VIII : Precipitation & Agglutination
1/122
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
123 Terms
d. Precipitation involves a soluble antigen, whereas agglutination involves a particulate antigen.
Precipitation differs from agglutination in which way?
a. Precipitation can only be measured by an automated instrument.
b. Precipitation occurs with univalent antigen, whereas agglutination requires multivalent antigen.
c. Precipitation does not readily occur because few antibodies can form aggregates with antigen.
d. Precipitation involves a soluble antigen, whereas agglutination involves a particulate antigen.
c. High affinity and high avidity
In a precipitation reaction, how can the ideal antibody be characterized?
a. Low affinity and low avidity
b. High affinity and low avidity
c. High affinity and high avidity
d. Low affinity and high avidity
b. Zone of equivalence
When soluble antigens diffuse in a gel that contains antibody, in which zone does optimum precipitation occur?
a. Prozone
b. Zone of equivalence
c. Postzone
d. Prezone
d. All of the above.
Which of the following statements apply to rate nephelometry?
a. Readings are taken before equivalence is reached.
b. It is more sensitive than turbidity.
c. Measurements are time dependent.
d. All of the above.
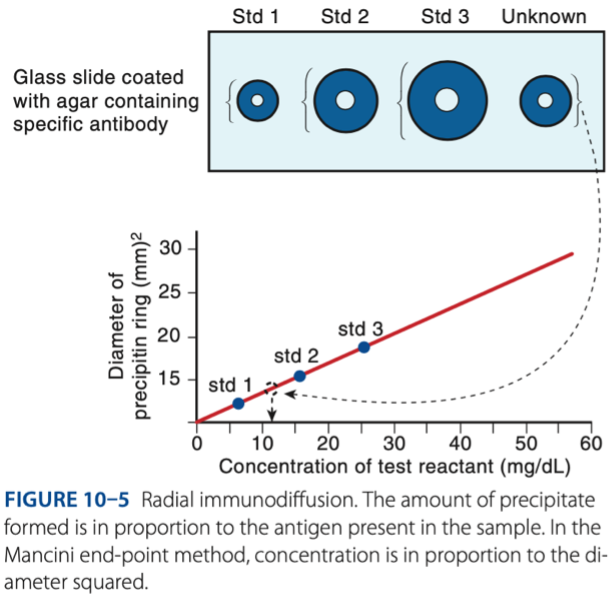
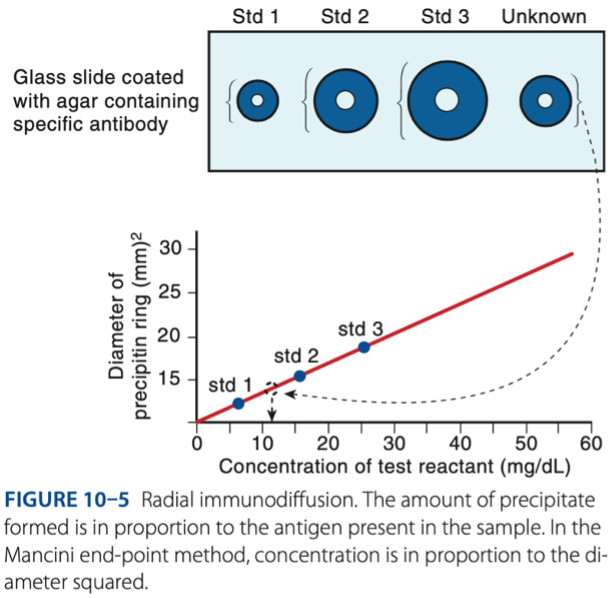
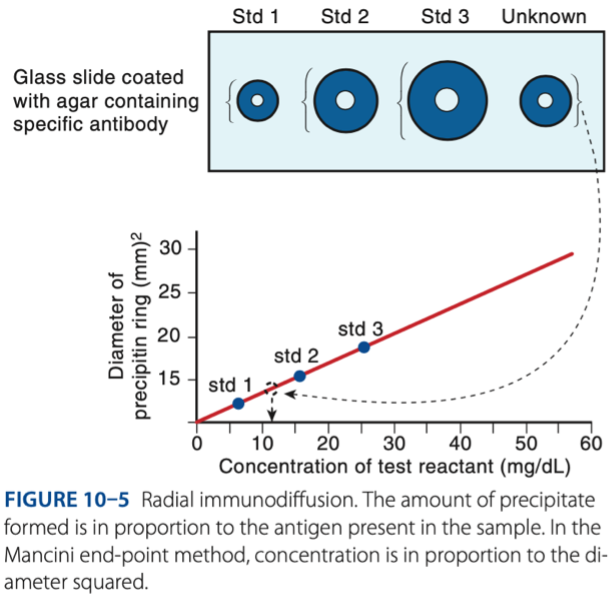
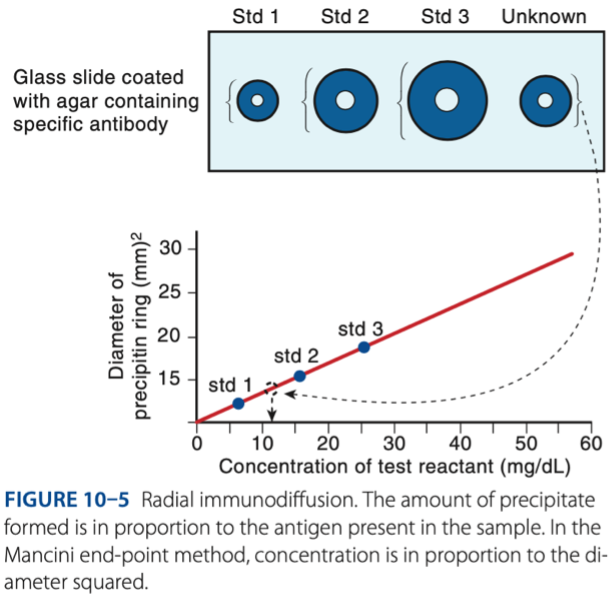
b. Concentration is directly in proportion to the square of the diameter.
Which of the following is characteristic of the end-point method of RID?
a. Readings are taken before equivalence.
b. Concentration is directly in proportion to the square of the diameter.
c. The diameter is plotted against the log of the concentration.
d. It is primarily a qualitative rather than a quantitative method.
a. Prozone
In which zone might an antibody-screening test be false negative?
a. Prozone
b. Zone of equivalence
c. Postzone
d. None of the above
b. Nephelometry measures light that is scattered at an angle.
How does measurement of turbidity differ from nephelometry?
a. Turbidity measures the increase in light after it passes through a solution.
b. Nephelometry measures light that is scattered at an angle.
c. Turbidity deals with univalent antigens only. d. Nephelometry is not affected by large particles
falling out of solution.
a. Affinity
Which of the following refers to the force of attraction between an antibody and a single antigenic determinant?
a. Affinity
b. Avidity
c. Van der Waals attraction
d. Covalence
c. In immunofixation electrophoresis, antibody is directly applied to the gel instead of being placed in a trough.
Immunofixation electrophoresis differs from immunoelectrophoresis in which way?
a. Electrophoresis takes place after diffusion has occurred in immunofixation electrophoresis.
b. Better separation of proteins with the same electrophoretic mobilities is obtained in immunoelectrophoresis.
c. In immunofixation electrophoresis, antibody is directly applied to the gel instead of being placed in a trough.
d. Immunoelectrophoresis is a much faster procedure.
d. The two antigens are unrelated.
If crossed lines result in an Ouchterlony immunodiffu- sion reaction with antigens 1 and 2, what does this indicate?
a. Antigens 1 and 2 are identical.
b. Antigen 2 is simpler than antigen 1.
c. Antigen 2 is more complex than antigen 1.
d. The two antigens are unrelated.
a. Radial immunodiffusion
Which technique represents a single-diffusion reaction?
a. Radial immunodiffusion
b. Ouchterlony diffusion
c. Immunoelectrophoresis
d. Immunofixation electrophoresis
c. The equilibrium constant is related to strength of antigen-antibody binding.
Which best describes the law of mass action?
a. Once antigen-antibody binding takes place, it is irreversible.
b. The equilibrium constant depends only on the forward reaction.
c. The equilibrium constant is related to strength of antigen-antibody binding.
d. If an antibody has a high avidity, it will dissociate from antigen easily.
a. Direct agglutination
Agglutination of dyed bacterial cells represents which type of reaction?
a. Direct agglutination
b. Passive agglutination
c. Reverse passive agglutination
d. Agglutination inhibition
c. Avidity
If a single IgM molecule can bind many more antigens than a molecule of IgG, which of the following is higher?
a. Affinity
b. Initial force of attraction
c. Avidity
d. Initial sensitization
b. Soluble haptens
Agglutination inhibition could best be used for which of the following types of antigens?
a. Large cellular antigens such as erythrocytes
b. Soluble haptens
c. Bacterial cells
d. Coated latex particles
c. It is used for identification of antigens.
Which of the following correctly describes reverse passive agglutination?
a. It is a negative test.
b. It can be used to detect autoantibodies.
c. It is used for identification of antigens.
d. It is used to detect sensitization of red blood
cells.
b. It may be too small to produce lattice formation.
Reactions involving IgG may need to be enhanced for which reason?
a. It is only active at 25°C.
b. It may be too small to produce lattice formation.
c. It has only one antigen-binding site.
d. It is only able to produce visible precipitation reactions.
d. Agglutination inhibition
For which of the following tests is a lack of agglutination a positive reaction?
a. Hemagglutination
b. Passive agglutination
c. Reverse passive agglutination
d. Agglutination inhibition
a. Direct hemagglutination
Typing of RBCs with reagent antiserum represents which type of reaction?
a. Direct hemagglutination
b. Passive hemagglutination
c. Hemagglutination inhibition
d. Reverse passive hemagglutination
c. The patient has a large amount of antigen present.
In a particle-counting immunoassay using reagent an- tibody attached to latex particles, if the particle count in solution is very low, what does this mean about the presence of patient antigen?
a. The patient has no antigen present.
b. The patient has a very small amount of antigen.
c. The patient has a large amount of antigen present.
d. The test is invalid.
• Precipitation
• Agglutination
• Complement Fixation
• Labeled Immunoassays
Complement
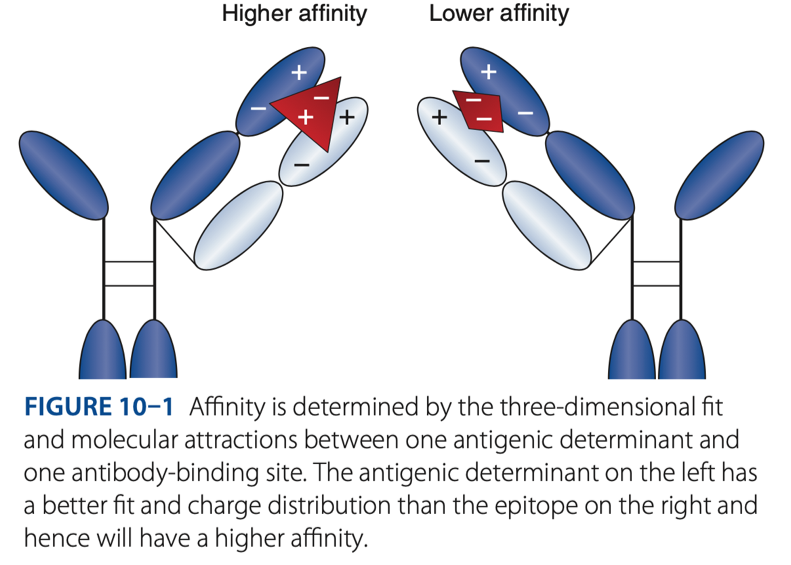
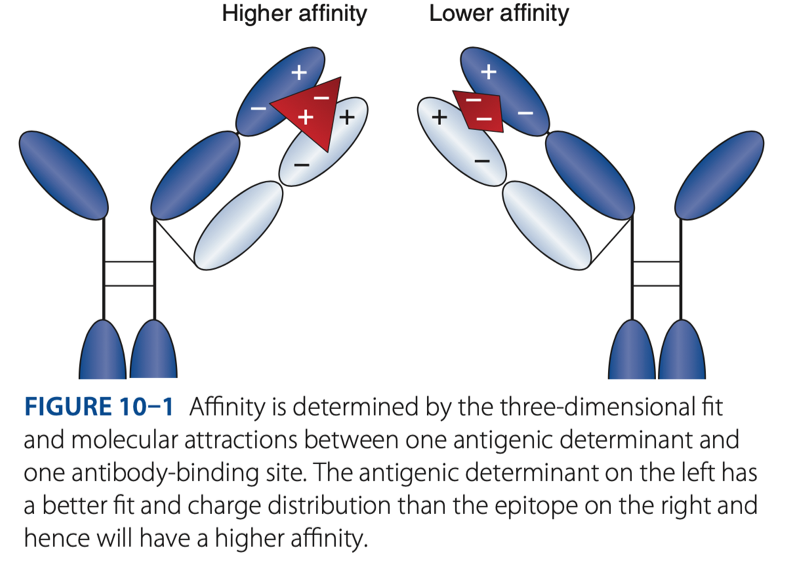
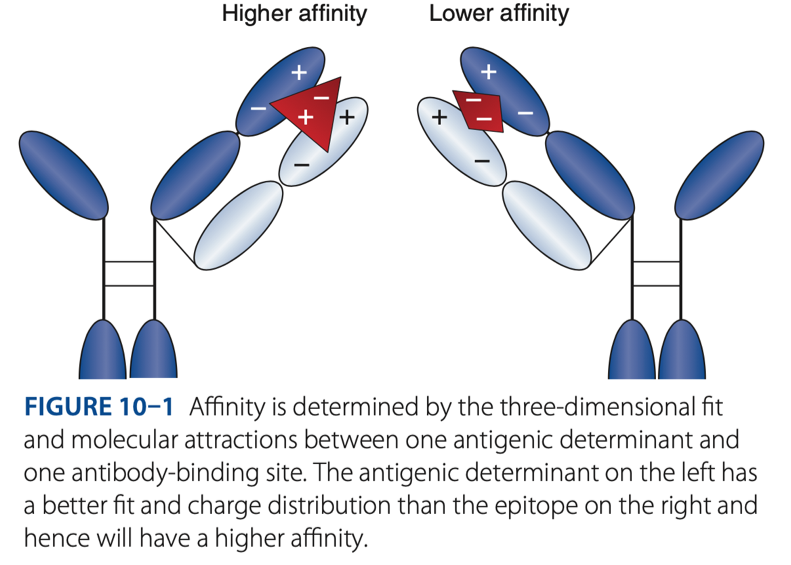
Affinity
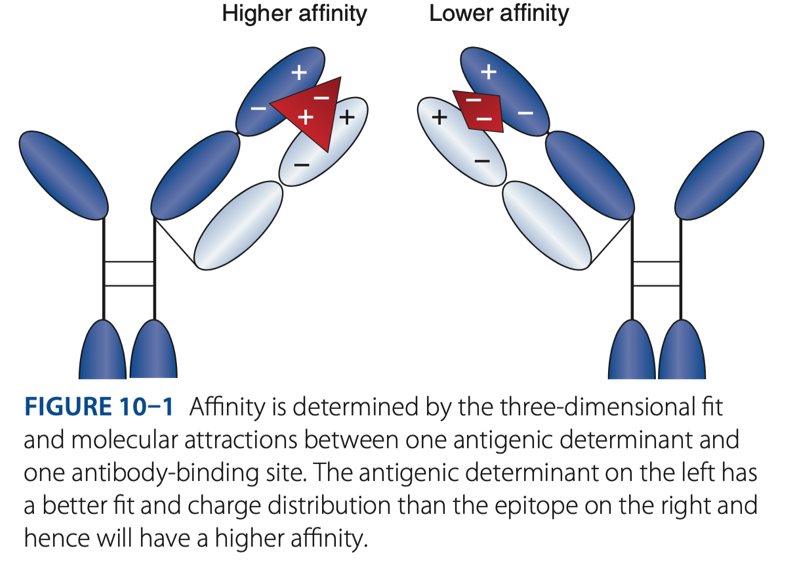
- The initial force of attraction that exists between a single Fab site on an antibody molecule & an epitope/determinant site on an antigen.
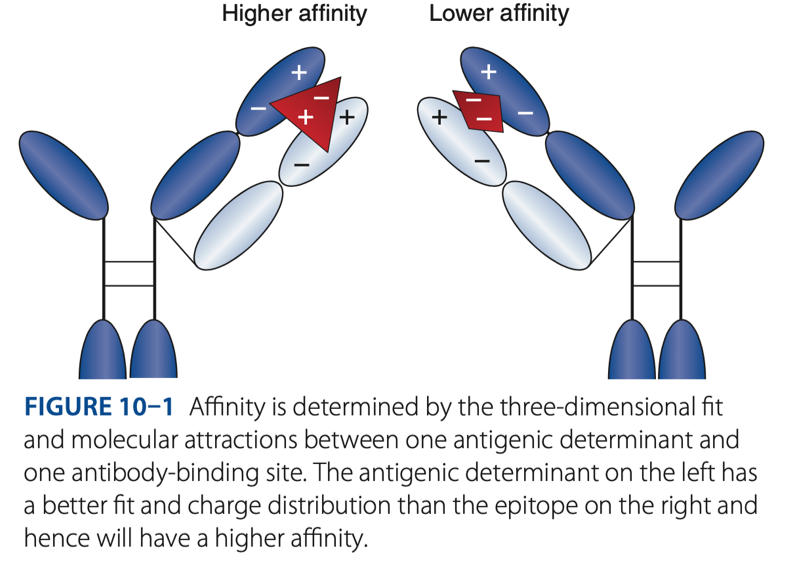
Affinity
- The strength of attraction depends on the specificity of the antibody for a particular antigen.
F
- The more the cross-reacting antigen resembles the original antigen, the stronger the bond will be between the antigen & the binding site.
Antigen-Antibody Binding: Affinity
- The less the cross-reacting antigen resembles the original antigen, the weaker the bond will be between the antigen & the binding site.
Original Ag
Antigen-Antibody Binding: Affinity
– antigen that causes Ab attraction
F
Cross-reaction (resembles) – has similarities with the orginal antigen (mimic). Therefore, they create a false + reaction.
Antigen-Antibody Binding: Affinity
- Cross-reaction (resembles) – has similarities with the orginal antigen (mimic). Therefore, they create a false – reaction.
Avidity
- Is the sum of all attractive forces between an antigen & antibody that keeps the molecules together.
Avidity
Involves the overall strength with which a multivalent antibody binds a multivalent antigen.
Avidity
- Is a measure of the overall
F
All antigen–antibody binding is reversible and is governed by the law of mass action.
Antigen-Antibody Binding: Law of Mass Action
- All antigen–antibody binding is irreversible and is governed by the law of mass action. (T/F)
Free reactants
Antigen-Antibody Binding: Law of Mass Action
what are equilibrium with bound reactants.
Value of K
Antigen-Antibody Binding: Law of Mass Action
- Value of - depends on the strength of binding between antibody & antigen.
• The larger the amount of antigen-antibody complex.
• The more visible or easily detectable the reaction.
Antigen-Antibody Binding: Law of Mass Action (T/F)
- The higher the value of K:
The - the amount of antigen-antibody complex.
The - visible or easily detectable the reaction.
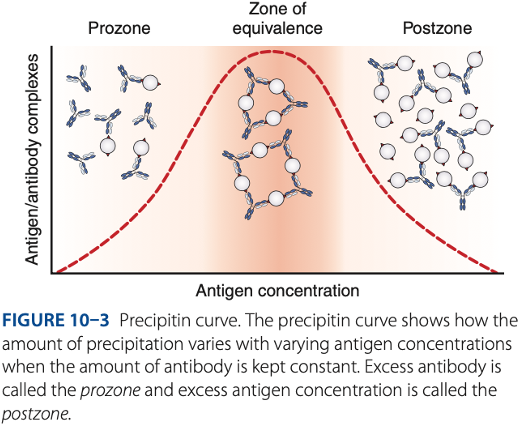
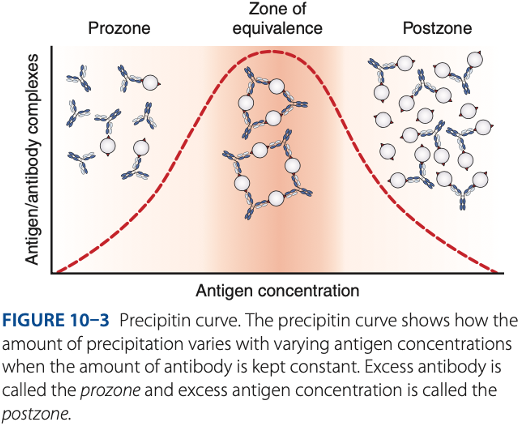
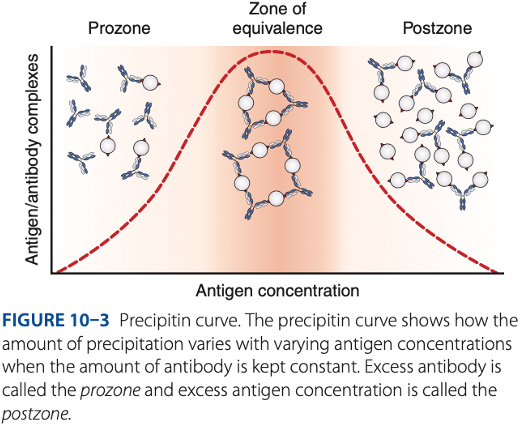
Precipitation Reactions
- Involve combining soluble antigen with soluble antibody to produce insoluble complexes that are visible.
Soluble Antigen
precipitinogen
Soluble Antibody
precipitin
Visible
precipitin line ( a + reaction indicates the binding of a soluble antigen & soluble antibody)
Euqal
should have zone of equivalence
• Multiple binding sites for one another.
• Equal relative concentration for each.
Precipitation Reactions
- Require antigen & antibody to have:
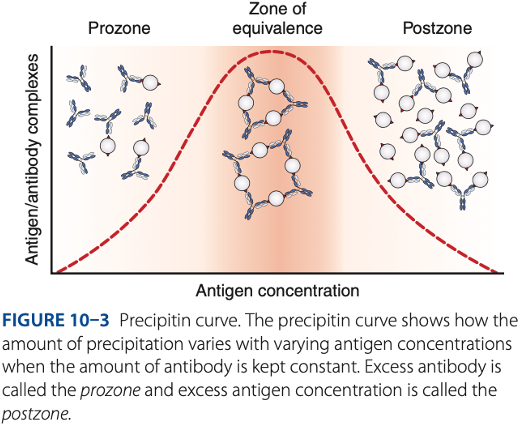
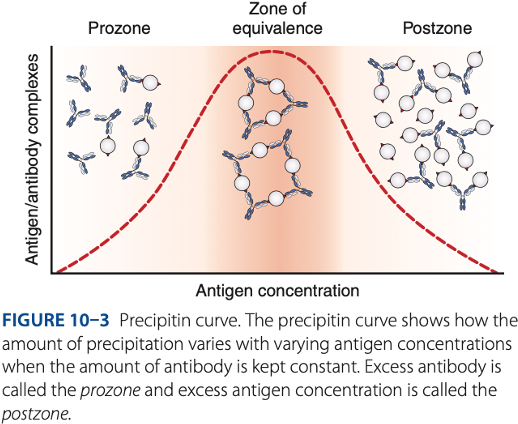
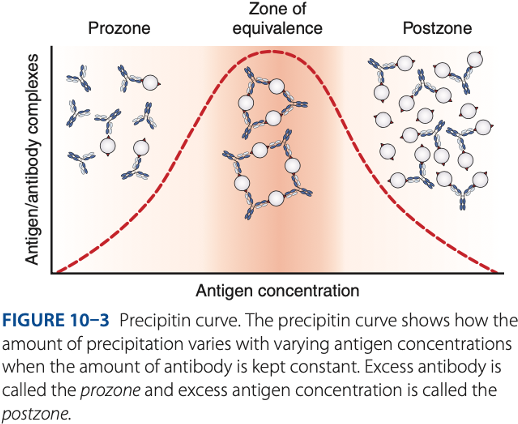
Zone of equivalence
- Number of multivalent sites of antigen & antibody are approximately equal.
zone of equivalence
- Optimum concentration of antigen & antibody
zone of equivalence
Visible reaction should have the
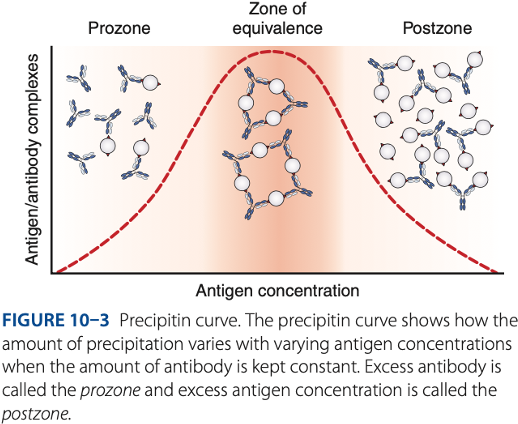
Prozone
– antibody excess, result to false – reaction (no visible reaction)
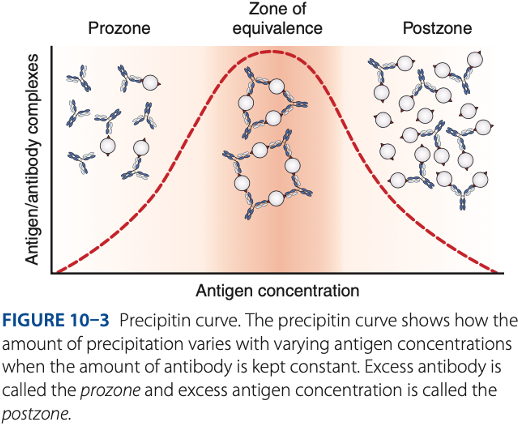
Postzone
– antigen excess, result to false – reaction (no visible reaction
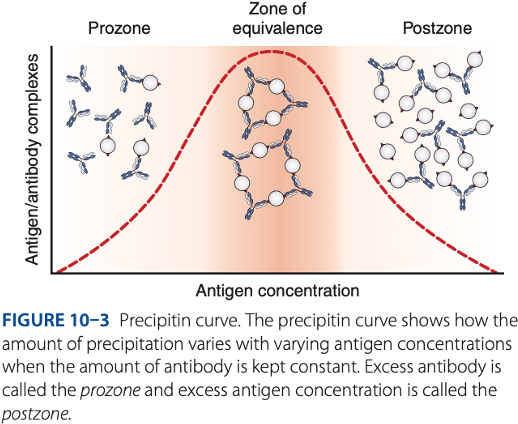
zone of equivalence
To be detectable, precipitation of reactions must be run in the -
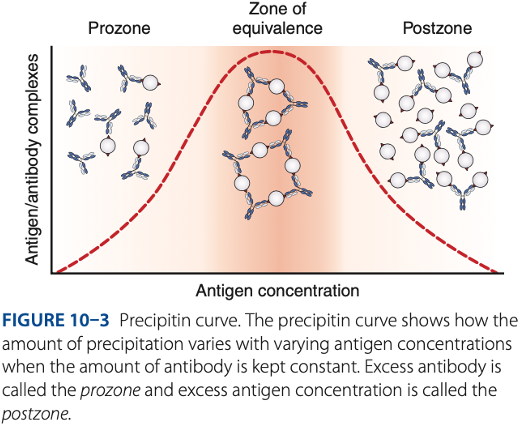
Antibody excess
Prozone phenomenon (- excess)
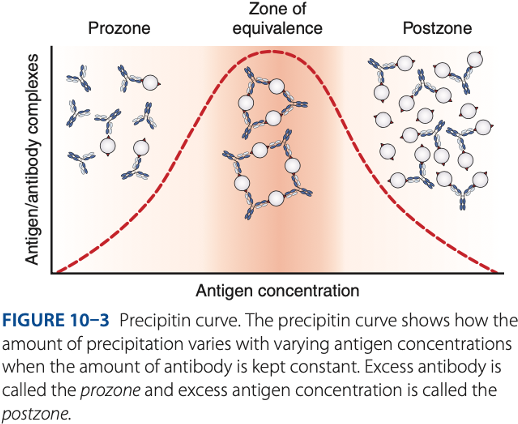
Prozone
- Antigen combines with only 1 or 2 antibody molecules.
Prozone
- No cross-linkages are formed.
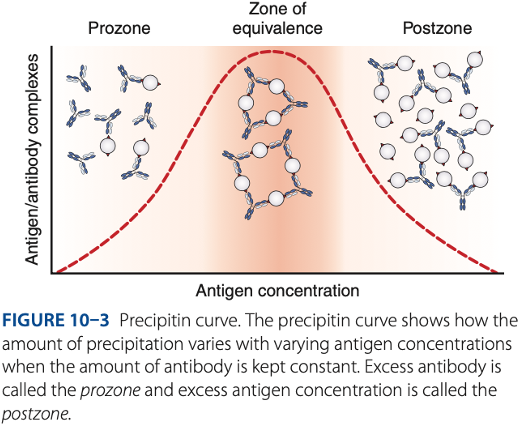
False – reactions
Precipitation Curve : Prozone
What reactions may occur as a result of high antibody concentration.
If a false – reaction is suspected, diluting out the antibody & performing the test again may produce a + result.
Precipitation Curve : Prozone
If a false – reaction is suspected, - the antibody & performing the test again may produce a + result.
Antigen
- Postzone phenomenon (- excess)
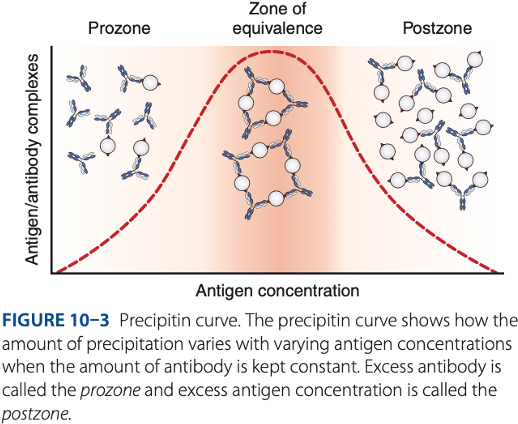
Postzone
- Small aggregates are surrounded by excess antigen.
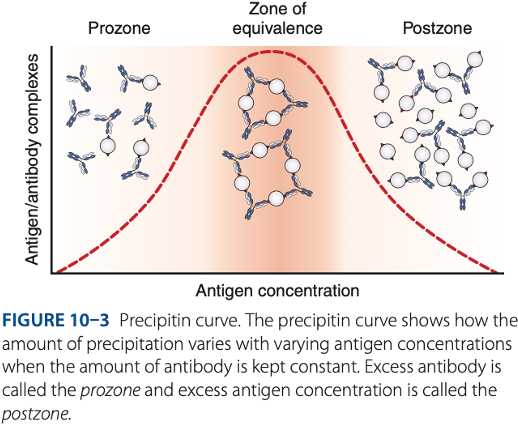
Postzone
- No lattice network is formed.
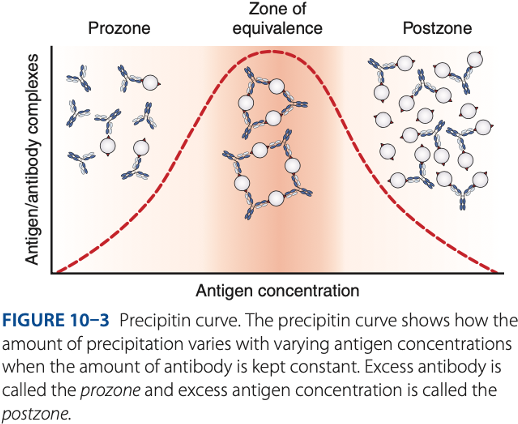
false – results
Postzone
- The presence of a small amount of antibody may be obscured, causing what results.
T
Postzone false – results
- Test is repeated about a week later with a spx to give time for further production of antibody. (t/f)
F
If the test is negative again, it is unlikely that the px has the antigen. (t/f)
Postzone false – results
- If the test is negative again, it is unlikely that the px has the -antigen. (t/f)
Nephelometry
- Light that is scattered at an angle is measured, indicating the amount of antigen / antibody present.
Nephelometry
- Measures the scattered light that pass thru the solution.
Turbidimetry
measures the blocked light that didn’t pass thru the solution (light block by precipitin)
1 – 10
Sensitivity (µgAB / ML) of Nephelometry
• Immunoglobulins
• Complement
• C-reactive protein
• Other serum proteins
Application of Nephelometry
10 – 50
Sensitivity (µgAB / ML) of Radial Immunodiffusion
• Immunoglobulins
• Complement
Application of Radial Immunodiffusion
Radial Immunodiffusion
- Antigen diffuses out into gel that is infused with antibody.
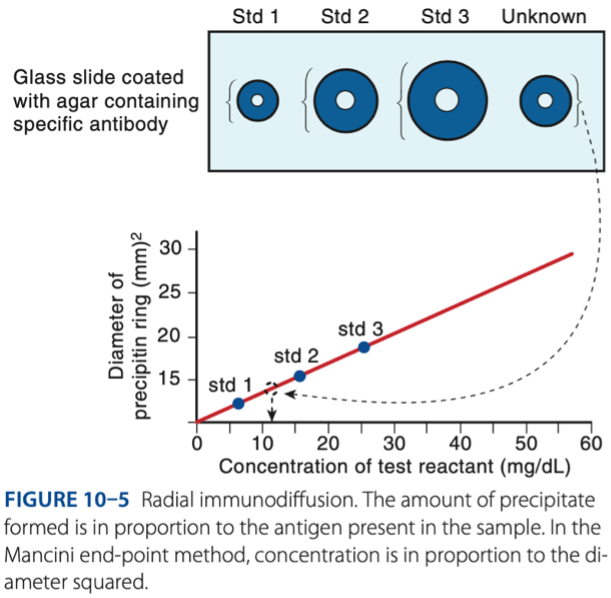
Radial Immunodiffusion
- Measurement of the radius indicates concentration of antigen.
Standard
Radial Immunodiffusion
– a substance with known concentrations.
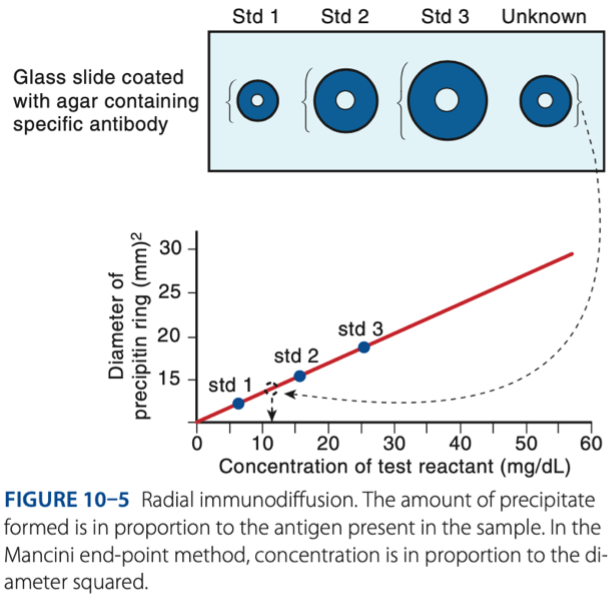
Radial Immunodiffusion
- Antigen diffuses out into gel that is infused with antibody.
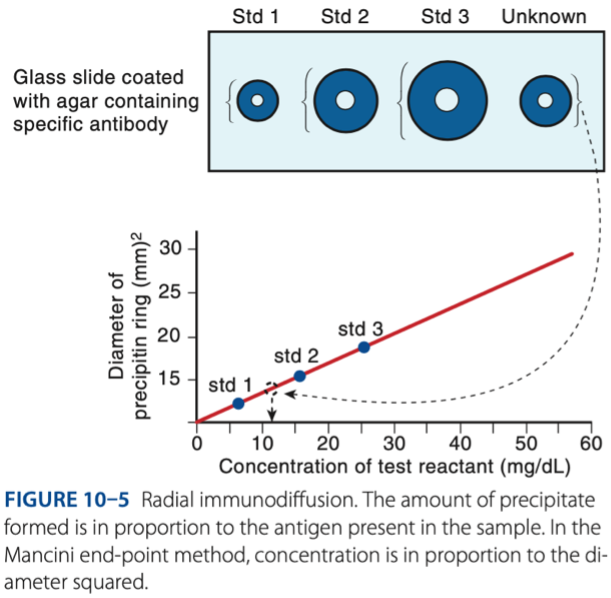
Radial Immunodiffusion
- Measurement of the radius indicates concentration of antigen.
Radial Immunodiffusion
- Is a single diffusion technique.
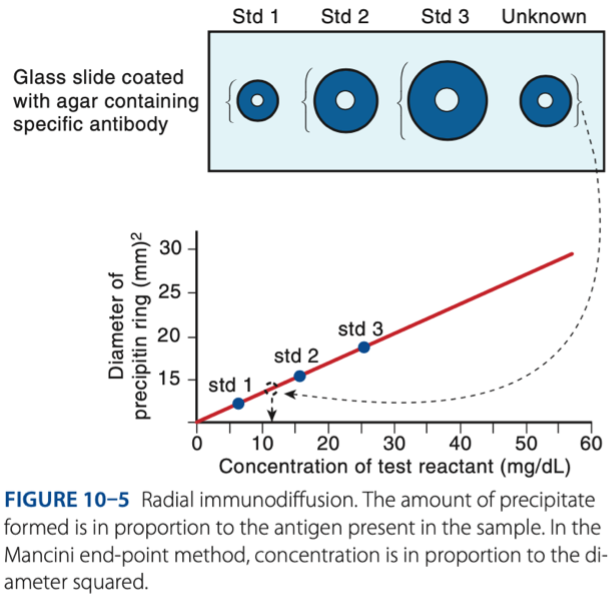
Radial Immunodiffusion
- Antibody is in the support gel, & antigen is applied in a well cut in the gel.
- Both antigen & antibody diffuse out from wells in a gel.
- The lines of precipitate formed indicate the relationship of antigens.
- Is a double diffusion technique.
- Wells are cut in a gel & both antigen & antibody diffuse out radially.
- A line of precipitate forms where antigen & antibody meet.
• Identity
• Partial identity
• Nonidentity
3 possible patterns of Ouchterlony Double Diffusion
Identity
Ouchterlony Double Diffusion
– arc line
Partial identity
Ouchterlony Double Diffusion
– spur formation
Nonidentity
Ouchterlony Double Diffusion
– cross line
20 – 200
Sensitivity (µgAB / ML) of Ouchterlony Double Diffusion
Complex antigens, such as fungal antigens
Application of Ouchterlony Double Diffusion
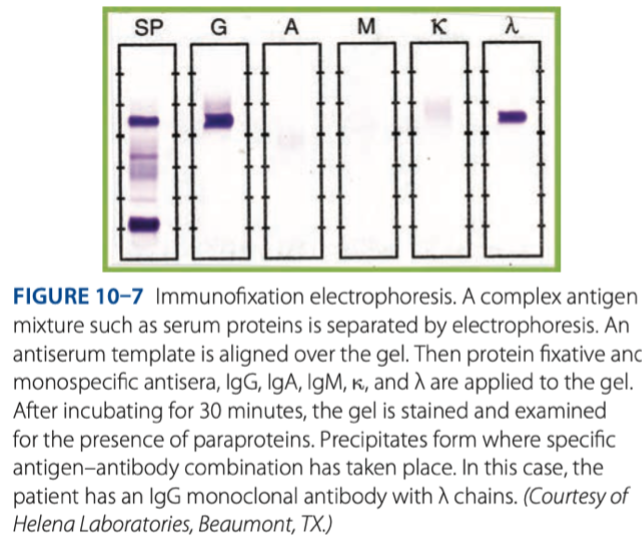
- Electrophoresis of serum is followed by direct application of antibody to the gel.
Elecrtophoretic Principle
The migration of protein in an electrically charge field. The bigger the molecular weight the slower the migration.
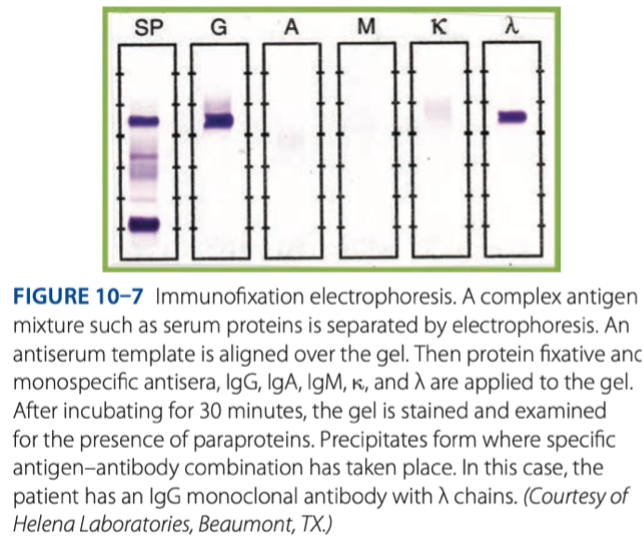
Immunofixation Electrophoresis
- Unknown antigen is electrophoresed, & then antibody is applied directly to the gel.
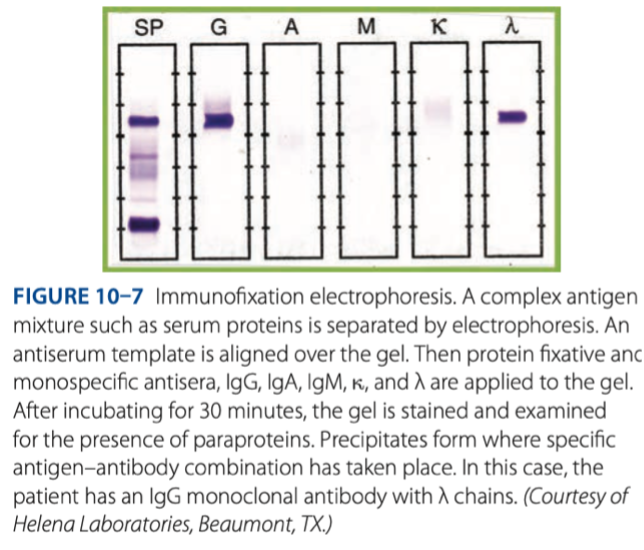
Immunofixation Electrophoresis
- Precipitate from where antigen-antibody combination has taken place in the gel.
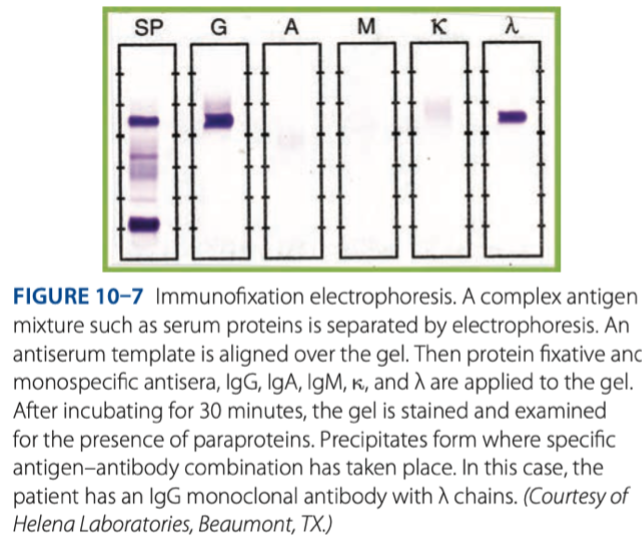
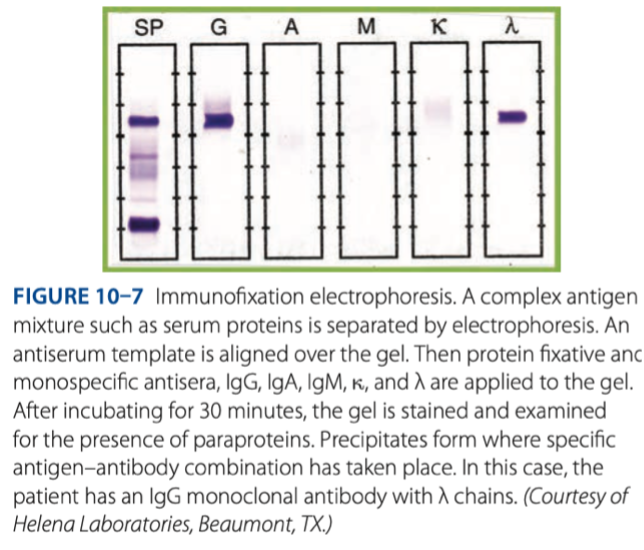
Immunofixation Electrophoresis
- Technique is used with serum as the antigen to determine over-or underproduction of antibody types.
Variable
Sensitivity (µgAB / ML) \
]]]]]]]]]]of Immunofixation Electrophoresis ;[[[=
Over-or underproduction of antibody
Application of Immunofixation Electrophoresis
Agglutination
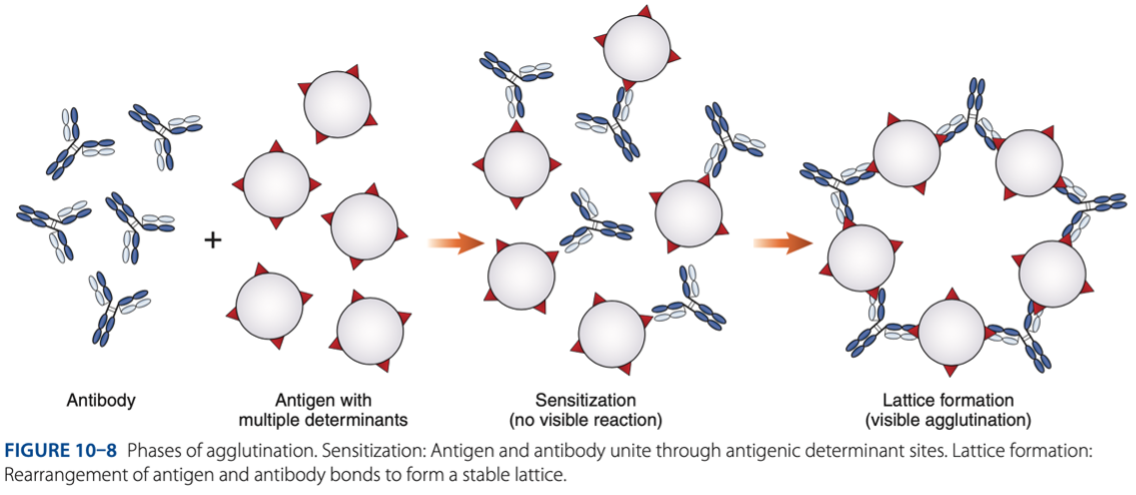
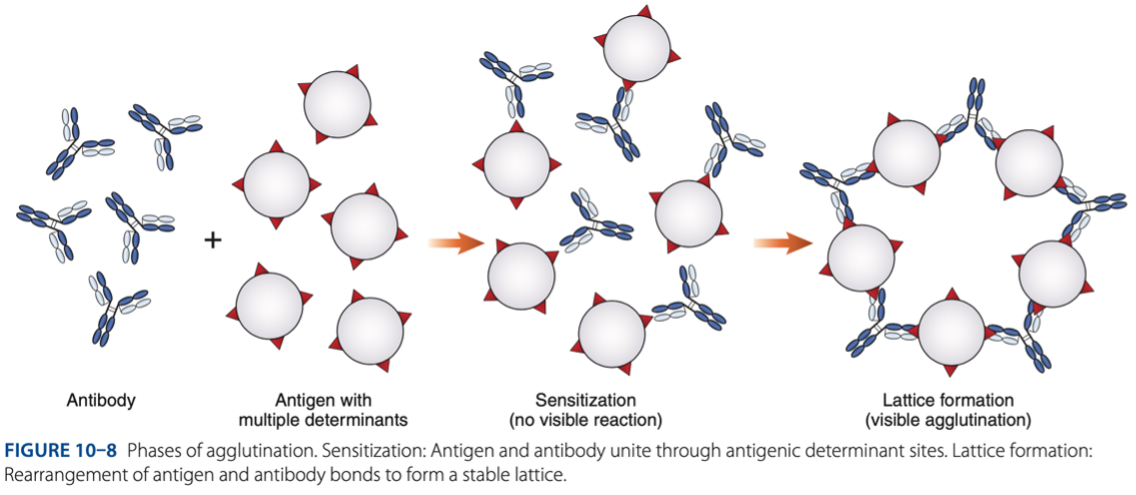
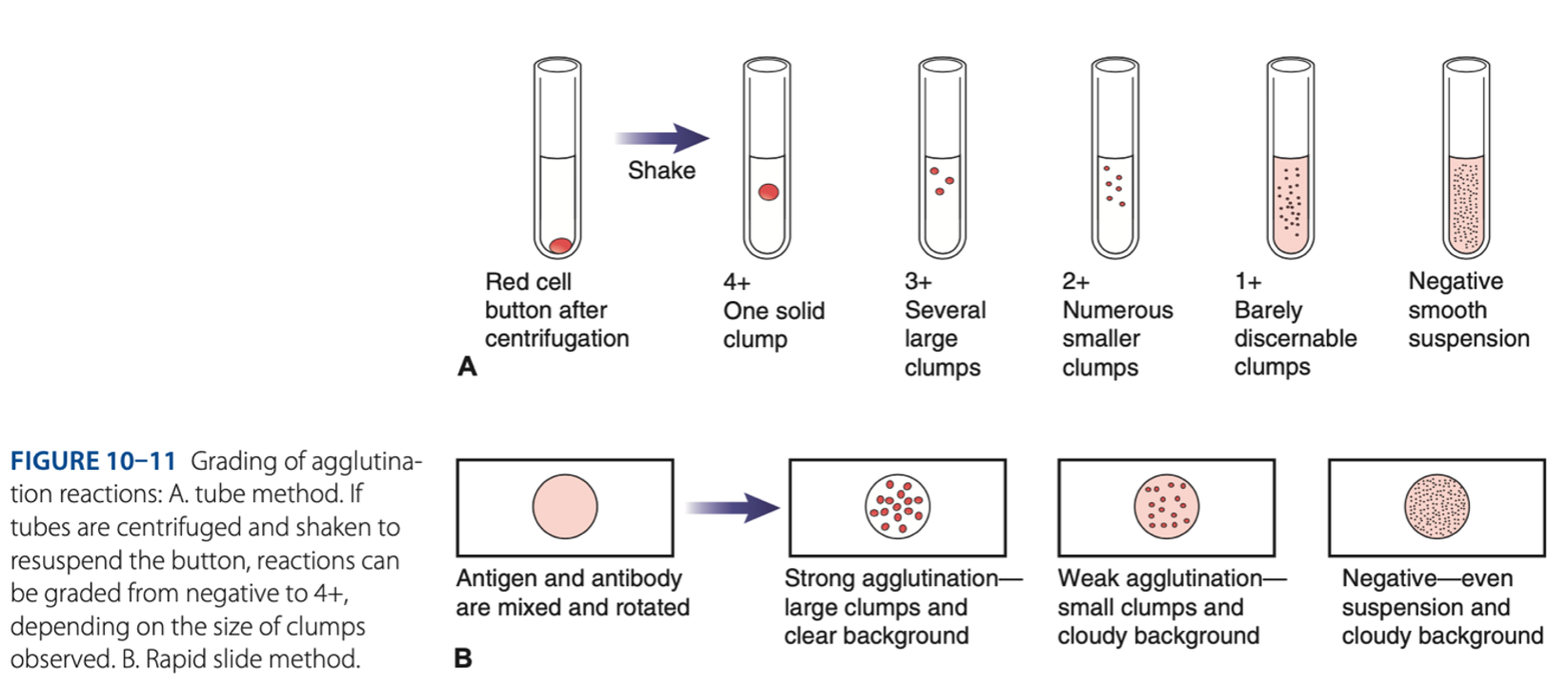
- Is the visible aggregation of particles resulting from combination with specific antibody.
agglutinins
Agglutination is produced by antibodies called -
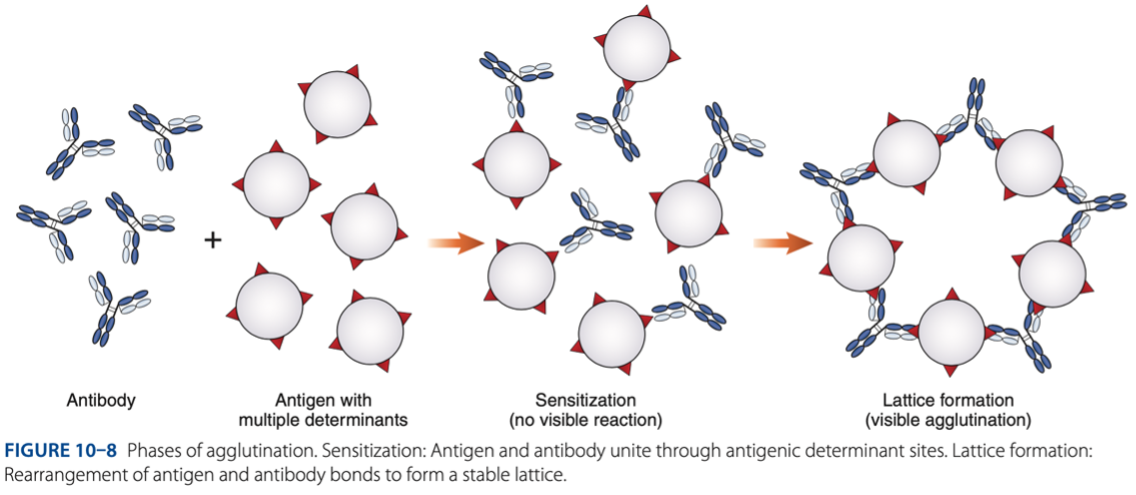
• Sensitization (initial binding)
• Lattice Formation (formation of large aggregates)
Agglutination is a 2 step process:
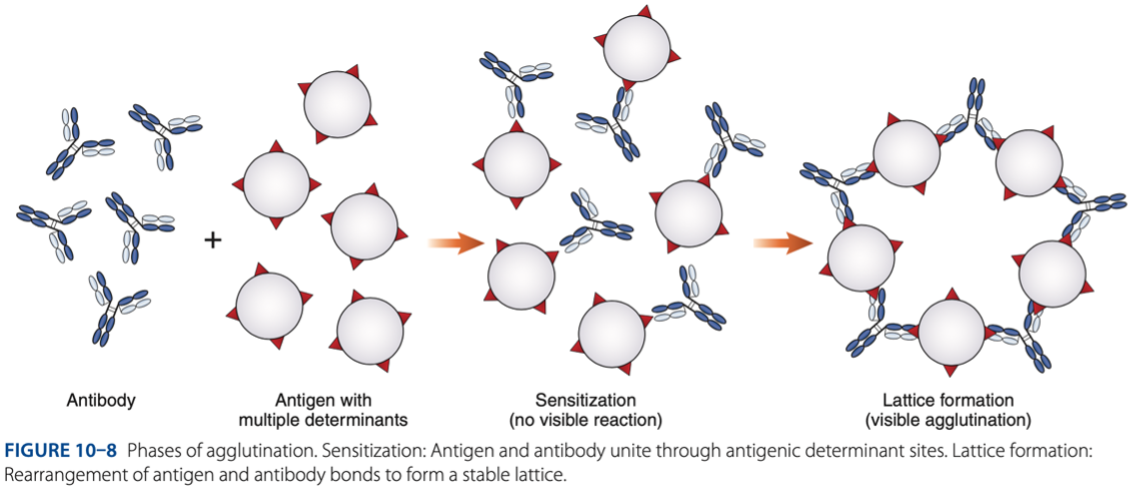
Sensitization (initial binding)
– 1st reaction, antigen & antibody unite through antigenic determinant sites.
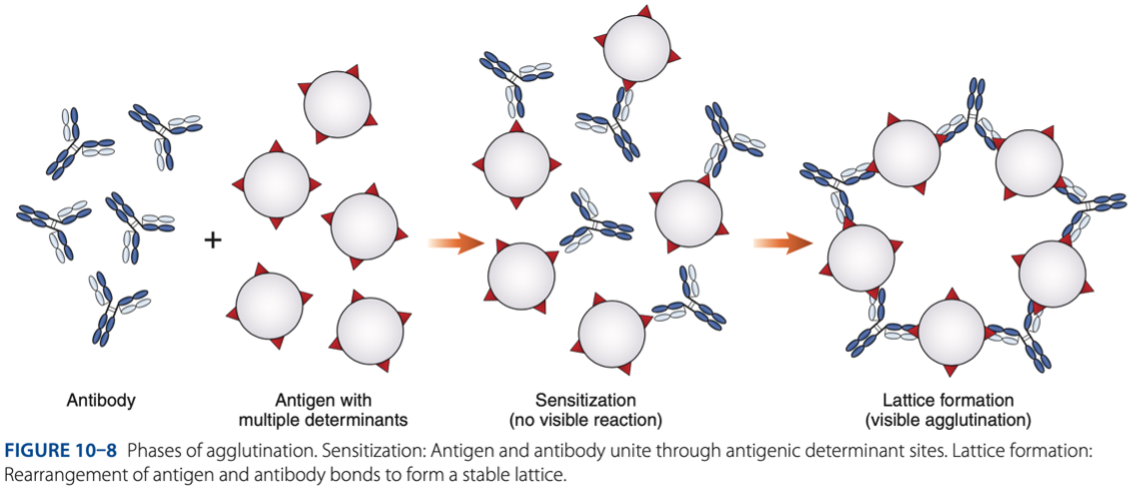
Lattice Formation (formation of large aggregates)
– 2nd reaction, rearrangement of antigen & antibody bonds to form a stable lattice.
Direct Agglutination
- Uses known bacterial antigens to test for the presence of unknown antibodies in the patient.
Direct Agglutination
- Found in particle (bacteria, RBCs)
px antibody.
Result of Direct Agglutination: Agglutination indicates the presence of
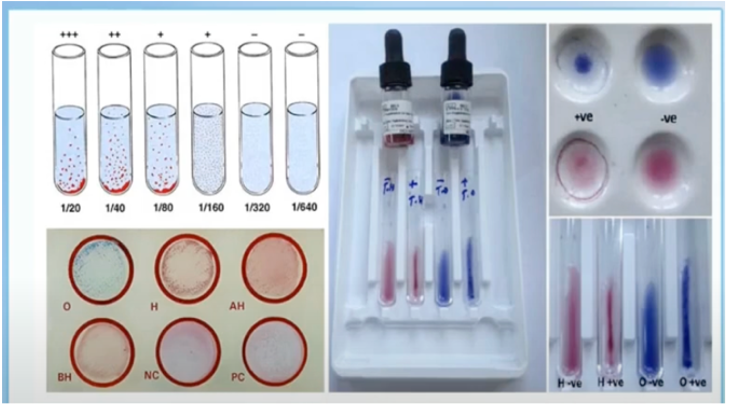
Widal Test
Hemagglutination
Types of Direct Agglutination
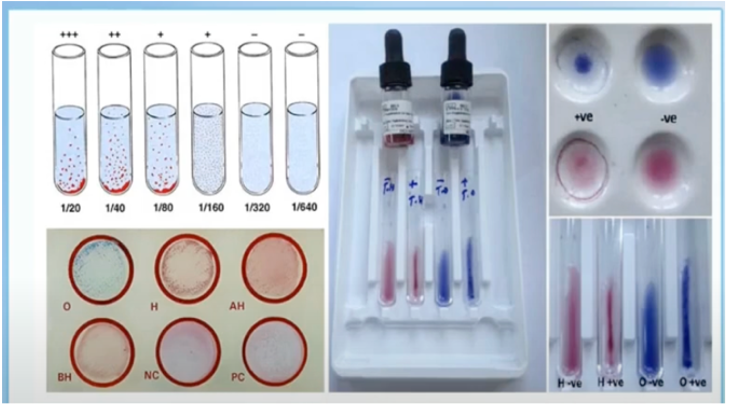
Widal Test
- A rapid screening test used to determine the possibility of typhoid fever.
Widal Test
- Uses Salmonella O (somatic) & H (flagellar) antigens.
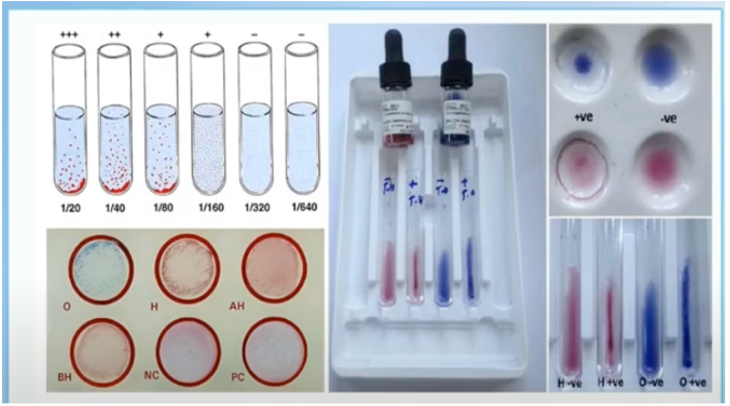
Somatic Antigen
Widal Test
– came from the cell wall of the bacteria