Anantomy spine osteology
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
The axial skeleton consists of (4)
❑ Vertebral column
❑ Cranium
❑ Sternum
❑ Ribs
The vertebral column is composed of a series of
individual _____ (vertebrae) articulated in a series of _____ bound together by deformable ____
bones, curves, discs
Vertebral column function
Provides a rigid but flexible axis for movement
❑ Provides a ____ _____ for suspending structures (ie. ribs) that allow body to maintain cavities with relative constant shape and size
❑ Creates a ____ between the upper and lower extremities
❑ Provides ______ for the spinal cord
firm base
link
protection
5 regions of vertebral column
Cervical
❑ Thoracic
❑ Lumbar
❑ Sacrum
❑ Coccyx
CERVICAL
__ cervical vertebrae of the neck
■ Appearance varies greatly from C1 to C7
■ Connects the ___ to the rest of the ____
■ Allows for a great deal of ___
■ Distinctive feature is ____ _____ !!!!
CRUNCHY BREAKFAST AT 7AM
WHAT HEAD??
7
head, body
movement
transverse foramen
ELEPHANT HEAD
Cervical Curvature
Lordotic (anterior) (left)
THORACIC
__ thoracic vertebrae
■ Suspends the ____
■ Less ____ and more ____ than cervical because of rib Articulations
■ Supports the ____ (respiratory) cavity
■ Distinctive feature is ____ ____!!!
TASTY LUNCH AT 12PM
WHAT ANIMAL HEAD??
7
ribs
flexible, stable
thoracic cavity
costal facets
GIRAFFE
Thoracic curvature
Kyphotic (right) (posterior)
LUMBAR
___ lumbar vertebrae
■ Posterior to the abdominal cavity
■ Allows mobility between the ____and the ____
■ Provides support for the upper skeleton and______
■ Distinctive feature is ____ ____
LIGHT DINNER AT 5PM
WHAT ANIMAL HEAD?
5
thorax and pelvis
upper extremities
mamilary process
MOOSE HEAD
Lumbar curvature
Lordotic (left) (anterior)
SACRUM
__ fused sacral vertebrae
■ Unites vertebral column with the pelvic girdle to which it is strongly bound
■ support body _____
transmits upper extremity forces to the lower extremities
SMALL SNACK AT 5pm
-fused together
5
weight
Sacrum curvature
kyphotic (right) (posterior)
Coccyx has
_ segments
_____ curvature
-fused together
4
kyphotic
Kyphotic curves (right) (posterior) (2)
thoracic region
sacral region
Lordotic curves (left) (anterior) (2)
found in regions of greatest mobility
cervical region
lumbar region
Each vertebra has the following:
❑ Vertebral ____
❑ Vertebral ___
❑ 7 _____
body
arch
processes
__ and __ have their own bony landmarks that are generally distinct from the other vertebra
C1 and C2
which increases in size from C2 to L5 to accommodate progressively increasing loads?
vertebral body
Verterbral body is made up of (3)
Trabeculae
❑ Ring apophyses
❑ Vertebral endplates
Joins vertebral foramen to vertebral body
-protects and creates a safe space for spinal cord
■ Protects neural tissue
■ Primarily made of cortical bone
vertebral arch
verterbal arch contains (3)
the body
lamina
pedicle
Ventral part of vertebral arch
❑ Superior and inferior vertebral notch
pedicle
Extend dorsally from the pedicles and fuse at midline
-vertebral arch
lamina -
Projects dorsally from junction between the two laminae
❑ Function as levers for the back extensors
spinous process
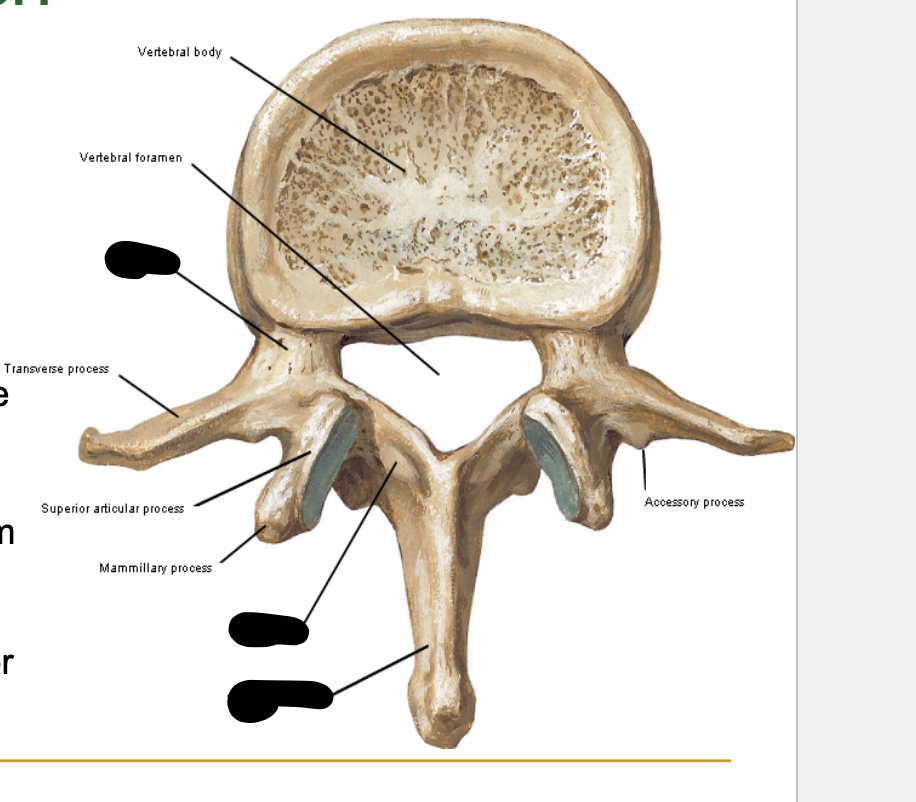
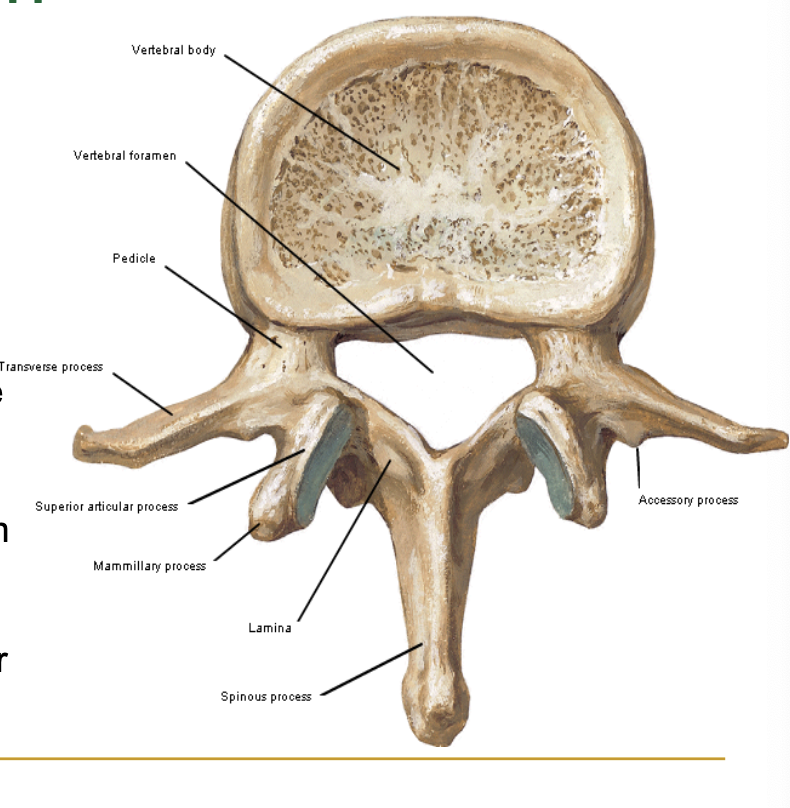
Project laterally from the junction between the pedicles and laminae
(apart of vertebral arch)
Transverse processes
what houses the spinal cord???
vertebral foramen
What passes through the intervertebral foramen?
spinal nerves from spinal cord
The ____ vertebral ____ of the ___ vertebra
with the ____ vertebral notch of the ____ vertebra
form an intervertebral foramina
inferior verterbral notch of the above
superior vertebral notch of the below
Paired articular processes extending from junctions of pedicles and laminae
zygapophyses - vertebral arch
Between superior and inferior facets
pars interarticularis - vertebral arch - location
transverse processes serve as ___ for muscles
levers
Synovial joints between superior articular process and inferior articular process of adjacent
vertebra?
-they Extend from junctions of pedicles and laminae
zygapophyses (facet)
Zygapophyses are enclosed by a ____ ____ ___
fibrous joint capsule
do zygapoohyses have the same or different characteristics in cervical, thoracic, and
lumbar spine?
different
Region between the superior and inferior articular processes?
Pars interarticularis
defective pars interacrticularis?
Spondylolysis
anterior displacement of pars interarticularis
-lower back pain, buttocks, posterior leg
Spondylolisthesis
Vertebrae that some characteristic features of both adjacent spinal segments?
transitional vertebrae
transitional vertebrae occurs where ____ of vertebrae markedly changes from one level to the next
morphology
3 transitional vertebrae
Cervicothoracic
❑ Thoracolumbar
❑ Lumbosacral
Intervertebral Disc
■ General Characteristics
❑ Fibrocartilaginous
❑ Major _____-______ structures of the spine
❑ Interposed between adjacent vertebrae
❑ Relatively ______ (no blood flow)
❑ Deeper anteriorly in lumbar and cervical regions contributing to the anterior convexities
compression bearings
Avascular
where do intervertebral discs present themselves?
C2 to S1
Fibrous strands within proteoglycan gel
❑ Smallest cervical, largest lumbar
1 out of two making up intervertebral discs
nucleus pulposus
Attaches to rim of vertebral body
❑ Concentric fibrocartilage and collagen bands
2 out of two making up intervertebral discs
annulus fibrosus
ligaments of intervertebral joints (2)
❑ Anterior longitudinal ligament (ALL)
❑ Posterior longitudinal ligament (PLL)
ligaments of veterbral arch (5)
❑ Ligamentum flavum
❑ Supraspinous ligament
❑ Interspinous ligament
❑ Nuchal ligament
❑ Intertransverse ligaments
location of anterior longitudinal ligament
anterior occiput to S1
Firmly attached to margins of the vertebral bodies and discs and less firmly to the midparts of the bodies
action of Anterior Longitudinal Ligament A.L.L
limits hyperextension
A.L.L is ____ and ____ in thoracic region and
_____ and _____ in cervical and lumbar
thicker and narrow
broad and thinner
what ligament is located in Body of axis (C2) to S1 along the posterior aspect of the vertebral bodies
■ Lies within the vertebral canal
PREVENTS HYPERFLEXION
Posterior longitudinal ligament
what ligament prevents posterior displacement of disc?
■ and Does not attach to discs in cervical spine?
Posterior longitudinal ligament
P.L.L is _____ in lumbar spine and thickest in _____
narrow, thoracic
what ligament connects laminae of adjacent vertebrae from C1-Sacrum
■ Thickest in the lumbar spine
Composed of yellow elastic tissue (elastin)
Ligamentum Flavum
whats the action of ligamentum flavum?
helps maintain curvature of spine
what ligament extends from C7 to sacrum
■ Connects the tips of spinous processes
thick in the lumbar spine
LIMITS FLEXION
supraspinous ligament
what ligament extends between spinous processes to attach along the length of the spinous process
LIMITS FLEXION
■ Thickest in the lumbar spine
■ lacking in the cervical spine
interspinous ligament
what ligament is from the external occipital protuberance and the foramen magnum to the spinous processes cervical vertebra
■ Continuation of supraspinous ligament
nuchal ligament
what liagment is from C1 to S5
■ Connects adjacent transverse processes
■ Limits contralateral side-= bending
■ Inconsistent in cervical spine, thicker in thoracic, thin sheets in lumbar
intertransverse ligament
what is contained within the vertebral canal
part of central nervous system (CNS)
spinal cord
spinal cord has enlargements in gray matter in _____ and _____ regions
cervical and lumber
spinal cord Gives off spinal nerves that combine in plexi to form ____ nerves
■ Developmentally the cord segments initially line up with the bony vertebral _____
peripheral
column
The spinal cord stops growing, but the vertebral_____ continues to grow, thus out distancing the spinal cord in length
■ Conus Medullaris of the spinal cord is usually at L2-L3
❑ Attaches to the _____ via: filum terminale
■ The collection of terminal spinal nerves at the end of the spinal cord is called the Cauda Equina
column
Coccyx