Chemistry in a Nutshell
1/161
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
162 Terms
Chemistry
branch of science that deals with the study of matter and the ways in which different form of matter combine with each other
element
a substance that cannot be broken down into any substance and made with its own type of atom
compound
a molecule made from two or more different element that have been chemically joines (ex. H2O and NaCl)
molecule
two or more atoms connected by chemical bonds which form the smallest unit of a substance that retains the composition and properties of that substance
mixtures
a physical combination of two or more substances that aren’t chemically joined
homogenous mixture
is a mixture that has the same composition throughout
heterogenous mixture
a mixture with distinguishable features and not spread throughout
solution
a homogenous mixture with tiny particles that are too small to see and filtered out of the mixture
colloid
homogenous mixture with medium-sized particles that are large enough to see but not large enough to settle
suspension
heterogenous mixture that is large enough to see and to settle and be filtered out of the mixture
matter
is anything that occupies space and has mass
plasma
an extremely hot, ionized gas; compromised of negatively charged atoms and positively charged atoms
Bose-Einstein condensate
forms at temperatures near absolute zero Kelvin, without additional energy to transfer, the atoms began to clump into a super-atom
Quark-gluon plasma
forms at extremely high temperatures that are so hot, the individual quarks
degenerate matter
an extremely denser state of high energy atter found in the heart of neutron stars and white dwarfs
liquid
a substance that retains its size and shape of a container; has definite volume but no definite shape
solid
substance that retains its size and shape without a container; has definite shape and volume
gas
substance that can move freely and can take the shape of the container; has no definite shape and volume
melting
phase change where solid turn to liquid
freezing
phase change where liquid turns to solid
evaporation
phase change where liquid turns to gas
condensation
phase change where gas turns to liquid
sublimation
phase change where solid turns to gas
deposition
phase change where gas turns to solid
intensive property of matter
properties of matter that does not depend on the size or quantity of matter in any way
intensive property of matter
odor, color, melting point, ductility, malleability, electric conductivity, pressure, boiling point, luster, freezing point and density is an example of what properties of matter?
extensive property of matter
properties of matter that depends on the system size or the amount of matter on the system
extensive property of matter
mass, length, weight, and volume are example of what properties of matter
atomic number
the number of protons in an atom is referred as?
isotopes
forms of the same atom that differ only in their number of neutrons
isomers
forms of the same molecule that differs only in its structure
allotropes
forms of the same element that differs only on its physical appearance
atomic mass
simply the total mass of an atom that is generally expressed in atomic mass unit (amu)
radioisotopes
process of isotopes in which they release, emit, kick out, subatomic particles to reach a more stable, low energy configuration
decay
process in which radioisotopes release particles and energy
half-life
period in which half of the material will decay to a different, relatively stable product
subatomic particles
particles smaller than atoms
protons, neutrons, electrons
what are the three subatomic particles
protons
origination of positive charges of an atom
electrons
negatively-charged atoms found outside the nucleus
neutrons
neutrally-charged subatomic particles
Ernest Rutherford
discovered the proton’s existence in 1919 when he projected alpha particles in the gold foil and the positive alpha particles were deflected
Sir John Joseph Thomson
discovered the electrons in 1897 after experimenting involving cathode rays
electrons, protons - neutrons
___________ have less mass than _________ and ________.
ions
are produced if the number if protons and electrons are unequal
cations - anions
positive ions are _______ while negative ions are ________
James Chadwick
discovered neutrons when he demonstrates a penetrating radiation incorporated beams of neutral particles
ionic compounds
formed when metal compounds lose one or more electrons to nonmetal atoms
molecular compounds
inorganic compounds that take the form of discrete molecules
chemical formula
expression that shows the elements in a compound and the relative proportions of those elements
combination reaction
also known as synthesis reaction; it is a reaction in which two ir more substance combine to form a single new substance
combination reaction
A + B = AB
decomposition reaction
decomposition reaction
AB —> A + B
single replacement method
reaction in which one element replaces the similar element in a compound; happens mostly in the interswitch of metals and nonmetals
single replacement method
A + BC —> AC + B
double replacement method
reaction in which the positive and negative ions of two ionic compounds exchange places to form two new compounds
double replacement method
AB + CD —> AD + BC
combustion method
is a reaction in which a substance react eith oxygen gas releasing energy in the form of light and heat, it must involve oxygen as a reactant as well as hydrocarbons
hydrocarbons, carbon dioxide - water
in a combustion reaction, ________ react with oxygen gas to form _______ and ______.
H2, N2, O2, F2, Cl2, Br2,and I2
What are the seven diatomic molecules that exist in nature?
mole
it is the SI quantity for chemical entity
6.022 × 1023
Avogadro’s number that states the absolute number of elementary entities in one mole
molar mass
the mass of a given substance divided by its amount of substance presented in g/mol
valence electrons
are the electrons found in the outermost shell
subshells
consist of s-subshell. p-subshell, and more; it determines the placement of electrons from the nucleus
principal values
also referred as the periods in the periodic table; the horizontal array of elements that determines the subshell of an atom
electron configuration
refers to the arrangements of electrons in an atom
non-metals
these are anions with negative charge (ex. H, C, N, O, P, S, Se)
metals
cations with positive charge
halogens
these are chemical elements that forms salt when reacted with nonmetals (ex. F, Cl, Br, I, As, Ts)
atomic element
an element represented with no subscript (ex. Fe)
molecular compound
compound made up of two nonmetals
ionic compound
compound made up of a metal and a nonmetal
molecular element
a substance made of atoms of the same element
Stock system
a formal and modern distinction of naming an ion by using roman numerals (ex. iron (iii) ion)
Classical/Common name
prelavent distinction of naming ions majorilly used in health science (ex. ferric ion)
-ic, -ous, -ide
cations use suffix ____ if it uses three or more cation charges and _____ if it uses two charges, however the suffix ____ ide is used for anions
acid
a molecular compound that contains one or more hydrogen atoms and produces hydrogen ions when dissolved in water
binary acid
an acid that consists of a hydrogen and one other element mostly halogens
hydro - (base name of nonmetal) - ic + acid
how do we name binary acid?
oxyacid
an acid that contains a hydrogen, an oxygen, and a third element, mostly nonmetal
Boron group
elements who belong in group 13 or Group3A and classified as metalloids having properties of both metals and nonmetals
Carbon group
elements that belong in Group 14 (ex. carbon, silicon, tin, and lead)
Nitrogen group
elements that belong in Group 1 or 5A (ex. nitrogen, phosphorus, arsenic)
halogens
elements in group 17 or Group 7A; they are reactive non-metals that form very acidic compounds with hydrogen to form simple salts (-ine elements)
Chalcogens
elements in Group 16 or group 6A (ex. oxygen, sulfur, selenium)
noble gases
occupies group 0 or group 18 and known to be unreactive because they are stable and follows an octet rule (except hydrogen) (ex. hydrogen, argon, neon, krypton. xenon, radon, organesson)
metals
the one highlighted as blue in the periodic table is considered as ___________
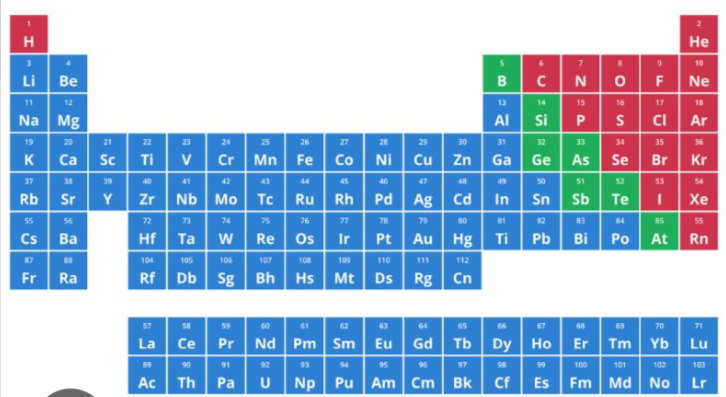
metalloids
the one highlighted as green in the periodic table is considered as ___________
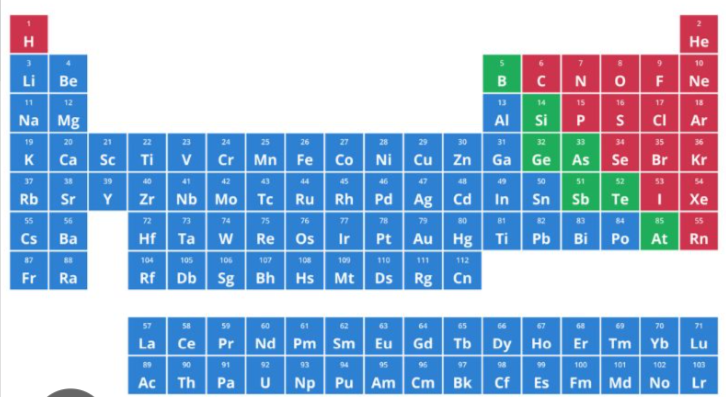
nonmetals
the one highlighted as red in the periodic table is considered as ___________
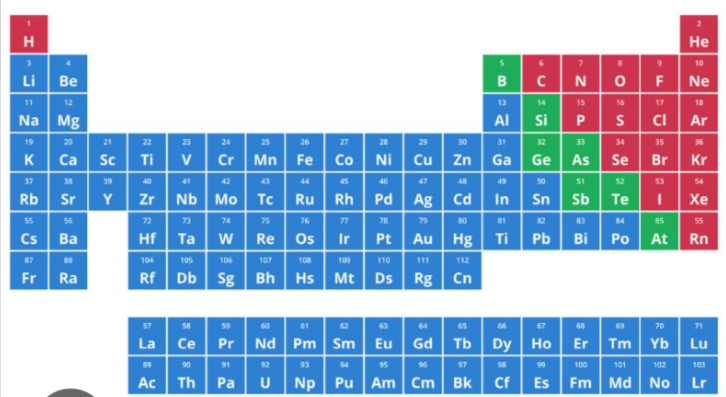
7 periods and 18 families
how many periods and families does the periodic table have?
electronegativity
ability of an atom to attract electrons in a chemical bond
electro-positivity
ability of an atom to lose electrons
increases
the electronegativity of an atom _______ from lowest group to the highest group
decreases
the electronegativity of an atom _______ from lowest period to the highest group
florine
it is the most electronegative element
cesium
it is the most electropositive element
intermolecular forces
basically knows as the attractive and repulsive forces that arise between the molecules of a substance; dependent reason why physical and chemical changes occurs