L2: Multi-Dimensional Approach to Psychopathology, Clinical Assessment & Diagnosis (copy)
1/143
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
144 Terms
Multidimensional Integrative Approach
Biological Dimension, psychological dimension, emotional influences or social influences that contributes a variety of psychopathology.
Multidimensional Model
Term for the model of multiple influences
Biological
Behavioral
Social
3 Multidimensional Aspects
Biological
Brain dysfunction, biochemical imbalances, genetic abnormalities. Can also be accidents/traumatic experiences.
Behavioral
Conditioning, learning, modeling, observations
Social
Support system, people or environment, events and experiences
Genes
Long molecules of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) at various locations on chromosomes, within the cell nucleus.
46 Chromosomes
Total number of chromosomes of a normal human cell.
Autosomes
23 pairs and 22 pairs
Sex Chromosomes
23rd pair of `chromosome
X Chromosome
Chromosome that the mother contributes
Y Chromosome
Chromosome that the father contributes
Dominant Gene
Recessive Gene
2 Types of Genes
Dominant Gene
Pair of genes strongly influence a particular trait
Recessive Gene
Trait that is only expressed when both allele is present.
Mandelian Lws of Genetics
Predict fairly accurately how many offspring will develop a certain trait, characteristic or disorder.
Huntington’s Disease
Degenerative brain disease that causes deterioration in a specific area of the brain.
Basal ganglia
Area of the brain that is damaged, resulting to Huntington’s Disease.
Chromosome 4
Defective chromosome number in HD
Phenylketonuria (PKU)
Mental retardation which present at birth, unable to metabolize or break down foods, caused by a defect in a single gene.
Chromosome 12
Defective chromosome number in PKU
Seizure
Small head size
Coordination difficulties
Dwarfism/Short stature
Backward-sloping forehead
Hyperactivity
Facial distortions
Delays in speech & movement
Defects/Physical Looks of Individual with PKU
Diathesis
Condition that makes someone susceptible or vulnerable to developing disorder.
The smaller the vulnerability, the greater the life stress required to produce the disorder. With greater vulnerability, less life stress is required.
Complete the sentence:
The smaller the vulnerability, _______ to produce the disorder. With _____,_________ is required.
Predisposing Factor
Precipitating Factor
Perpetuating Factor
Protective Factor
4 Factors in Developing a Disorder
Predisposing Factor
Cause of a disorder
Precipitating Factor
Allow disorders to develop
Perpetuating Factor
Allow to persist
Protective Factor
Help to protect buffer the development of a disorder.
5 HTT Genes
substance called chemical transporter that affects the transmission of serotonin in the brain.
SS Allele (Short)
Risk for having a MDD, tend to doubled if they had atleast 4 stressful life events.
LL Allele (Long)
Able to cope better with stress, any stressful childhood experiences did not affect the incidence of MDD in adulthood.
Central Nervous System
Processes all information received from our sense organs.
140 Billion
Number of average nerve cells that functions inside our brain daily.
Neurons
Term for the 140 billion nerve cells the brain uses.
Dendrites
Axon
Synapses
Action Potentials
Terminal Button
Synaptic Cleft
Nodes of Ranvier
Parts of the Nervous System
Dendrite
Myelin Sheath
Axon Terminal
Nodes of Ranvier
Axon
Nucleus
Name the parts of the Neurons
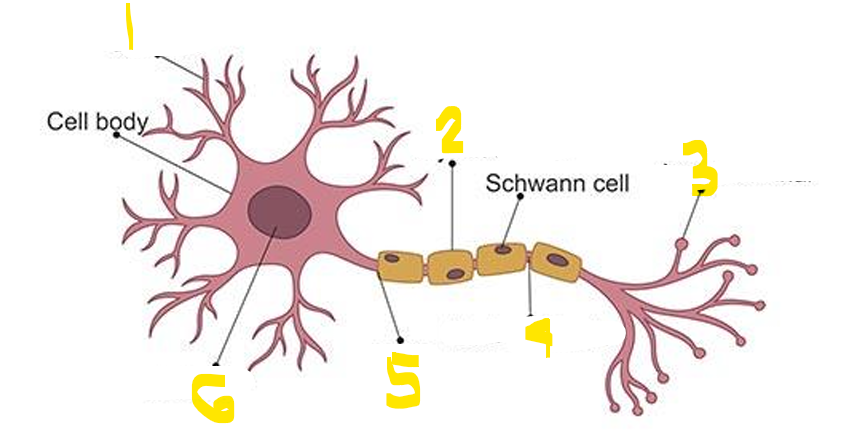
Dendrites
Receive messages from other nerve cells
Axon
Transmit impulses to other neurons
Synapses
Connections to other neurons
Action Potentials
Electric impulses where information is transmitted
Terminal Button
End of axon
Synaptic Cleft
Space between terminal button of one neuron and dendrite of another
Nodes of Ranvier
Gaps between myelin sheath
Disorder occurs when the chemicals from axon terminal is incomplete or was not absorbed by the dendrite.
How does a disorder occur?
Neurotransmitters
Often referred to as the body’s chemical messengers. They are the molecules used by the nervous system to transmit messages between neurons or from neurons to muscles.
Excitatory
Inhibitory
2 Effects of Neurotransmitters
Excitatory
Individual may be aggressive or agitated
Inhibitory
Individual is relaxed or clam.
Reuptake
Neurotransmitter released quickly broken down and brought back to the synaptic cleft again.
Agonists
Antagonists
Inverse Agonists
3 Production of Neurotransmitter
Agonists
Increase the activity of neurotransmitter
Antagonists
Decrease/block the neurotransmitter
Inverse Agonists
Produces effect opposite to those produced by the neurotransmitters.
Monoamine Class
Amino Acid Class
2 Categories of Neurotransmitters
Monoamine Class
Modulation of psychomotor function
Cardiovascular, Respiratory, and Gastrointestinal control
Sleep mechanisms
Hormone secretion
Body temperature
Pain
Amino Acid Class
Inhibitory and Excitatory Messengers in the nervous system.
Glutamate
GABA (gamma amino butyric acid)
2 Kinds of AMINO ACIDS
Glutamate
Excitatory transmitter that turn on many different neurons leading to action.
GABA
Inhibit the transmission of information and action potentials; relaxed.
Anxiety
Perseverating
Restlessness
Migraines
Tics
Motor Stereotypies
Too much glutamate may cause:
Serotonin
Norepinephrine
Dopamine
Types of Monoamine
Serotonin
Regulates the behavior, moods, and thought processes
Norepinephrine
Also called noradrenaline responsible for alertness and arousal
Dopamine
Also known as catecholamine turn on brain circuits.
L-dopa
Dopamine Agonists (Increases dopamine activities)
Glutamate
High: Psychosis
Low: Huntington’s Disease
GABA
High: Relaxation
Low: Anxiety, OCD
Serotonin
High: Mania
Low: MDD, Anxiety, ED
Norepinephrine
High: PTSD, Anxiety, Mania
Low: MDD
Dopamine
High: Schizoprenia
Low: Mania, PD (Psychotic Disorder)
Hormones
Released directly to the blood streams.
Epinephrine
Thyroxine
Cortisol
Oxytocin
Kinds of Hormones
Epinephrine
Response to stress
Thyroxine
Metabolism and growth, PKU individuals have problems with this.
Cortisol
Stress hormone
Oxytocin
Love hormone
Brain Stem
Most ancient part of the brain responsible for moving, breathing, sleeping, and present in animals.
Hindbrain
Regulates many automatic activities, such as breathing, pumping action of the heart, and digestion
Medulla
Pons
Cerebellum
Parts of Hindbrain
Medulla
Blood pressure, breathing, and circulation
Pons
Coordinating movements
Cerebellum
Motor coordination and balance
Midbrain
Coordinates movement with sensory input and contains parts of reticular activating system (RAS)
Reticular Activating System (RAS)
Contributes to processes of arousal and tension, such as whether we are awake or asleep.
Thalamus
Hypothalamus
Corpus Callosum
Limbic System
Basal Ganglia
Cerebral Cortex
Parts of the Forebrain
Thalamus
Relay sensory information to higher region of the brain
Hypothalamus
Vital body functions, emotional and motivational state.
Corpus Callosum
Connect the right and left hemisphere
Limbic System
Emotional processing and memory
Amygdala
Hippocampus
Nucleus Accumbens
Parts of Limbic System A
Amygdala
Response (fear), memory, and emotions
Hippocampus
Short and long term memory
Nucleus Accumbens
Motivational and action
Basal Ganglia
Includes caudate nucleus
Cerebral Cortex
Largest part of the brain—plan, reason, create, contains 80% of neurons.
Frontal Lobe
Parietal Lobe
Temporal Lobe
Occipital Lobe
Brain Lobes:
Frontal Lobe
Higher cognitive functions, such as thinking, reasoning, planning.
Parietal Lobe
Sensations of touch and body functioning
Temporal Lobe
Sounds, hearing, auditory