AP Chemistry: Polyatomic Ions | Quizlet
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
acetate
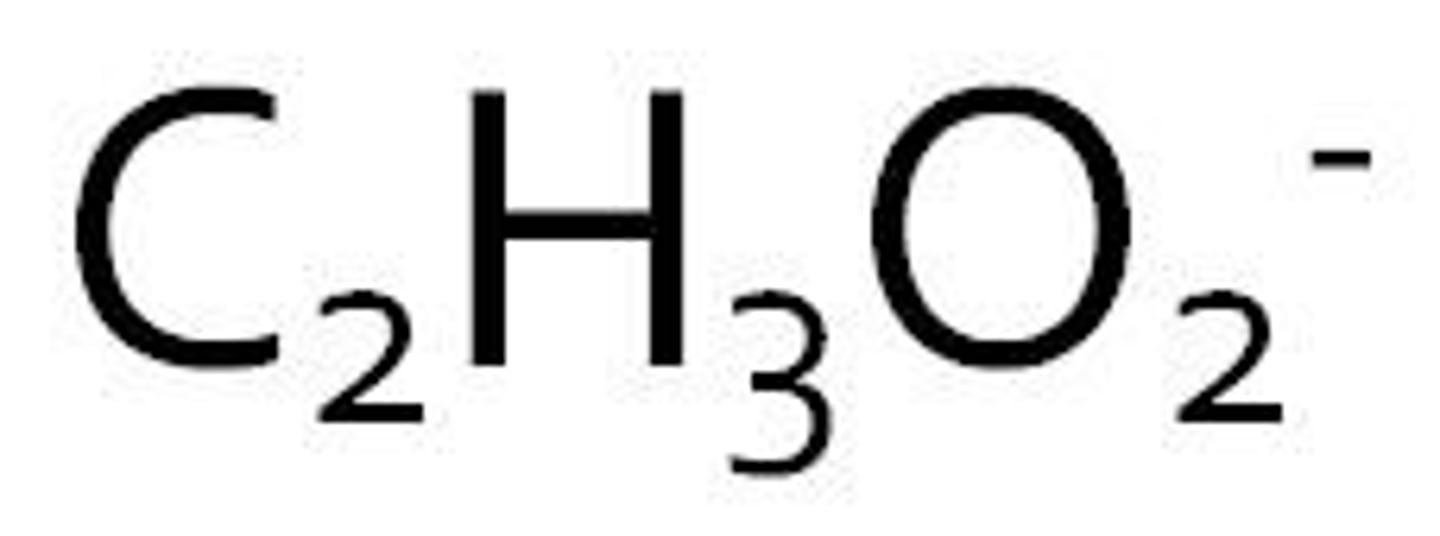
ammonium
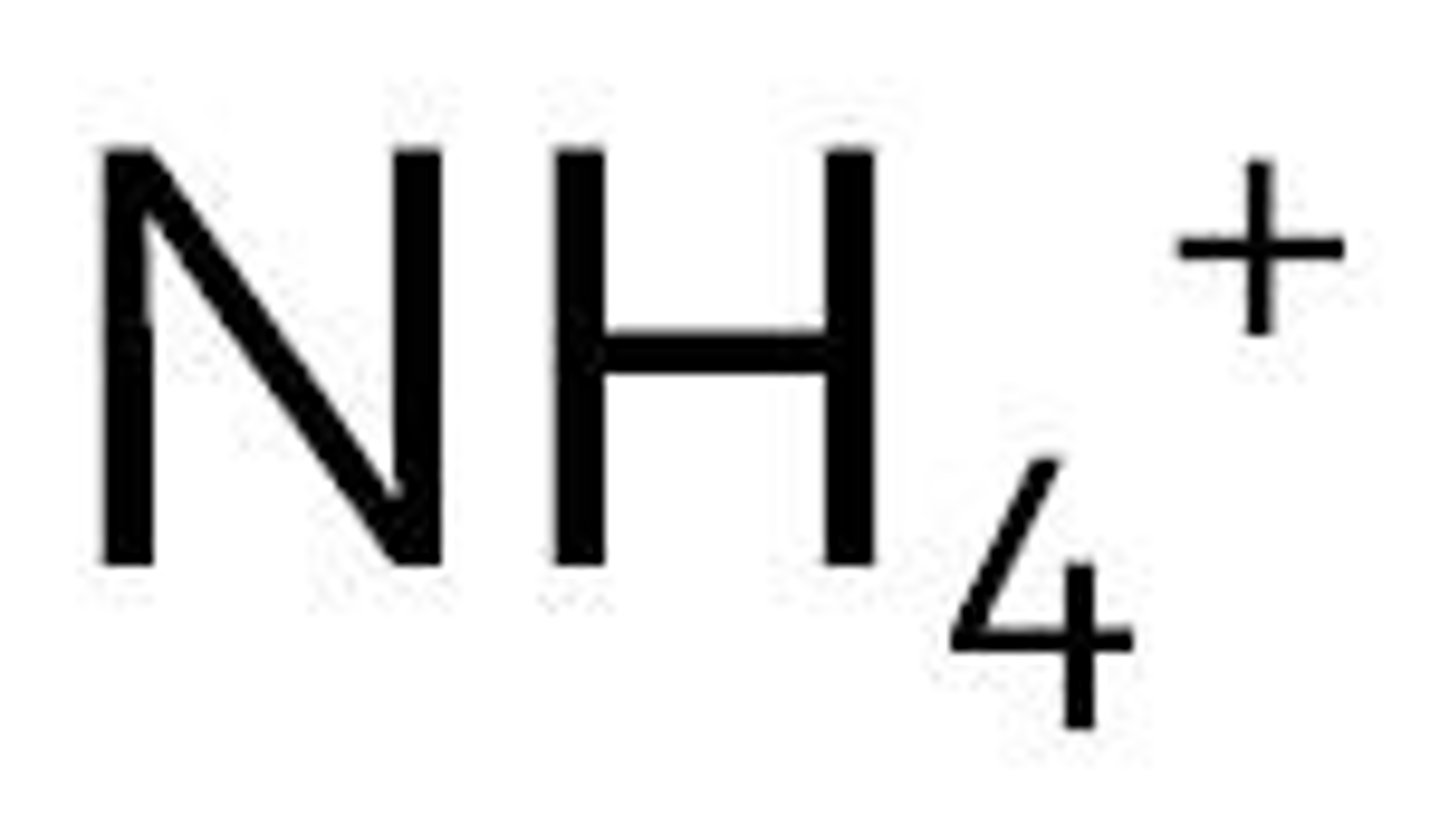
arsenate
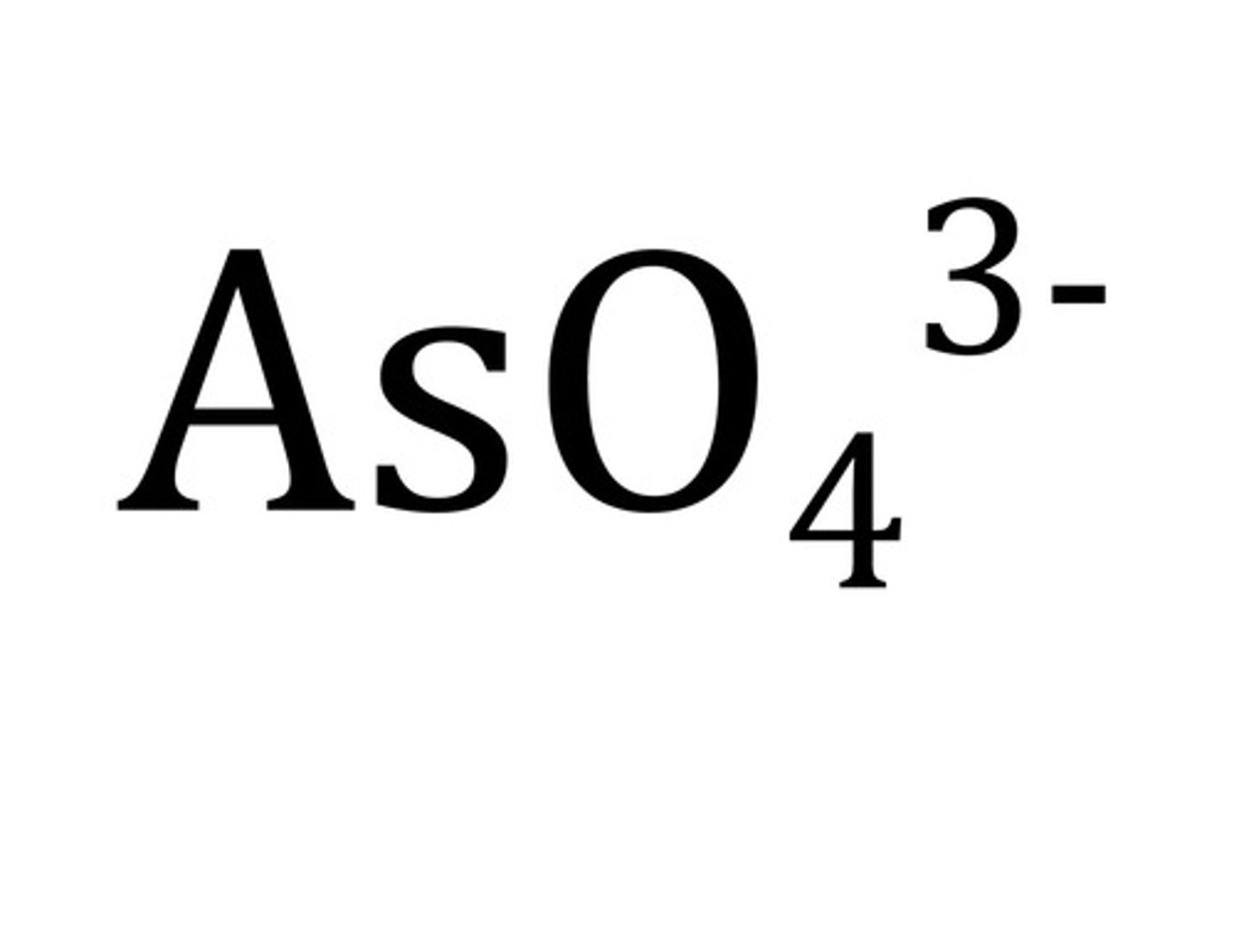
bicarbonate (hydrogen carbonate)
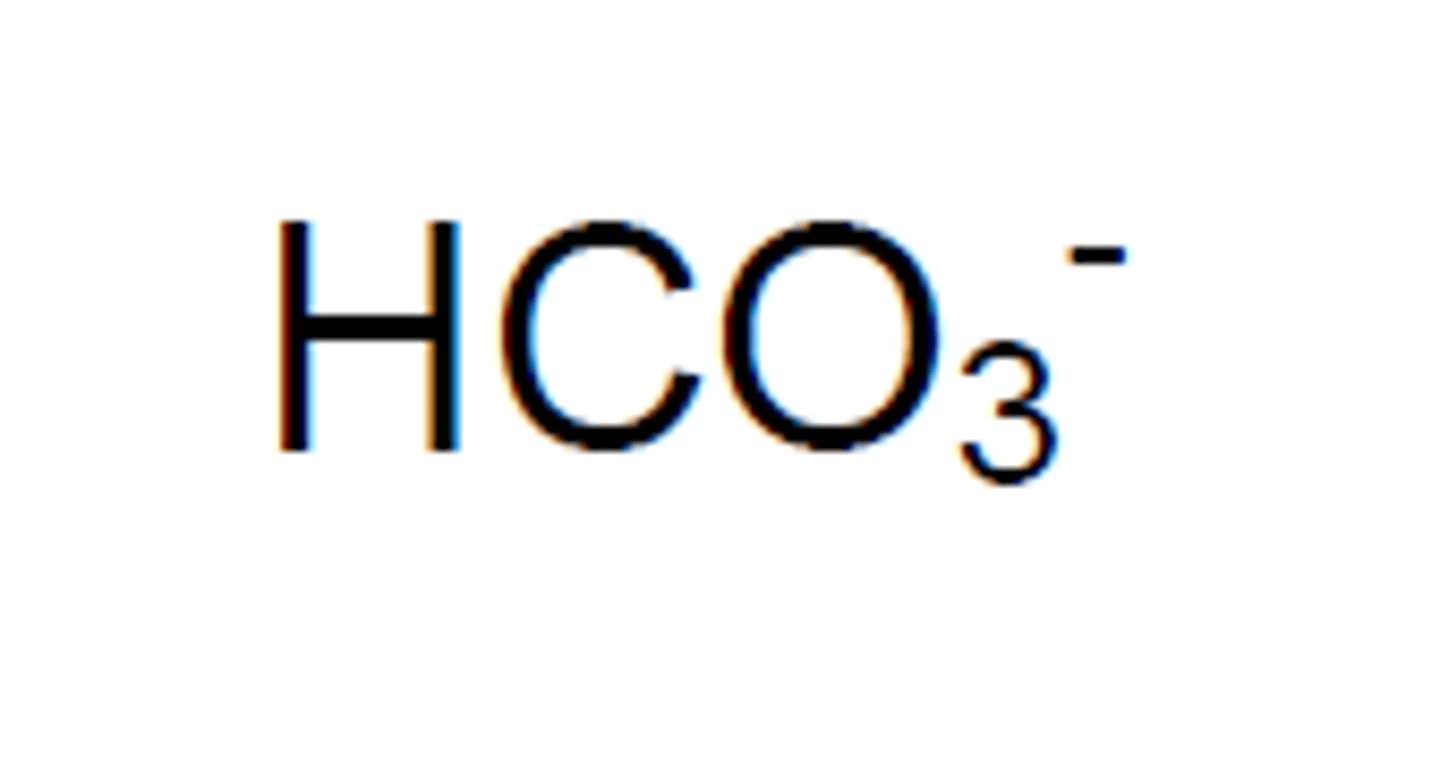
bisulfate (hydrogen sulfate)
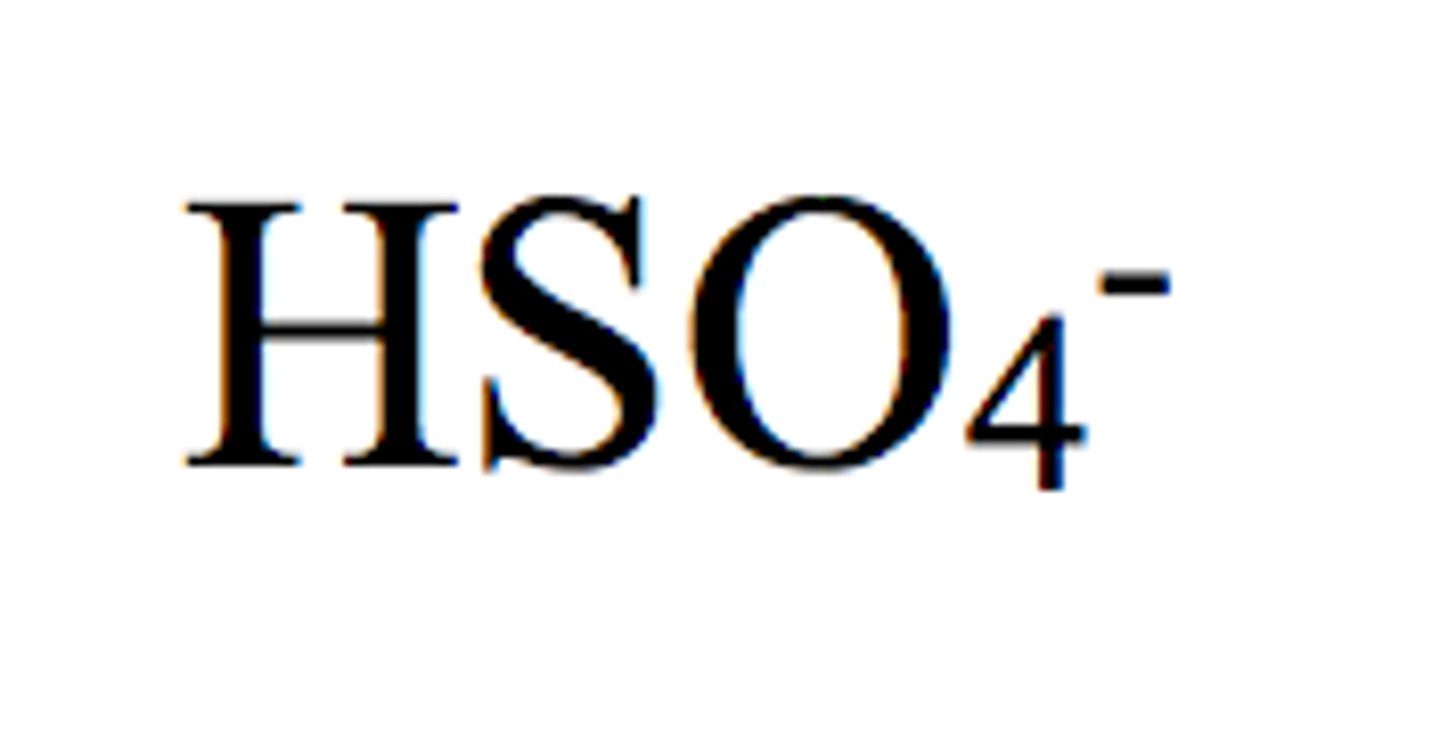
borate
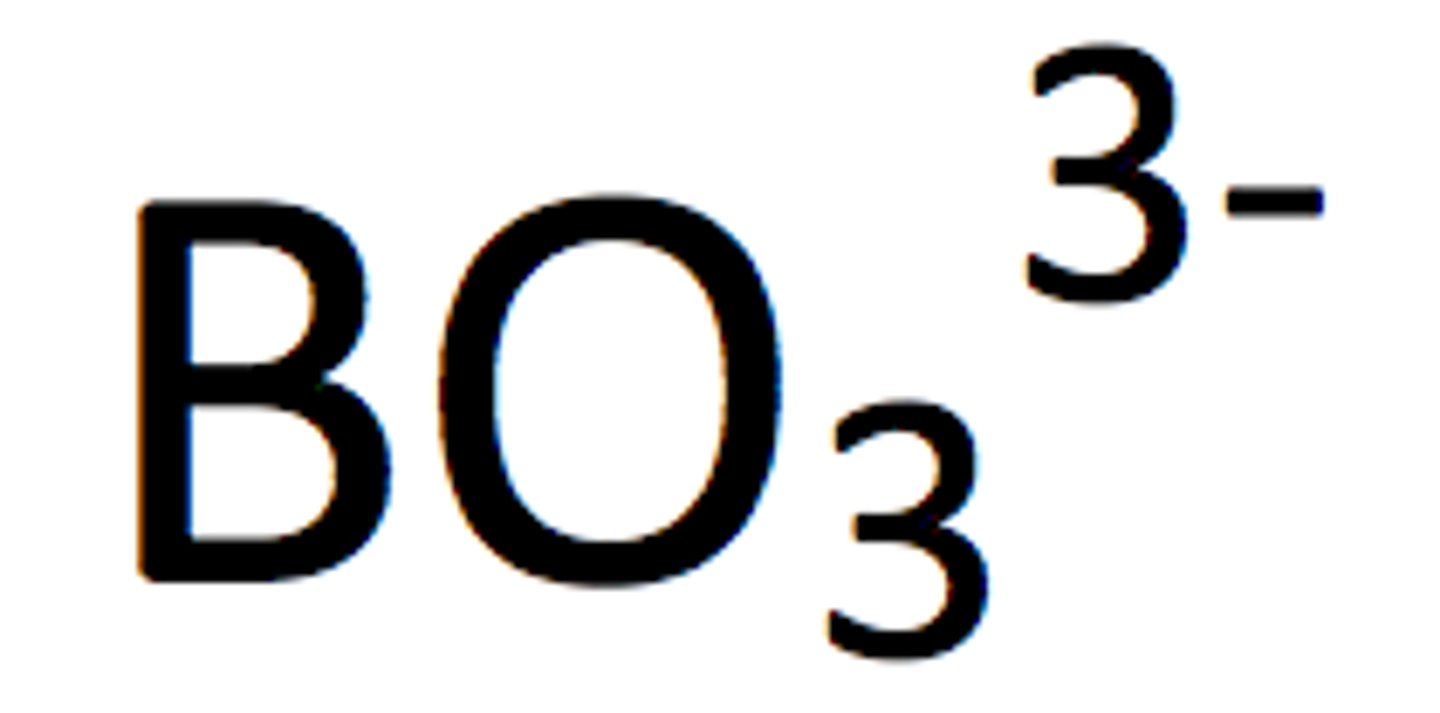
bromate
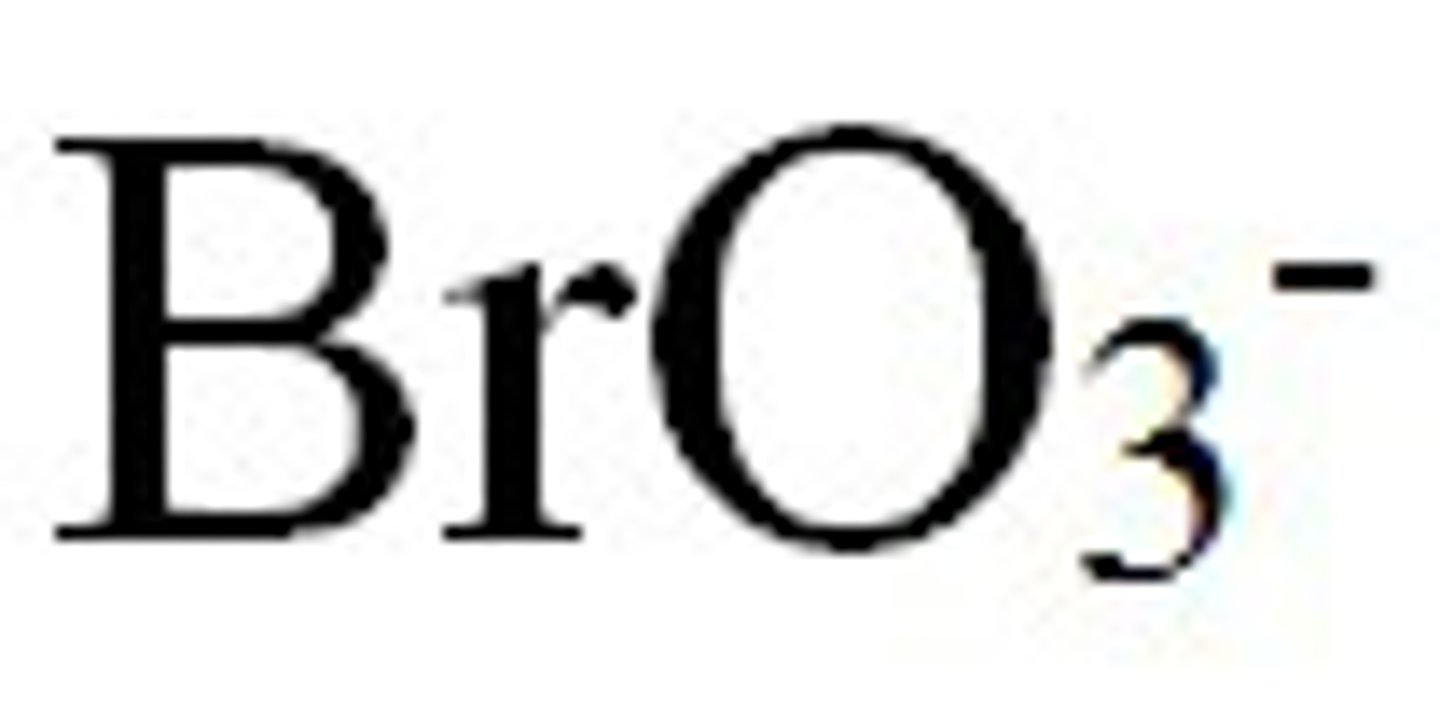
bromite
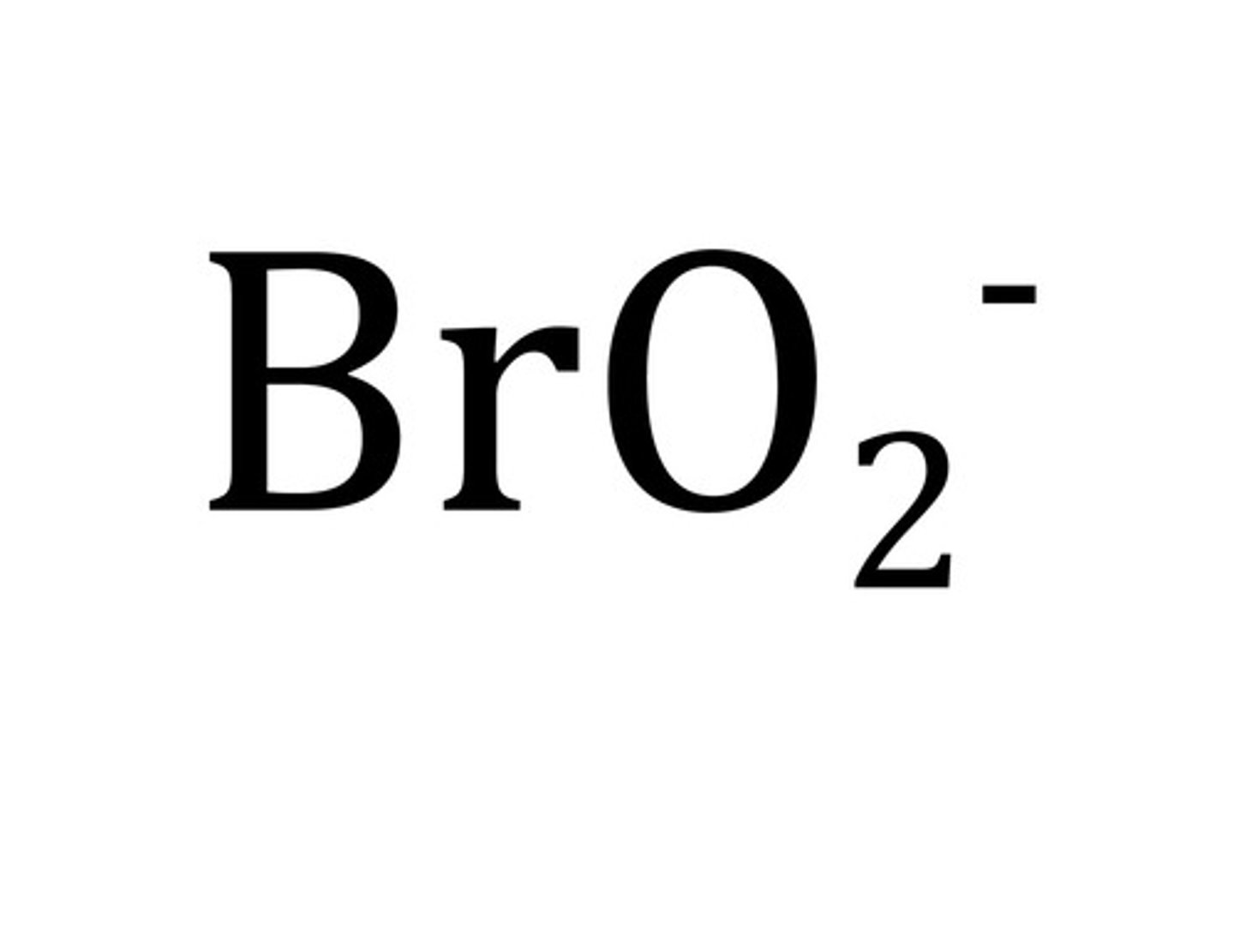
carbonate
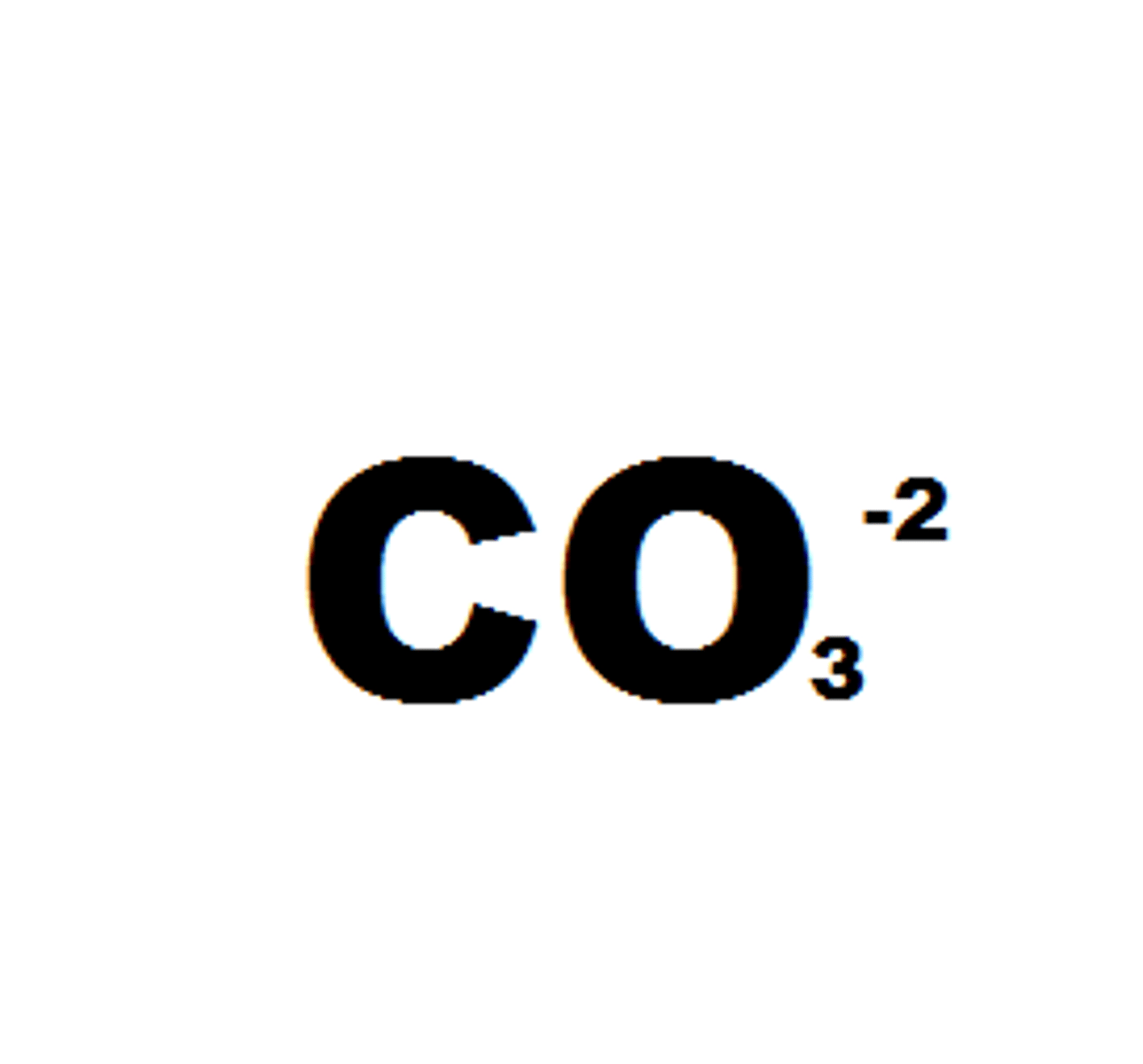
chlorate
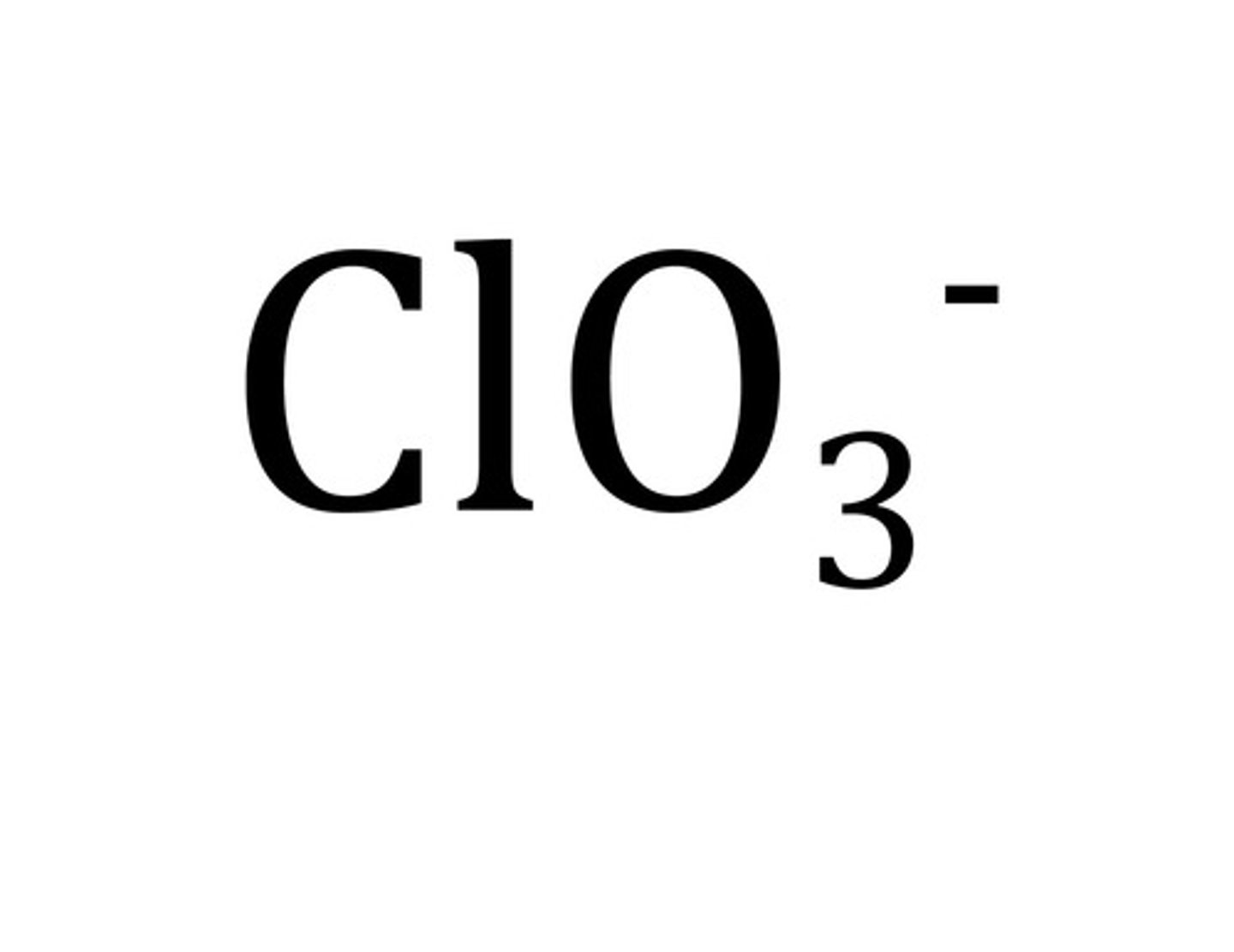
chlorite
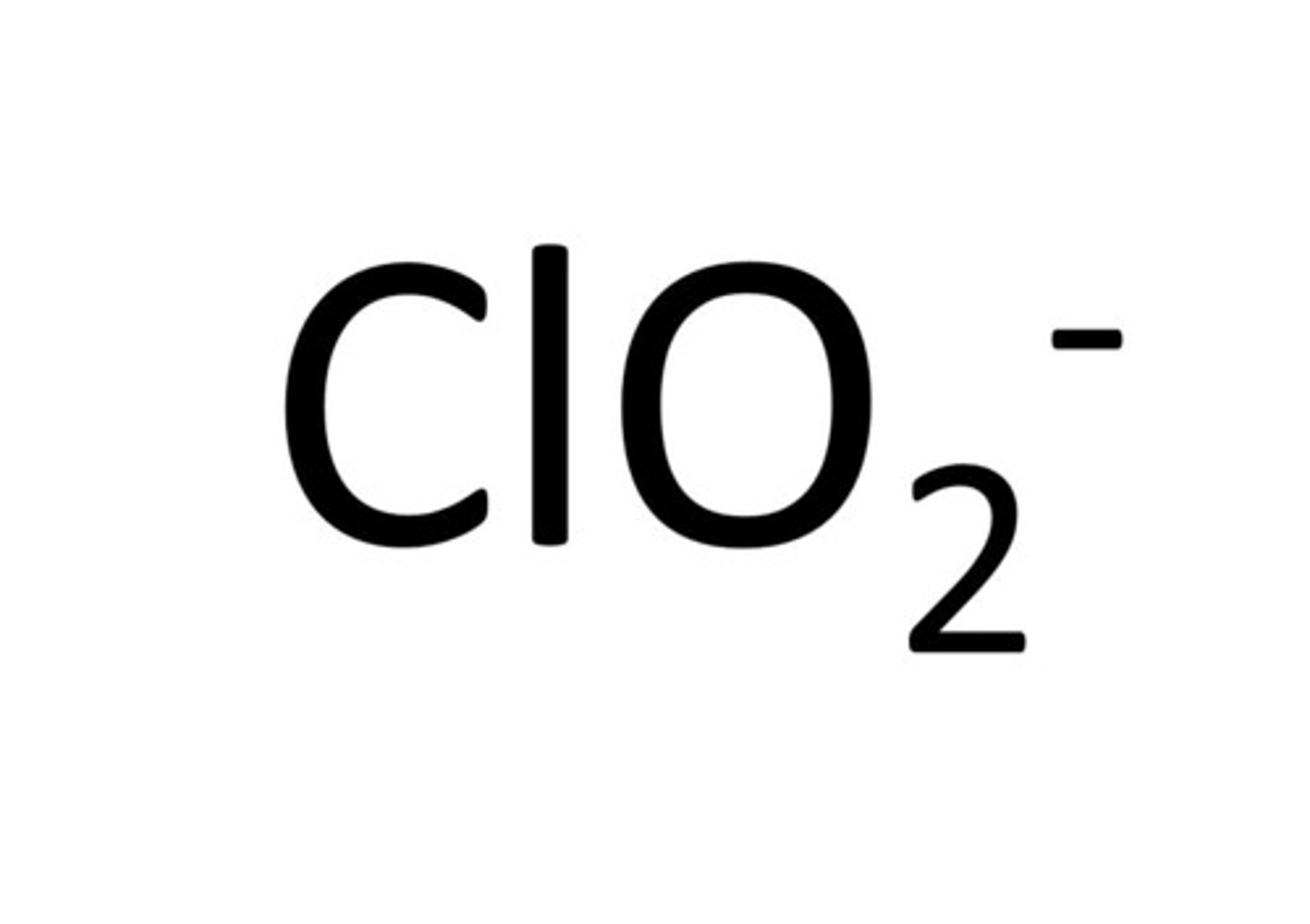
chromate
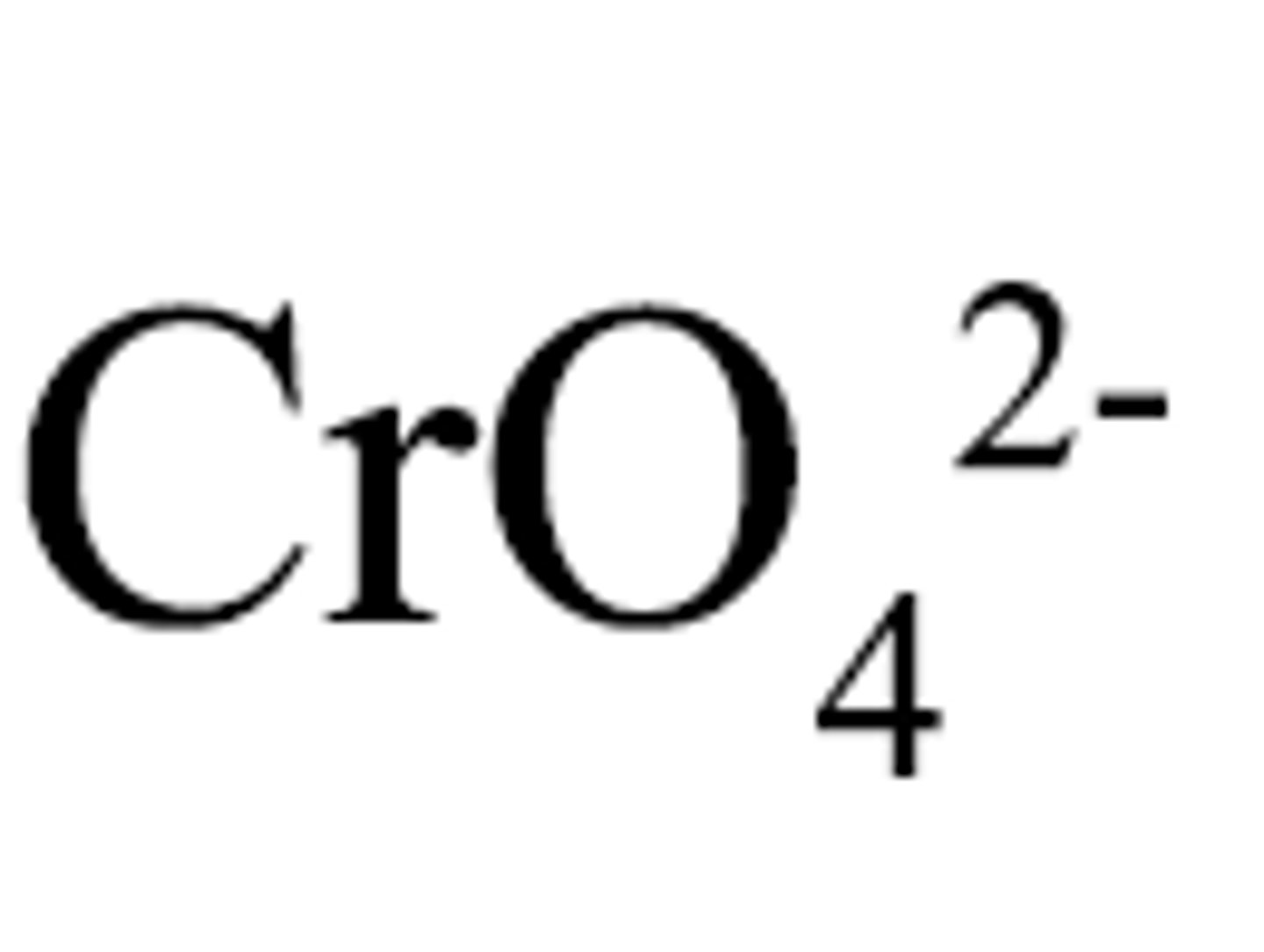
cyanide

dichromate
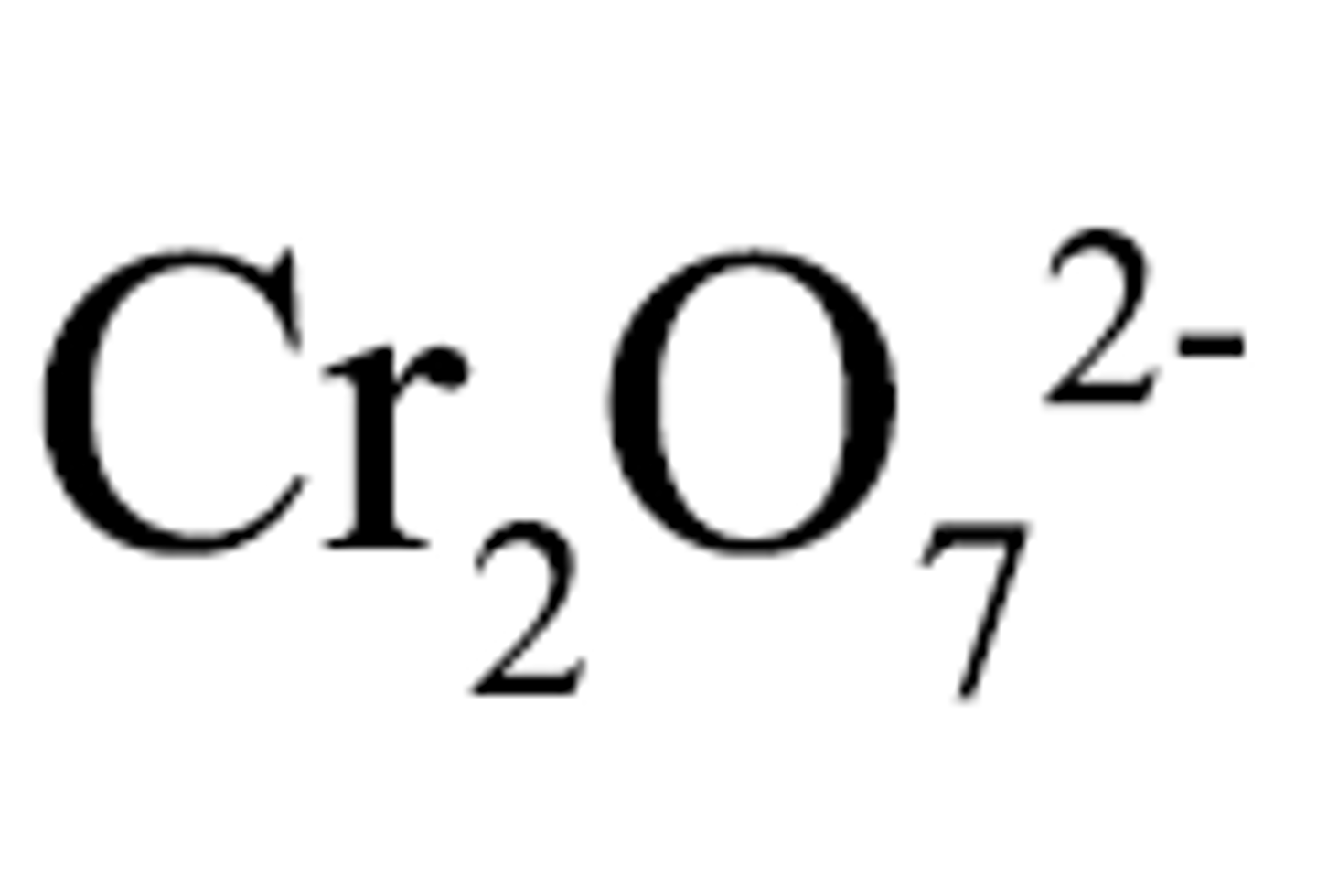
dihydrogen phosphate
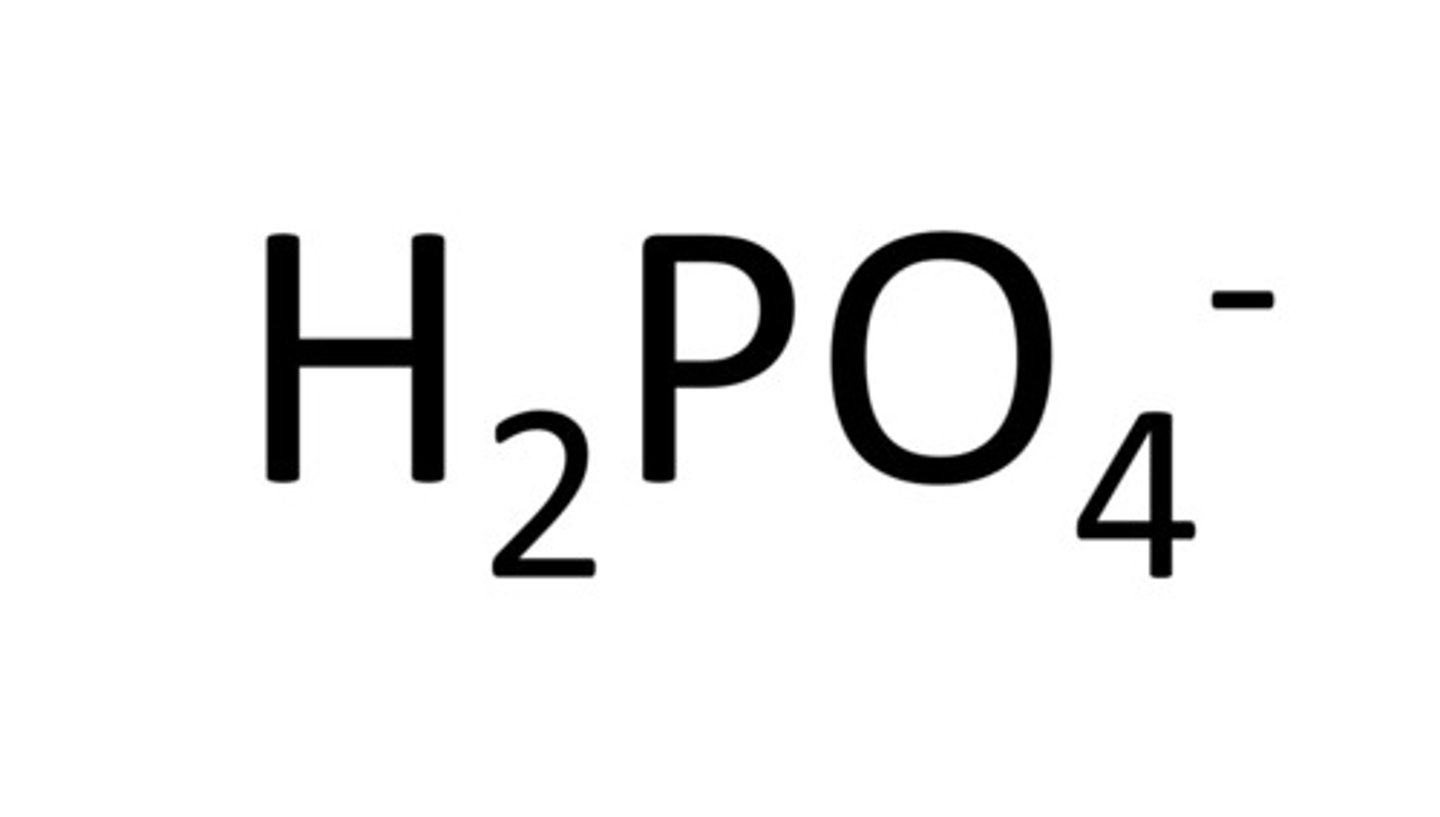
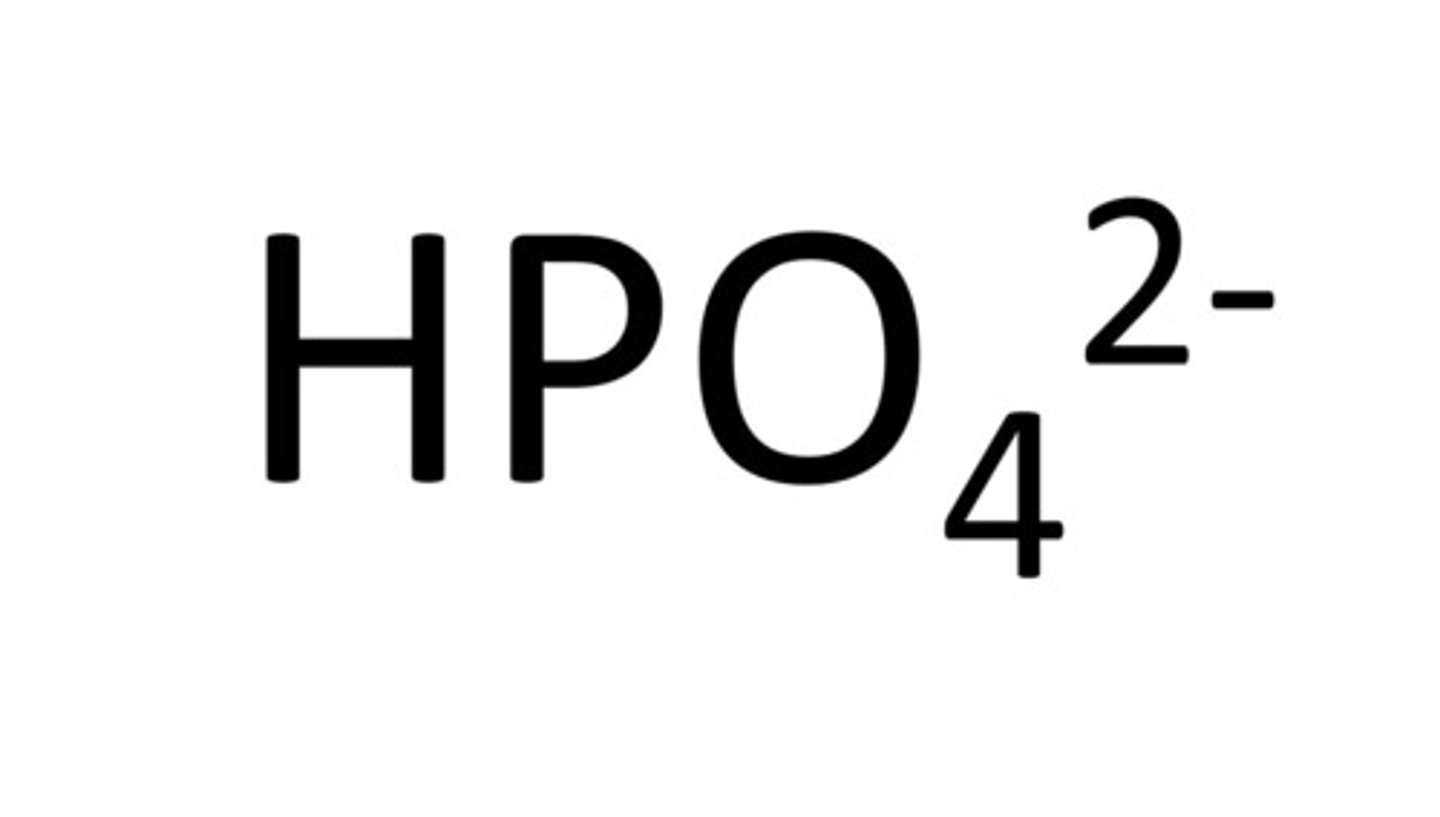
hydrogen phosphate (no "bi" because -3 charge. Number of hydrogens is ambiguous)
hydroxide
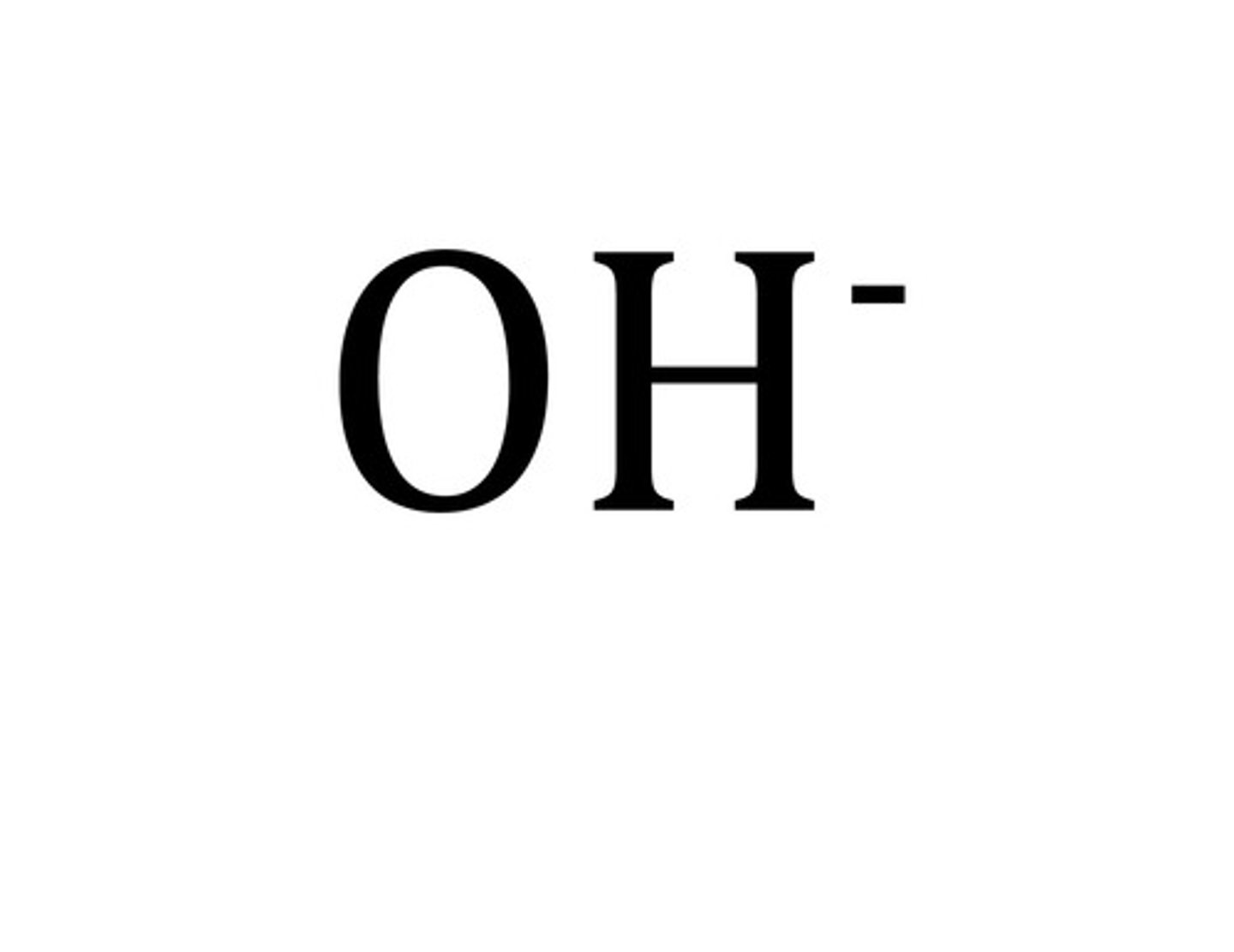
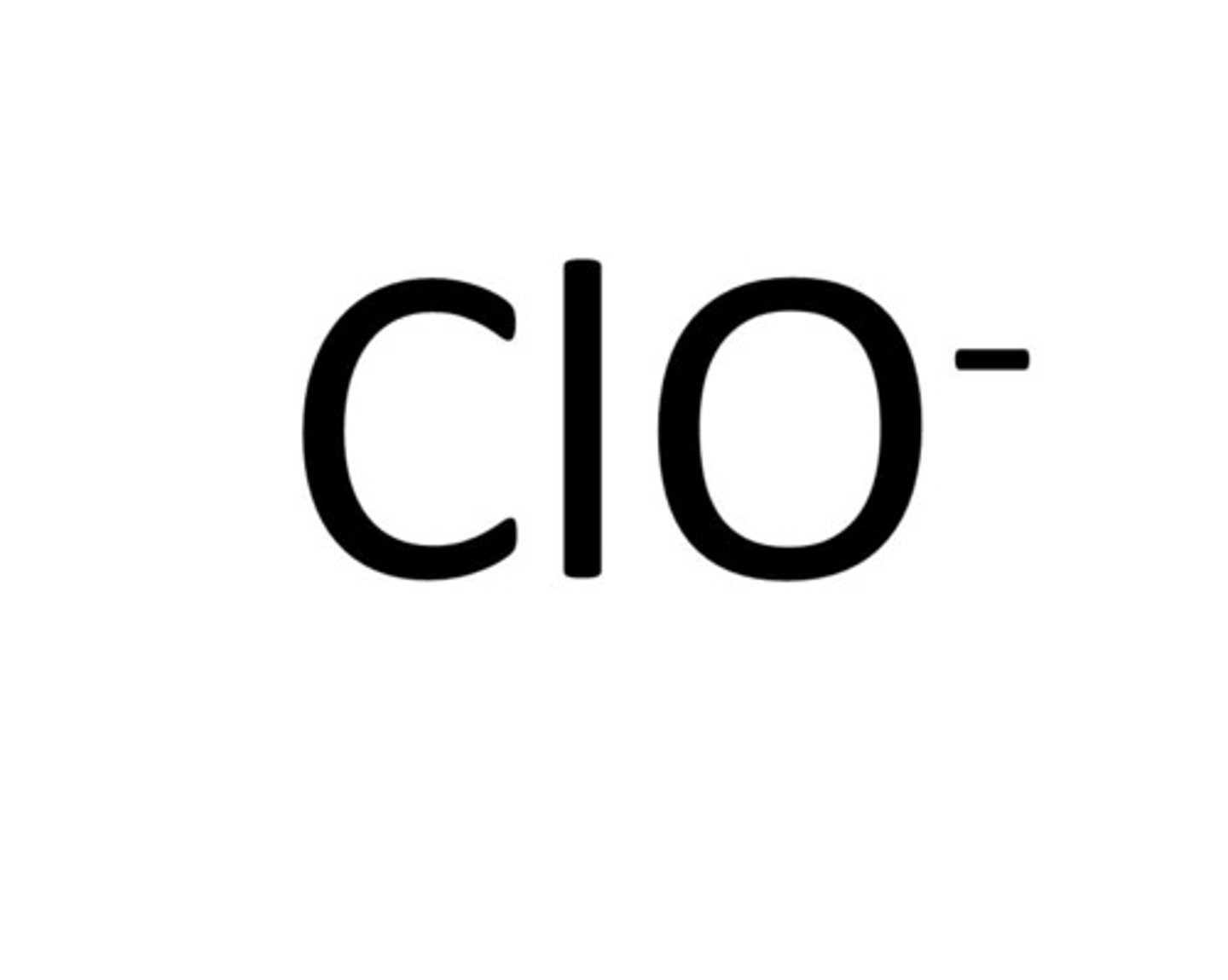
hypochlorite
iodate
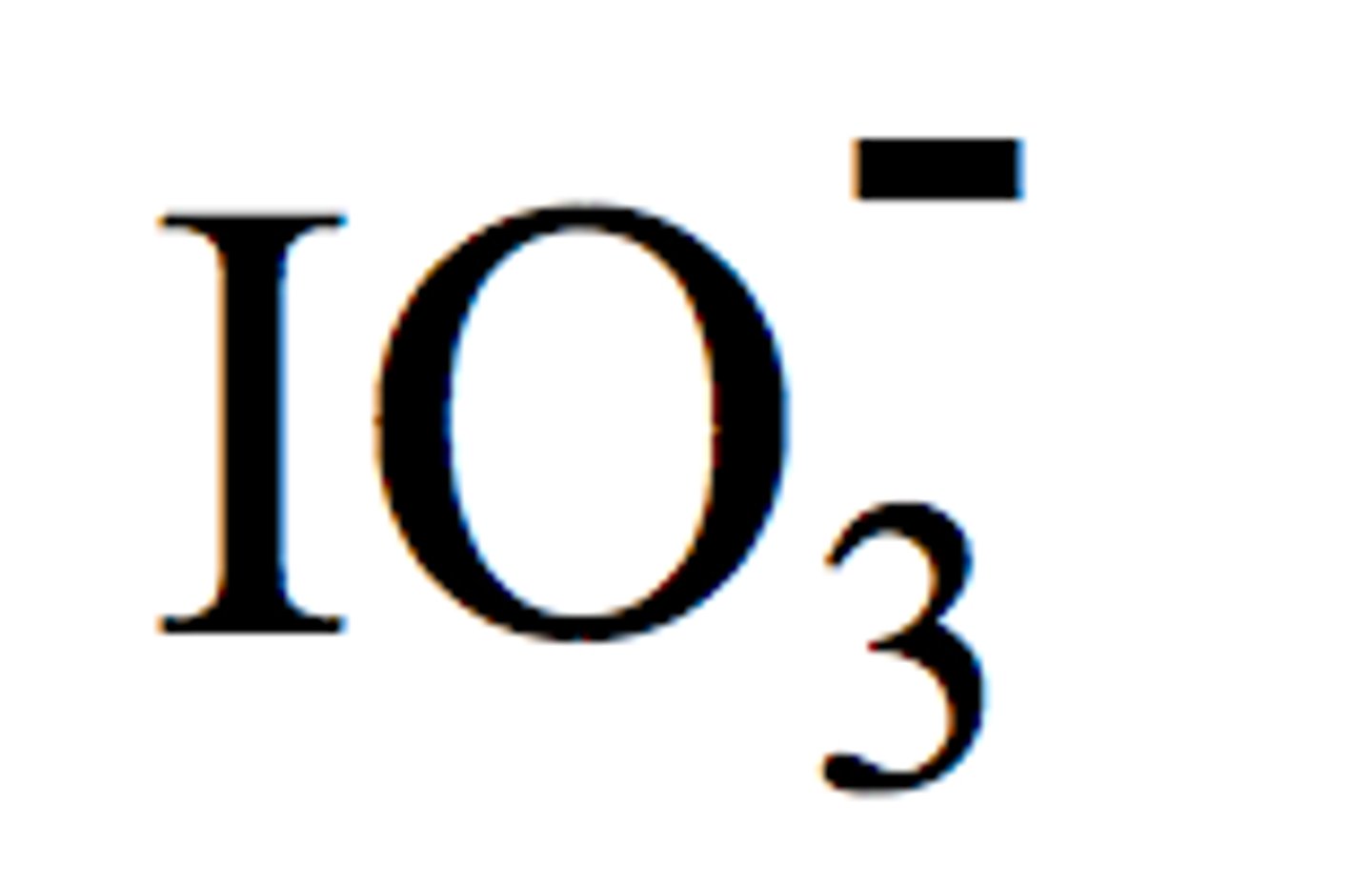
nitrate
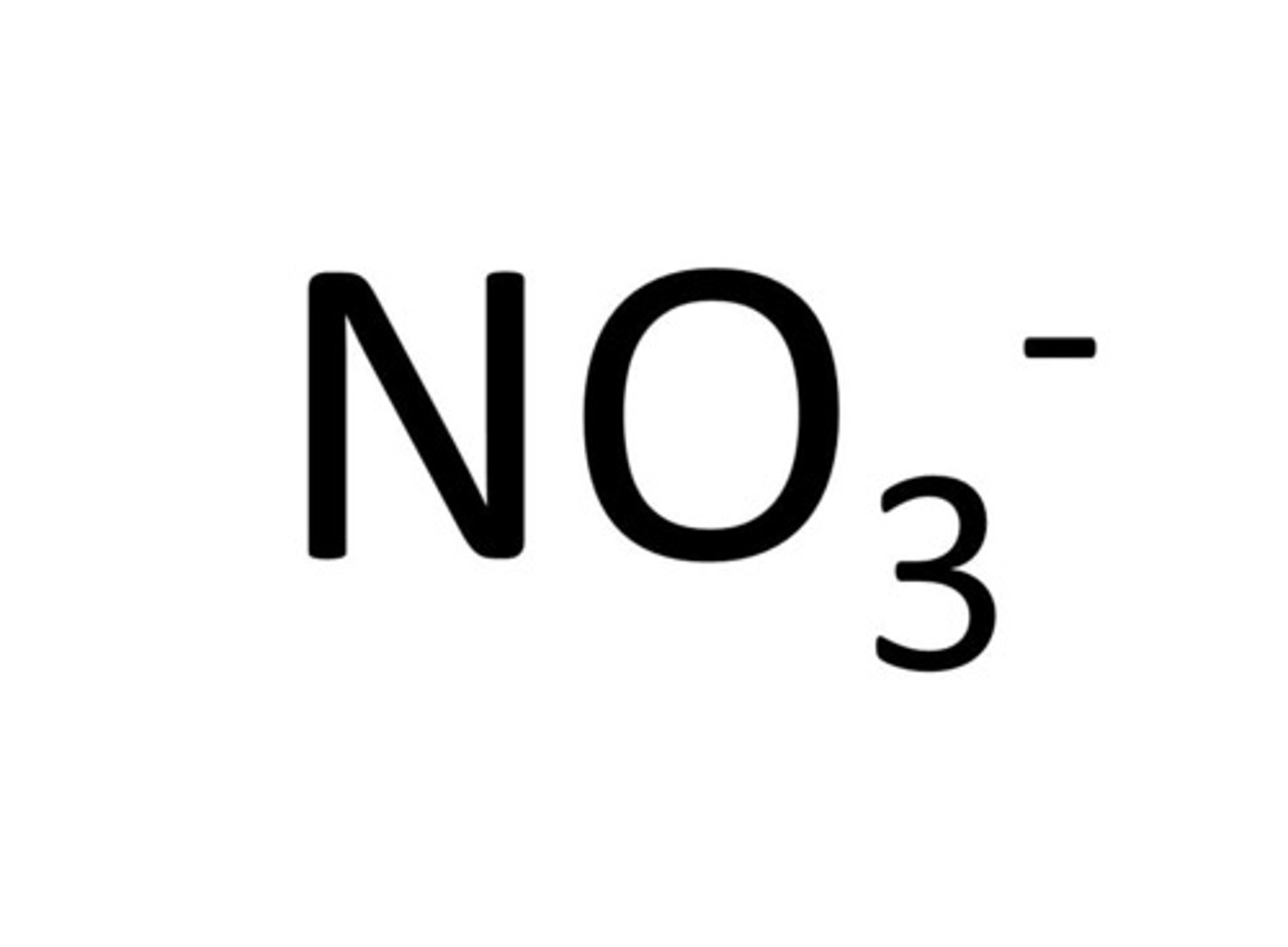
nitrite
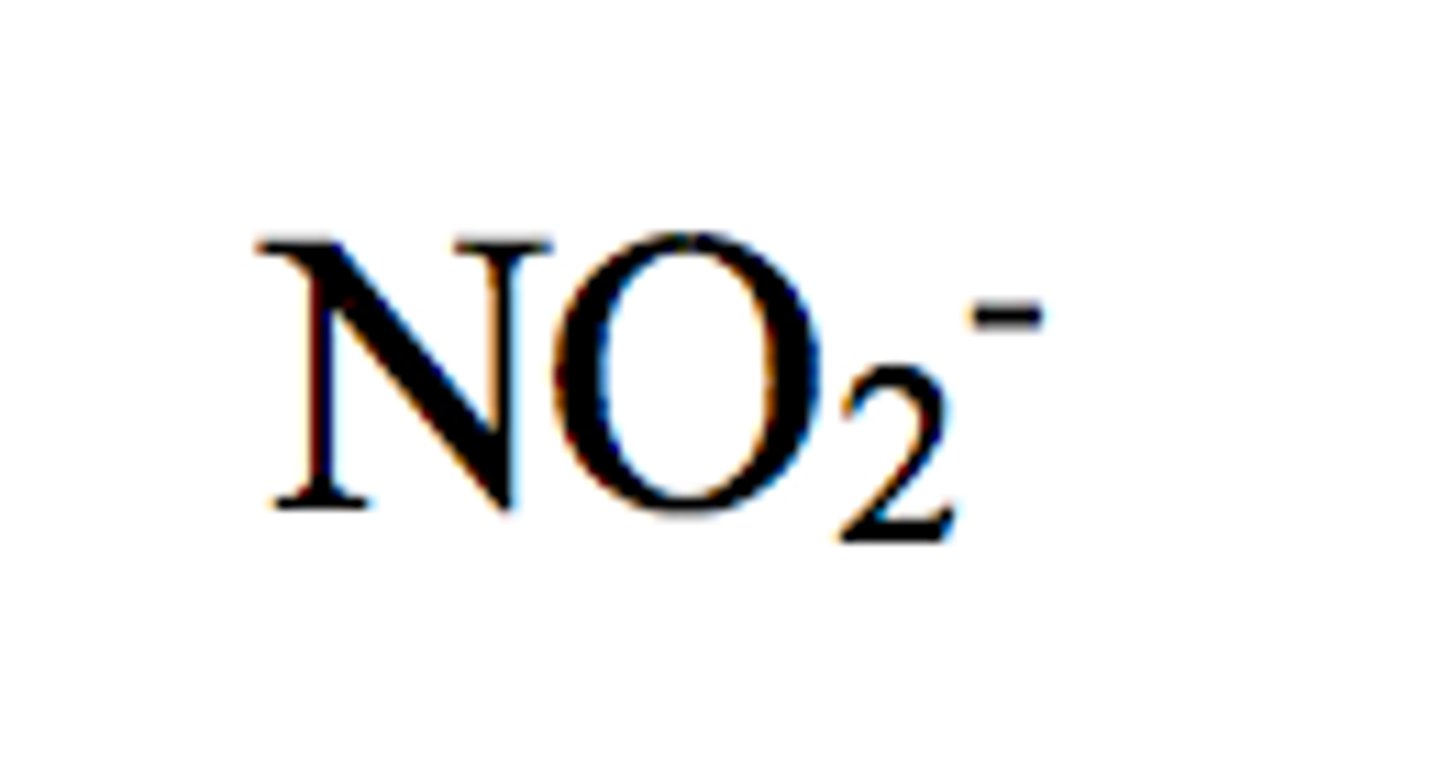
oxalate
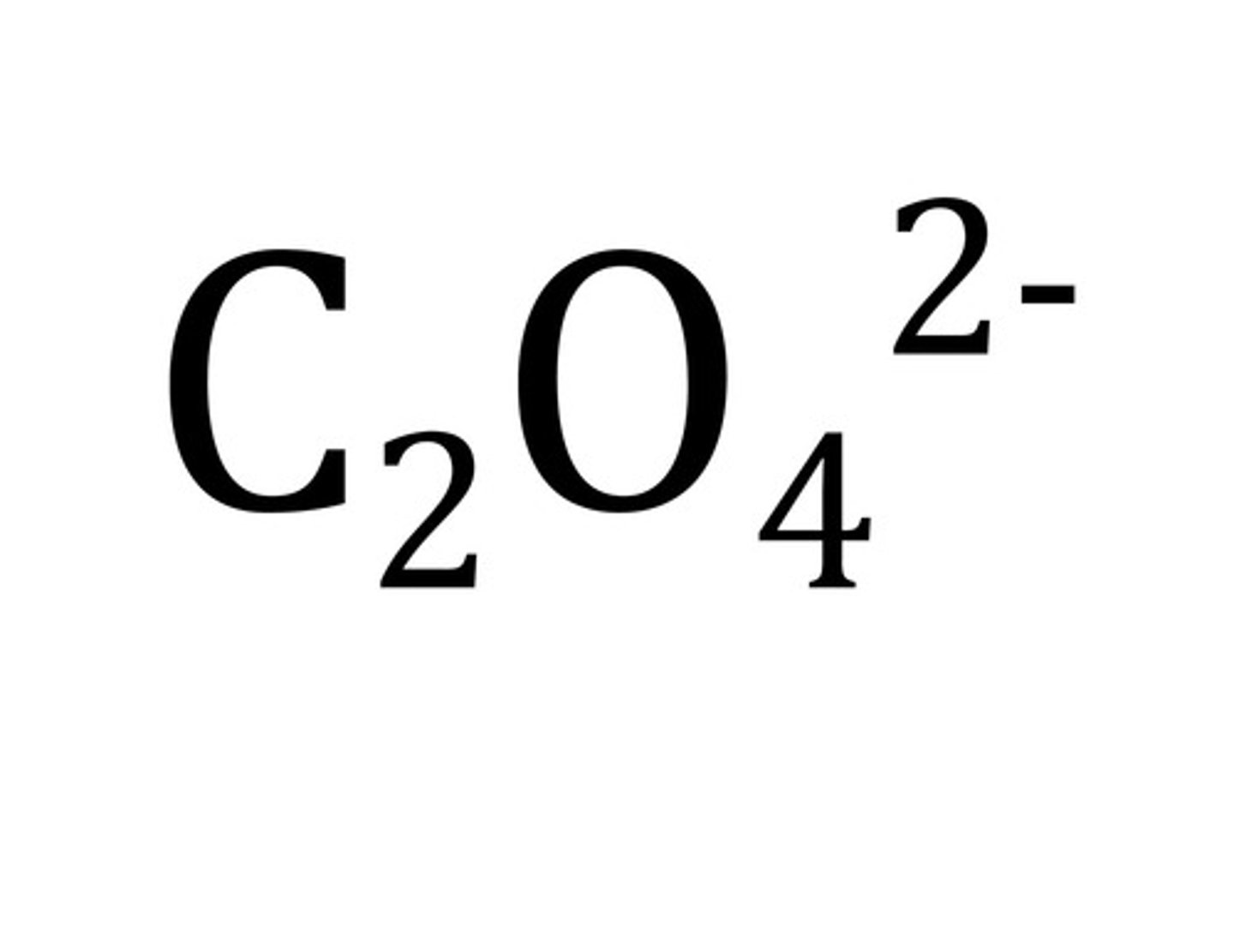
perchlorate
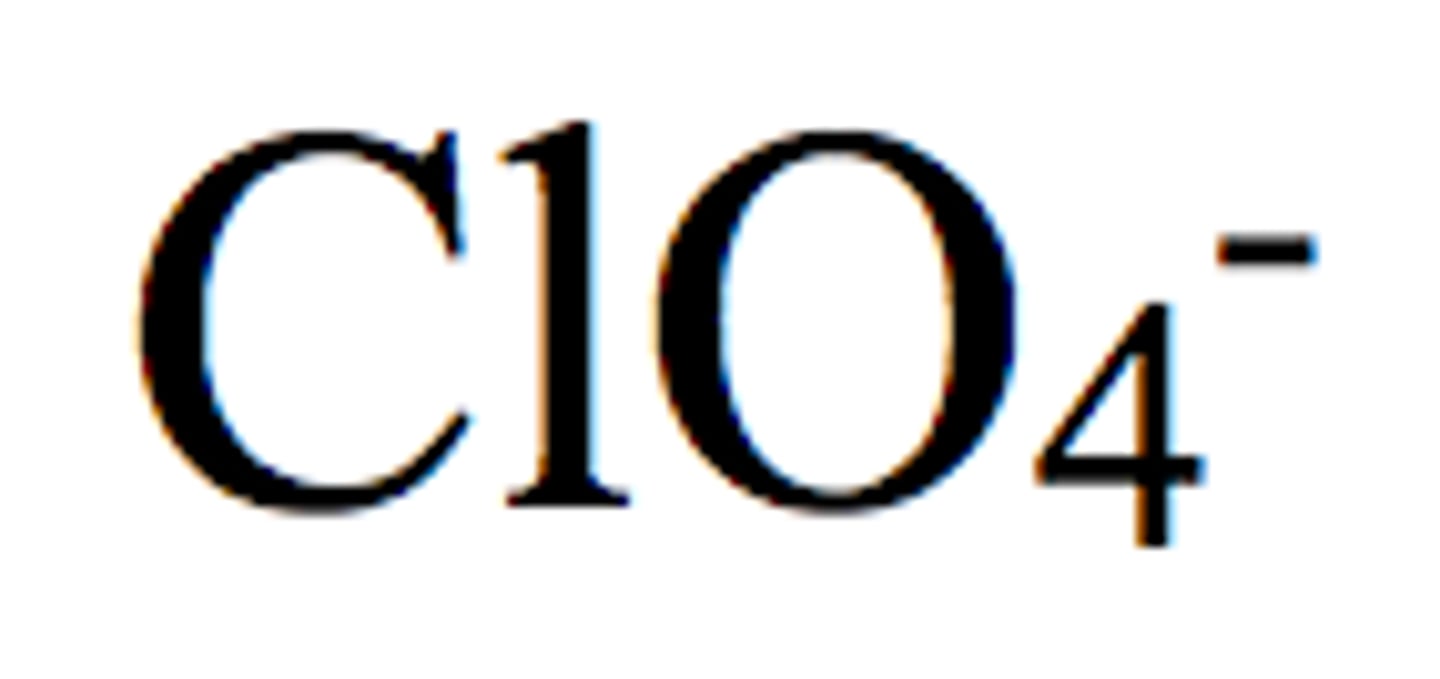
permanganate
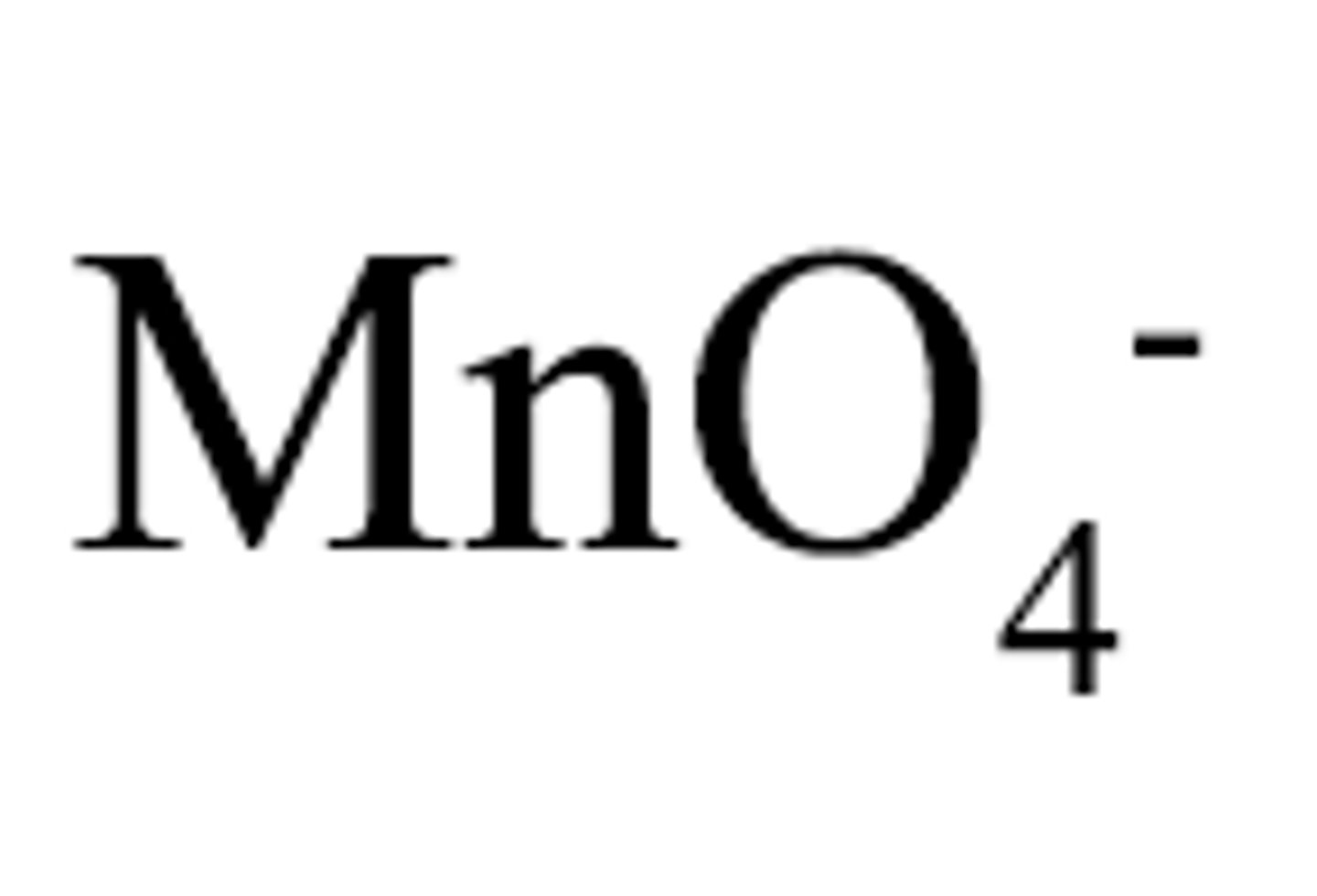
peroxide
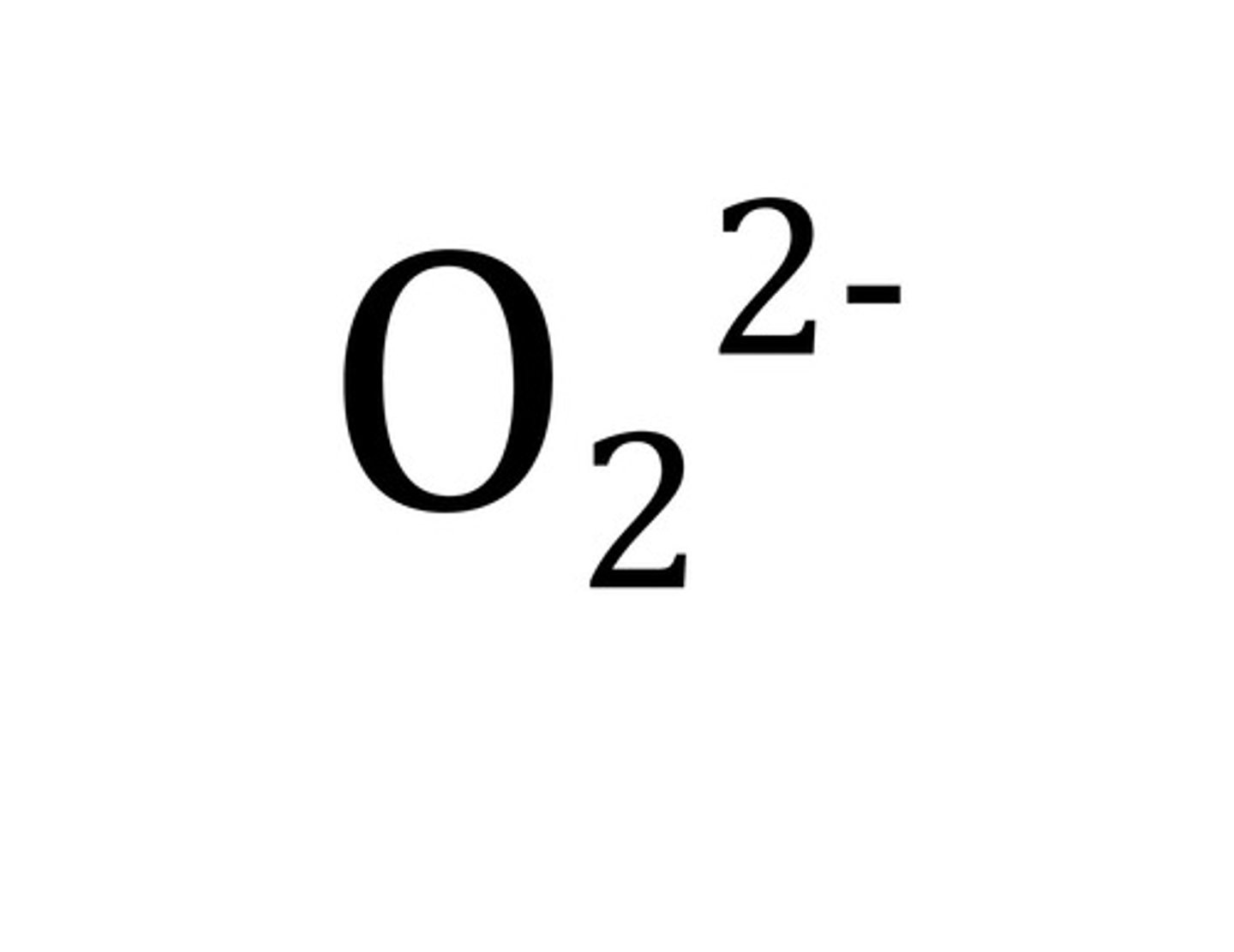
phosphate
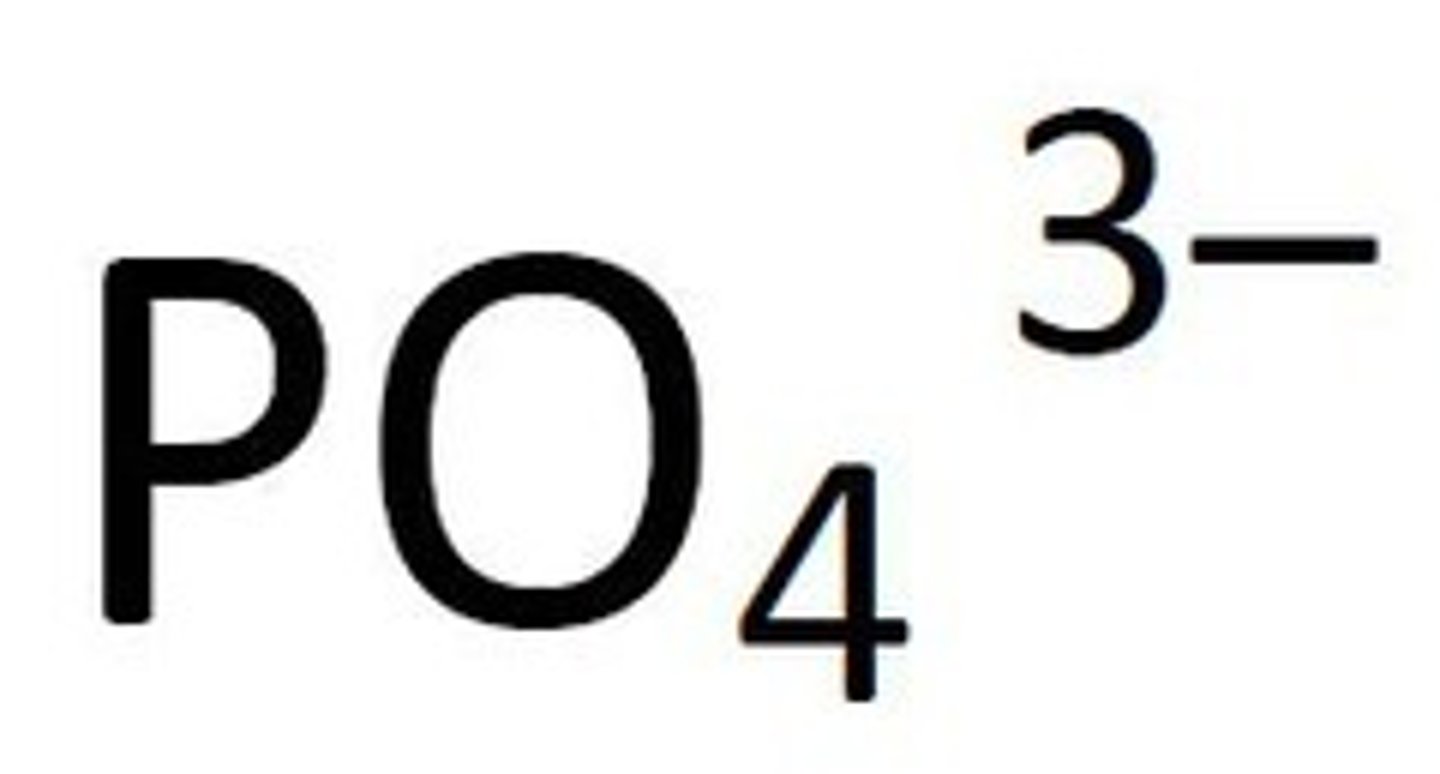
sulfate
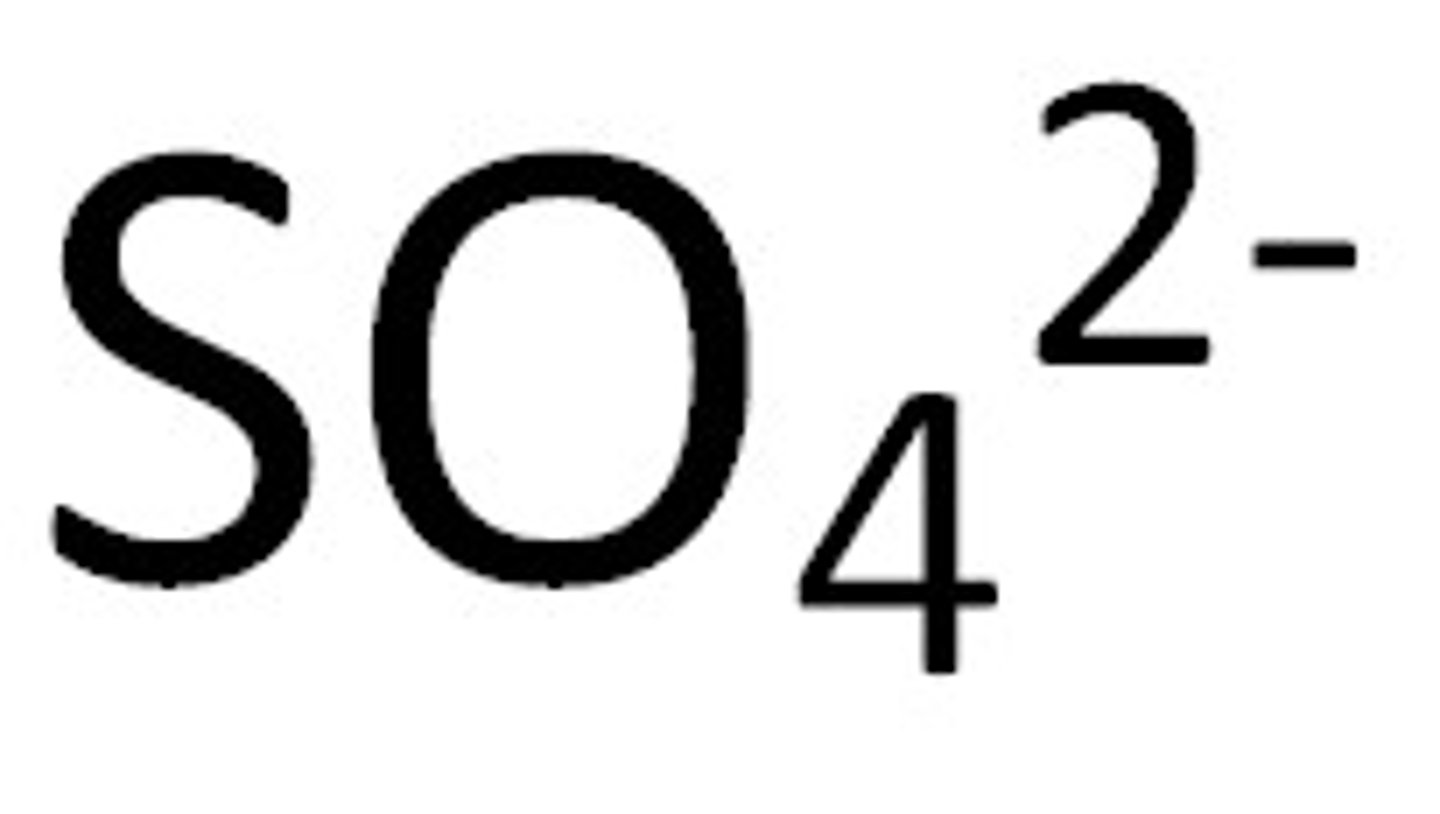
sulfite
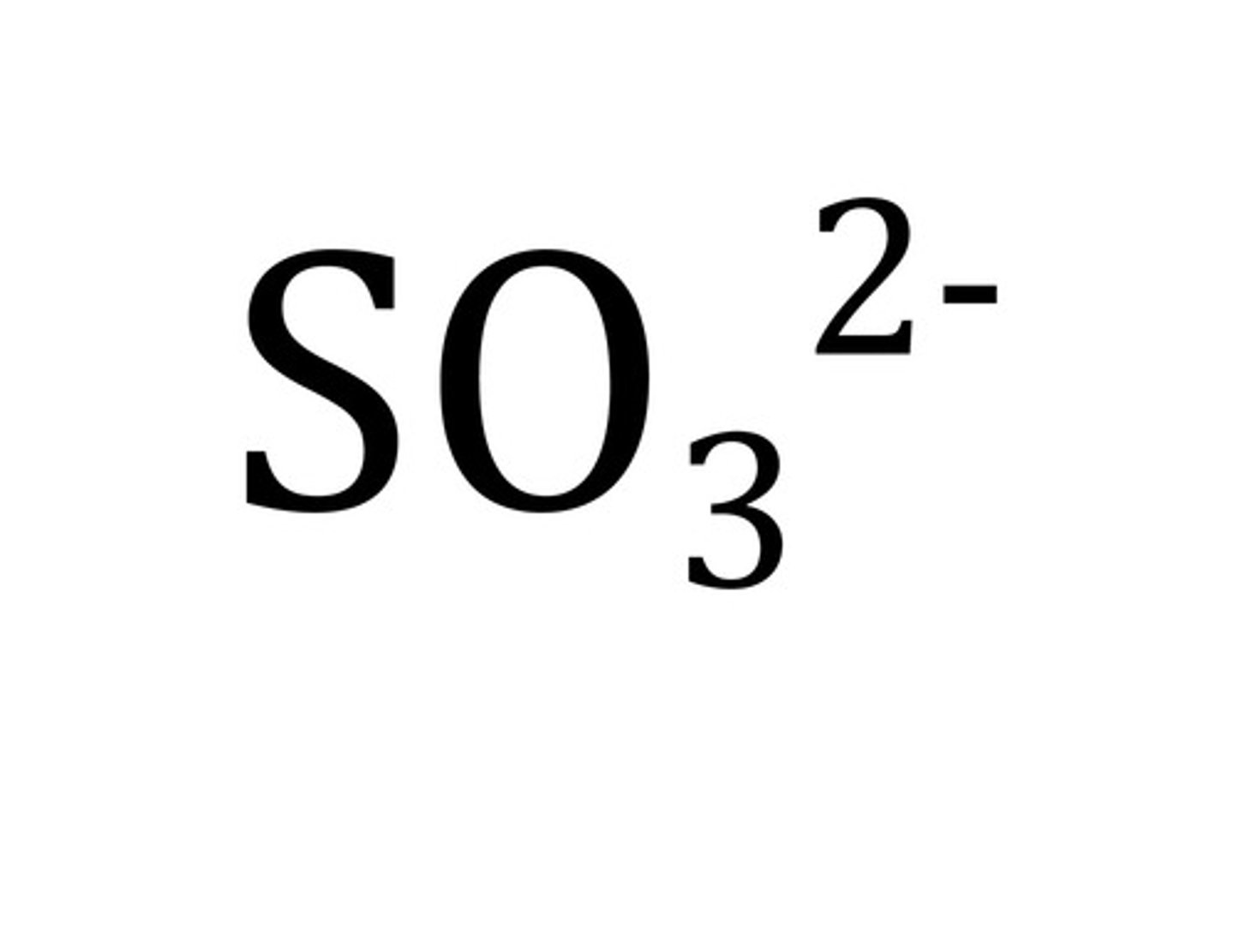
silicate
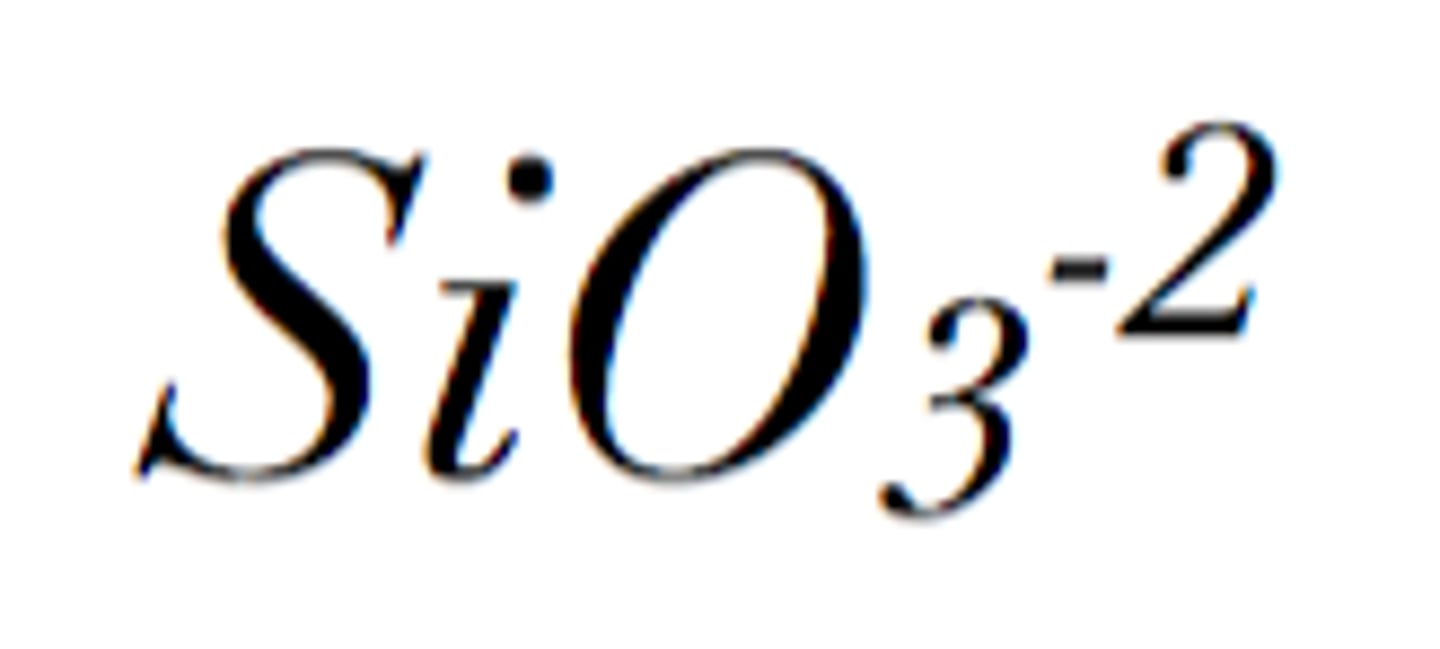
thiocyanate

thiosulfate
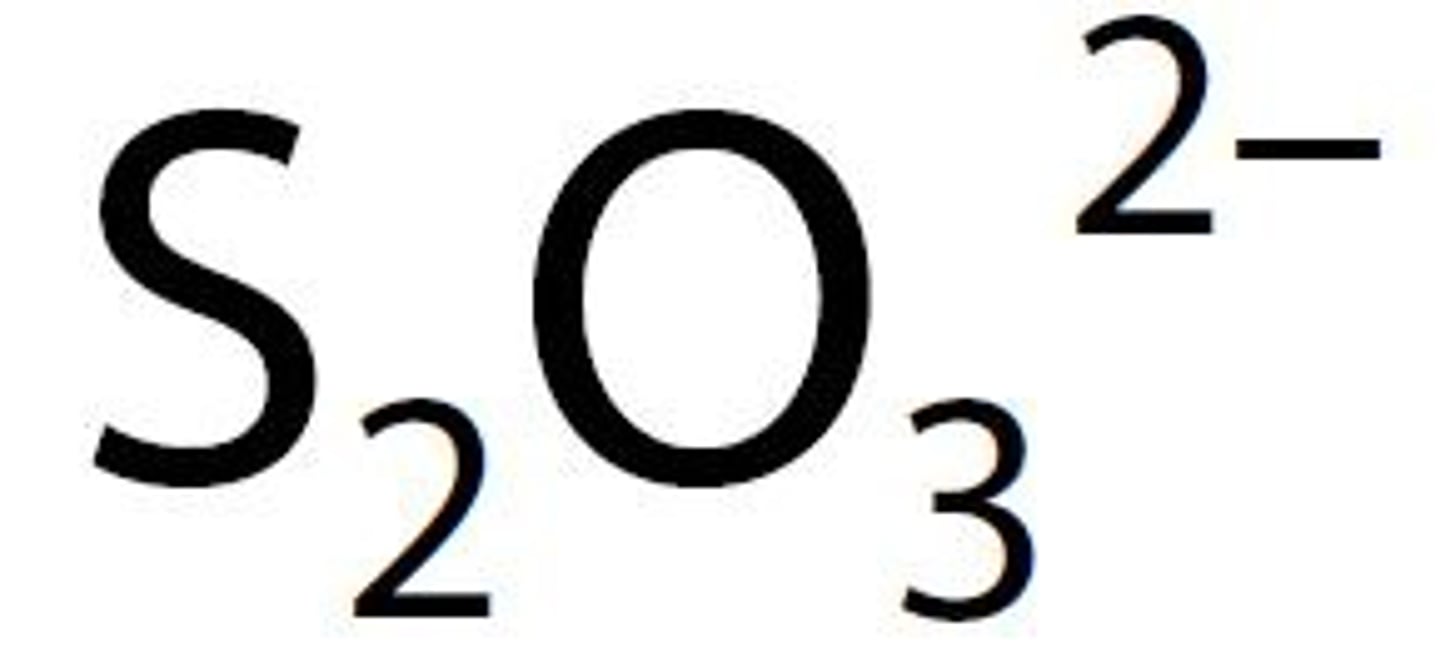
ions that end in -ate
have oxygen in them
elements in the same family
make similar ions. (same charge. Ex: chlorate, bromate, iodate)
per-
add oxygen atom to -ate ion. (ex: iodate IO3 - → periodate IO4 -)

hypo-
remove oxygen from -ite ion. (ex: iodite IO2 - → hypoiodite IO -)

per, ate, ite, hypo
order of decreasing oxygens
thio-
sulfur replaces oxygen. (ex: cyanate CNO - → thiocyanate SCN -)

-ide
monatomic anions (chloride, iodide, bromide)
bonding H+ to an ion
--adds +1 to the charge
--adds "hydrogen" to name
(ex: carbonate CO3 2- → hydrogen carbonate HCO3 -)
di-
2 hydrogens added

bi-
indicates addition of hydrogen cation (H+)
bi- is not used with
-3 charge ions (how many H+ are added is ambiguous)
-3 charge ions
can take one or two hydrogens
Ag +

Zn 2+

Cd 2+

Hg2 2+
mercury (I). (each mercury in +1 state, bonded together = 2+ charge)

Pb 2+, Pb 4+

Sn 2+, Sn 4+

No estudiados (49)
¡Todavía no has estudiado estos términos!