16 - Apicomplexans (Continued)
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Cryptosporidum
Which apicomplexan protozoan measures 4-6 um, is found worldwide, infects all vertebrates, is most severe in young and immunocompromised animals, and is associated with significant diarrhea and respiratory symptoms? It is a notifiable disease, is spread fecal-oral, and is shed as an oocyst in feces. It can be spread in water parks as it is resistant to chlorine. Species include parvum, andersoni, and felis among others.
Direct
What type of life cycle is found in Cryptosporidium? They are spread fecal-oral.
Four
Each Cryptosporidium oocyst has how many sporozoites? Most of the oocysts are thick-walled and these will sporulate before leaving the host and can remain viable for months.
Microvillus
Cryptosporidium parasites inhabit what border of the gastric glands (c. muris)? Other species (C. parvum) can infect the lower half of the small intestine. They replicate in these borders, as well as the gallbladder, respiratory system, and kidneys.
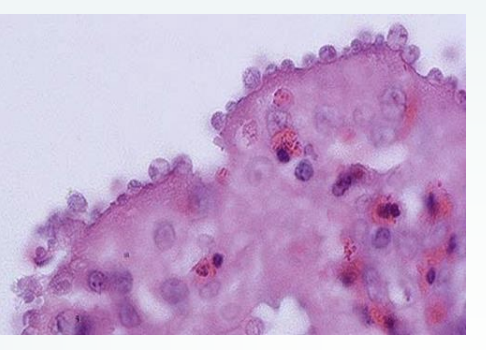
parvum
Which species of Cryptosporidium is common in dairy calves under one month old? They cause yellow, watery diarrhea with mucous/blood/gas, can be projectile and severe, cause lethargy, fever, weight loss, and emaciation. There is high morbidity and occasional mortality. They also infect lambs/kids causing diarrhea and weight loss, shed oocytes, and have high morbidity/mortality.
Foals
C. parvum infections in which animals are not common, but have a specific equine genotype, cause diarrhea affecting 80% of them under six months old, and cause persistent infections in the Arabian breed (SCID)?
Pigs
C. parvum infections in which species seldom cause clinical signs of enteritis or colitis and cause mild inflammatory lesions?
Chronic wasting
C. parvum infections in snakes cause what disease? Hypertrophic gastritis results with markedly thickened mucosal folds, numerous pinpoint foci of hyperemia, gastric epithelial tropism, anorexia, lethargy, regurgitation, midbody swelling and weight loss, poor prognosis, and culling of the animal.
Turkeys
C. parvum infections are more severe in which animals than in chickens, develop in the proventriculus, conjunctiva, and other locations, and cause diarrhea, dehydration, weight loss, coughing, and gasping?
Acid-fast
Which stain, also called Ziel-Neelsen, is used to diagnose Cryptosporidium in fecal smears? They stain the oocysts present, which are approximately 5 um in diameter and appear red-pink.
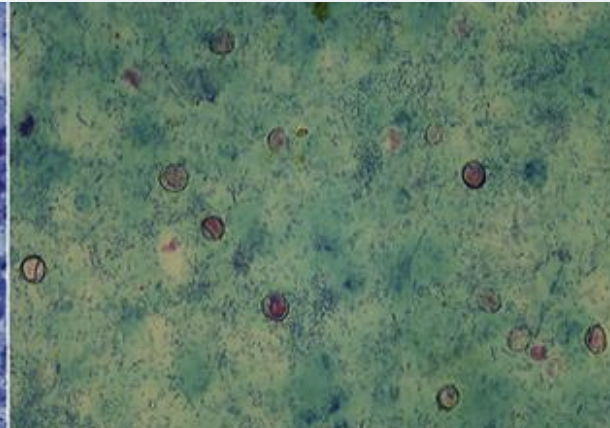
Babesia
Which protozoan is a pyriform, round, or oval parasite of mammalian RBCs? Trophozoites develop after sporozoites infect the RBCs and merozoites develop as trophozoites mature, resemble four trophozoites, and are attached in a maltese cross formation. It is reportable and is transmitted by ticks.
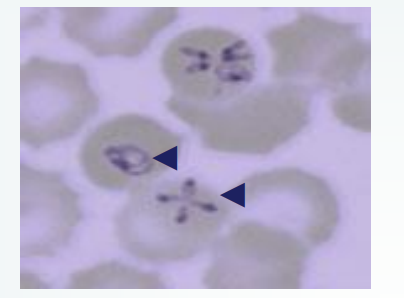
Sporozoite
Which stage of Babesia infect the RBCs? They will then become trophozoites, then produce merozoites.
Canine
Babesia infecting what species (B. vogeli, B. gibsoni) are found worldwide, are spread by R. sanguineus ticks, and cause intravascular hemolysis, hemolytic anemia, lethargy, fever, and icterus?
R. sanguineus
What tick spreads canine Babesia?
Bovine
Babesia infecting what species is found in the tropics/subtropics, is spread by Boophilus ticks, includes the species B. bigemina, and causes fever, anemia, and hemoglobinuria?
Boophilus
Which tick spreads bovine Babesia?
Equine
Babesia infecting what species is also called piroplasmosis, includes the species Theileria equi, B. cabali, and T. haneyi, is reportable in the US, and is spread by Amblyomma and Dermacentor ticks? It causes fever, subclinical periods, clearing of infection is possible, and thrombocytopenia.
Amblyomma
Which tick spreads T. equi, causing equine Babesia?
Dermacentor
Which tick spreads B. caballi and T. haneyi, causing equine Babesia?
Sporozoites
Which stage of Babesia is spread to animals through tick saliva? They invade the erythrocytes and multiply by binary fission, forming merozoites.
Piroplasms
Which structures resulting from Babesia infection pass into the tick’s ovary and multiply? They are incorporated into the eggs, transmit to the host through larva, and transmit through molting from the nymph to adult stages. This will not occur, however, in T. equi.
Yes
Is transmission of Babesia possible through mechanical vectors like needles?
Texas Fever
What is another term for Babesia in cows? It was once endemic to the US south, was eradicated through cattle dipping, and was reintroduced through Mexico.
Quarantine
In the US, all equine Babesia positive horses are placed under what, and the owner is given the option of long-term quarantine, permanent quarantine, euthanasia, and exportation from the US?
PCR
Equine Babesia is tested with Antibody ELISA and confirmed with what test? IFAT can distinguish species and USDA protocol uses imidocarb diprionpionate to clear the organism.
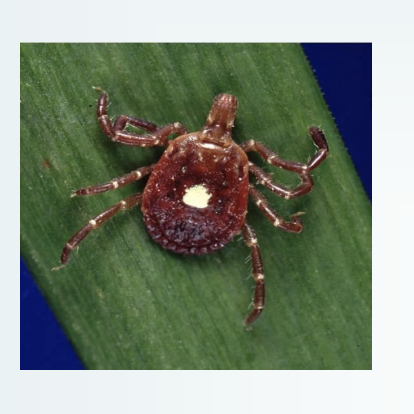
Cytauxzoon felis
What protozoan is sporadic but rapidly and uniformly a fatal disease of cats? Bobcats are the natural reservoir hosts and domestic cats surviving non-lethal infections will become reservoirs. It causes anorexia, depression, hepatosplenomegaly, leukopenia, toxic neutrophils, thrombocytopenia, and icterus/congestion of mesenteric veins.
Amblyomma americanum
What tick spreads C. felis?

Piroplasms
What structures can be seen in peripheral blood smears of cats with Cytauxzoon felis?
