Medchem Exam 2
1/117
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
118 Terms
First Generation Antipsychotics
SAR
Chlorine substituent desymmetrizes the compound - an electron withdrawing substituent is important to activity
Side chain amine is protonated at pH 7 - associates with chlorinated ring
Side chain has three carbo chain linker, often separated by two amines
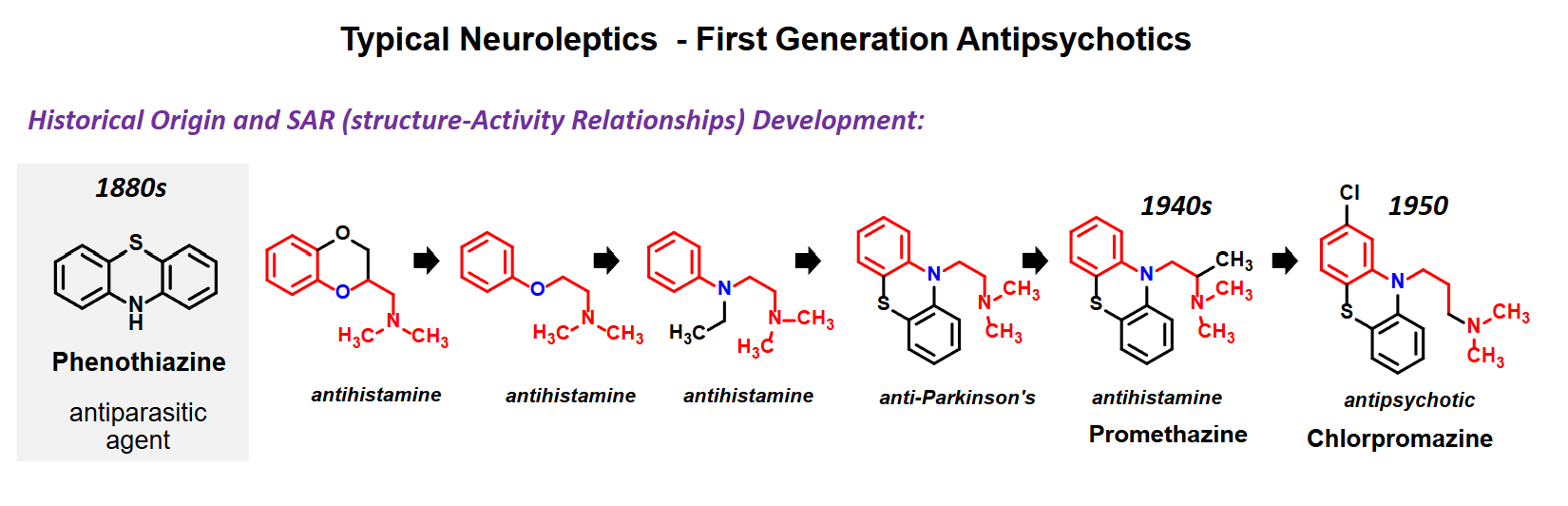
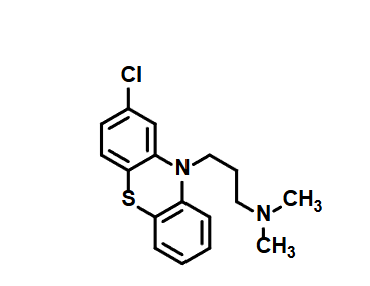
Chlorpropazine
First antipsychotic
Usually administered as injectable
D2 antagonist
Elderly patients with dementia related psychosis treated with antipsychotic drugs are at an increased risk of death
SE: sedative, EPS
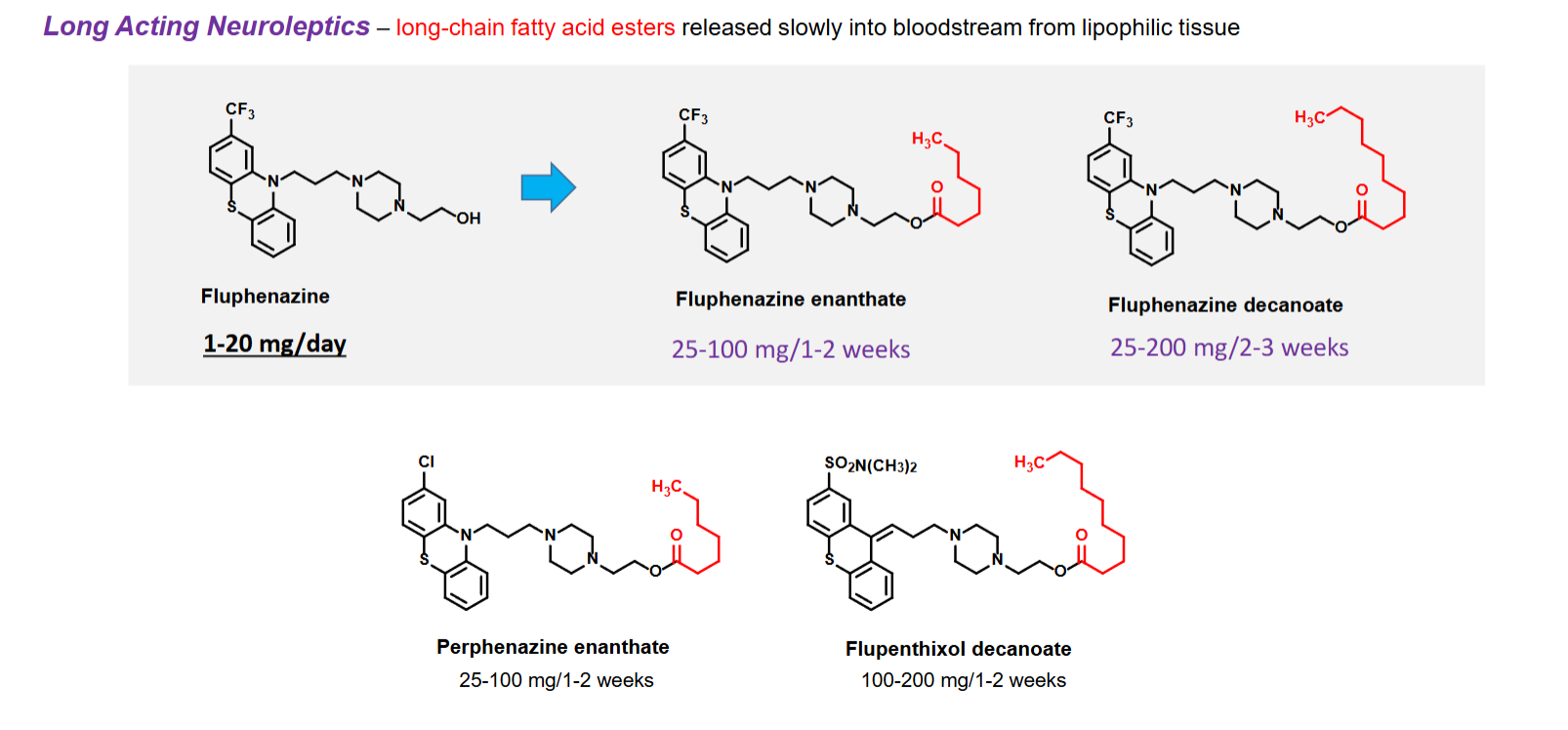
Long acting Neurolpetics
Have long chain fatty acid esters released slowly into blood stream from lipophilic tissue
Helps with adherence issues in schizophrenic patients
Some believe they do not have an illness that needs to be treated
Patients forget to take medication on schedule
SE can lead to patients avoiding medication
Poor efficacy of therapy used
Increasing DOA of a neuroleptic means administering medication less often
Patients who need injection
Drugs that are poorly absorbed
Haloperidol
D2 antagonist (greater affinity than chlorpromazine)
Less weight gain that chlorpromazine
Used for manic phase of bipolar disorder, schizophrenia
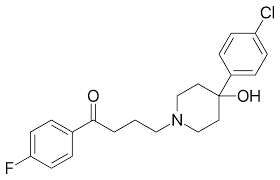
Haloperidol Decanoate
D2 Antagonist
Injection (every 4-6 weeks)
Has long-chain fatty ester
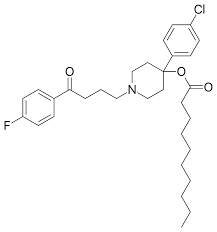
Droperidol
D2 antagonist
Short-acting
Use: anesthesia for its sedating and antiemetic effects, psychiatric emergency as a sedative-neuroleptic
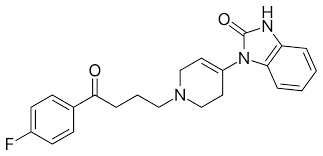
Lumateperone
-Second Gen Antipsychotic
D2 antagonist and 5-HT2 receptor
Treats positivve and negative symptoms of schizophrenia
Oral administration
Clozapine
Atypical Neuroleptics - Second Generation Antipsychotics
5-HT2A, moderate D4 and weak D2 receptor antagonism → Antipsychotic properties
Good for patients who don’t respond to 1st gen neuroleptics
Minimal EPS
Also treats negative symptoms of schizophrenia (with positive symptoms)
1-2% patients suffer fatal agranulocytosis (uncommon for drugs in this class)
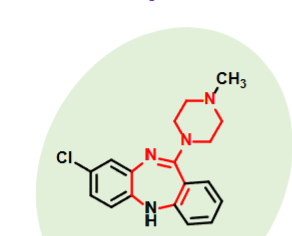
Olanzapine
Atypical Neuroleptics—Second Generation Antipsychotics
High affinity at D2 and 5-HT2 receptors than Clozapine
Antagonist activity at these receptors
Similar side effect profile to Clozapine
Minimal EPS
Treats negative and positive symptoms of schizophrenia
Orally Active
T1/2 20-50 hrs
Longer acting injectable formulation also available
Schizophrenia and bipolar disorder
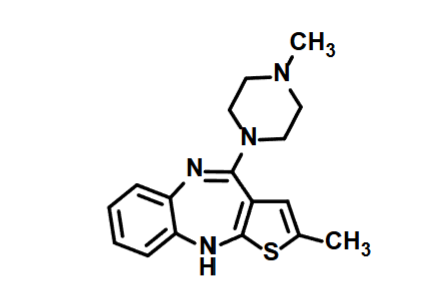
Quetiapine
-Atypical Neuroleptics —> Second Gen Antipsychotics
-DA, D2 and 5-HT2 recptor Antagonists
-Minimal EPS
Treats negative/positive symptoms
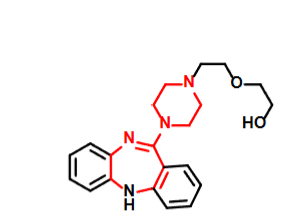
Loxapine
Atypical Neuroleptics - Second Gen Antipsychotics
High affinity at D2, 5-HT2 and H1 receptors (not muscarinic)
N-Dealkylation of loxapine —→ Amoxapine —> Moderate SERT and NET blocking activity, which gives it some antidepressants
Schizoprhrenia and Biopolar disorder
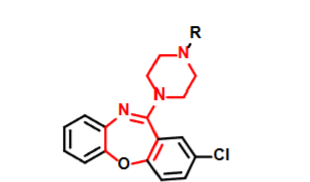
Lybalvi
Olanzapine —> Atypical Neuroleptics—Second Generation Antipsychotics
High affinity at D2 and 5-HT2 receptors than Clozapine
Samidorphan —> An opioid receptor antagonist which reduces weight gain associated with olanzapine
Oral tablet
Contraindicated in patients using opioids
Asenapine
-Atypical Neuroleptics —> Second Gen Antipsychotics
-DA, D2 and 5-HT2 recptor Antagonists
-Minimal EPS
Treats negative/positive symptoms
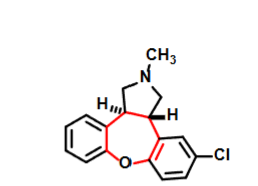
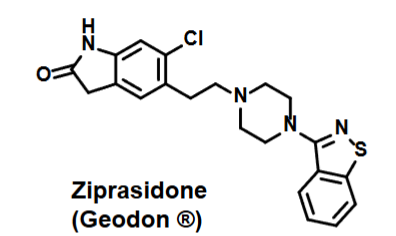
Ziprasidone
Schizophrenia treatment
Treats both positive and negative symptoms
Lower incidence of EPS
High affinity for 5HT2A, D2, H1 and a1/a2 —> antagonist at each
Partial Agonist activity at 5-HT1
Blocks reuptake of SERT and NET
Risperidone
Atypical Neurolpetics —> Second Generation Antipsychotic
Attempt to combine high levels of D2 and 5-HT antagonist activity
Schizophrenia treatment
Treats both positive and negative symptoms
Injectables last 2-4 weeks
Weight gain is a SE
Higher incidecne of EPS than other 2nd gen neuroleptics
Very high affinity for 5-HT2 antagonist
High affinity for dopmaine D2 - antagonist
High affinity for H1 and a1 receptors
No affinity for muscarinic receptors
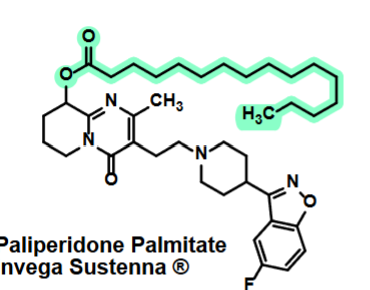
Paliperidone Palmitate
Atypical Neuroleptics—Second Gen Antipsychotics
Attempt to combine high levels of D2 and 5-HT antagonist activity
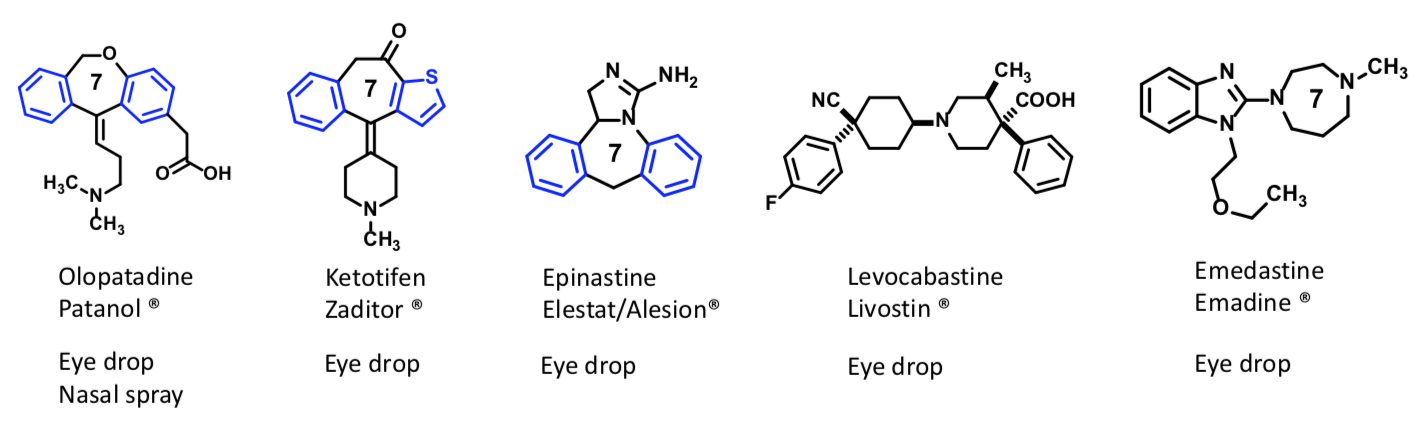
Abilify
Atypical Neuroleptics—Second Generation Antipsychotic
Aripiprazole
Partial agonist at D2
Partial agonist of 5-HT2
Moderate affinity for H1 and a1/a2
Low chance of hyperprolactinemia and EPS
T1/2 of 90 hrs
Oral tablet or solution, injectable forms available
Brexpiprazole
Atypical Neuroleptics - Second Generation Antipsychotics
Partial agonist at D2
Used to treat Schizophrenia / adjunct therapy for MDD
Less EPS and maybe less weight gain than Abilify
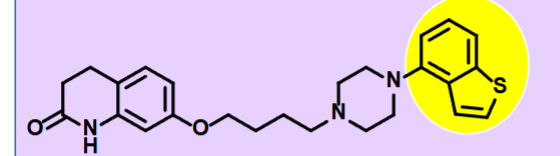
Cariprazine
Atypical Neuroleptics - Second Generation antipsychotics
Partial agonist at D2 and D3
Used to treat schizophrenia / adjunct therapy for MDD
Used for biopolar mania / depression
Oral capsule, once a day treatment
Treats negative and positive symptoms
Cons (-)
Cost compared to other options, fewer dosage forms than Abilify
Pros (+)
Longer half life (21 days or ~ 3 weeks)
Missing a dose may be not be as problematic (avoiding relapse)
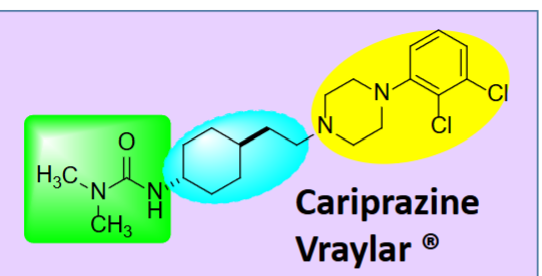
Environmental Toxins effect on PD
MPTP selectively binds MAO-B which is highly concentrated in human substantia nigra area
MPP+ concentrates in mitochondria
inhibits mitochondria complex I
ATP depleted at mitochondrial level
In PD patients, 30-40% reduction in mitochondrial complex I activity in substantia nigra
MAO-B inhibitors shown to inhibit MPTP-induced PD in primates – further evidence of this pathway primates – further evidence of this pathway
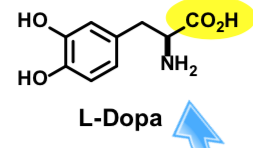
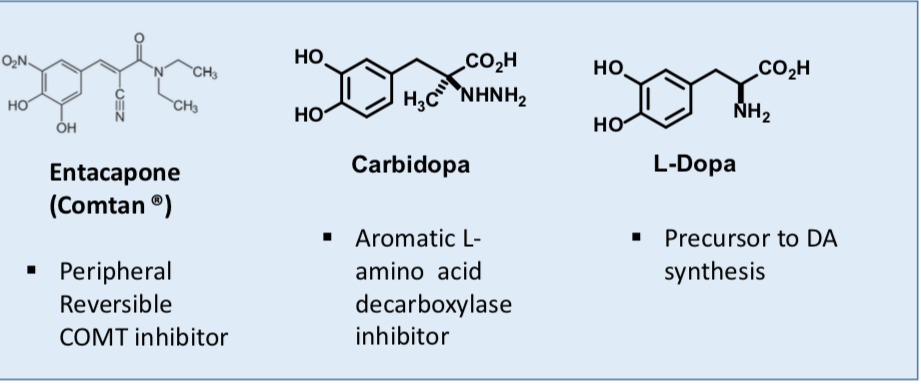
L-DOPA
L-DOPA crosses the blood brain barrier but dopamine does not
Most exogenous L-DOPA is rapidly decarboxylated in peripheral tissues including heart, lung, and kidneys
Only ~ 1% of an oral dose reaches the brain
typically 3-6 grams administered daily to compensate
Vitamin B6 is a co-factor for aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase (high vit B6 can increase activityreducing L-DOPA)
Carbidopa
Inhibits aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase peripherally 2.5-30-fold lower dose is possible with Sinemet (0.2 to 1.2 g/day)
Vitamin B6 is a co-factor for aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase (high vit B6 can increase activityreducing L-DOPA concentrations)
Side effects: nausea, vomiting; “on-off” effects after 5-15 years of continuous treatment; behavioral/psychological disturbances
Apokyn
Agonizes D1 and D2 type receptors
Crosses BBB
Short duration of action
No oral bioavailability
Subcutaneous administration/self
injector or continuous pump
Controls motor dysfunction in PD
Improves on-off syndrome
Dizziness, nausea can be side effects
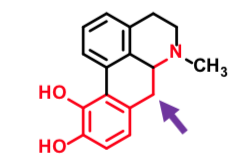
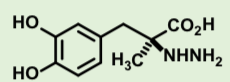
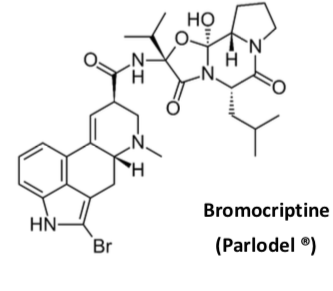
Bromocriptine
Ergot alkaloid peptide
Partial agonist at D2 and D3 receptor
Inhibits prolactin release from pituitary cells which
exclusively expresses D2 receptors
Orally absorbed
Half life 3 hrs
Pramipexole and Ropinirole
Both commonly prescribed for PD
First line treatment sometimes before L-DOPA
(L-DOPA associated with motor fluctuations and reactive intermediate formation risk) Both are D2 receptor agonists
Side effects: initial nausea, vomiting, postural hypotension, fatigue
Hallucinations, delusions, confusion – especially in elderly dementia patients with PD

Selegiline
Irreversible, MAO-B selective
Reduces dosage needs of L-DOPA
N-dealkylated by CYPs to (-) methamphetamine [L isomer]
(+)-methamphetamine [D isomer] is the abused substance
(-) Methamphetamine metabolized to (-) amphetamine vasoactive activity
metabolites derived thereof associated with cardiovascular (orthostatic hypotension) and psychiatric (hallucinations) side effects
![<p><span>Irreversible, MAO-B selective</span></p><ul><li><p><span>Reduces dosage needs of L-DOPA</span></p></li><li><p><span>N-dealkylated by CYPs to (-) methamphetamine [L isomer]</span></p></li></ul><p><span style="color: rgb(255, 0, 0)"><strong><em>(+)-methamphetamine [D isomer] is the abused substance</em></strong></span></p><ul><li><p><span>(-) Methamphetamine metabolized to (-) amphetamine vasoactive activity</span></p></li><li><p><span>metabolites derived thereof associated with cardiovascular (orthostatic hypotension) and psychiatric (hallucinations) side effects</span></p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/d858596d-3ea3-4aed-b50e-f1c6b5c4d12c.png)
Rasagiline
Irreversible, MAO-B selective
Reduces dosage needs of L-DOPA
N-dealkylated by CYPs
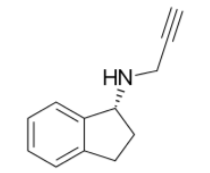
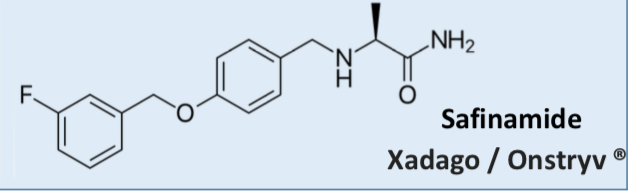
Safinamide
Multiple mechanisms of action:
Reversible, MAO-B selective inhibitor (preserves DA) Inhibits glutamate release
(reduces excess “excitability” neurotransmitter)
Add-On therapy:
Reduces dosage needs of L-DOPA
Oral administration
Contraindications:
Patients with severe liver impairment
Patients with retinal disorders (can exacerbate)
Pregnancy and breast feeding
In combination with certain other MAOIs / SSRIs / tyramine containing foods
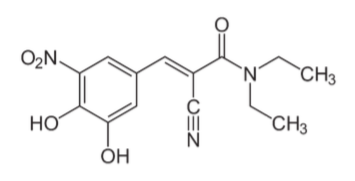
Entacapone
Reversible COMT inhibitor
Short duration of action 2 hrs
Works only in periphery
Side effect: severe diarrhea
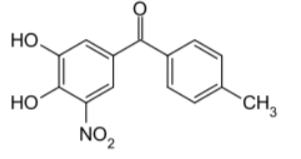
Tolcapone
Reversible COMT inhibitor
Long duration of action 8-12 hrs
Works in brain and periphery
Side effect: Hepatic toxicity – 3 fatalities after marketing
Side effect: severe diarrhea
Stalevo
Helpful as a combination therapy to:
replace equivalent dosage of individual components
Help with wearing off effects of L-Dopa/carbidopa alone (low dose/no dyskinesia)
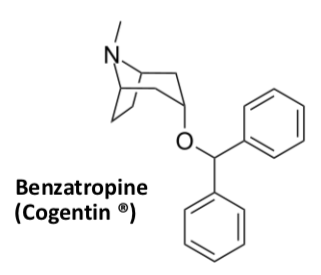
Benzatropine
Adjunct therapy
Muscarinic antagonist
(relaxes muscles to avoid spasm)
Control extrapyramidal effects well so still used despite adverse effects
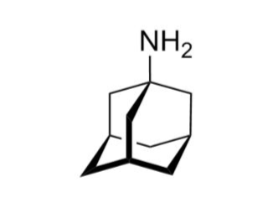
Amantidine
Adjunct therapy
Antidyskinetic (helps with sudden uncontrolled movements)
Causes release of DA and NE from storage vesicles
Blocks reuptake of DA
N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) glutamate receptor antagonist
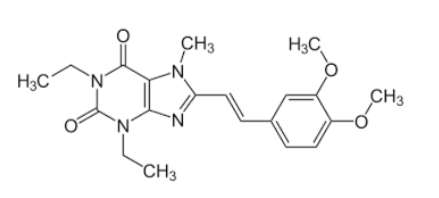
Nourianz
Adjunct therapy with L-dopa/carbidopa
For treating “off time” in PD
Adenosine A2A receptor antagonist
Oral, once a day dosing
Metabolized by CYP3A4avoid grapefruit juice or other CYP3A4 inhibitors to avoid high plasma concentrations Renal excretion is important – patients with renal failure may need to adjust dose down
Baclofen
muscle relaxant
GABAB1 agonist
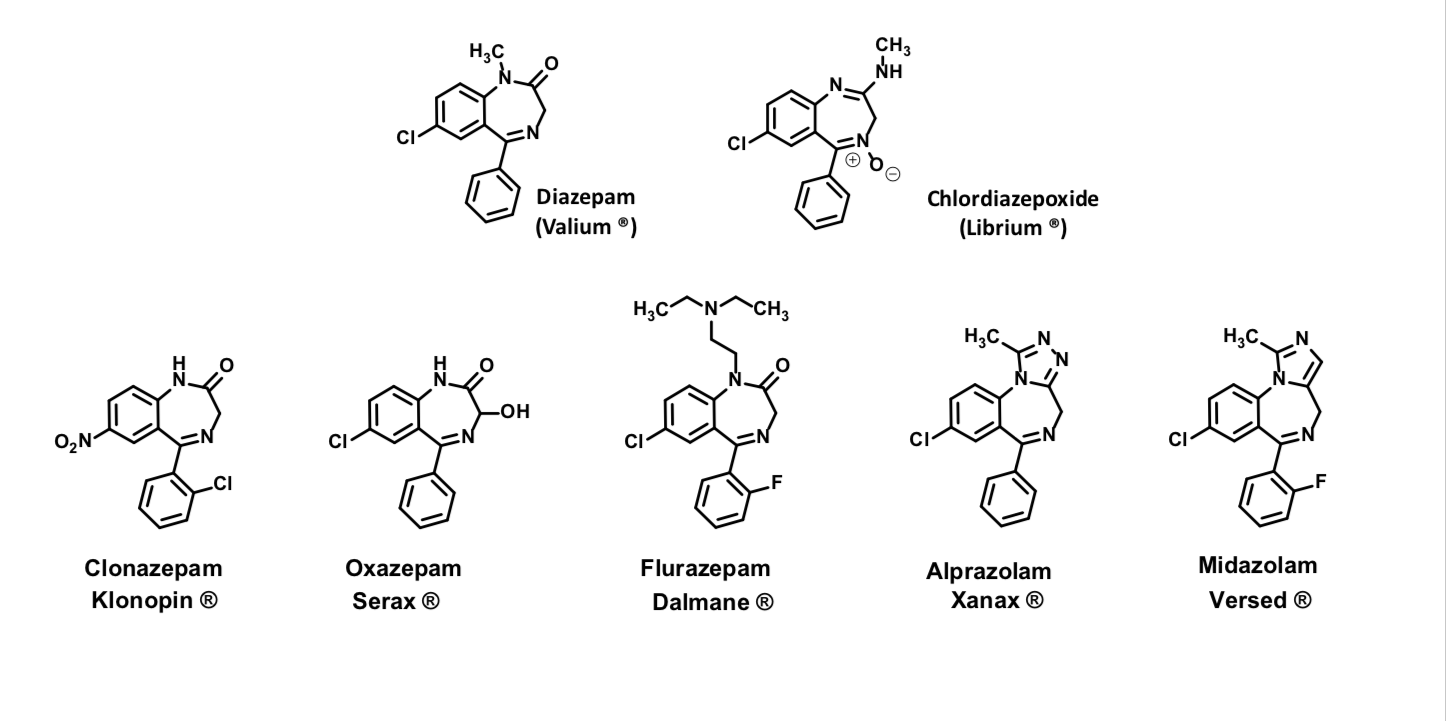
Chlordiazepoxide
Anxiolytic
Sedative properties
Oral tablets
Half life 24-48 hrs
Light sensitive
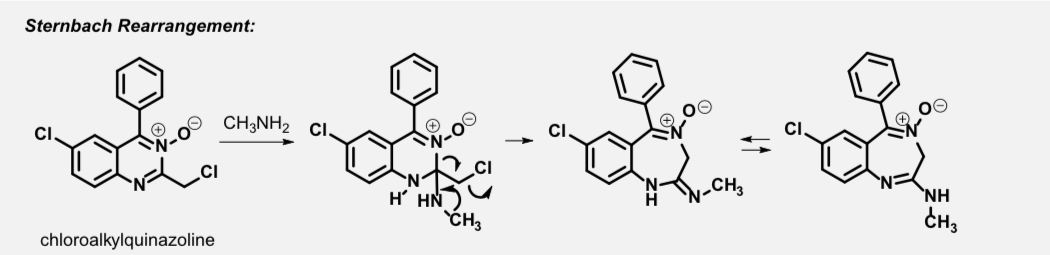
Diazepam
anxiolytic, sedative, muscle-relaxant, anticonvulsant and amnestic effects
increased risk of congenital malformations and other developmental abnormalities in pregnancy
Passes into breast milk
Half-life: 20-50 hours
N-dealkylation (CYP3A4) - one of several metabolic pathways observed (active, common metabolite with Librium)
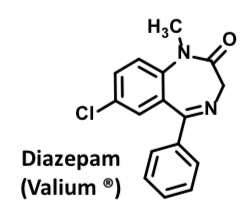
N-Desmethyldiazepam
– Active metabolite undergoes slower metabolism than parent. – Common intermediate from both Valium and Librium
– Accumulates with repeated administration
– After 1 wk discontinuation, it is detected in blood
Flurazepam
Oral formulation
Rapidly N-dealkylated (CYP3A4)
Accumulation with chronic usesedation
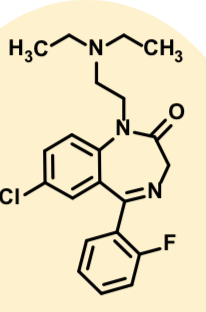
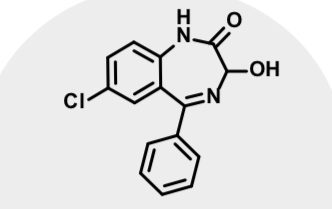
Oxazepam
Active metabolite of diazepam and chlordiazepoxide Marketed separately
Short acting anxiolytic
Half life 4-8 hrs
Accumulation with chronic use occurs less for this one
Anxiolytic Benzodiazepines
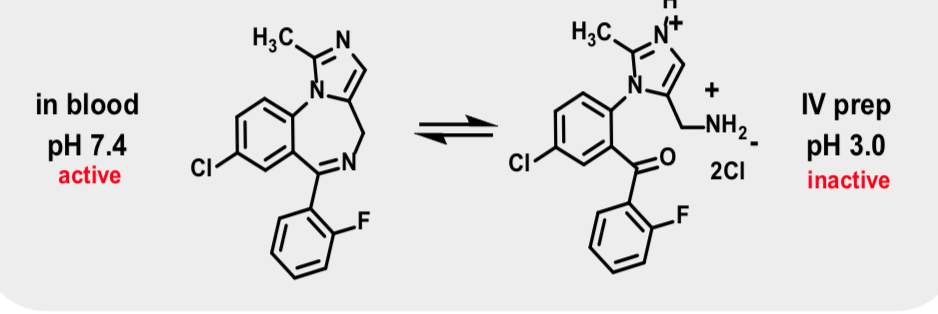
Midazolam
Anxiolytic BZ
Use: Premedication for anesthesia
Quick onset 1-2 min
Recovery to full alertness (40 minutes)
Injectable or oral formulation
pH dependent solubility: Highly water soluble at pH <4 and lipid soluble at pH > 4
Flumazenil
GABA receptor antagonist A
Bind with high affinity to BZR and blocks effects of classical benzodiazepines (same binding site)
Binding is not affected by GABA or ions that induce receptor conformation changes
insensitivity to conformation changes suggests the drug does not induce structural changes to impart a response (pure antagonist)
Used to treat benzodiazepine overdose
Flumazenil can cause seizures – care to be taken in those patients with low threshold for seizure
Zopiclone
Not subtype selective (high affinity for alpha-1 and alpha-3 receptors)
Affinity for alpha-1 subunit-containing GABAA receptors is less than for other nonbenzodiazepines
Rapid onset, moderate duration (T1/2 = 6 h) - of the nonbenzodiazepines, longest half life
Binds an allosteric site away from BZ binding site
Binding is not affected by GABA
Sedative hypnotic
Improves sleep onset and maintenance
Zaleplon
High affinity for α1-containing BZRs
Produce effects at other BZRs/GABAA subtypes too
Improves sleep onset - no evidence that it helps with sleep maintenance or duration
No withdrawal symptoms or rebound insomnia on discontinuation in studies with use up to 5 weeks
Cimetidine and grapefruit can increase blood plasma concentrations (CYP3A4 interference)extends the half-life and effects
Zolpidem
Highly selective for α1 subunit-expressing GABAA receptors (5-10 fold higher affinity over α2 and α3 receptors)
Lack of affinity for α5 –containing receptors
Weaker anxiolytic activity, anticonvulsant and muscle relaxant properties than classical BZsLow risk of withdrawal and tolerance; does not accumulate
Women clear Ambien more slowly than men
Good for initiating sleep (within 15-20 min)
Controlled release formulation used for maintaining sleep (Intermezzo ®)
AE (adverse events): sensory distortion, amnesia, psychotic symptoms, “sleep-actions” Flumazenil reverses sedative/hypnotic and memory-impairing effects
Elderly dose adjustment required due to 50% increase in elimination half life
Ganaxolone
Treats certain types of seizure (those with CDKL5 deficiency disorder) Reduces seizure potential
Binds allosteric site of GABA-A receptor
opens chloride channel
hyperpolarization (desensitization towards stimuli)Treats certain types of seizure (those with CDKL5 deficiency disorder) Reduces seizure potential
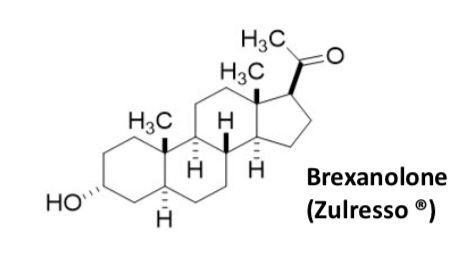
Brexanolone
Used for PPD
IV only
More expensive
SE of sedation during administration and need to be monitored
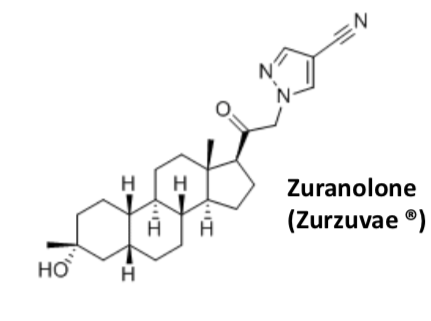
Zuranolone
Used for PPD
Oral dosage form
Less expensive
SE of sedation during administration and need to be monitored
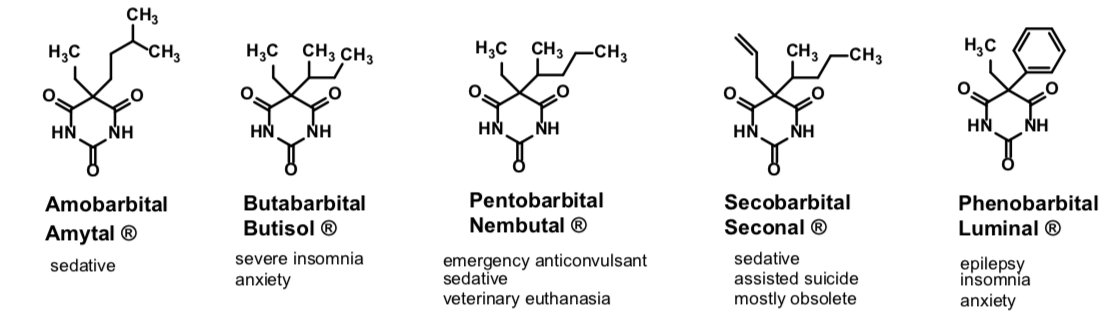
Barbituates
Sedative hypnotics, anesthetic, anticonvulsant activities
Sedative hypnotic agents of choice until benzodiazepines discovered
Side effects: tolerance, dependence, withdrawal (seizures, respiratory spasm), memory impairment, potential for abuse, low therapeutic index
overdose and death
No antidote to overdose!
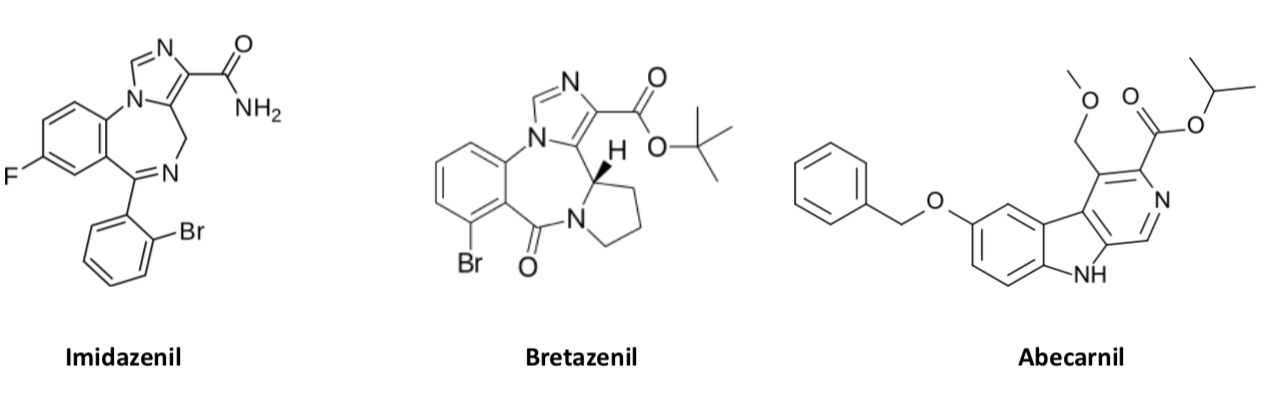
GABA A partial allosteric modulators - Experimental
Side effects (sedation and potentiation of alcohol) are less extreme and potential for abuse is less for partial agonists compared to full agonist BZs
Because they are partial agonists, higher doses are required for anxiolytic activity which then introduces sedative properties
SSRIs
Block serotonin reuptake
First line treatment for some anxiety disorders
Use: OCD, Panic disorder, social phobia
Lack the addictive effect associated with benzodiazepines
Dampens brain excitability – mechanism differs from mechanism in depression
Gabapentin
FDA approved for:
Anticonvulsant; adjunctive therapy for treating partial seizures Certain types of nerve pain (shingles, diabetic neuropathy) Restless leg syndrome
Does not affect GABA metabolism or modulate GABA receptors or affect GABA reuptake
Reduces abnormal brain excitability by modulating voltage gated calcium channel density —> reducing excitatory activity
off-label use: alcohol withdrawal, neuropathic pain, fibromyalgia, bipolar disorder, postmenopausal hot flashes, essential tremors, anxiety, resistant depressant and mood disorders, irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), alcohol withdrawal, postoperative analgesia, nausea and vomiting, migraine prophylaxis, headache, interstitial cystitis, painful diabetic neuropathy, social phobia, generalized tonic-seizures, pruritus (itching), insomnia, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), and refractory chronic cough
Histamine
Synthesized in many tissues (mast cells, gastric mucosa, neurons in CNS and periphery)
Stored in granules/vesicles within mast cells and basophils
Mediator in allergic inflammatory response and secretion of gastric acid
Nodocromil
Mast cell stabilizer
Ophthalmic solution
Seasonal/perennial allergic conjunctivitis
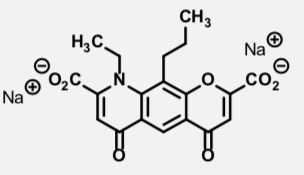
Lodoxamine
Mast cell stabilizer
Ophthalmic solution
Seasonal/perennial allergic conjunctivitis
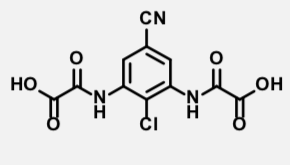
Cromolyn
Mast cell stabilizer
Prophylactic Use for:
Exercise induced bronchospasm (Inhaled powder) Bronchial asthma (Inhaled powder) Seasonal/perennial allergic rhinitis (nasal solution) Allergic conjunctivitis (ophthalmic solution)
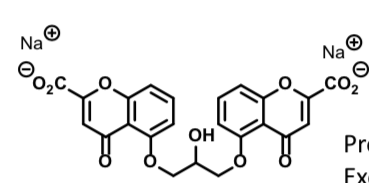
Pemirolast
Mast cell stabilizer
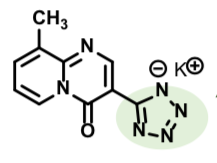
Ophthalmic solution
Relieves itching due to allergic conjunctivitis
First gen H1 receptor antihistamines - Anticholinergics
Significant anticholinergic side effects include dry mouth, blurred
vision, tachycardia, urinary retention, constipation
SAR
Two aryl groups (Ar1, Ar2) attached to X
X = N, CH-O-, CH2-N-, or CH
Spacer = un/branched methylene linker (CH2)n n = 2 or 3
R1, R2 = usually a small alkyl group, sometimes an alkylaryl
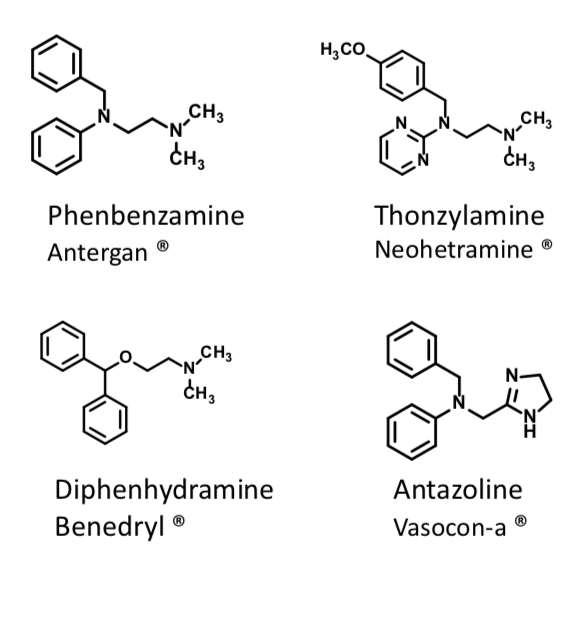
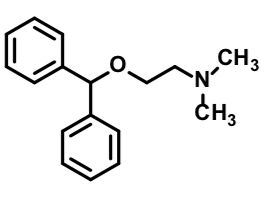
Diphenhydramine
First Gen H1 Antihistamine
Used for allergic conditions Oldest marketed antihistamine Oral tablet
Short half life
Wide safety margin
Sedation is a side effectused as an OTC sleep aid (Tylenol PM)
Clemastine
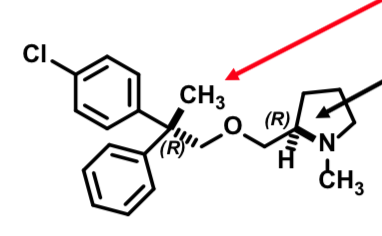
First Gen H1 Antihistamine
First stereocenter influences potency significantly
Second stereocenter is less important to potency
Indicated for the relief of symptoms associated with allergic rhinitis such as sneezing, rhinorrhea (runny nose), pruritus (itching), and lacrimation (watery eyes)
(R,R) isomer is most potent – sold as single diastereomer Less sedative than diphenhydramine
Oral tablet
First Gen H1 Antihistamines - Alylamines/Propylamines
First Gen H1 Antihistamine
Have longer half lives that permits once-a-day dosing Extended duration of action
Significantly fewer CNS side effects
Decreased anticholinergic affects
Decreased antiemetic effects
Cyclizine
First Gen H1 Antihistamine
Primary Uses:
vertigo, motion sickness (antiemetic effect)
Significant antihistamine and anticholinergic effects Drowsiness common
Hydroxyzine
First Gen H1 Antihistamine
Used for pruritus (itchy skin)
Significant antihistamine and anticholinergic effects Drowsiness common
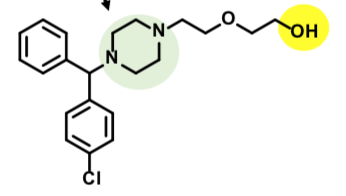
Cetirizine
Second generation H1 receptor antihistamine
“Nonsedating”
Oxidative Metabolized from Hydroxyzine (OH group attacked) and Cyclizine
No cardiotoxicity
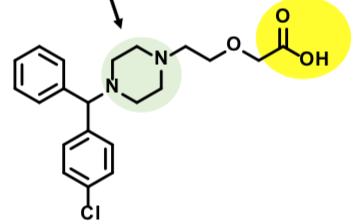
Promethazine
First Gen H1 Antihistamine
Usually have long durations of action
Pronounced sedative effects
Potent antihistamines
Also treats nausea/vomiting associated with anesthesia and motion sickness
*Sometimes combined with codeine for cough
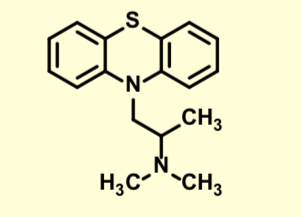
Cyproheptadine
First Gen H1 Antihistamine
Usually have long durations of action
Pronounced sedative effects
Potent antihistamines
Also treats nausea/vomiting associated with anesthesia and motion sickness
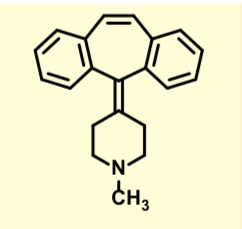
Tefinidine
Second Gen H1 Antihistamine
High concentrations of parent lead to hERG K+ channel inhibition
prolonged QT interval of heart
ventricular arrhythmias
Allegra
Second Gen H1 Antihistamine
Metabolite of Terfenidine/Seldane
Lacks hERG problem (no cardiac toxicity) Accounted for antihistamine activity of Seldane
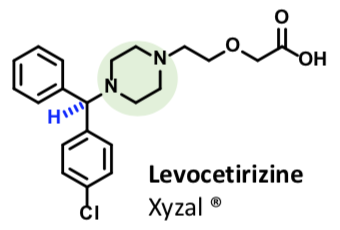
Xyzal/Levocetirizine
Second Gen H1 Antihistamine
Claims of increased efficacy and fewer side effects: (R) isomer dissociates from receptor more slowly than (S) isomer
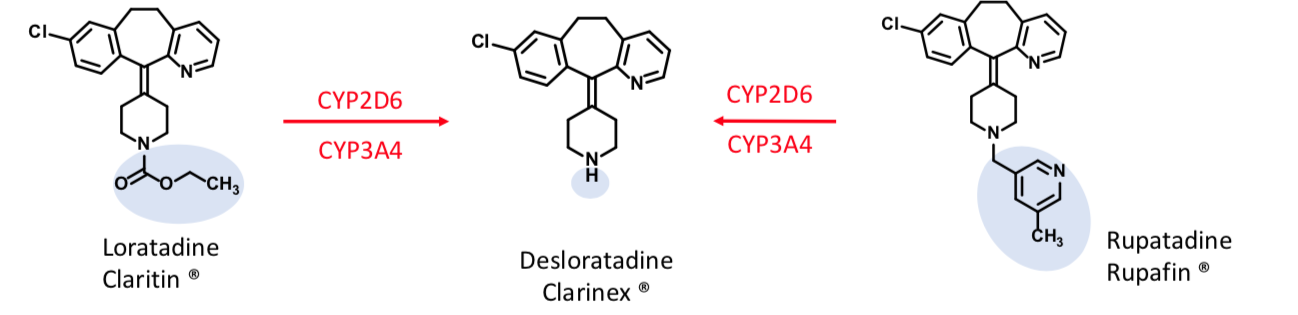
Desloratadine
Second Gen H1 Antihistamine
Loratadine:
Parent half-life ~ 8 h
Desloratadine:
Major metabolite of Loratadine and Rupatadine
Half-life ~ 24 h
More potent H1 inverse agonist than loratadine
Rupatadine:
Parent half life: 5-6 h
Also has anti-inflammatory activity: inhibits release of tumor necrosis factor (TNFα) and IL-6 in human mast cells and monocytes
Topical Antihistamines
MAST CELL STABILIZERS—> inhibit release of inflammatory mediators (including histamine)
H1 RECEPTOR INVERSE AGONISTS —> block histamine at its receptor
Applied to eye for relief of itching and congestion of the conjunctiva
Outside of US, some approved for systemic use
Azelastine
3 MOA:
Antihistamine at H1 receptor as inverse agonist
Stabilizes Mast cells to attenuate release of histamine and other allergy mediators
Anti-inflammatory (reduces production and concentrations of inflammatory mediators)
Most often used as nasal spray
Fast onset (minutes)
1-2 times daily application
Astepro Nasal Spray: hay fever/seasonal allergy (allergic rhinitis) Optivar Eye Drop: itchy eyes due to allergy (allergic conjunctivitis)
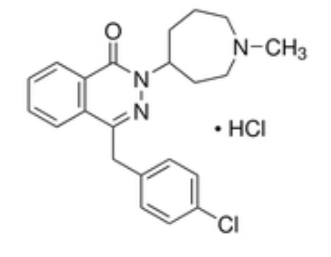
Thiourea
H2 Selective Inverse Agonist
Antihistamine
In clinical trials,
patients developed agranulocytosis
Thiourea responsible for toxicity
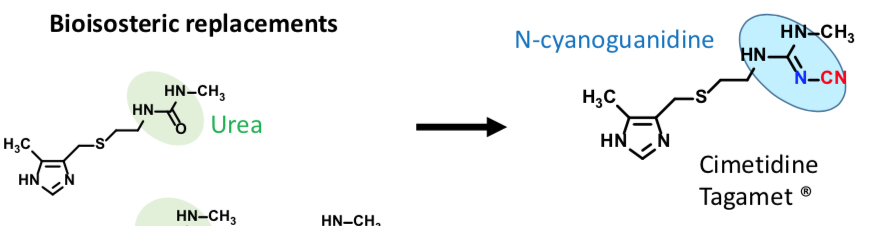
Cimetidine
H2 Selective Inverse Agonist
Active H2 antihistamine
Does not cause agranulocytosis
CYP450 inhibitor (due to imidazole) —> drug interactions
Ranitidine
H2 Selective Inverse Agonist
Was most widely used
Caused formation of NDMA which is a carcinogen
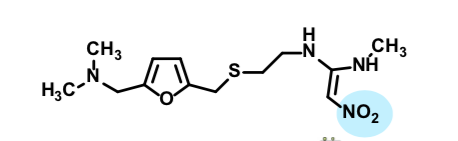
Famotidine
H2 selective inverse agonist
can be combined in formulations with antacid
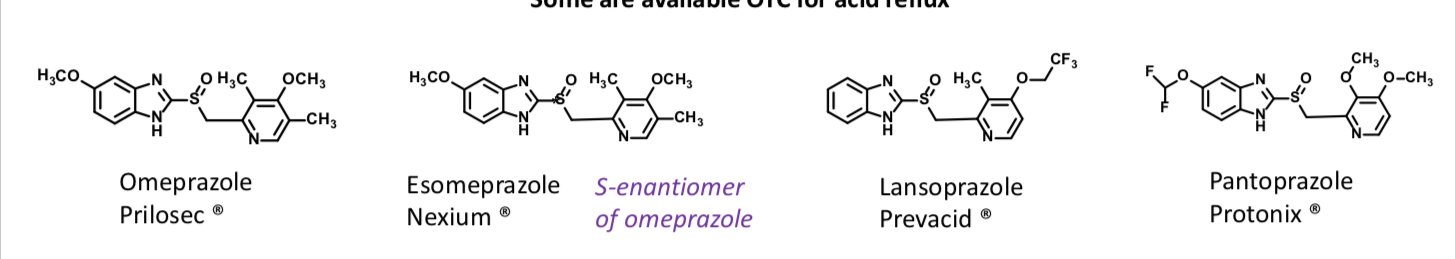
Proton Pump inhibitors
Proton pump inhibitor
Among the most widely sold drugs in the world
Inhibit the H+/K+-ATPase (proton pump)
Inhibits acid secretion even if receptors are activated by agonists
Sometimes combined with antibiotics to treat H. pylori infection
Irreversible, covalent inhibitors
Targets activated proton pumps that are acid-exposed
MOA:
The drug is unchanged in the blood – but at low pH (gastric acid), it rearranges to form an electrophilic intermediate A Cysteinyl sulfhydryl groups (SH) of the proton pump attack A to afford a covalently modified complex
The result is a disulfide bond (S-S) and an inactive enzyme
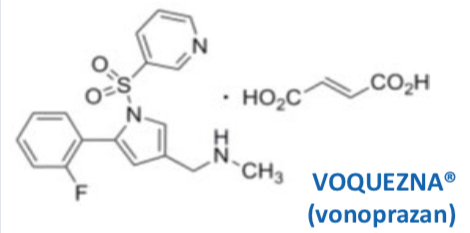
Voquenza
Potassium-Competitive Acid Blocker (PCAB)
Inhibits the H+/K+-ATPase (proton pump) – like PPIs
Inhibits acid secretion even if receptors are activated by agonists – like PPIs
No acid activation/ no PPIs) – NOT A PRODRUG
REVERSIBLE inhibitor (ionic bonding)
Targets activated proton pumps that are acid-exposed and resting state pumps
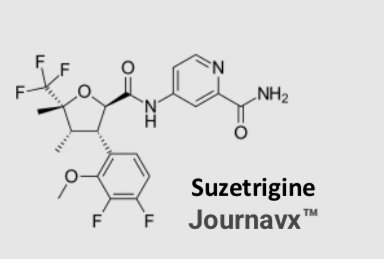
Jouravx
Approved for treating moderate to severe acute pain in adults
Oral drug
Selectively inhibits peripheral sodium NaV1.8 channels that modulate pain
Non-addictive - no evidence of withdrawal or drug-seeking behaviors (not linked to reward centers in brain)
Risk of Drug Interactions with Certain Hormonal Contraceptives
Risk of Adverse Reactions in Patients with Moderate and Severe Hepatic Impairment
Increased Risk of Adverse Reactions with Concomitant Use with Strong or Moderate CYP3A Inhibitors
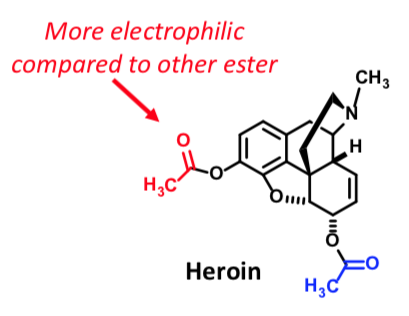
Heroin
PRODRUG: INACTIVE AT OP RECEPTORS AS IS!
More lipophilic than morphine
better BBB access
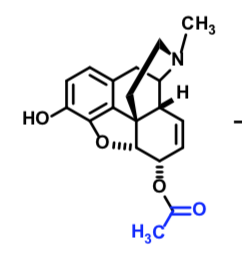
6-MAM
Heroin —→ (fast hydrolysis) This intermediate —→ (slow hydrolysis) Morphine
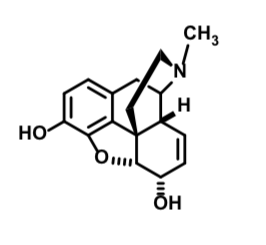
Morphine
Mu agonist
Metabolized by CYP450 to Normorphone
Codeine
poor μ agonist
but effective anti-tussive
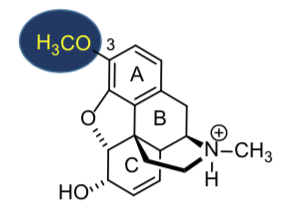
Morphine Sulfate
Full Mu agonist
More potent than codeine sulfate
Poor oral bioavailability due to GI and first pass (liver) metabolism
Metabolite can accumulate in patients with renal failure or poor function—>overdose
Extended release forms (Avinza ® and Kadian ®) available only for opioid tolerant patients
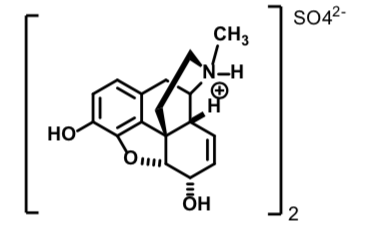
Codeine Sulfate
Full Mu agonist
(~ 10x less potent than morphine)
Prodrug: requires O-demethylation
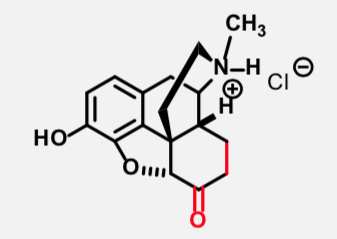
Hydromorphone
Multicyclic Full Mu Agonist
(8-10x more potent than morphine)
Also increases toxicity, constipation, especially respiratory depression (black box warning)
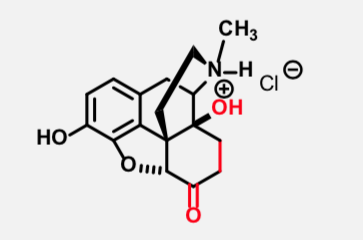
Oxymorphone
Multicyclic Full Mu Agonist
(~ 10x more potent than morphine)
Uses: chronic pain, maintain anesthesia, and obstetric analgesic
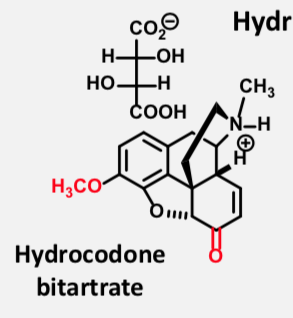
Hydrocodone Barbituate
Multicyclic Full Mu Agonist
Only available as combo with acetaminophen (Vicodin), ibuprofen (Vicoprofen), or cough suppressant preps (Hycodan)
Prodrug
Good oral bioavailability; much more active than codeine
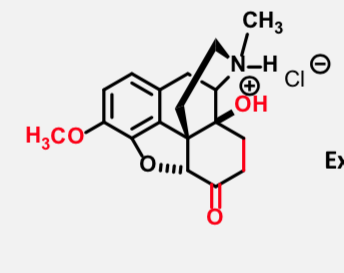
Oxycodone
Multicylic Full Mu Agonist
Extended release: oxycontin
High abuse potential
Prodrug
Good oral bioavailability; much more active than codeine
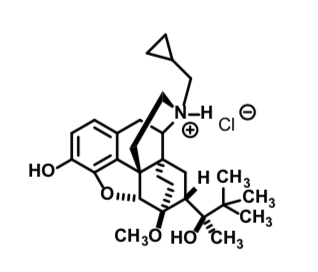
Buprenorphine HCL
Partial Mu agonist (note the alkylcyclopropyl group, aside from other structure changes) 25-40x more potent than morphine
Pseudo-irreversiblehalf life ~ 37 hours Can be useful in detoxification
Will precipitate withdrawal in patients dependent on full agonists but will also suppress symptoms of full blown withdrawal
Formulations: IV, sublingual, transdermal patch
Transdermal patch (Butrans ®) – avoid high temperatures or release of drug is higher
Use: Opioid Addiction Recovery
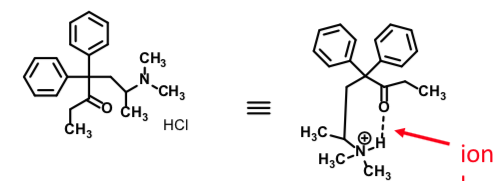
Methadone HCL
Flexible Opioid receptor agonist
Full mu agonist (and activity at non opioid receptors)
Oral tablet/solution/IV inj for pain; ‘Swish and spit’ – 2.5 minutes, 85% dose absorbed; avoids 1st pass metabolism
Use: IV addiction recovery (most common); neuropathic and opioid resistant pain
Respiratory depression and cardiac toxicity side effect
outlast the analgesia effects
Metabolized to seve
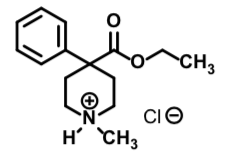
Meperidine Hydrochloride
Flexible Opioid receptor agonist
1/10th the potency of morphine
Full mu agonist
No GI motility inhibition
No cough suppression
Half life ~ 3-4 h
Use: obstetrics, post operative pain, low dose short term pain management
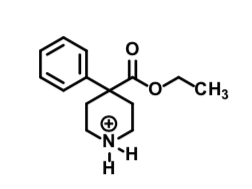
Normeperidine
Flexible Opioid receptor agonist
Full mu agonist
About 1⁄2 potency as meperidine
T1/2 = 14-21 h (normal renal function)
Can induce seizure not easily reversed by naloxone
Fentanyl Citrate
Flexible Opioid receptor agonist
Full mu agonist
Rapid onset, short duration, half life ~ 30-60 min
Use: IV adjunct to anesthesia (most common);
chronic pain due to cancer, pediatric burn patients
CAUTION: overdose risk, esp kids handling patches
SE:
High abuse potential
Respiratory depression risk is significant
Fentanyl effects can outlast reversing agents
Black box warning
Sufentanyl citrate
Flexible Opioid receptor agonist
600-800x the potency of morphine
Full mu agonist
Rapid onset, short duration
Half life ~ 15-20 min
Shorter post-anesthesia recovery
Use: IV adjunct to anesthesia in opioid tolerant/dependent patients
Remifentanil
Flexible Opioid receptor agonist
Full Mu agonist
Use: IV adjunct to anesthesia: has sedative effects in addition to analgesic effects
less hypnotic anesthesia needed
(enables use of high dose opioid/low dose anesthesia)
Administration: continuous infusion during surgery or post-operative
Very short post-anesthesia recovery
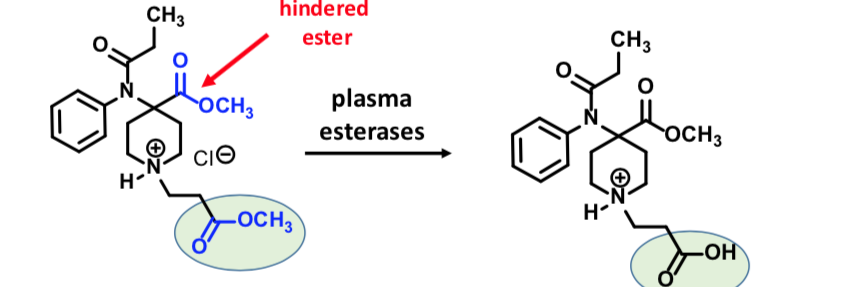
Seglentis
Atypical Opioid Receptor Agonist
Combines an analgesic (tramadol) + anti-inflammatory (celecoxib)
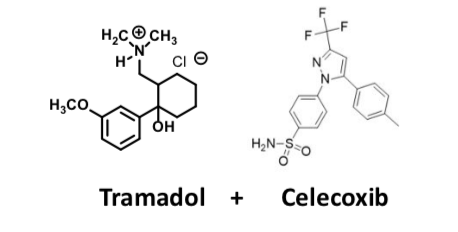
Tramadol
Atypical Opioid Receptor Agonist
used to treat severe acute pain; Second line for neuropathic pain!!!
Dual action – inhibits serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake (SNRI) AND is a mu (μ) agonist
Must be careful with other 5-HT-NE reuptake of 5-HT enriching agents to avoid toxicity
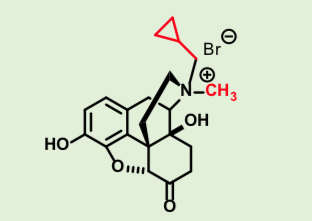
Methylnaltrexone Bromide
Multicyclic Opioid Receptor antagonist
4° salt - can’t penetrate CNS
Effective in periphery
Use: reverse opioid
induced constipation
subQ, every other day