Week 9: Technological hazards + meteors
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/71
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
1
New cards
Technological hazards
These have a wide and varied interpretation.
\
They can vary from a single toxic chemical accident to an entire industry (e.g., nuclear energy).
\
other examples may include exposure to pollutants or hazardous waste
\
They can vary from a single toxic chemical accident to an entire industry (e.g., nuclear energy).
\
other examples may include exposure to pollutants or hazardous waste
2
New cards
Examples of technological hazards
Hybrid disasters may fit into this category.
\
**Ex:**
* An earthquake that causes an oil or chemical spill from a pipeline
\
Technological disasters involving the environment are included in this category as well.
\
**Ex:**
* the sinking of the titanic and explosion of the challenger space shuttle
\
**Ex:**
* An earthquake that causes an oil or chemical spill from a pipeline
\
Technological disasters involving the environment are included in this category as well.
\
**Ex:**
* the sinking of the titanic and explosion of the challenger space shuttle
3
New cards
Vulnerability to technological hazards
Typically, the death tolls from technological hazards are relatively low.
\
Vulnerability is greatest for those involved in industry or transportation systems.
\
Workers in resource industries in hinterlands are at higher risk
(eg. miners)
\
Vulnerability is greatest for those involved in industry or transportation systems.
\
Workers in resource industries in hinterlands are at higher risk
(eg. miners)
4
New cards
Categories
__Widespread__
* long term (nuclear accidents)
* hazards leading to cumulative effects
\
__Rare Events__
* airplane crashes
* mine collapses
* shipwrecks
\
__Relatively Common__
* automobile accidents
* poisons
* long term (nuclear accidents)
* hazards leading to cumulative effects
\
__Rare Events__
* airplane crashes
* mine collapses
* shipwrecks
\
__Relatively Common__
* automobile accidents
* poisons
5
New cards
Cumulative effects
These are conditions that worsen slowly over time as exposure to a concentration increases.
\
Eventually, the concentration reaches a threshold critical to human health.
\
Hazards with cumulative effects include exposure to radiation, toxic chemicals, acid precipitation, and groundwater contamination
\
Eventually, the concentration reaches a threshold critical to human health.
\
Hazards with cumulative effects include exposure to radiation, toxic chemicals, acid precipitation, and groundwater contamination
6
New cards
Calculating risk
Large-Scale Structures (buildings, bridges, dams):
Risk is defined as the probability of failure during the lifetime of the structure.
\
__**Transportation (road, sea, rail):**__
* risk is the probability of death or injury per km travelled
\
__**Industry (manufacturing, power production):**__
* risk is the probability of death or injury per person per number of hours exposed
Risk is defined as the probability of failure during the lifetime of the structure.
\
__**Transportation (road, sea, rail):**__
* risk is the probability of death or injury per km travelled
\
__**Industry (manufacturing, power production):**__
* risk is the probability of death or injury per person per number of hours exposed
7
New cards
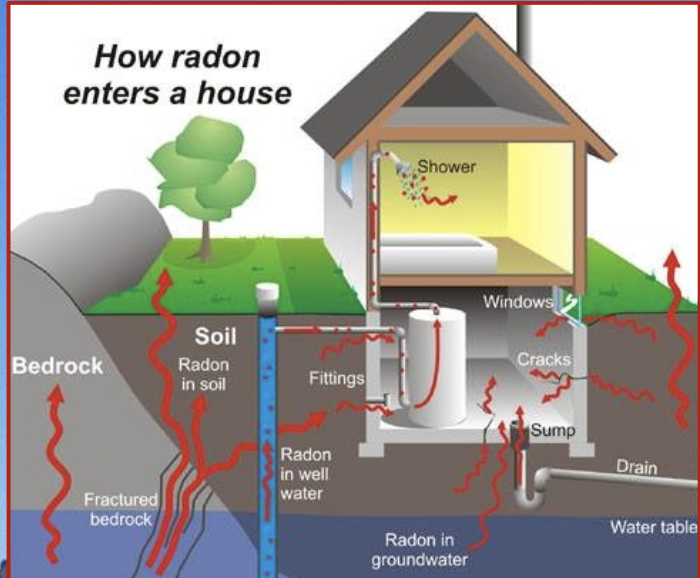
Radon
The primary source of radon gas is from the natural decay of uranium in rock and soil.
\
When radon is inhaled it then decays to polonium and lodges in the lungs where it damages tissues.
\
It is the 2nd leading cause of lung cancer in North America
\
When radon is inhaled it then decays to polonium and lodges in the lungs where it damages tissues.
\
It is the 2nd leading cause of lung cancer in North America
8
New cards
When does Radon become a hazard
when it is released into our living space.
* it is difficult to detect because the gas is odorless, colourless, and tasteless
\
\
\
Radon detectors are commercially available in areas where it is of greater concern.
* it is difficult to detect because the gas is odorless, colourless, and tasteless
\
\
\
Radon detectors are commercially available in areas where it is of greater concern.
9
New cards
Potentially high radon levels are present in ___% of homes in North America
5-10%
10
New cards
How Radon moves
The gas can move quickly through non-saturated soil and can seep into homes.
\
Basements are at higher risk especially in winter due to reduced air concentration
\
Basements are at higher risk especially in winter due to reduced air concentration
11
New cards
Genetically modified organisms
These are organisms that have had changes made to their DNA by the transfer of genes.
\
Examples of feats in genetic engineering:
* chickens that lay low-cholesterol eggs
* tomatoes that can reduce the risk of cancer
* bananas and potatoes to treat some viral disease that are common in developing countries
* rice that contains vitamin A
* bacteria that can clean up oil and toxic spills
\
Examples of feats in genetic engineering:
* chickens that lay low-cholesterol eggs
* tomatoes that can reduce the risk of cancer
* bananas and potatoes to treat some viral disease that are common in developing countries
* rice that contains vitamin A
* bacteria that can clean up oil and toxic spills
12
New cards
Genetically modified food
The most common crops that are genetically modified are corn, soybeans, and canola.
\
Crops are modified to **increase yields.**
\
Some crops have been genetically engineered to have greater resistance to:
* extreme changes in temp or precipitation
* herbicides
* pests
* acidic soil
\
Crops are modified to **increase yields.**
\
Some crops have been genetically engineered to have greater resistance to:
* extreme changes in temp or precipitation
* herbicides
* pests
* acidic soil
13
New cards
Bioengineers have been able to alter citrus trees (that would normally take __**six years**__ to produce fruit) to yield fruit in only
____________.
____________.
one year
14
New cards
How safe are genetically modified foods?
Scientists believe that the benefits outweigh the potential risks but most support more research studies.
\
UN food and agriculture organization believes that genetically modified crops have great benefits especially in developing countries.
\
UN food and agriculture organization believes that genetically modified crops have great benefits especially in developing countries.
15
New cards
Radiation
The pathways of radiation include inhalation and, ingestion (food, water).
\
The impact can be __**direct**__ (effects are evident within days of exposure) or delayed and chronic (leukemia, cancer).
\
The impact could also be __**indirect**__ in the form of genteic effects
\
A person may not experience effects but may pass them on to their children in the form of chromosomal changes or birth defects.
\
The impact can be __**direct**__ (effects are evident within days of exposure) or delayed and chronic (leukemia, cancer).
\
The impact could also be __**indirect**__ in the form of genteic effects
\
A person may not experience effects but may pass them on to their children in the form of chromosomal changes or birth defects.
16
New cards
Sources of radiation
__**Mining of Uranium**__
* In Canada, uranium is mined in northern Saskatchewan and northern Ontario.
\
\
__**Production of Electricity**__
* uranium is used in nuclear power plants
* In Canada, uranium is mined in northern Saskatchewan and northern Ontario.
\
\
__**Production of Electricity**__
* uranium is used in nuclear power plants
17
New cards
mines produce wastes known as _____ that can be a radioactive hazard
tailings
18
New cards
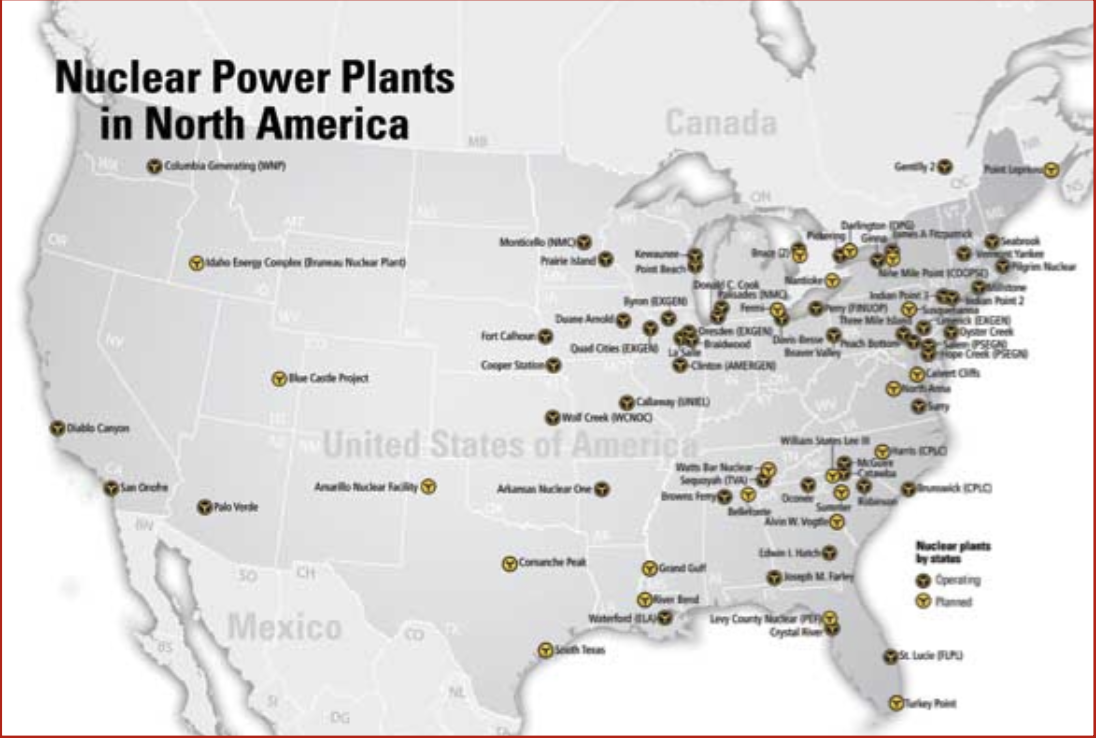
Nuclear power plants
Most nuclear plants in North America are in the __**eastern half**__ of the continent. (where most of the population is)
\
They must be near sources of coolant (rivers or lakes)
\
\
They must be located near a market for electricity (eastern North America is much more populated).
\
Nuclear is considered a clean source of energy because it does not emit the greenhouse gases that cause climate change
\
They must be near sources of coolant (rivers or lakes)
\
\
They must be located near a market for electricity (eastern North America is much more populated).
\
Nuclear is considered a clean source of energy because it does not emit the greenhouse gases that cause climate change
19
New cards
locations of nuclear power plants
20
New cards
Nuclear accidents
A *nuclear* *meltdown* is an informal term for an accident that results in damage from overheating.
\
It occurs when the heat generated by a nuclear plant exceeds the heat removed by cooling systems.
\
In a meltdown, fuel rods turn to liquid and the walls of the plant core could melt from extreme heat.
\
The hot liquid could melt through the bottom of the plant and seep through the soil
\
It occurs when the heat generated by a nuclear plant exceeds the heat removed by cooling systems.
\
In a meltdown, fuel rods turn to liquid and the walls of the plant core could melt from extreme heat.
\
The hot liquid could melt through the bottom of the plant and seep through the soil
21
New cards
Three mile island nuclear accident
This is the __**worst nuclear disaster in US history**__; it occured on March 28th, 1979.
\
One of the two power plants on Three Mile Island in central Pennsylvania experienced a partial meltdown.
\
It was caused by a failure of a valve that controlled cool water entering the plant core.
\
There were no direct injuries; minor amounts of radiation were released around the site.
\
One of the two power plants on Three Mile Island in central Pennsylvania experienced a partial meltdown.
\
It was caused by a failure of a valve that controlled cool water entering the plant core.
\
There were no direct injuries; minor amounts of radiation were released around the site.
22
New cards
Chernobyl Nuclear accident
This is the __**worst nuclear disaster in world history**__; it occurred on April 26, 1986.
\
The accident was a result of a flawed design, operator error, and disregard of safety regulations.
\
An explosion at the plant caused the immediate deaths of 3 workers. Within one year, 28 more workers died from extreme radiation exposure.
\
An estimated 6000 people in the area developed thyroid cancer because of radiation poisoning.
\
The accident was a result of a flawed design, operator error, and disregard of safety regulations.
\
An explosion at the plant caused the immediate deaths of 3 workers. Within one year, 28 more workers died from extreme radiation exposure.
\
An estimated 6000 people in the area developed thyroid cancer because of radiation poisoning.
23
New cards
Nuclear energy
The combined concern over Three Mile Island and Chernobyl slowed nuclear development for a time.
\
However, concern over greenhouse gas emissions has created a greater demand for cleaner sources of energy.
\
for example, Ontario has recently closed all its coal power plants🙏😍
\
The province has invested in refurbishing existing nuclear power plants and is planning to build new ones as well.
\
However, concern over greenhouse gas emissions has created a greater demand for cleaner sources of energy.
\
for example, Ontario has recently closed all its coal power plants🙏😍
\
The province has invested in refurbishing existing nuclear power plants and is planning to build new ones as well.
24
New cards
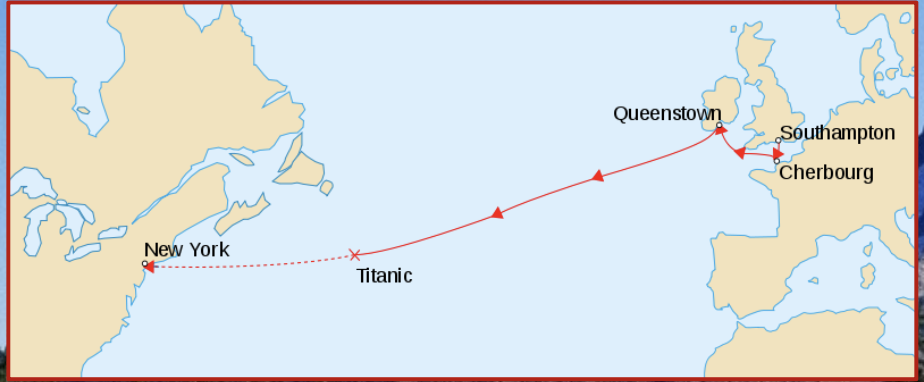
Titanic shipwreck
The *Titanic* was a passenger ocean liner that struck an iceberg and sank on its maiden voyage (April 15, 1912).
\
The ship left Southampton, England on april 10th and was bound for new york city with 2224 passengers
\
The ship left Southampton, England on april 10th and was bound for new york city with 2224 passengers
25
New cards
the titanic
The ship was designed using advanced technology and was believed to be unsinkable.
\
The death toll ws 1517; the high number was due to the lack of lifeboats for all passengers
\
The wreckage was found by SONAR in 1985 at a depth of 3.8km
\
The death toll ws 1517; the high number was due to the lack of lifeboats for all passengers
\
The wreckage was found by SONAR in 1985 at a depth of 3.8km
26
New cards
Chronology of the the titanic shipwreck
A lookout on the ship spotted an iceberg in the ship’s path at 11:40 PM and alerted the captain.
\
The ship struck the iceberg 37 seconds later; 18 lifeboats were launched, and *Titanic* sank at 2:20 AM.
\
The Carpatha arrived at 4:10am and picked up survivors from the lifeboats
\
The ship struck the iceberg 37 seconds later; 18 lifeboats were launched, and *Titanic* sank at 2:20 AM.
\
The Carpatha arrived at 4:10am and picked up survivors from the lifeboats
27
New cards
Oil spills
Oil spills most commonly occur in marine areas but can also occur on land due to pipeline bursts.
\
The environmental impact can be devastating, and clean-up can take months to years.
\
Oil penetrates bird feathers and mammal fur reducing their ability to insulate
\
Animals and birds are left vulnerable to temperature changes and become less buoyant in water
\
The environmental impact can be devastating, and clean-up can take months to years.
\
Oil penetrates bird feathers and mammal fur reducing their ability to insulate
\
Animals and birds are left vulnerable to temperature changes and become less buoyant in water
28
New cards
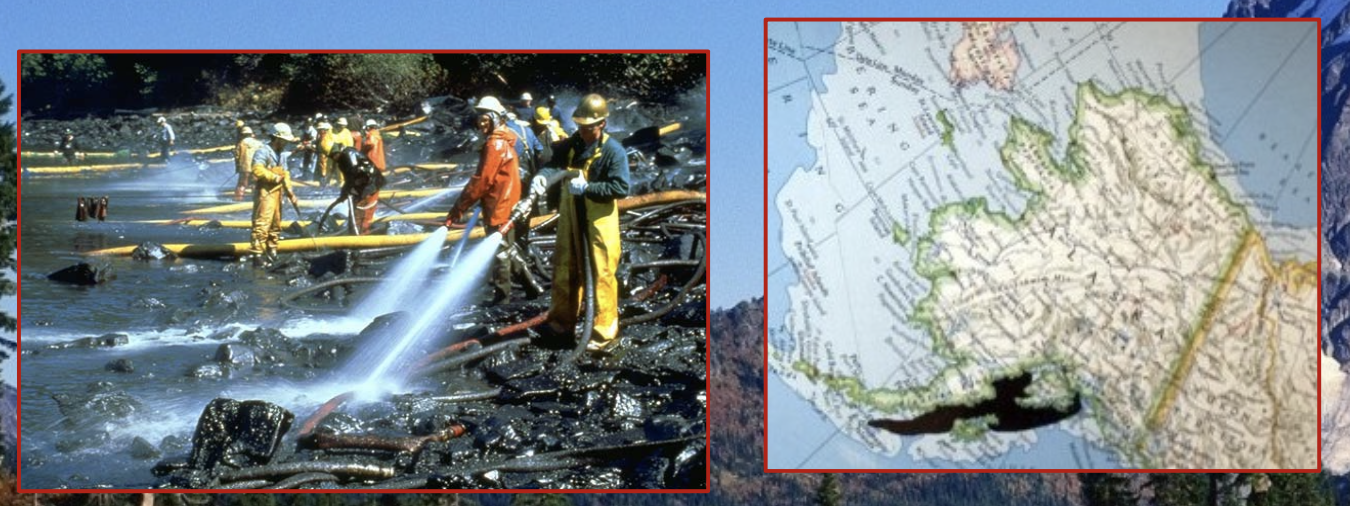
Exxon Valdez oil spill
This spill was caused by an oil tanker striking a rocky reef off the south coast of Alaska on March 24, 1989.
* the region is an important habitat for salmon, seals, sea otters, killer whales and seabirds
\
There were 75 million litres of oil spilled; the remote location made recovery efforts difficult.
\
It remained the worst oil spill in north american history until the deepwater horizon oil spill.
* the region is an important habitat for salmon, seals, sea otters, killer whales and seabirds
\
There were 75 million litres of oil spilled; the remote location made recovery efforts difficult.
\
It remained the worst oil spill in north american history until the deepwater horizon oil spill.

29
New cards
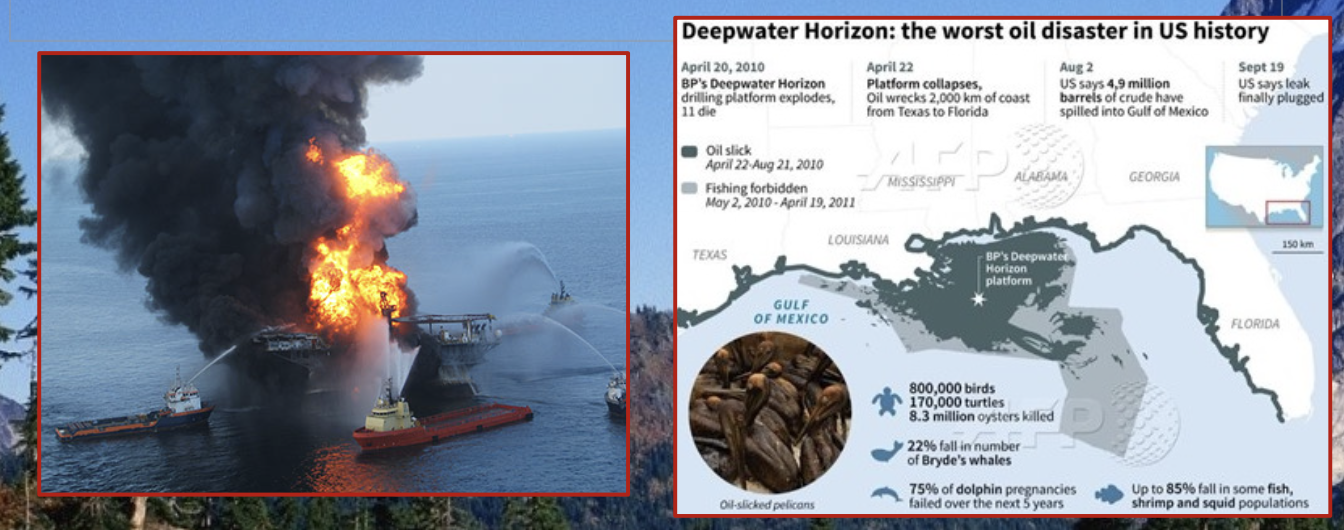
Deepwater horizon oil spill
The spill was caused by an oil rig that exploded in the Gulf of Mexico on April 20, 2010.
\
The explosion killed 11 workers. It was caused by methane rising upward through a drill pipe.
\
The explosion killed 11 workers. It was caused by methane rising upward through a drill pipe.
30
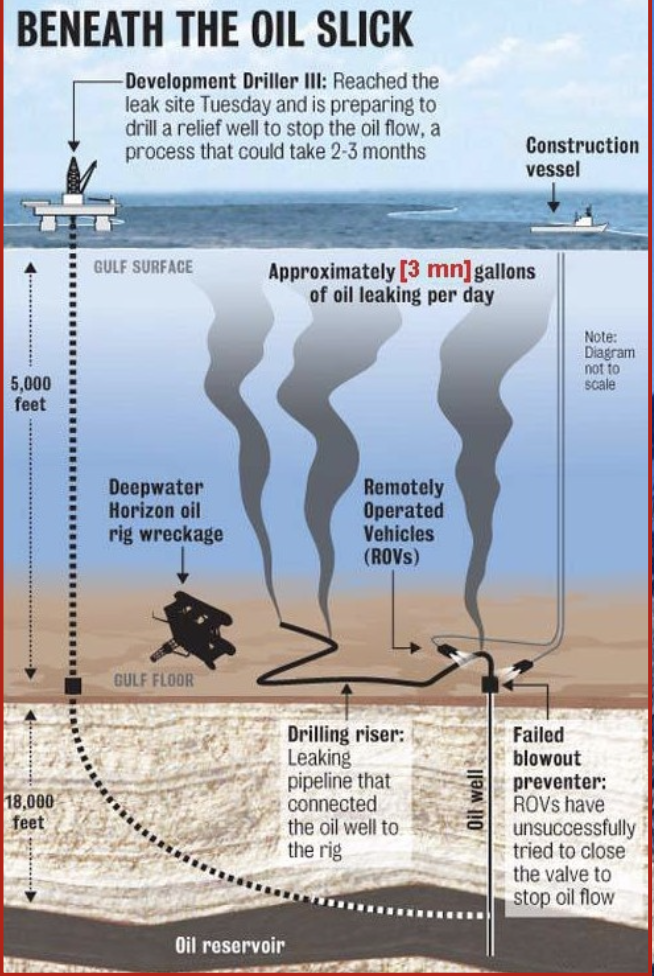
New cards
Approximately __ million liters of oil escaped from the well every day for months
11 million
\
\*After several failed attempts, the well was finally capped with cement on september 19th 2010
\
\*After several failed attempts, the well was finally capped with cement on september 19th 2010
31
New cards
repercussions of the spill
The spill caused extensive damage to wetlands and beaches along the U. S. Gulf of Mexico coastline.
\
* The tourism industry faced severe economic loss during Summer 2010.
\
The U.S. federal investigative report ultimately blamed the B.P. oil company for the disaster. The report found that the company:
* made a series of cist-cutting choices on maintenance
* did not have a proper system in place to ensure safety
\
* The tourism industry faced severe economic loss during Summer 2010.
\
The U.S. federal investigative report ultimately blamed the B.P. oil company for the disaster. The report found that the company:
* made a series of cist-cutting choices on maintenance
* did not have a proper system in place to ensure safety
32
New cards
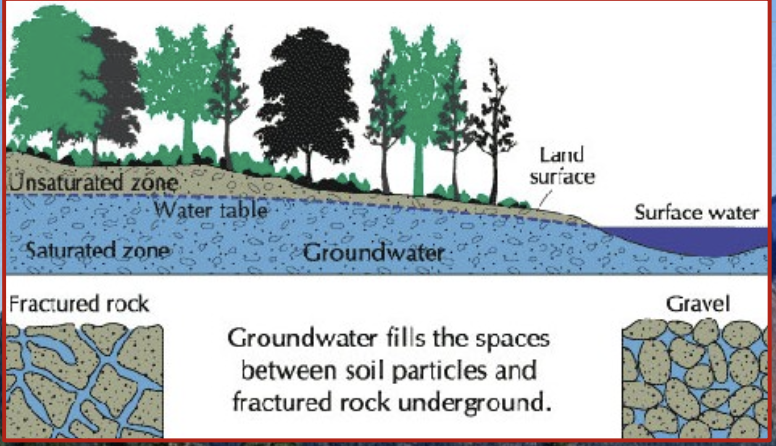
Groundwater
Groundwater is water that is found underground within the cracks and spaces in soil, sand, and rock.
\
These materials are permeable because they have connected spaces that allow water to flow through
\
These materials are permeable because they have connected spaces that allow water to flow through
33
New cards
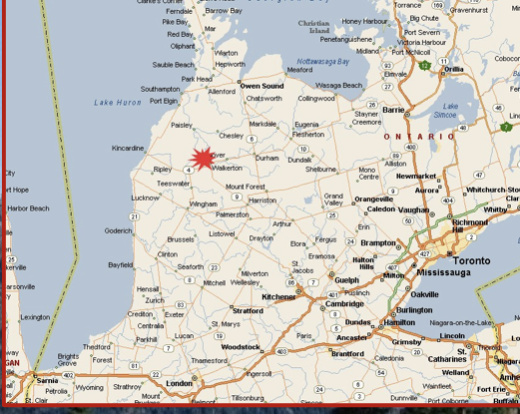
Groundwater contamination
Many cities and towns obtain drinking water from groundwater. If the water supply becomes contaminated, this presents a risk.
\
In 2000, water contaminated with *E. coli* bacteria killed 7 people in Walkerton, Ontario.
\
The baceteria came from fertilizer manure that had leached into a well during a heavy rainfall
\
In 2000, water contaminated with *E. coli* bacteria killed 7 people in Walkerton, Ontario.
\
The baceteria came from fertilizer manure that had leached into a well during a heavy rainfall
34
New cards
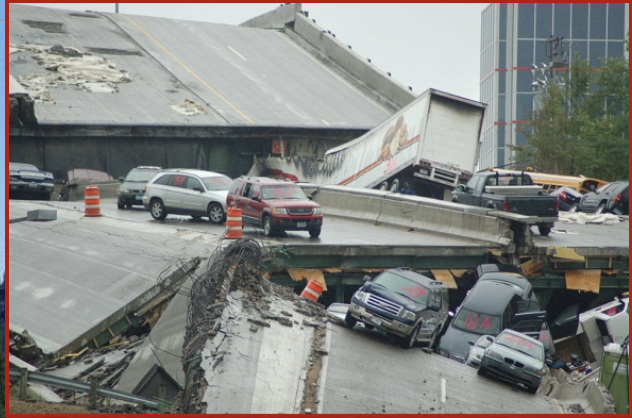
Infrastructure failure
An example of infrastructure failure in North America occurred in Minneapolis in 2007.
\
A highway bridge over the Mississippi River collapsed during evening rush hour killing 13 people.
\
A highway bridge over the Mississippi River collapsed during evening rush hour killing 13 people.
35
New cards
Minneapolis bridge collapse
The cause was deemed to be excessive weight from vehicles and construction equipment
\
The bridge supports were not of proper thickness and an extra 2 inches of concrete that was added to the roadway also contributed to the collapse.
\
The bridge supports were not of proper thickness and an extra 2 inches of concrete that was added to the roadway also contributed to the collapse.

36
New cards
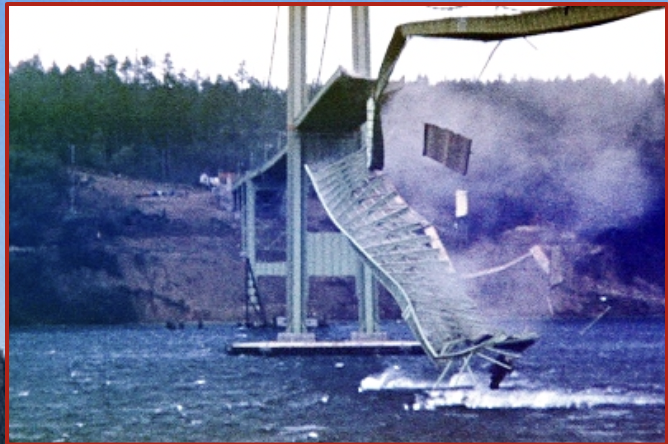
Tacoma narrows bridge collapse
In 1940, high winds caused the collapse of a suspension bridge in Tacoma, Washington.
\
There were no human casualties from the collapse
\
There were no human casualties from the collapse

37
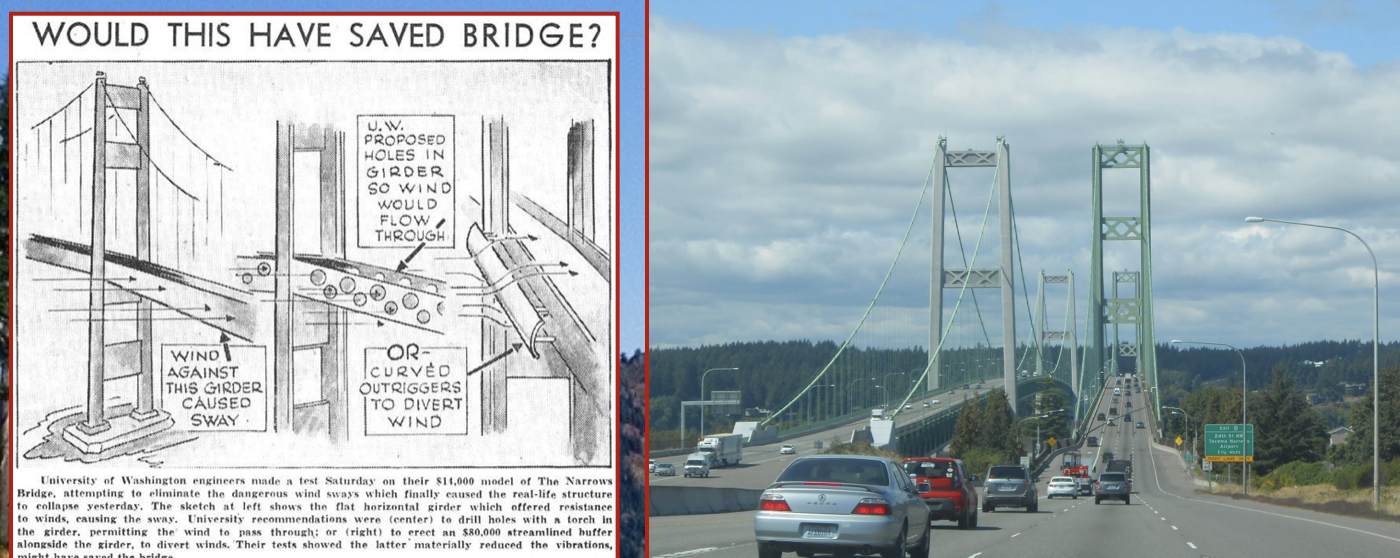
New cards
The bridge design
The design of the bridge did not provide any open trusses for wind to pass through.
\
The incident has served as a good case study for engineering and architecture for students
\
The incident has served as a good case study for engineering and architecture for students
38
New cards
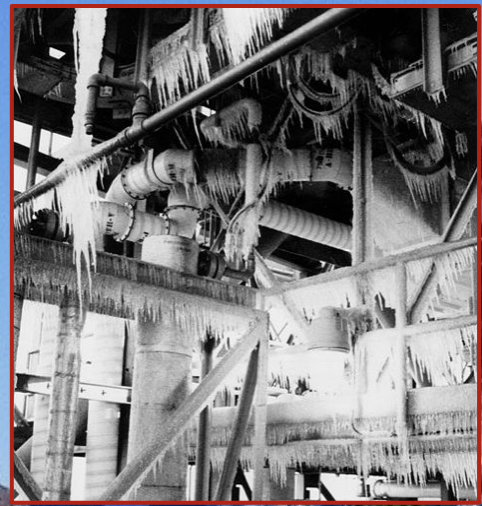
Space shuttle accidents
There have been two major space shuttle disasters: the shuttles *Challenger* and *Columbia*.
\
The challenger exploded 73 seconds into its flight on Jan. 28, 1986
\
All 7 crew members were killed as the space shuttle disintegrated; its remains were scattered over the Atlantic Ocean.
\
The challenger exploded 73 seconds into its flight on Jan. 28, 1986
\
All 7 crew members were killed as the space shuttle disintegrated; its remains were scattered over the Atlantic Ocean.
39
New cards
The challenger shuttle
The cause was found to be a faulty O-ring seal.
\
It is believed the cold weather lowered the resiliency of the rubber O-ring.
\
* It failed to seal a joint leading to the release of hot gas that led to failure of the rocket booster
\
\
The night before the launch was particularly cold; frost and ice had developed on the rocket.
\
It is believed the cold weather lowered the resiliency of the rubber O-ring.
\
* It failed to seal a joint leading to the release of hot gas that led to failure of the rocket booster
\
\
The night before the launch was particularly cold; frost and ice had developed on the rocket.

40
New cards
The columbia Shuttle
The *Columbia* disintegrated on Feb. 1, 2003, upon re-entry into Earth’s atmosphere after 16 days in space.
\
During launch, a piece of insulation broke off from the external tank
\
It struck the left wing and damaged the system that protects the wing from the intense heat produced by atmospheric gases upon re-entry.
\
Pieces of the shuttle were found in Texas and Louisiana
\
During launch, a piece of insulation broke off from the external tank
\
It struck the left wing and damaged the system that protects the wing from the intense heat produced by atmospheric gases upon re-entry.
\
Pieces of the shuttle were found in Texas and Louisiana
41
New cards
Formation of the solar system
How was the solar system formed?
Scientists believe a cloud of gas and dust in space was disturbed by a *supernova.*
\
**When did this occur?**
* 4.6 billion years ago
\
\
^^The Nebular Hypothesis^^
* the explosion of waves in space
\
This caused formation of a ^^solar nebula^^
(flattened disc)
Scientists believe a cloud of gas and dust in space was disturbed by a *supernova.*
\
**When did this occur?**
* 4.6 billion years ago
\
\
^^The Nebular Hypothesis^^
* the explosion of waves in space
\
This caused formation of a ^^solar nebula^^
(flattened disc)
42
New cards
Supernova
The explosion of a star that has reached the end of its life cycle
43
New cards
formation of planets
The centre of the solar nebula grew hotter resulting in the formation of the Sun.
\
The outer edges cooled causing clumps of particles to stick together and form planets
\
The outer edges cooled causing clumps of particles to stick together and form planets
44
New cards
galaxy + star definitions
**Galaxy**
* a cluster of billions of stars. Our solar system makes up a tiny portion of the milky way galaxy
\
\
**Star**
* A hot glowing ball of gas that generates energy by converting hydrogen to helium
* a cluster of billions of stars. Our solar system makes up a tiny portion of the milky way galaxy
\
\
**Star**
* A hot glowing ball of gas that generates energy by converting hydrogen to helium
45
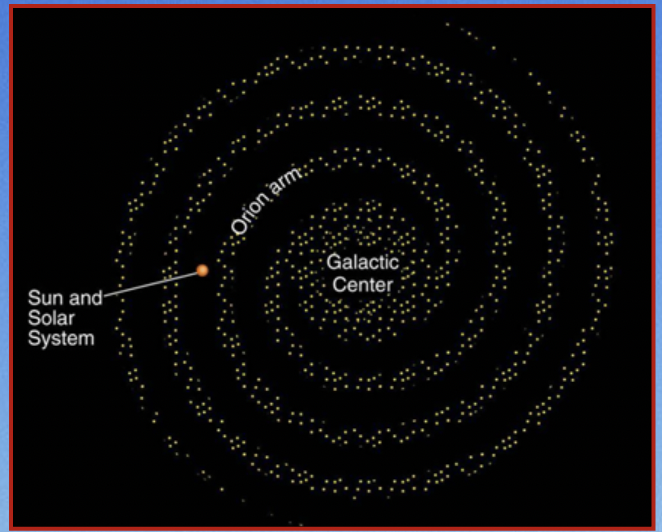
New cards
The Sun is located approximately __**_______**__ from the centre of the Milky Way galaxy.
**30 quintillion km**
\
\
\
\
46
New cards
It takes ______ years to travel from one side of the galaxy to the other
100,000 years
47
New cards
The sun
In the core of the Sun, the temperature is ==15,000,000°C.==
\
The outermost part of the Sun is called the __**photosphere**__ and it is ==6000°C.==
\
Energy from the sun controls the earth’s climate system
\
The earth only receives one two-billionths of the sun’s total energy!
\
The outermost part of the Sun is called the __**photosphere**__ and it is ==6000°C.==
\
Energy from the sun controls the earth’s climate system
\
The earth only receives one two-billionths of the sun’s total energy!
48
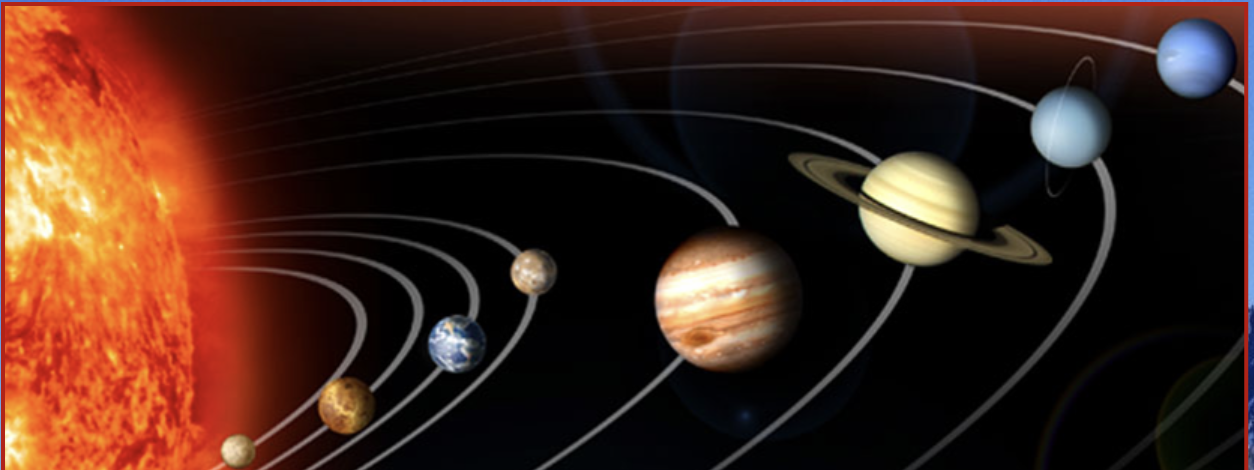
New cards
The solar system
The solar system is composed of 8 planets, 60 moons, and millions of *bolides*.
\
__**Order of the planets:**__
* Mercury
* Venus
* Earth
* Mars
* Jupiter
* Saturn
* Uranus
* Neptune
\
__**Order of the planets:**__
* Mercury
* Venus
* Earth
* Mars
* Jupiter
* Saturn
* Uranus
* Neptune
49
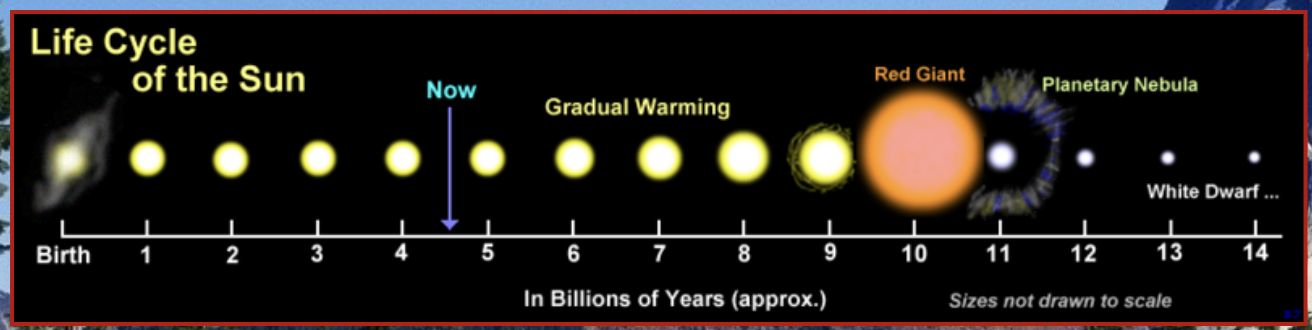
New cards
Life cycle of stars
The Sun is the closest star to Earth; it has a life expectancy of 10 billion years.
\
At the end of the life cycle of a star, massive amounts of energy are released into the solar system.
\
At the end of the life cycle of a star, massive amounts of energy are released into the solar system.
50
New cards
Bolides - definition
__**Definition:**__
* any extraterrestrial body that originates in outer space
\
* any extraterrestrial body that originates in outer space
\
51
New cards
Bolide examples
==Asteroid:==
* A rocky metallic material in space 10 m to 1000 km in diameter originating in the Asteroid Belt (between Mars and Jupiter).
\
==Meteoroid:==
* Similar to an asteroid, but only up to 10m in diameter
* so just a smaller asteroid
\
==Meteor:==
* A meteoroid that has entered Earth’s atmosphere.
\
==Meteorite:==
* a meteor that strikes earths surface
\
==Comet:==
* these are distinguishable by a glowing tail of gas and dust
* It is believed that comets formed in an area outside the solar system called the Kuiper Belt.
* A rocky metallic material in space 10 m to 1000 km in diameter originating in the Asteroid Belt (between Mars and Jupiter).
\
==Meteoroid:==
* Similar to an asteroid, but only up to 10m in diameter
* so just a smaller asteroid
\
==Meteor:==
* A meteoroid that has entered Earth’s atmosphere.
\
==Meteorite:==
* a meteor that strikes earths surface
\
==Comet:==
* these are distinguishable by a glowing tail of gas and dust
* It is believed that comets formed in an area outside the solar system called the Kuiper Belt.
52
New cards
Comets
Comets are composed of a rocky core of gas and ice.
\
They create light as gases are released as the comet is heated by solar radiation.
\
Halley’s comet is the most famous because it is visible with the naked eye and passes close to earth every 75 years
\
it will next be visible in __**2061**__
\
They create light as gases are released as the comet is heated by solar radiation.
\
Halley’s comet is the most famous because it is visible with the naked eye and passes close to earth every 75 years
\
it will next be visible in __**2061**__
53
New cards
Airbursts
Bolides travel at velocities of __**12-72 km/s.**__
\
As they heat up upon earth entering earth’s atmosphere, they produce bright light
\
The object may explode in an *airburst* at an altitude between 12 km and 50 km, or it will collide with Earth’s surface.
\
\
\
As they heat up upon earth entering earth’s atmosphere, they produce bright light
\
The object may explode in an *airburst* at an altitude between 12 km and 50 km, or it will collide with Earth’s surface.
\
\
54
New cards
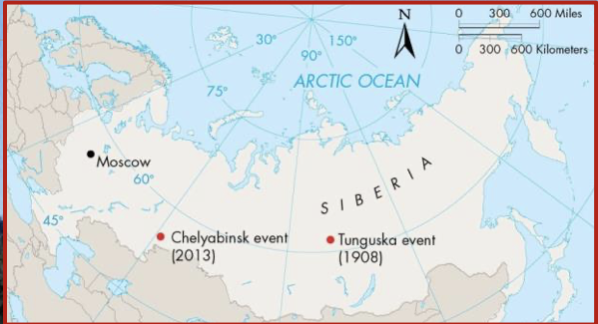
Tunguska Airburst
The explosion destroyed over 2000 km2 of forest in a sparsely populated area of northeast Russia in 1908.
\
Scientists have determined it was an airburst because no crater has ever been found
\
The asteroid responsible is believed to be 25 to 50 metres in diameter.
\
Scientists have determined it was an airburst because no crater has ever been found
\
The asteroid responsible is believed to be 25 to 50 metres in diameter.
55
New cards
Chelyabinsk airburst
On Feb. 15, 2013, a meteor exploded over the city of Chelyabinsk in southwest Russia.
\
It was the largest bolide to enter earth’s atmosphere since the tunguska airburst
\
Over 1500 people were injured, mainly from broken glass.
\
It was the largest bolide to enter earth’s atmosphere since the tunguska airburst
\
Over 1500 people were injured, mainly from broken glass.
56
New cards
Impact cratoers
These provide evidence of past meteorite impacts.
\
A layer of debris called an %%*ejecta blanket*%% consists of rock fragments that were blown out of the crater on impact.
\
Craters today are not as deep as the original impact crater due to erosion and fragmented rock falling back into it shortly after
\
* This rock is referred to as %%*breccia*.%%
\
A layer of debris called an %%*ejecta blanket*%% consists of rock fragments that were blown out of the crater on impact.
\
Craters today are not as deep as the original impact crater due to erosion and fragmented rock falling back into it shortly after
\
* This rock is referred to as %%*breccia*.%%
57
New cards
Meteor crater
This crater is in Arizona and was formed about 50,000 years ago.

58
New cards
Impact craters
Impact craters can be defined as either simple or complex.
\
Simple craters are less than a few km in diameter and do not have an uplifted centre.
\
A complex crater consists of a rim that collapses under extreme faulting and a centre floor that rises following impact.
\
Complex craters are generally greater than 6km in diameter
\
Simple craters are less than a few km in diameter and do not have an uplifted centre.
\
A complex crater consists of a rim that collapses under extreme faulting and a centre floor that rises following impact.
\
Complex craters are generally greater than 6km in diameter
59
New cards
Manicouagan crater
This complex impact crater is 100 km in diameter and is one of the 5 largest in the world.
\
It is in central Quebec and was formed approximately 214 million years ago
\
Faulting caused the rim to collapse, and the rock has eroded to form a ring-shaped lake.
\
It is in central Quebec and was formed approximately 214 million years ago
\
Faulting caused the rim to collapse, and the rock has eroded to form a ring-shaped lake.

60
New cards
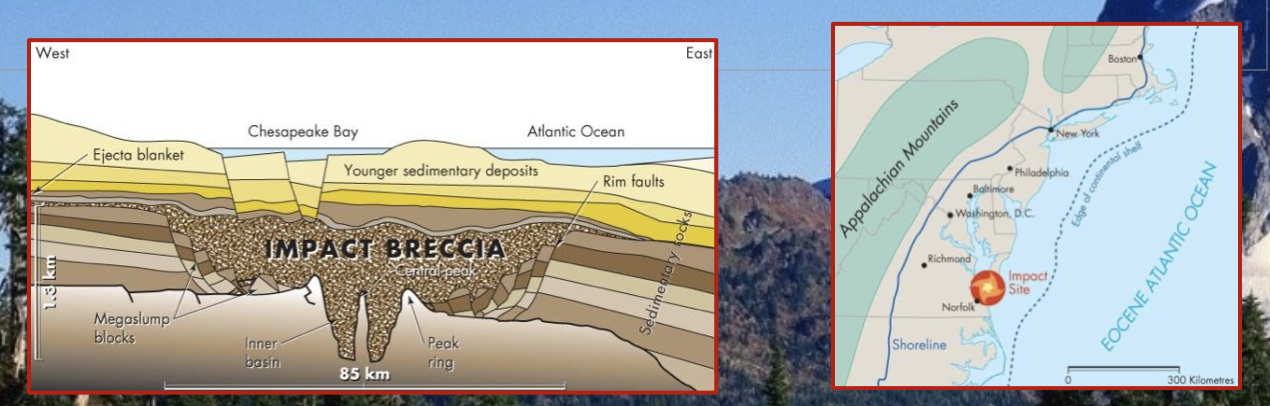
Chesapeake crater
This is a crater that was not discovered until subsurface imaging and drilling revealed its presence.
\
The crater formed 35.5 million years ago.
\
Since then, it has been overlain by sediment and seawater as sea levels have risen.
\
The crater formed 35.5 million years ago.
\
Since then, it has been overlain by sediment and seawater as sea levels have risen.
61
New cards
**Why are craters much more common on the Moon than on Earth?**
\
* most impacts with Earth are over oceans where craters are not produced
* impacts with Earth’s land have been eroded or buried and thus have more subtle features than Moon craters
* smaller bolides often burn up and disintegrate in earth’s atmosphere before striking its surface
* most impacts with Earth are over oceans where craters are not produced
* impacts with Earth’s land have been eroded or buried and thus have more subtle features than Moon craters
* smaller bolides often burn up and disintegrate in earth’s atmosphere before striking its surface
62
New cards
Shoemaker-levy comet
This comet entered Jupiter’s atmosphere in 1994.
\
Massive amounts of energy were released, and gas plumes were produced as 21 fragments of the comet collided with Jupiter.
\
After this impact, it was universally accepted that a similar impact could one day strike earth
\
Massive amounts of energy were released, and gas plumes were produced as 21 fragments of the comet collided with Jupiter.
\
After this impact, it was universally accepted that a similar impact could one day strike earth
63
New cards
Mass extinctions
Extinctions coincide with boundaries of geologic periods on the geologic time scale.
\
These are usually consistent with abrupt changes in climate from plate tectonics, volcanism, bolides, or human impacts.
\
There have been 5 major extinctions during the past 550 million years and a 6th is occurring today (climate change)
\
These are usually consistent with abrupt changes in climate from plate tectonics, volcanism, bolides, or human impacts.
\
There have been 5 major extinctions during the past 550 million years and a 6th is occurring today (climate change)
64
New cards
K-T boundary mass extinction (cretaceous - tertiary)
It occurred 65 million years ago from the abrupt cooling caused by an asteroid impact.
\
It is named for the boundary separating the Cretaceous and Tertiary Periods. In some languages, Cretaceous is spelled with a “K”.
\
This event caused extinction of the dinosaurs which had been at the top of the food chain for 100 million years.
\
It caused the extinction of 70% of all plant and animal species that existed at the time.
\
It is named for the boundary separating the Cretaceous and Tertiary Periods. In some languages, Cretaceous is spelled with a “K”.
\
This event caused extinction of the dinosaurs which had been at the top of the food chain for 100 million years.
\
It caused the extinction of 70% of all plant and animal species that existed at the time.
65
New cards
K-T boundary mass extinction cont.
How did we discover there was an impact?
\
Scientists found large amounts of iridium in rock that was dated at 65 millions old.
\
^^Iridium^^ is a rare element on earth, but is found in bolides.
\
The hypothesis of an impact was at first criticized because no crater had been found.
\
Scientists found large amounts of iridium in rock that was dated at 65 millions old.
\
^^Iridium^^ is a rare element on earth, but is found in bolides.
\
The hypothesis of an impact was at first criticized because no crater had been found.
66
New cards
K-T Boundary Crater
The K-T crater was discovered in 1991; it is 180 km in diameter and was found underlying sediment and seawater.
\
It is located on the yucatan peninsula in mexico and was given the name ==Chicxulub crater==
\
Analysis of the crater suggests the impact produced 10,000 times the energy of the entire nuclear arsenal of the world today.
\
It is located on the yucatan peninsula in mexico and was given the name ==Chicxulub crater==
\
Analysis of the crater suggests the impact produced 10,000 times the energy of the entire nuclear arsenal of the world today.
67
New cards
Linkages with other Hazards
Bolide impacts can trigger tsunamis, earthquakes, landslides, and cause climate change.
68
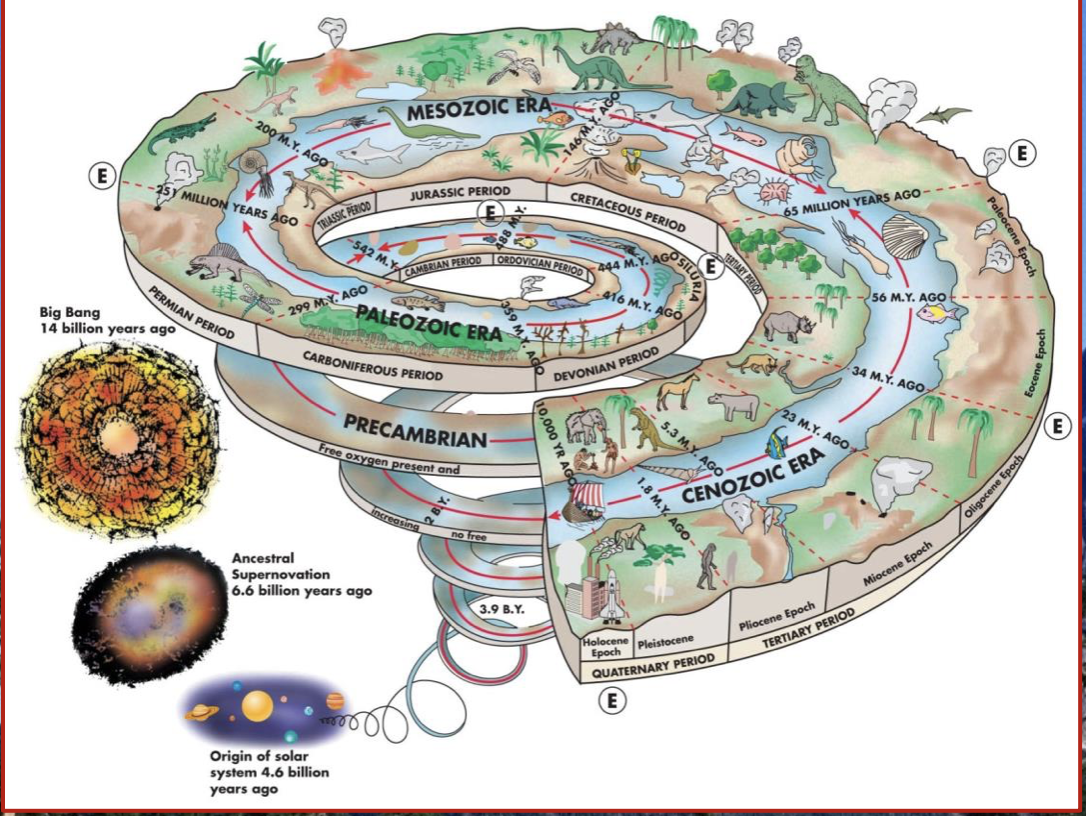
New cards
Earth history
69
New cards
Risk from Bolide Impacts
If an asteroid remains in the asteroid belt (between Mars and Jupiter), it poses no hazard to Earth.
\
The orbital path of an asteroid could be disturbed by a collision with another object
\
It is estimated that there are about 1100 asteroids larger than 1km in diameter with near-earth orbits.
\
\
Scientists estimate that an urban area would be destroyed once every 30,000 years by an asteroid similar in size to the Tunguska airburst (which has a 1000-year recurrence interval).
\
The orbital path of an asteroid could be disturbed by a collision with another object
\
It is estimated that there are about 1100 asteroids larger than 1km in diameter with near-earth orbits.
\
\
Scientists estimate that an urban area would be destroyed once every 30,000 years by an asteroid similar in size to the Tunguska airburst (which has a 1000-year recurrence interval).
70
New cards
bolide impact frequency
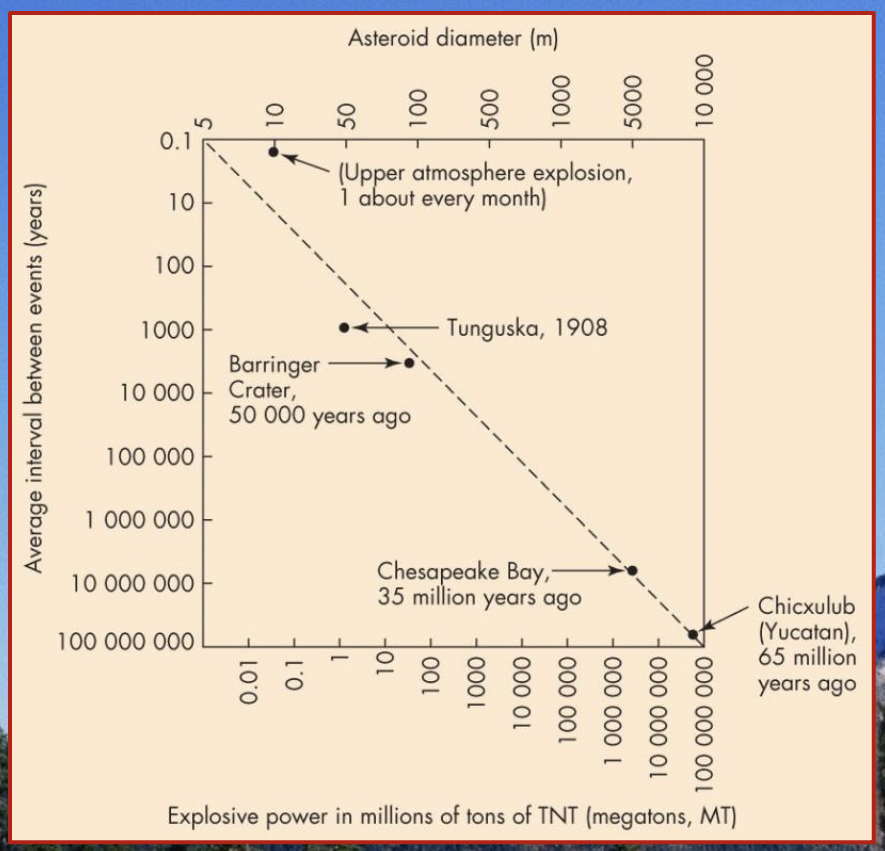
71
New cards
Managing the bolide impact hazard
The Spaceguard survey program has catalogued all near-Earth orbits larger than 1 km in diameter.
\
Extending the inventory to bolides as small as 100 metres in diameter is a current objective.
\
If a large bolide is determined to be approaching
\
Extending the inventory to bolides as small as 100 metres in diameter is a current objective.
\
If a large bolide is determined to be approaching
72
New cards
Managing the bolide impact hazard cont.
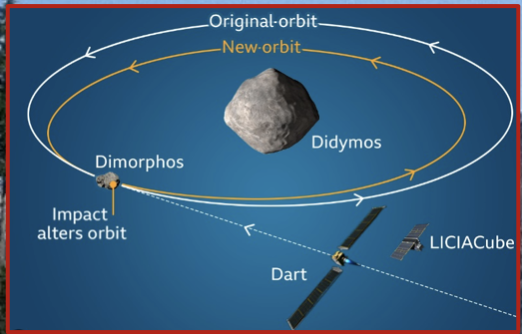
Blowing up an approaching bolide will cause fragments to rain down and is not advisable.
\
Pushing a bolide off course by ramming it with a spacecraft is the recommended approach.
\
This was tested for the first time in september 2022 when a spacecraft impacted the asteroid dimorphous 11 million km from earth
\
Pushing a bolide off course by ramming it with a spacecraft is the recommended approach.
\
This was tested for the first time in september 2022 when a spacecraft impacted the asteroid dimorphous 11 million km from earth