CHEM 320 - lecture13 - Simple bonding theory & Symmetry
1/12
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
symmetry elements
geometrical entity such as a line, a plane, or a point, with respect to which one or more symmetry operations can be carried out
symmetry operation
a movement of a body such that the appearance after the operation is indistinguishable from the original appearance
AKA after moving the elements around, the molecule shoudl look the same
E
identity operation
all molecules have it by existing
Cn
rotation by 360/n degrees around a n-fold symmetry axis
Ex: C2 means a rotation axis that you rotate 180 degrees around
σ
reflection operation across a mirror plane
exchange of points through a plane to an opposite and equidistant point
i
inversion of a molecule about a center/point of inversion
each point moves through a common central point to a position opposite and equidistant
Sn
rotation by 360/n degrees followed by reflection perpendicular to rotation axis
n-fold axis of IMPROPER ROTATION
principal axis of rotation
the axis of rotation with the HIGHEST n value (Cn)
trigonal planar
___ molecules often have a C3 principal axis of rotation and additional C2 rotation axes through the outer atoms
linear
__ molecules tend to have a principal rotation axis of infinite order/value C_infinity
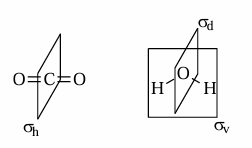
σv
mirror plane CONTAINING principal axis of rotation
vertical plane
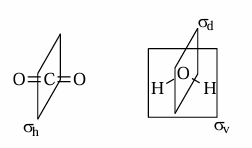
σd
mirror plane CONTAINING the principal axis of rotation but NOT the outer atom
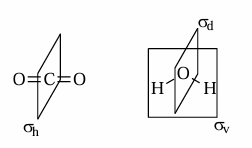
σh
mirror plane PERPENDICULAR to principal axis of rotation