(1.8-1.13) Elements, compounds and mixtures
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
What is an element?
A substance in which all atoms have the same atomic number.
What is a compound?
The combination of two or more elements through a chemical reaction so the atoms are chemically bonded to one another.
What is a mixture?
A substance in which atoms from 2 or more different elements are present but they are not chemically bonded.
What distinguishes a pure substance from a mixture?
A pure substance has a fixed melting/boiling point but a mixture can melt or boil over a range of temperatures.
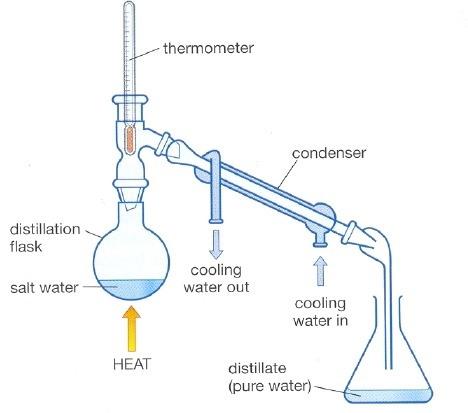
Describe simple distillation to separate mixtures.
A process that uses evaporation and condensation to separate solution:
Water from the salt solution boils and becomes steam.
The steam travels from the flask into the condenser and cools down.
It condenses and becomes liquid water which drips into the beaker.
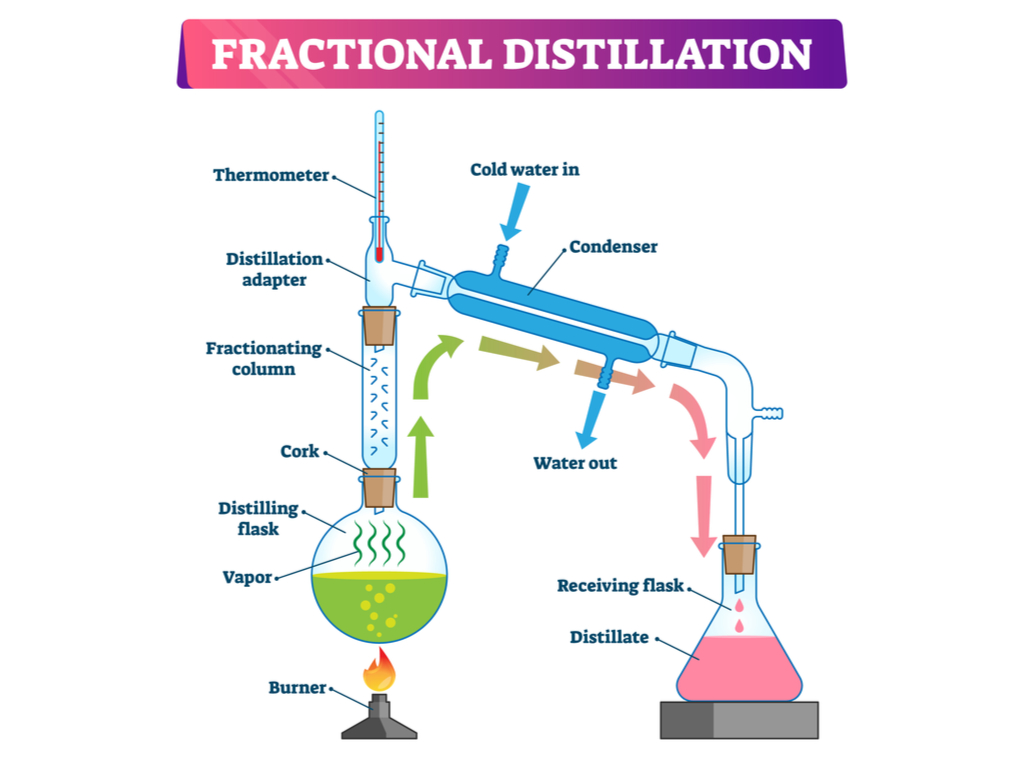
Describe fractional distillation to separate mixtures.
The mixture is heated to a temperature at which part of it will vaporise.
The fractionating column ensures that the separate parts are collected separately (different substances have different boiling points.)
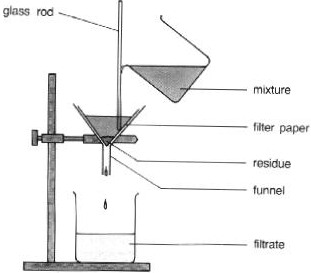
Describe filtration to separate mixtures.
Filter paper is put into a funnel which is held over a beaker.
The mixture is poured into the funnel and the filter paper. due to its tiny holes, collects the residue and lets the filtrate into the beaker.
Describe crystallisation to separate mixtures.
Heat the mixture in an evaporating dish over a Bunsen burner.
The majority of the water will evaporate away.
Leave the dish, now containing the salt and some water, in a warm place and leave the water to slowly evaporate, leaving crystals.

Describe chromatography to separate mixtures.
Draw a line on chromatography paper in pencil and mark an x.
Put mixture on the x and put the paper into the solvent, dot shouldn’t touch water.
As the solvent travels up the paper, it takes the mixture with it to different distances.
Measure how far each substance has reached.
How does a chromatogram provide information about a mixture’s composition?
By measuring the solvent front, we can find out how many substances are present in the mixture.
State the Rf value equation. How is it helpful?
Rf value =
distance travelled by substance
——————————————
distance travelled by solvent front
If dots have the same Rf value, they are the same substance.