Properties of period three elements and their oxides
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
Which period 3 elements do not combine with oxygen to form an oxide?
chlorine and argon
Oxygen + sodium →
State properties as well
2Na2O (4Na)
White solid and yellow flame.
Oxygen + magnesium →
State properties as well
2MgO
white solid and white flame
Oxygen + aluminium →
State properties as well
2Al2O3
white solid and white flame
What type of oxides are magnesium and sodium oxide?
basic oxides
Which period 3 oxides have giant ionic structures?
sodium
magnesium
aluminium
Why does aluminium foil not readily react with oxygen?
It has a protective oxide layer that prevents reaction. protects aluminium from corrosion
What are basic oxides?
they react with acids
What type of oxide is aluminium oxide?
amphoteric oxide
What is an amphoteric oxide?
has acidic and basic properties
Oxygen + silicone →
State properties as well
SiO2
White solid
smoke and white flame
giant covalent
What type of oxide is silicon oxide?
acidic
Oxygen + phosphorus →
State properties as well
P4O10
white solid and white flame
simple covalent
What type of acid is phosphor oxide?
acidic
Why is phosphor oxide stored under water?
prevent contact with air
Oxygen + sulfur →
State properties as well
SO2
blue flame and choking gas misty fumes
simple covalent
What type of oxide is sulfur dioxide?
acidic
How is SO3 formed? What type type of oxide is it`?
acidic
Sulfur dioxide is burned in air in the presence of vanadium (V) oxide catalyst.
Equation to form SO3
2SO2 + O2 → 2SO3
Going across the period what happens to the melting point of the oxides?
decreases
Why are ionic oxides bases? + equation
they contain oxide ion which is a basic ion.
Reacts with water by accepting a proton
O2- + H2O → 2OH-
What does the oxide ion behave as?
Bronsted Lowry base
Equation of sodium oxide and water
State pH and the ionic equation
Na2O(s) + H2O (l) → 2NaOH (aq)
ph 13/14
Na2O(s)+ H2O (l) → 2Na+(aq) + 2OH-(aq)
Sodium oxide + sulfuric acid
And its ionic equation
→ Na2SO4(aq) + H2O(l)
Na2O (s) + 2H+(aq) → 2Na+(aq) + H2O(l)
Sodium oxide + hydrochloric acid
And its ionic equation
→ 2NaCl(aq) + H2O(l)
Na2O (s) + 2H+(aq) → 2Na+(aq) + H2O(l)
Equation of magnesium and water
State pH and the ionic equation
MgO(s) + H2O → Mg(OH)2
ph 9
MgO + H2O → Mg2+ + 2OH-
Magnesium oxide + Hydrochloric acid
→ MgCl2 + H2O
Magnesium oxide + phosphoric acid
3MgO + 2H3PO4 → Mg3(PO4)2 + 3H2O
Magnesium oxide + nitric acid
Ionic equation too
→ Mg(NO3)2 + H2O
MgO + 2H+ → Mg2+ + H2O
Describe aluminium oxide reaction with water and state ph
does not react
insoluble in water
ph 7
Why is aluminium oxide insoluble in water?
hydration enthalpy is less than the very high attic enthalpy
Aluminium oxide and hydrochloric acid and the ionic equation
Al2O3 + 6HCl -→ 2AlCl3 + 3H2O
Al2O3 + 6H+ → 2Al3+ + 3H2O
Aluminium oxide and sulfuric acid and the ionic equation
Al2O3 + 3H2SO4 -→ 2Al(SO4)3 + 3H2O
Al2O3 + 6H+ → 2Al3+ + 3H2O
How does aluminium oxide behave when reacting with sulfuric and hydrochloric acid?
base
Write an equation of aluminium oxide reacting as an acid and the ionic equation
Al2O3(s) + 2NaOH(aq) +H2O(l) → 2NaAl(OH)4(aq)
Al2O3(s) + 2OH-(aq) + 3H2O(l) → 2Al(OH)4-(aq)
What are all simple covalent molecules?
acidic
Describe reaction of silicon dioxide with water and the ph
ph 7
does not react
insoluble in water
Why is silicon dioxide insoluble in water?
hydration enthalpy is less than bond enthalpy
Equation for silicon dioxide and sodium hydroxide and ionic
SiO2(s) + 2NaOH → Na2SiO3 + H2O
SiO2 + 2OH- → SiO32- + H2O
Silicon dioxide and potassium hydroxide
SiO2 + KOH → K2SiO3 + H2O
Silicond dixodie and potassium oxide
SiO2 + K2O → K2SiO3
Silicon dioxide and magnesium carbonate
SiO2 + MgCO3 → MgSiO3 + CO2
Phosphor oxide and water
state ph and ionic
P4O10 + 6H2O → 4H3PO4
ph1
P4O10 + 6H2O → 4H+ + 4H2PO4-
Equation and ionic equation of phosphor oxide and sodium hydroxide
P4O10 + 12NaOH → 4Na3PO4 + 6H2O
P4O10 + 12OH- → 4PO43- + 6H2O
Phosphate and sodium oxide
6Na2O + P4O10 → 4Na3PO4
Phosphate and magnesium oxide
P4O10 + 6MgO → 2Mg3(PO4)2
What type off reaction are these:
P4O10 + 6MgO → 2Mg3(PO4)2
6Na2O + P4O10 → 4Na3PO4
acid base
Sodium oxide and phosphoric acid
3Na2O + 2H3PO4 → 2Na3PO4 + 3H2O
Reaction of sulfur dioxide and water to form sulfuric (IV) acid
State pH and ionic
SO2 + H2O → H2SO3
ph3
SO2 + H2O → ← H+ + HSO3-
Reaction of sulfur trioxide and water
State pH and ionic
SO3 + H2O → H2SO4
ph 0
SO3 + H2O → H+ + HSO4-
Equations for sulfur dioxide and sodium hydroxide
SO2 + 2NaOH → Na2SO3 + H2O
SO2 + 2OH- → SO32- + H2O
Equations for sulfur trioxide and sodium hydroxide
SO3 + 2NaOH → Na2SO4 + H2O
SO3 + 2OH- → SO42- + H2O
Sulfur trioxide and magnesium hydroxide
SO3 + Mg(OH)2 → MgSO4 + H2O
Which oxides have the highest and lowest pH?
high = basic oxides
low = acidic oxides
pg10 questions
s
How do oxyacids form?
When acidic oxides react with water
What are oxyacids?
covalent compounds that form ions in aqueous solutions
Draw structure of phosphoric acid and state the shape and angle
tetra 109.5
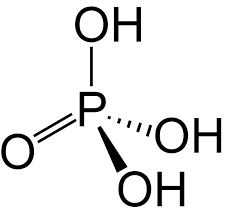
Describe structure of phosphoric acid and what type of acid it is
3 hydrogen atoms are acidic as bonded to electronegative O.
triprotic acid
forming 3 different anions as H+ leaves when reacted with bases
Phosphoric acid + sodium hydroxide (2)
→ NaH2PO4 + H2O
3NaOH + H3PO4 → Na3PO4 + 3H2O
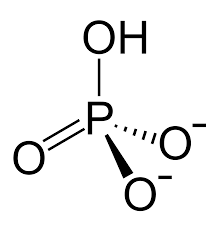
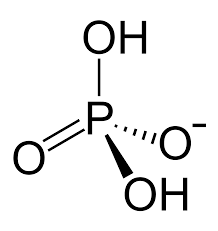
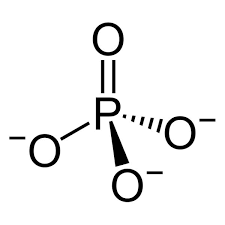
Shape and bond angles of dihydrogenphosphate ion and hydrogenphosphate(V) ion and phosphate ion (include lone pairs)
H2PO4-
HPO42-
PO43-
all tetrahedral and 109.5
Structure and angle of sulfuric(IV) acid
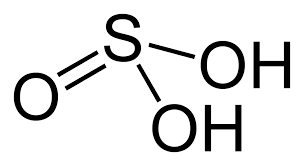
Sulfuric IV acid and sodium hydroxide
H2SO3 + NaOH → NaHSO3 + H2O
Sulfuric IV acid and excess sodium hydroxide
H2SO3 + 2NaOH → Na2SO3 + H2O
Shape and angle of hydrogensulfate(IV) ion and sulfate(IV) ion
HSO3-
SO32-
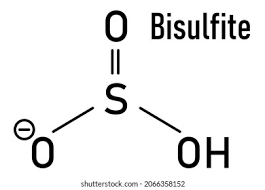
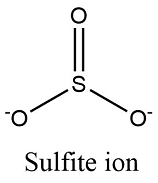
Trigonal pyramidal 107
Structure and angle for sulfuric acid
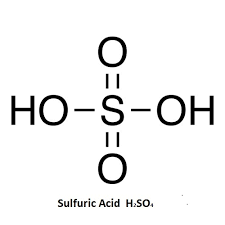
Shape and angle of hydrogensulfate(VI) ion and sulfate(VI) ion
HSO4-
SO42-
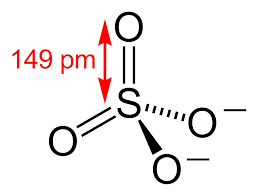
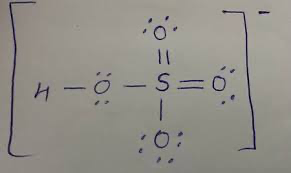
tetrahedral 109.5
Copper ion charge
2+
SiO3 charge
2-
Phosphate ion charge
3-
sulfate ion charge
2-
nitrate ion charge
-