from causing a fire
Branch Circuit
Portion of an electrical system extending from the final overcurrent device protecting a circuit to the outlets served by the circuit
General Purpose Circuit
A branch circuit that supplies current to a number of outlets for lighting and appliances
Appliance Circuit
Branch circuit that supplies current to one or more outlets specifically intended for appliances
Individual Circuit
Branch circuit that supplies current only to a single piece of electrical equipment
Distribution Panel
A panel for distributing power to other panels or Motors another heavy power consuming loads
Conductor
A substance, body, or device that conducts heat, sound, or electricity
Copper
What material is preferred in all conductor types?
Wire
A plastic connector containing a threaded metal fitting for screwing into the intertwined and of two or more conductors
No. 14
What is the smallest size of wire permitted?
Insulator
A material that is a poor conductor of heat
Cable
A single insulated conductor or a bound or sheathed combination of conductors insulated from one another
Busbar
A heavy conductor, usually in the form of a solid copper bar, used for collecting, carrying, and distributing large electric current
Cable
A single insulated conductor or a bound or sheathed combination of conductors insulated from one another
Armored Cable (BX)
Electric cable consisting or more insulated conductors protected by a flexible, helically wounded metal wrapping
Mineral-Insulated Cable
Electric cable consisting of a tubular copper sheath containing one or more conductors embedded in a highly compressed, insulating refractory mineral
Nonmetallic Sheated Cable
Also called Romex Cable; Electrical cable consisting of two or more insulated conductors enclosed in and nonmetallic, moisture resistant, flame retardant sheath
Coaxial Cable
Cable for transmitting high frequency telephone, digital, or television signals, consisting of an insulated conducting to enclosing an insulated conducting core
Shielded Cable
An electric cable enclosed within a metallic sheath in order to reduce the effect of external electric or magnetic fields
Conduit
A tube, pipe, or duct for enclosing and protecting electric wires or cable
Rigid Metal Conduit
Heavy-walled, tubular steel conduit joined by screwing directly into a threaded hub with lock nuts and bushings

Flexible Metal Conduit
A flexible, helically wound metal conduit, used for connections to motors or other vibrating equipment
Electrical Metallic Tubing
Thin-walled, tubular steel conduit joined by compression or setscrew couplings

Raceway
A channel expressly designed to hold and protect electric wires and cables
Underfloor Raceway
A raceway suitable for installation under a floor, often used in office buildings to allow for the flexible placement of power, signal, and telephone outlets
Surface Raceway
Raceway design for exposed insulation in dry, non-hazardous, non corrosive locations
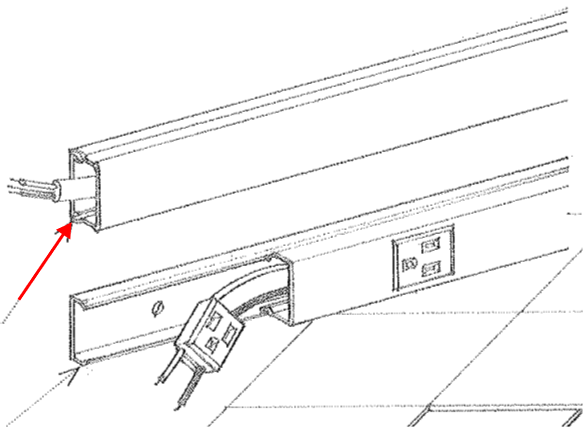
Multi-outlet Assembly
Surface mounted Raceway designed to house and electrical wires for a circuit and series of receptacles
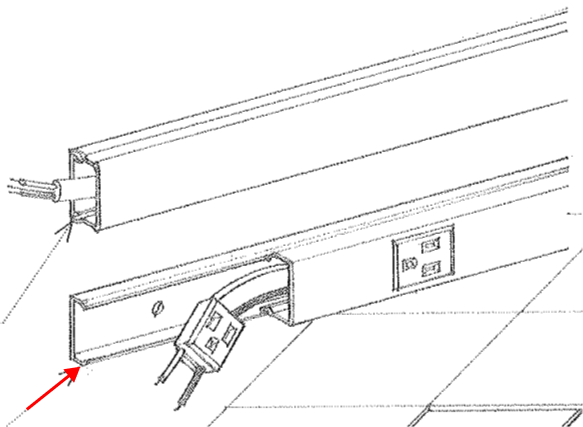
Outlet
A point on the wiring system at which current is taken to supply an electric device or apparatus
Outlet Box
The junction box designed to facilitate connecting an electric device or receptacle to a wiring system
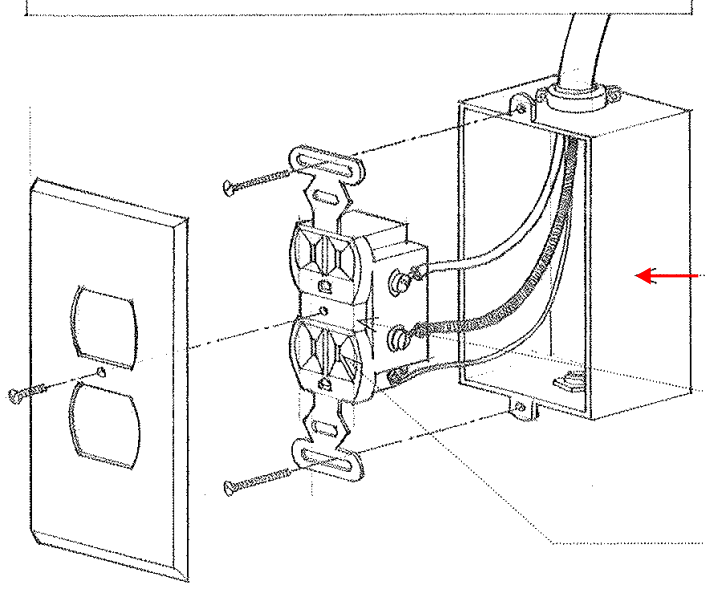
Convenience Outlet
An outlet usually mounted on the wall in housing one or more receptacles for portable lamps or appliances
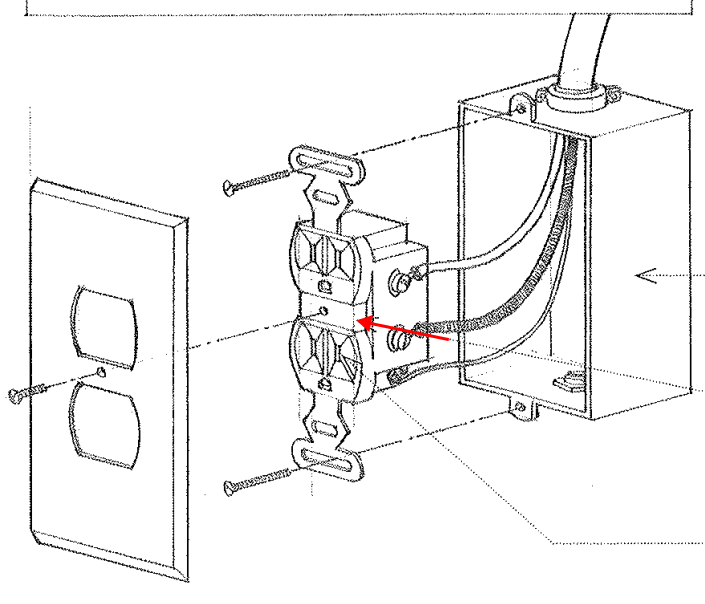
Receptacle
Also known as socket; A female fitting connected to a power supply and equipped to received a plug
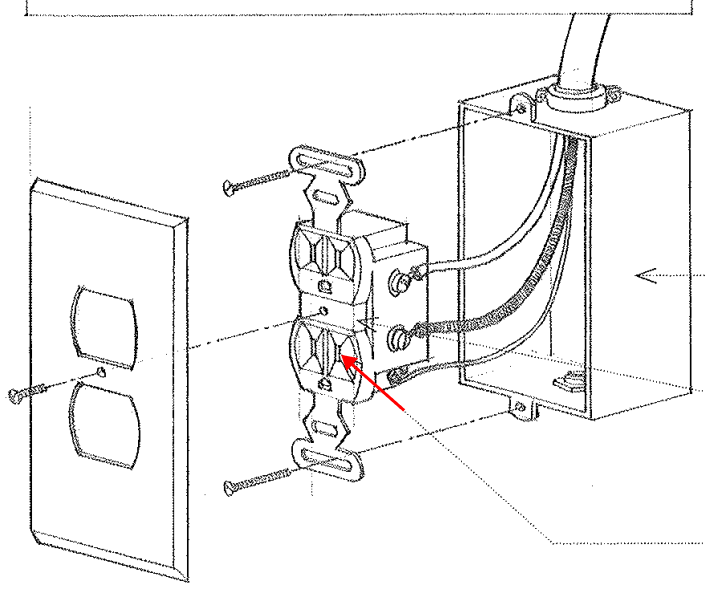
Switch
A device for making, breaking, or changing the connections in an electrical circuit
250V, 600V, 5V
What are the ratings of a switch?
Toggle Switch
Switch in which a lever or knob, moving through a small arc causes the contact to open or close an electric circuit
Normal Duty (ND)
Switch intended for normal use in light and power circuits as in general-purpose switches
Heavy Duty (HD)
Switch intended for frequent interrupting
Light Duty (LD)
Switch intended to connect the loads occasionally, such as service switches
Three-way Switch
A single pole double throw switch used in conjunction with another to control lights from locations
Four-way Switch
A switch used in conjunction with two three-way switches to control lights from three location
Service Switch
Intended to disconnect all the electric service in the building except emergency equipment; May compromise one to six properly rated switches that are assembled into a switchboard
General Purpose Switch
Intended for use in general distribution and branch circuits
Disconnecting or Isolating Switches
Intended for disconnecting or isolating circuits; Used for circuits rated at more than 600 volts
Wiring Switches
Include all relatively small switches that are employed in interior wiring installations for the control of branch circuits, individual lamps or appliances
General-purpose Switches
Single-pole or double-pole switches for the general purpose use of connecting or cutting-off circuits for the control of lamps or other loads from a single point
Dimmer
Rheostat or similar device for regulating the intensity of an electric light without appreciably affecting spatial of the distribution
Electrolier or Multi-Circuit Switch
Used for the control of lights in multi-lamp fixtures so that one lamp or one set of lamps may be turned on alone in combination with other lamps
Momentary Contact Switch
Used where it is desired to connect or cut-off a circuit for only a short duration; Switch is provided with a spring so that it will return to its original position as soon as the handle or button is released
Rotary Switch
A type of electrical switch that uses a rotating mechanism to select one of multiple positions or circuits
Time Controlled Switch
Device comprises a precision low speed miniature drive motor (timer) to which some type of electric contact-making device is connected
Air Switch
A switch in which the interruption of a circuit occurs in air
Knife Switch
A form of air switch in which a hinged copper blade is placed between two contact clips
Float Switch
A switch controlled by a conductor floating in a liquid
Mercury Switch
An especially quiet switch that opens and closes an electric circuit by shifting a sealed glass tube of mercury so as to uncover or cover the contacts
Key Switch
A switch operated only by inserting a key
Automatic Transfer Switch
Device used to automatically transfer electrical power supply between two sources in the event of a power outage or other abnormal condition
Faceplate
A protective plate surrounding an electric outlet or light switch
Fuse
A device containing a strip or wire of usable metal that melts under the heat produced by excess current, thereby interrupting the circuit
Panelboard
A board or which are mounted the switches, fuses and circuit breakers for controlling and protecting a number of similar branch circuits, installed in a cabinet and accessible from the front only
Cable tray
An open metal framework for supporting insulated electrical conductors
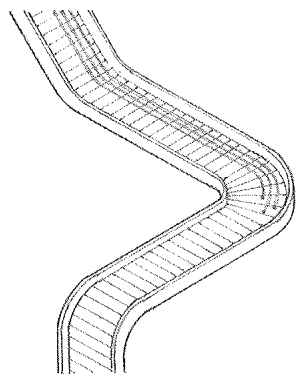
Underfloor Ducts
A system of ductwork installed beneath the floor of a building; Ducts are hidden beneath the floor surface
Cellular Metal Floor Raceway
A type of cable management system used in buildings to route and conceal electrical, data, and communication cables beneath a raised floor surface
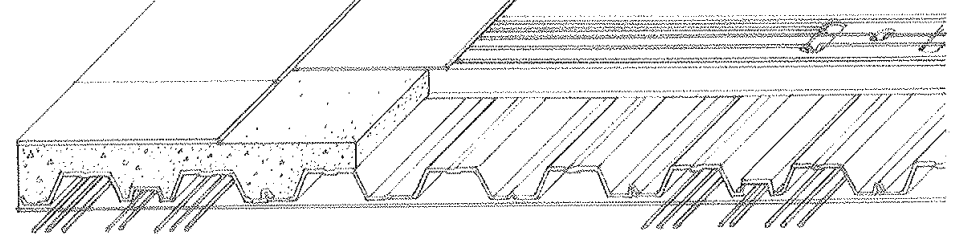
Precast Cellular Concrete
A type of cable management system using a mixture of cement, water, aggregates, and a foaming agent; Includes interconnected voids or cells distributed throughout the raceway
Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter (GCFI)
Designed to protect against ground faults, which occur when electrical current leaks from a circuit and flows through an unintended path, such as through water or a person; Used in any area where water and electricity may come into contact
Arc Fault Circuit Interrupter (AFCI)
Designed to protect against arc faults, which occur when electrical current flows through an unintended arc or spark between conductors in a circuit, potentially leading to electrical fires