Muscular Unit
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/52
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
1
New cards
functions of muscle tissue
movement facilitation
2
New cards
functions of muscle tissue
postural support
3
New cards
functions of muscle tissue
regulation of organ volume
4
New cards
functions of muscle tissue
thermogenesis
5
New cards
functions of muscle tissue
protection of internal organs
6
New cards
elasticity
the ability of muscle tissue to return to its normal resting length after it has been stretched or contracted
7
New cards
excitability
the ability of muscle tissue to receive and respond to a stimulus like nerve impulses
8
New cards
extensibility
the ability of muscle tissue to be elongated or stretched
9
New cards
contractility
the ability of muscle tissue to become short and thick while producing movement
10
New cards
skeletal muscle
* attached to bones
* striated
* voluntary control
* multinucleated
* movement, thermogenesis, posture, protection of internal organs
* striated
* voluntary control
* multinucleated
* movement, thermogenesis, posture, protection of internal organs
11
New cards
smooth muscle
* hollow organs (stomach, bladder, blood vessels, etc.)
* non-striated
* involuntary control
* control diameter of blood vessels, peristalsis: propels food and waste through digestive system
* non-striated
* involuntary control
* control diameter of blood vessels, peristalsis: propels food and waste through digestive system
12
New cards
cardiac muscle
* myocardium (heart wall)
* striated
* involuntary
* intercalated disks
* contractions of the heart, pumps blood
* striated
* involuntary
* intercalated disks
* contractions of the heart, pumps blood
13
New cards
actin
* thin, light-colored myofilaments (protein fibers)
* anchored to the z-lines of sarcomeres
* contain two regulatory proteins:
tropomyosin
troponin
* anchored to the z-lines of sarcomeres
* contain two regulatory proteins:
tropomyosin
troponin
14
New cards
tropomyosin
-blocks muscle contraction
-thread-like intertwined protein molecules
-blocks actin's active sites preventing cross-bridge formation with myosin while the sarcomere is relaxed
-thread-like intertwined protein molecules
-blocks actin's active sites preventing cross-bridge formation with myosin while the sarcomere is relaxed
15
New cards
troponin
-promotes muscle contraction
-globular proteins composed of three subunits
-one subunit binds to actin, one to tropomyosin, and the last binds to Ca+
-globular proteins composed of three subunits
-one subunit binds to actin, one to tropomyosin, and the last binds to Ca+
16
New cards
myosin
-thick, dark-colored myofilaments
-found in the center of the sarcomere
-forms cross-bridges with actin molecules during muscle contraction
-alternate with actin myofilaments to form striations
-golf club shaped (long, thick protein molecule with a globular head)
-found in the center of the sarcomere
-forms cross-bridges with actin molecules during muscle contraction
-alternate with actin myofilaments to form striations
-golf club shaped (long, thick protein molecule with a globular head)
17
New cards
threshold stimulus
the weakest stimulus from a neuron that stimulates muscle contraction
18
New cards
all or nothing principle
the threshold stimulus contacts the motor unit, causes innervated muscle fibers to contract to their fullest potential
19
New cards
motor neuron
a nerve carrying nerve impulses from the brain and stimulates muscles to contract
20
New cards
neuromuscular junction
-also called the synaptic cleft
-the end of the axon terminal where it attaches to the muscle fiber
-the end of the axon terminal where it attaches to the muscle fiber
21
New cards
synaptic vesicles
-the synaptic end bulb, also called the axon terminal, store neurotransmitters
22
New cards
motor end plate
part of the muscle fiber at the end of the axon terminal
23
New cards
acetylcholine (Ach)
the neurotransmitter released from the synaptic vesicles that initiates an action potential in muscle fibers
24
New cards
the sliding filament theory
During muscle contraction, the globular heads of the myosin attach to the active sites of the actin myofilament and "ratchet" or swivel pulling the actin towards the center of the sarcomere (unit of contraction). This causes the actin myofilaments to slide past one another resulting in a shortening of a sarcomere. The sarcomere shortens and the muscle contracts.
25
New cards
cholinesterase
the enzyme that destroys acetylcholine
26
New cards
origin
-body segment with the most mass
-more proximally located
-large surface area of attachment
-immovable end of muscle
-more proximally located
-large surface area of attachment
-immovable end of muscle
27
New cards
insertion
-body segment with the least mass
-more distally located
-smaller surface area of attachment
-movable end of muscle
-more distally located
-smaller surface area of attachment
-movable end of muscle
28
New cards
gaster (belly)
the fleshy portion of a muscle between the origin and insertion
29
New cards
agonist
the muscle responsible for the majority of force during movement
30
New cards
antagonist
the muscle that performs the opposite movement of the agonist
31
New cards
synergist
a muscle that assists the agonist by providing additional force or directing the force of the agonist
32
New cards
fixator (stabilizer)
a muscle that stabilizes a point of body position
33
New cards
biceps brachii
anterior upper arm muscle, flexes the forearm
34
New cards
biceps femoris
long muscle in the posterior aspect in the thigh responsible for hip and knee joint movement, part of the hamstring muscle group
35
New cards
triceps brachii
posterior upper arm muscle, extends the forearm
36
New cards
sternocleidomastoid
anterior aspect of the neck (sternum --> clavicle --> mastoid process)
flexes the head and neck
flexes the head and neck
37
New cards
trapezius
posterior aspect of the neck, extends the head and neck
38
New cards
deltoid
covers the shoulder, abducts the arm
39
New cards
pectoralis major
chest, adducts the arm
40
New cards
latissimus dorsi
superficial muscle of the thoracic and lumbar region of the back, internal rotation, flexes or extends the arm
41
New cards
diaphragm
internal muscle separating the thoracic and abdominal cavities, increases and decreases volume of thoracic cavity (breathing muscle)
42
New cards
gastrocnemius
posterior aspect of the lower leg, plantar flexion
43
New cards
hamstring muscle group
posterior aspect of the thigh, flexes the lower leg
biceps femoris, semimembranosus, semitendinosus
biceps femoris, semimembranosus, semitendinosus
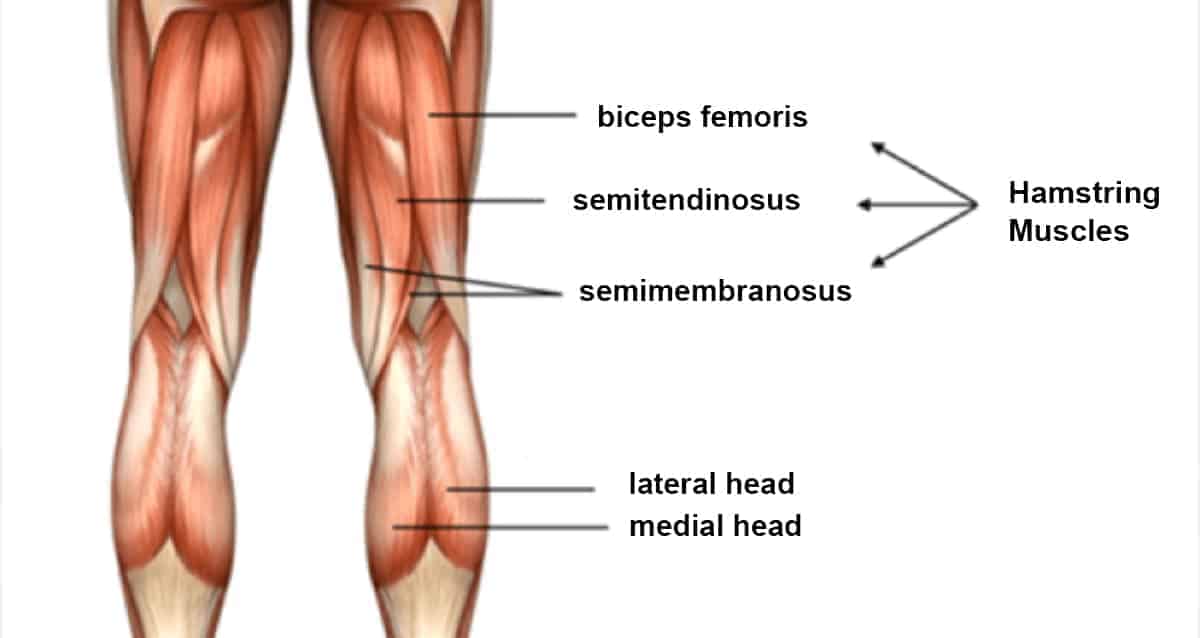
44
New cards
quadriceps muscle group
anterior aspect of the thigh, extends the lower leg
vastus femoris, vastus medialis+intermedialis+lateralis
vastus femoris, vastus medialis+intermedialis+lateralis
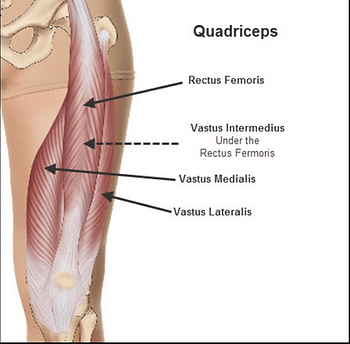
45
New cards
gluteus maximus
buttocks region, extends a flexed thigh or hyperextends the thigh from anatomical position
46
New cards
rectus femoris
anterior aspect of the thigh, part of the quadriceps muscle group, extends the lower leg at the knee
47
New cards
vastus lateralis + intermedialis + medialis
anterior compartment of the thigh, makes up the quadriceps muscle group
48
New cards
buccanator
cheek muscle, active role in mastication, swallowing, blowing, and sucking
49
New cards
masseter
runs from the cheek bone to either side of the lower jaw, main muscle in mastication
50
New cards
fibromyalgia
a widespread musculoskeletal pain and fatigue disorder with an unknown cause. pain in the muscles, tendons, and ligaments
51
New cards
muscular dystrophy
* Genetic diseases characterized by muscular atrophy of skeletal muscle tissue.
The most common form of muscular dystrophy is Duchenne's Muscular Dystrophy where the skeletal muscle is replaced by fat and fibrous tissue
The most common form of muscular dystrophy is Duchenne's Muscular Dystrophy where the skeletal muscle is replaced by fat and fibrous tissue
52
New cards
shin splints
soreness and pain in the front of the lower leg due to excessive strain of the tibialis posterior, which pulls the periosteum away from the bone affecting the tibialis anterior.
53
New cards
muscle strain
* muscle pain
1st degree: microtears
2nd degree: partial tear
3rd degree: complete rupture
1st degree: microtears
2nd degree: partial tear
3rd degree: complete rupture