HSC Chapter 6 Urinary System
1/122
Earn XP
Description and Tags
sf college
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
123 Terms
Urinary system
removes waste from the body, regulates fluid volume, assists in blood pressure regulation, and maintains electrolyte concentration in the body fluid
Kidneys
two bean-shaped organs on each side of the vertebral column
Nephron
urine-producing microscopic structure: 1 million __ in each kidney
Renal pelvis
funnel-shaped reservoir that collects urine and passes it to the ureter
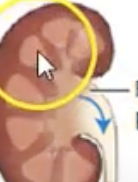
Ureters
two slender tubes (10-13 inches) that receive urine and carry it into bladder
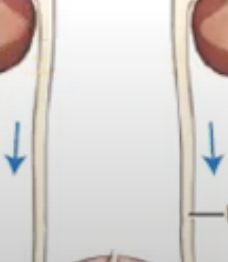
Urinary Bladder
muscular, hollow organ that temporarily holds urine
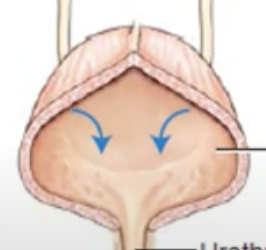
Urethra
lowest part of urinary tract through which urine passes from the urinary bladder to outside
Urinary meatus
the opening through which urine passes to outside

How long is female urethra
1.5 inches
How long is male urethra
8 inches
cyst/o, vesic/o
bladder
glomerul/o
glomerulus
meat/o
meatus
nephr/o, ren/o-
kidney
pyel/o
renal pelvis
ureter/o
ureter
urethr/o-
urethra
albumin/o
albumin
azot/o
urea/nitrogen
blast/o
developing cell
glycos/o, glyc/o
glucose/sugar
hydr/o
water
lith/o
stone
noct/i
nocturnal/night
olig/o
a few
urin/o, ur/o
urinary tract
-iasis
condition
-esis
condition
-lysis
dissolution, spreading, breaking down
-ptosis
suturing, repairing
-tripsy
surgical crushing
-trophy
developing
-uria
urine/urination
-rrhagia
excessive bleeding, dscharge
-gram
x-ray image
-graphy
process of recording
azotemia (uremia)
urea in blood
cystitis
inflammation of water
-cele
protrusion, hernia, swelling
cystocele
protrusion of the bladder
Cystolith
stone in the bladder
Melgaly
enlargement
hematuria
blood in urine
azotemia/uremia
urea and other waste products in blood
is hematuria a symptom
yes
is Azotemia a symptom
no, its a serious disorder
renal failure
kidney failure
acute kidney failure
Abrupt decline in kidney function that occurs over hours to days and it’s usually reversible
Chronic Kidney Disease
Progressive, irreversible loss of kidney function
End Stage Renal Disease
Condition in which kidneys no longer function on their own, Dialysis or kidney transplantation is necessary for survival.
Epispadias
congenital defect, urinary meatus is located on the upper surface of penis
Hypospadias
congenital defect, urinary meatus is located on the underside of penis of male and meatus is unusually located in females.
Polycystic Kidney Disease
progressive disease, kidney contains many cysts interfering with urine production
Renal Calculus/i
stone in the kidney
Renal Hypertension
elevated blood pressure from kidney disease
Urinary Retention
accumulation of urine in the bladder because of inability to urinate
Urinary Suppression
Sudden stoppage of urine formation
Urinary tract infection
infection of one or more organs of the urinary tract
Extracorporeal Shock Wave Lithotripsy
noninvasive, crushes stone(s) in the kidney or ureter by administration of repeated shockwaves (fragments passed in urine)
Fulguration
destruction of living tissue with an electrical spark (destroys bladder growths)
Renal Transplant
implantation of a donor kidney into a patient with inadequate renal function
Blood Urea Nitrogen
blood test that measures the amount of urea in the blood. If elevated can indicate abnormal renal function.
Creatinine
blood test that measures creatinine in the blood. If elevated indicates impaired kidney function
KUB (kidney, ureter, bladder)
Image of the abdomen. Determines size, shape and location of kidney, ureters, and bladder. Can also find stones and diagnose intestinal obstructions
Specific gravity
test performed on urine to measure the concentrating or dilution ability of the kidneys
Urinalysis
multiple routine tests performed on urine to look for glucose, protein, blood, and other substances in urine.
Urine Culture and Sensitivity
test performed on urine specimen to determine the presence of bacteria and yeast: used to diagnose urinary tract infections.
Catheter
flexible, tubelike device to withdrawal or instill fluids
Distended
stretched out bladder (full of urine)
Electrolytes
minerals in the body, such as sodium and potassium that carry an electrolyte charge
Enuresis
Involuntary urination
Hemodialysis
procedure for removing impurities from the blood because of an inability of the kidneys to do so
Incontinence
Inability to control the bladder or bowels
Micturate
to pass urine (urinate)
Peritoneal dialysis
procedure for removing toxic wastes when the kidney is unable to do so. The peritoneal cavity is used as a receptacle for the fluid used in the dialysis.
Prolapse
Displacement of an organ or anatomic structure from its normal position (also called prolapse)
Stricture
abnormal narrowing, such as a urethral stricture
Urinal
receptacle for urine
Urinary catheterization
passage of a catheter into the urinary bladder to withdraw urine
Urodynamics
pertaining to the force and flow of urine within the urinary trac
Void
to empty or evacuate waste material, especially urine
Acute renal failure (ARF)
sudden and can be fixed is treated immediately
Chronic kidney disease (CKD)
progessive failure but can be transplanted out
End-stage Renal Disease (ESRD)
kidney is too poor to sustain life
Are kidney’s more toward front or back
Back
Extracorpeal shock wave lithotripsy
breaking kidney stones so they can be passed through urine
Fulgaration
the destruction of small growths or areas of tissue using diathermy.
Renal transplant
kidney transplant
Dianostic imaging/ KUB
kidney, ureter, bladder
Labratory
Blood urea nitrogen, creatinine, specific gravity (SG), urinalysis (UA)
Catheter
thin tube that goes through urethra to drain urine
Distended
stretched out
Electrolytes
minerals within body
Enuresis
involuntary urination
Hemodialysis
procedure that removes fluid from body when kidneys are unable to
Incontinence
inability to control bladder/bowels
Micturate
urinate
Peritoneal dialysis
treatment that removes waste from kidney through bags being swapped out
Stricture
narrowing of tubular structure in body
Urinal
receptacle for collecting urine