bio shit
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/36
Last updated 10:28 PM on 3/5/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
1
New cards
cell
they are the “ unit of life”, they provide structure for the body, take nutrients, from food, convert those nutrients into energy, and carry out specialized functions
2
New cards
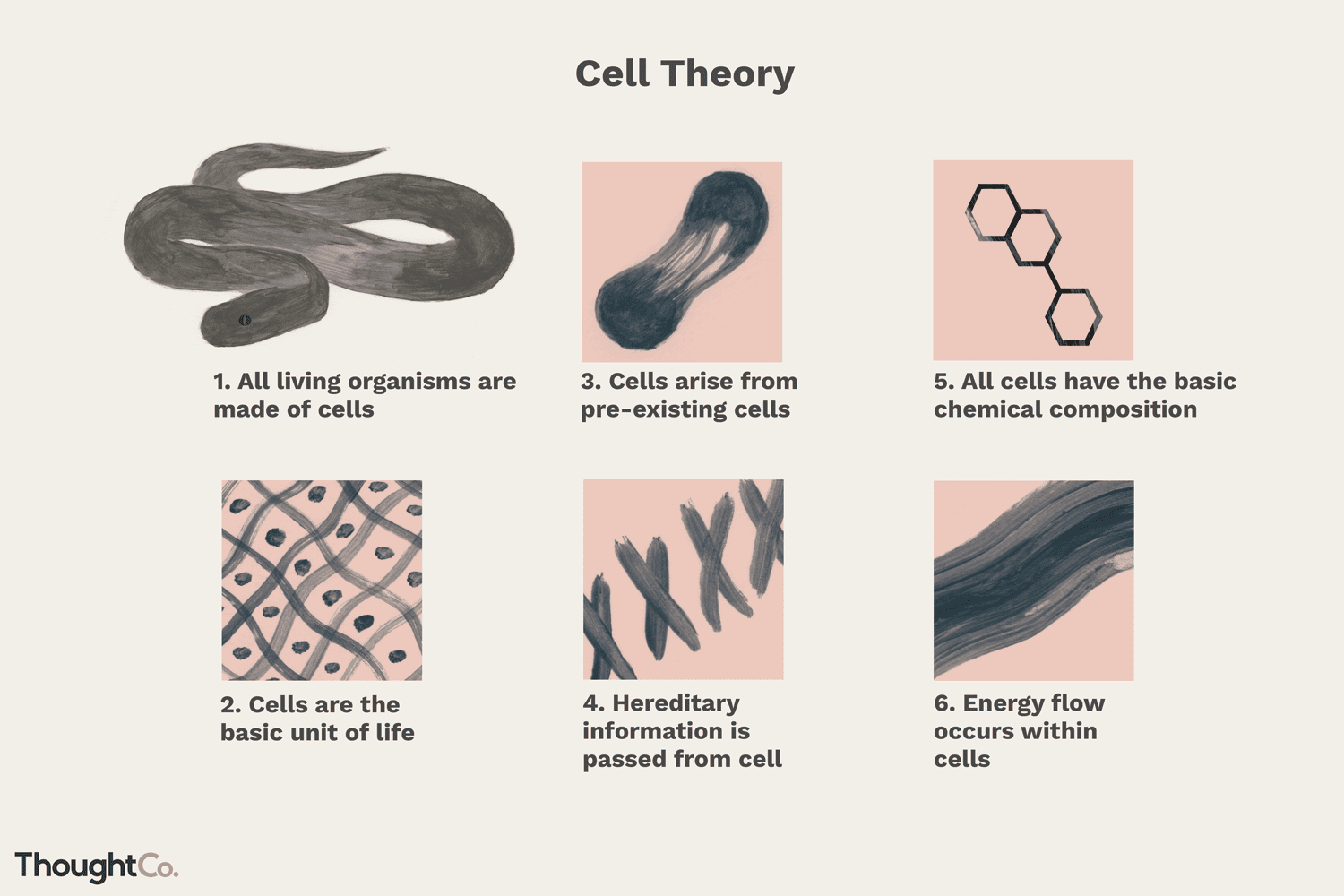
cell theory
1. the cell is the smallest living unit in all living organisms
2. all living things are made of cells
3. all cells come from other pre-existing cells
3
New cards
Cell membrane
controls what comes into and out of the cell, it’s found in plant and animal cells
4
New cards
cell wall
ridged outer layer of plant cell
5
New cards
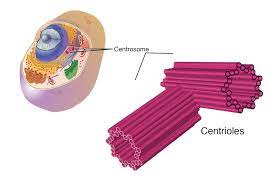
centriole
paired barrel-shaped organelles located in the cytoplasm of animal cells near the nuclear envelope
6
New cards
chloroplast
captures energy from the sunlight and uses it to produce food in a plant cell
7
New cards
cilium
moves water relative to the cell in a regular movement of the cilia. This process can either result in the cell moving through the water, typical for many single-celled organisms, or in moving water and its contents across the surface of the cell
8
New cards
cytoplasm
gel-like fluid where organelles are found
9
New cards
Endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
\n
passageways that carry proteins and other materials from one part of a cell to another, (transporter of proteins, etc.)
passageways that carry proteins and other materials from one part of a cell to another, (transporter of proteins, etc.)
10
New cards
Endsymbiosis
__symbiosis__ in which one of the __symbiotic__ __organisms__ lives inside the other.
11
New cards
Eukaryote
any cell or organism that possesses a clearly defined nucleus.
12
New cards
Flagellum
a motility organelle that enables movement and chemotaxis
13
New cards
golgi apparatus
a factory in which proteins received from the ER are further processed and sorted for transport to their eventual destinations: lysosomes, the plasma membrane, or secretion
14
New cards
lysosome
a membrane-bound cell organelle that contains digestive enzymes. They break down excess or worn-out cell parts.
15
New cards
nucleus
control center of the cell, contains DNA
16
New cards
mitochondria
produces the energy a cell needs to carry out its functions
17
New cards
organelle
A small structure in a cell that is surrounded by a membrane and has a specific function.
18
New cards
prokaryote
Prokaryotes are single-celled organisms belonging to the domains Bacteria and Archaea. Prokaryotic cells are much smaller than eukaryotic cells, have no nucleus, and lack organelles. All prokaryotic cells are encased by a cell wall. Many also have a capsule or slime layer made of polysaccharide.
19
New cards
ribosomes
assembles amino acids to create proteins
20
New cards
vacoles
stores food, water, waste, and other materials
21
New cards
active transport
molecules move across a concentration gradient from low to high concentration
22
New cards
aquaporins
protien channel which water flows thru
23
New cards
concentration gradient
measurement of how the concentration of something changes from one place to another
24
New cards
diffusion
the movement of individual molecules of a substance through a semipermeable barrier from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration
25
New cards
endocytosis
the ingestion of large particles (such as bacteria) and the uptake of fluids or macromolecules in small vesicles
26
New cards
Exocytosis
when nutrients and other things r pushed out/ leave the cell
27
New cards
Facilitated diffusion
the passive movement of molecules along the concentration gradient.
28
New cards
hypertonic
cell shrinks, water flows out of cell to “equal concentration”
29
New cards
hypotonic
the cell gets PHAT and bursts, water goes into the cell to balance solute, lower concentration of solute compared to cell
30
New cards
isotonic
equal concentration of solute inside and outside the cell, no net movement
31
New cards
lipid bilayer
A lipid bilayer is a biological membrane consisting of two layers of lipid molecules. Each lipid molecule, or phospholipid, contains a hydrophilic head and a hydrophobic tail.
32
New cards
osmosis
osmosis is the movement of water molecules from a solution with a high concentration of water molecules to a solution with a lower concentration of water molecules, through a cell's partially permeable membrane.
33
New cards
osmotic pressure
the pressure which needs to be applied to a solution to prevent the inward flow of water across a semipermeable membrane.
34
New cards
plasmolysis
typical response of plant cells exposed to hyperosmotic stress, ***when plant cells lose water after being placed in a solution that has a higher concentration of solutes than the cell does***.
35
New cards
passive transport
the process of transporting molecules from one side of the membrane to the other without any energy requirements
36
New cards
selectively permeable
Selective permeability of the cell membrane refers to its ability to differentiate between different types of molecules, only allowing some molecules through while blocking others
37
New cards
tonicity
the capability of a solution to modify the volume of cells by altering their water content.