Physics IGCSE - Thermal physics
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
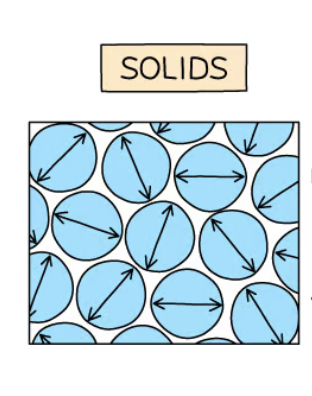
Properties of solids
Fixed shape + volume
Particles close together
Vibrate in fixed positions
Cannot be compressed
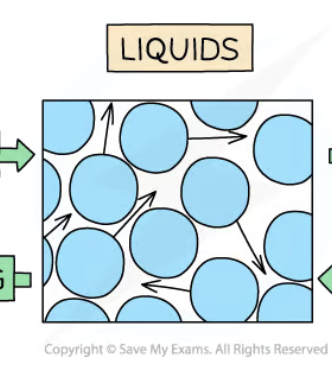
Properties of liquids
Fixed volume but no shape
Particles close together but can slide over each other
Not easily compressed
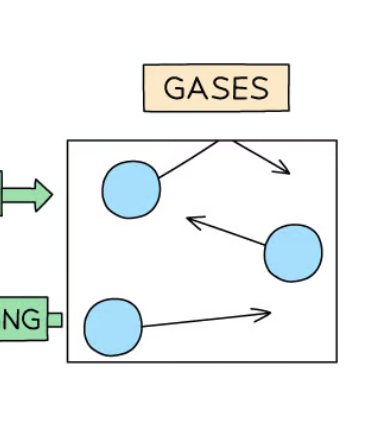
Properties of gases
No fixed shape and volume
Particles are far apart + move freely
Easily compressed
Changes inbetween states
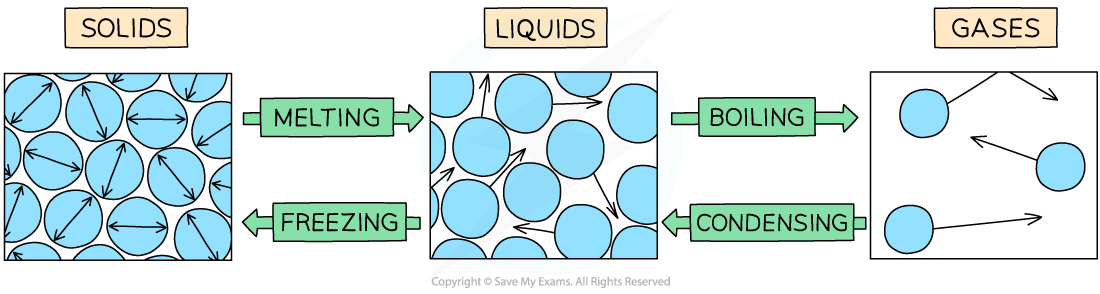
Relationship between temperature and the motion of particles
Temperature increases → particles energy increases → motion increases → moves faster
Evidence for the kinetic particle model of matter
The random motion of particles in a suspension → e.g. smoke particles can be viewed in microscopes
How forces and distance between particles affect the properties of matter → solids
Strong forces → particles close together → fixed shape
How forces and distance between particles affect the properties of matter → liquids
Weaker forces → particles slightly apart → flow
How forces and distance between particles affect the properties of matter → gases
Very weak/no forces → large distances → compressible + expandable
Brownian motion
Random movement of visible particles → due to collisions with smaller, fast moving particles in a gas or liquid
What causes gas pressure
Particle colliding with the walls of a container → creates force per unit area
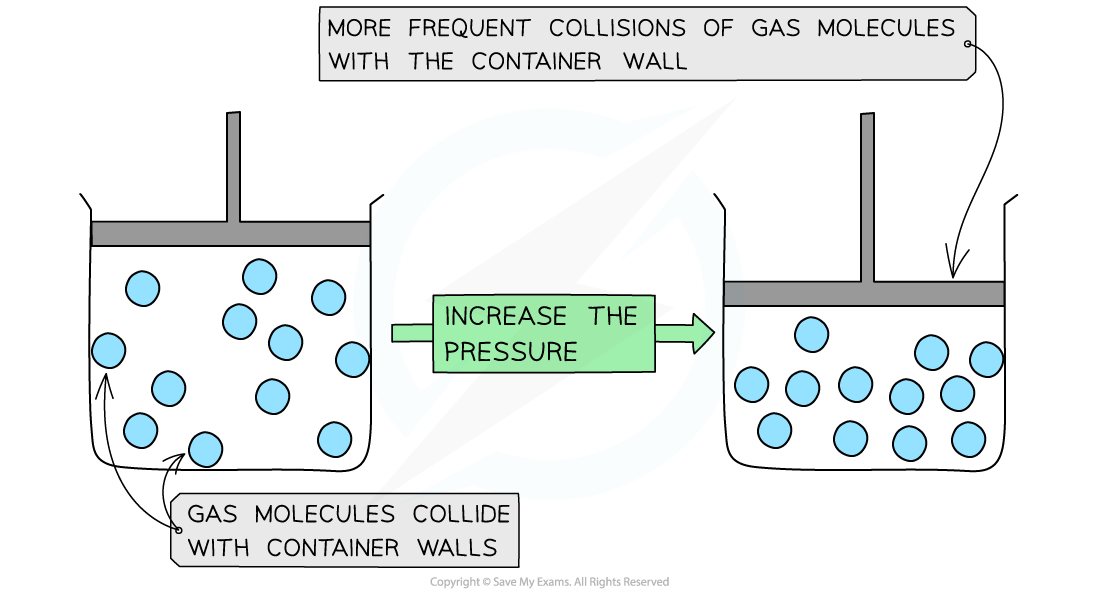
Gas pressure when temperature increases at a constant volume
Particles move faster → collide with wall more frequently + greater force → pressure increases
Gas pressure when volume increases at constant temperature
Particles have more space → collide with wall less frequently → pressure decreases
Thermal expansion of solids at constant pressure
Expands slightly → particles vibrate more
Thermal expansion of liquids at constant pressure
Expands more than solids
Thermal expansion of gases at constant pressure
Expands the most → particles move more freely + further apart
Everyday applications of thermal expansion
Gaps in railways → allow for expansion
Thermometers → liquid expansion
Bridges → have expansion joints
Overhead cables → sag in summer due to expansion
Condensation in terms of particles
Gas particles lose energy → move closer together → form a liquid
Solidification in terms of particles
Liquid particles lose more energy → become fixed in place as a solid
Evaporation
Only most energetic particles at the surface escape the liquid → those particles overcome attractive forces → become gases
Evaporation causes cooling of a liquid
What happens to energy inputs during melting or boiling
Energy breaks bonds between particles → not to raise temperature → temperature stays constant during melting/boiling
Difference between evaporation + boiling
Evaporation | Boiling |
|
|
Factors affecting evaporation
Higher temperature → faster particle motion
Larger surface area → more particles escape
Air movement → removes particles above surface → increase evaporation
Examples of good thermal conductors
Metals → e.g. copper, aluminium + silver
Examples of bad thermal conductors (insulators)
Wood, plastic, glass + air
What causes thermal conduction in solids
Vibrations of particles in a lattice → vibrations transfer energy to neighbouring particles → faster vibrations → higher temperature → more energy transfer
Why metals are good conductors
Delocalised electrons → move through the structure → electron transfers thermal energy quickly by colliding with ions + other electrons
Convection
Important method of heat transfer for liquids + gases
Convection in liquids and gases
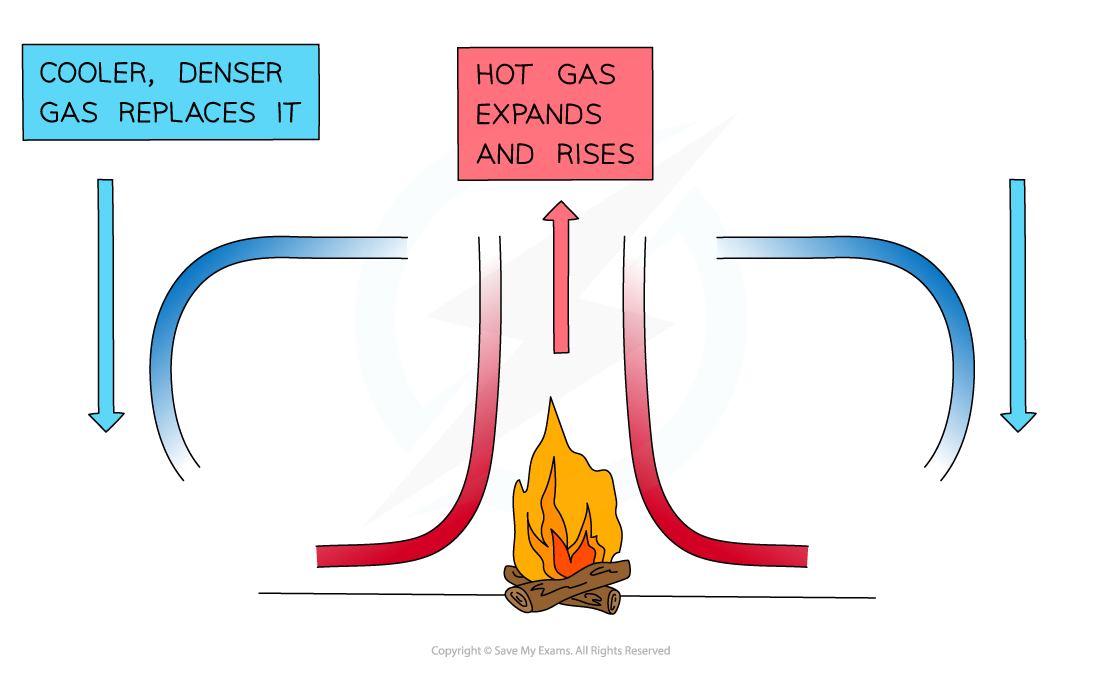
Heated fluid expands → becomes less dense → rises → cooler + denser liquids sinks → creates a convection current → transfers thermal energy through liquids → particles gain energy → move faster + spread out → decreases density
Convection in liquids + gases in terms of density changes
When a fluid is heated → particles gain energy + move apart → decreases its density → convection current occurs → movement transfers heat throughout the fluid
Thermal energy transfer by thermal radiation → doesn’t require a medium → due to infrared radiation
How black + dull surfaces affect thermal radiation
Black, dull surfaces → good absorbers + transmitters
How white + shiny surfaces affect thermal radiation
White, shiny surfaces → poor absorbers + transmitters → better at reflecting thermal radiation
How the temperature of the Earth is affected
Radiation absorbed by Earth
Radiation emitted by Earth
Experiment to find good + bad emitters of thermal radiation
2 metal cans (black + white) filled with hot water → measure how quickly they cool → black can emits radiation faster (cools faster) → better emitter
Experiment to find bad + good absorbers of thermal radiation
Black + white surface under heat lamp → measure temperature over time → black surface heats up faster → better absorber
Basic examples of conduction
Metal saucepan handles get hot → metals conduct heat
Plastic/wood handles → insulators → prevent burns
Basic examples of convection
Heaters → warm a room → sets up convection currents in the air
Hot air rise → cools → sinks → circulates heat
Basic examples of radiation
Black clothing feels hotter in sun → absorbs more radiation
Shiny foil blankets → reflects heat to keep person warm