Part of neurons, spinal cord and associated structures
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
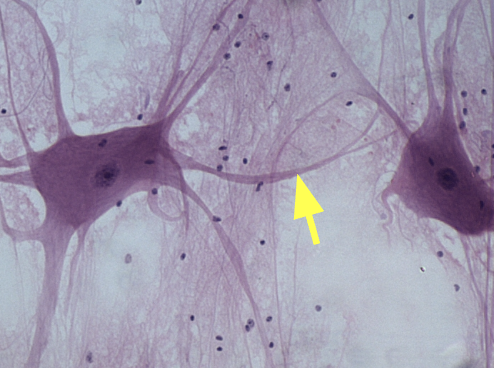
Dendrite
Receive signals from other neurons or special sensory cells
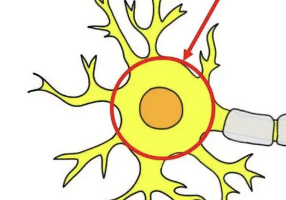
Soma/cell body
Where the nucleus is
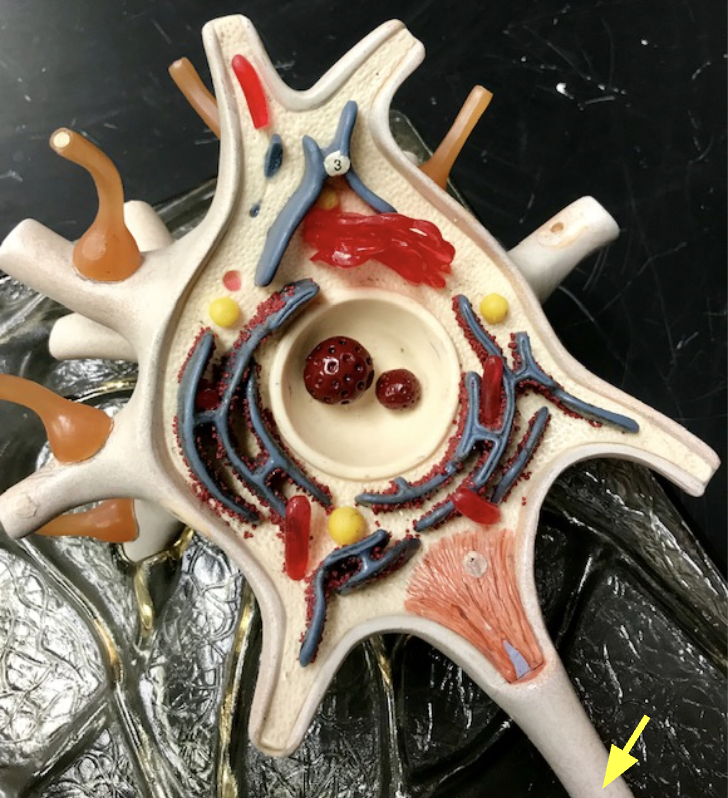
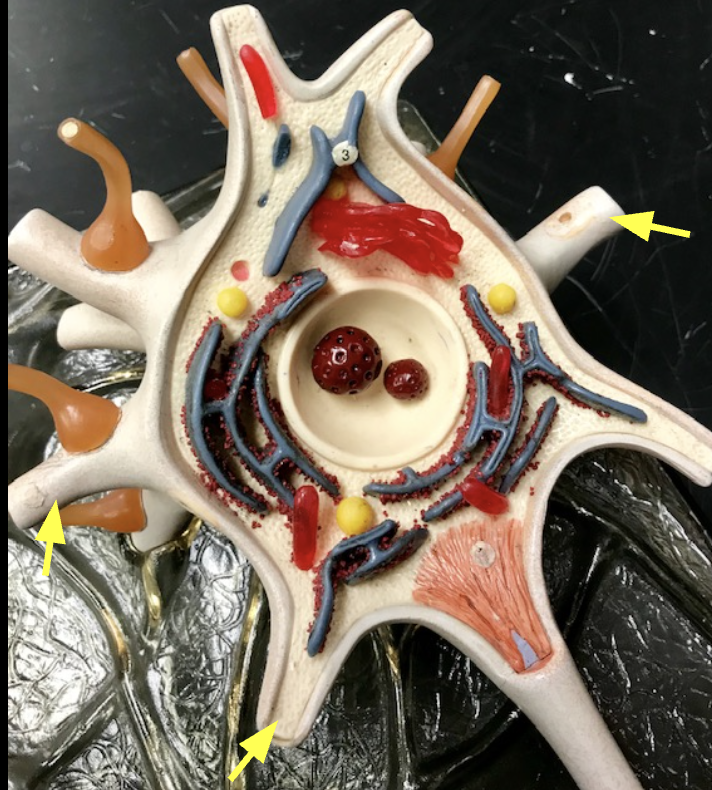
Axon
Light gray. Sends signals between brain cells
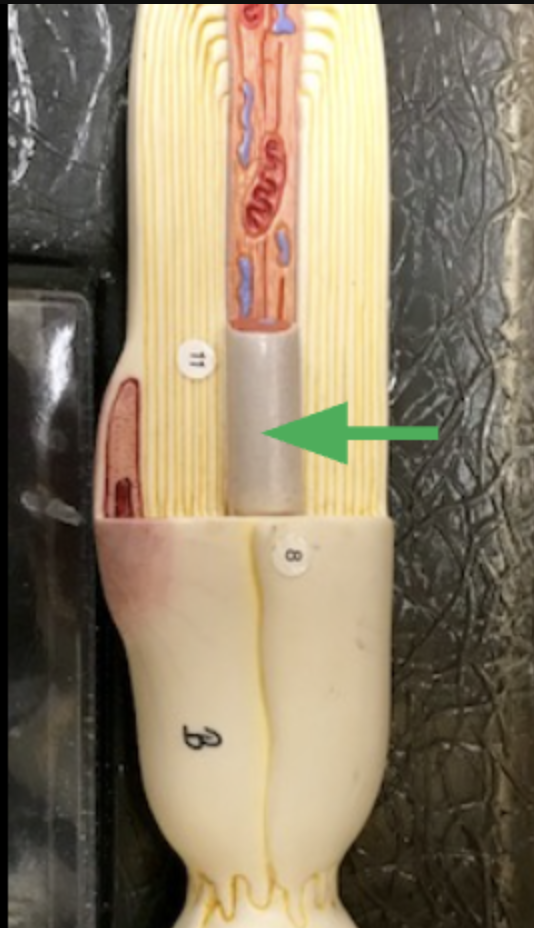
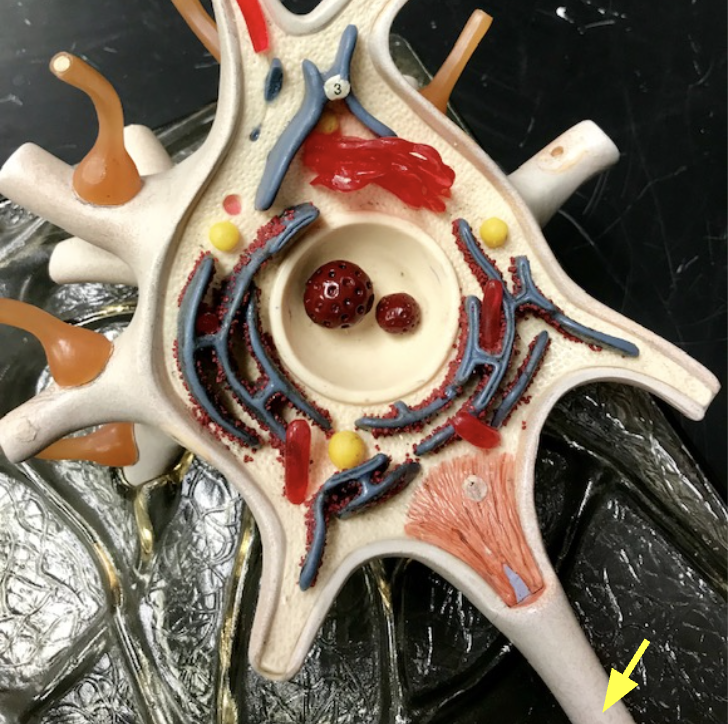

Axolemma
Controls ion flow to generate electrical signals. axon potential reaches threshold
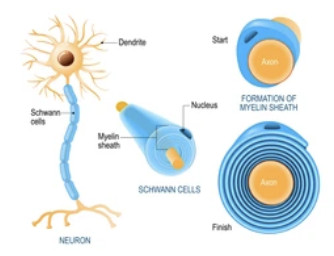
Neurolemmocyte
Forms myelin sheath (the cell)
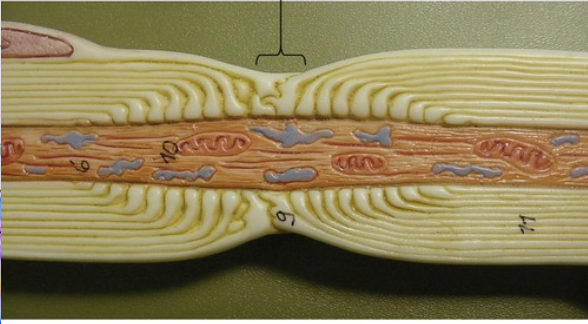
Neurofibril node/ node of ranvier
Where action potential happen
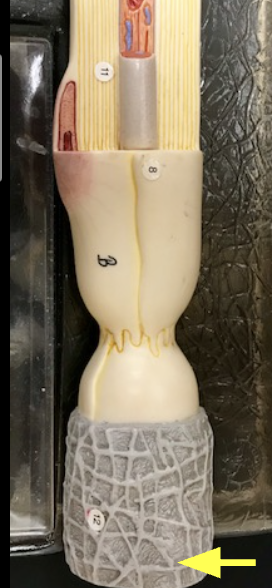
Endoneurium- connective tissue
Bind neighboring axons to one another
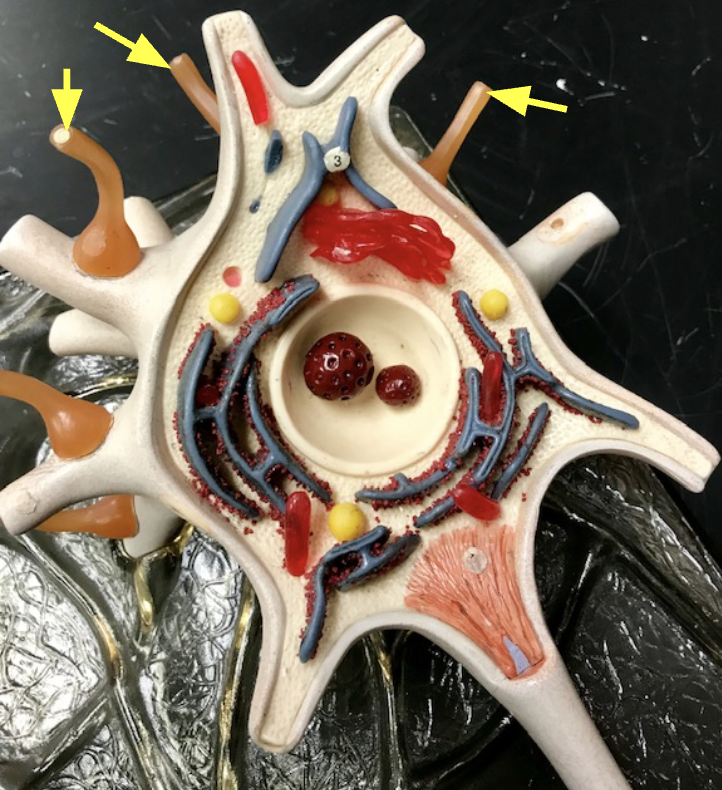
Telodendrion
helps send messages from one nerve cell to another by releasing chemicals at the end of a neuron

Synaptic knob
the rounded end of a neuron where neurotransmitters are released to send signals to the next cell
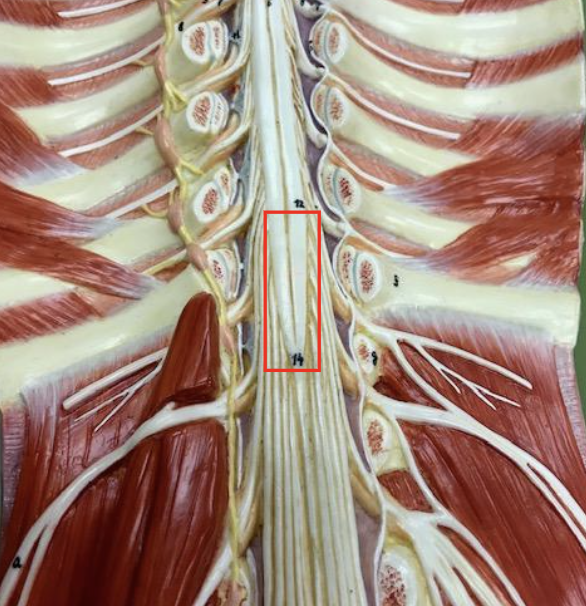
Conus medullaris
L1 vertebra, end of spinal cord
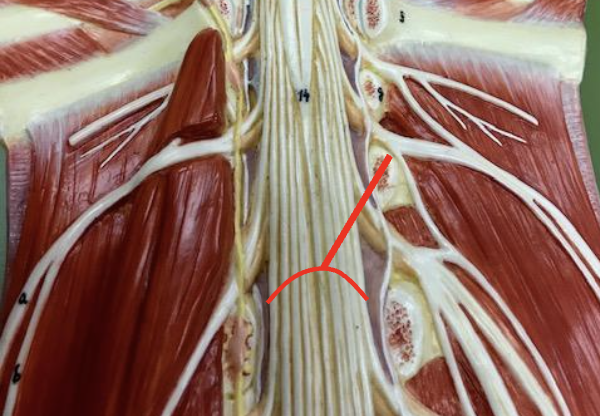
Cauda equina
Nerves runs through the vertebral canal inferior to the conus madullaris. sends nerve signals to and from the legs, feet, and pelvic organs
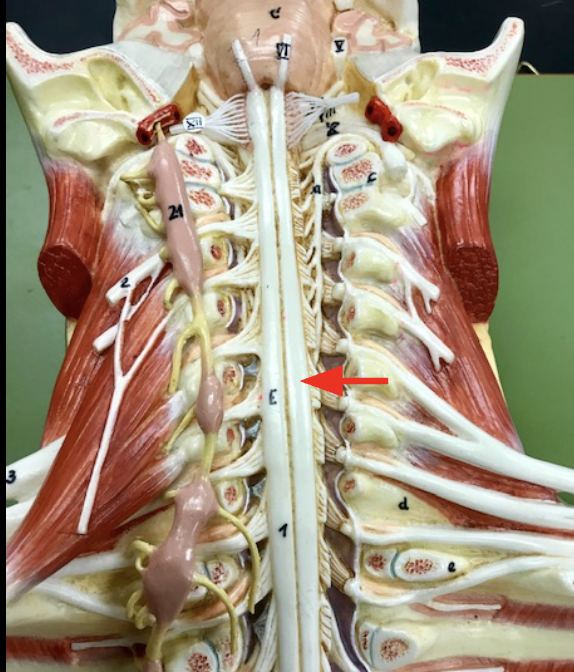
Cervical enlargement
motor & sensory neurons serving(providing to) the upper limbs
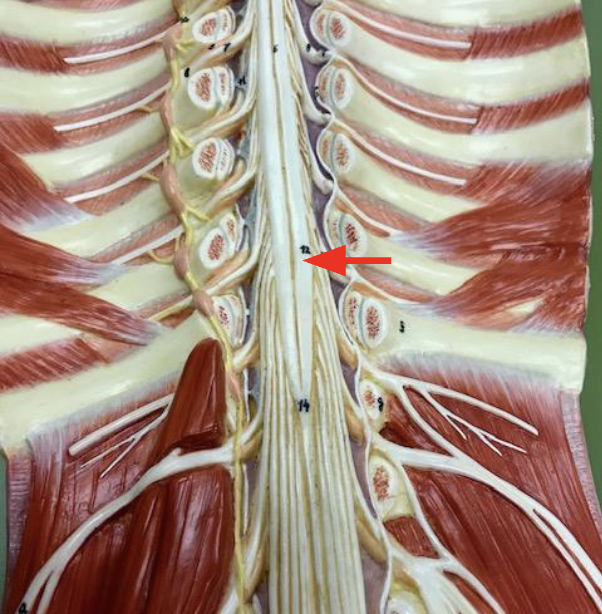
Lumbosacral enlargement
Motor and sensory nerves serving(provided to) lower limbs
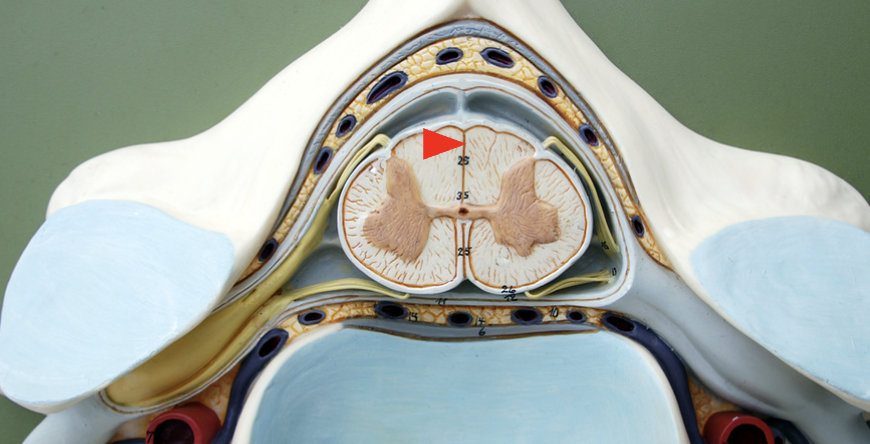
Posterior sulcus
Shallow groove divides
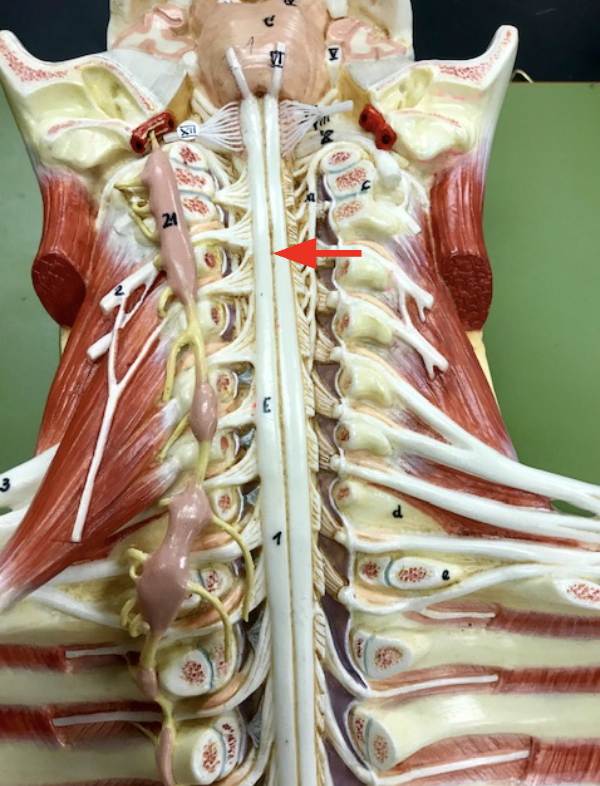
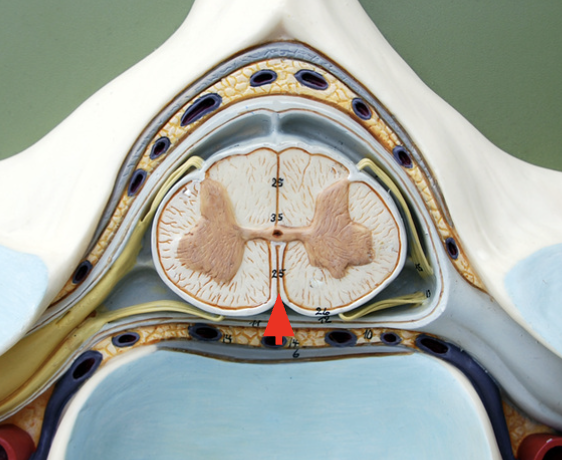
Anterior median fissure
Dissection of the vertebral canal with the spinal cord & spinal nerves exposed/ division
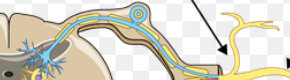
Anterior ramus
a branch of a spinal nerve that carries signals to and from the front and sides of the body, including the limbs
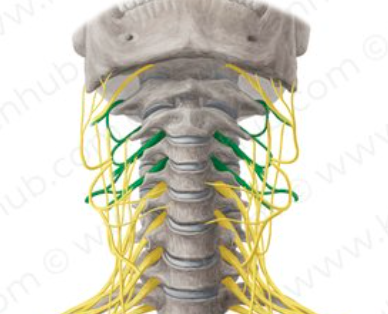
Cervical plexus
a network of nerves in the neck that sends signals to the head, neck, shoulders, and diaphragm
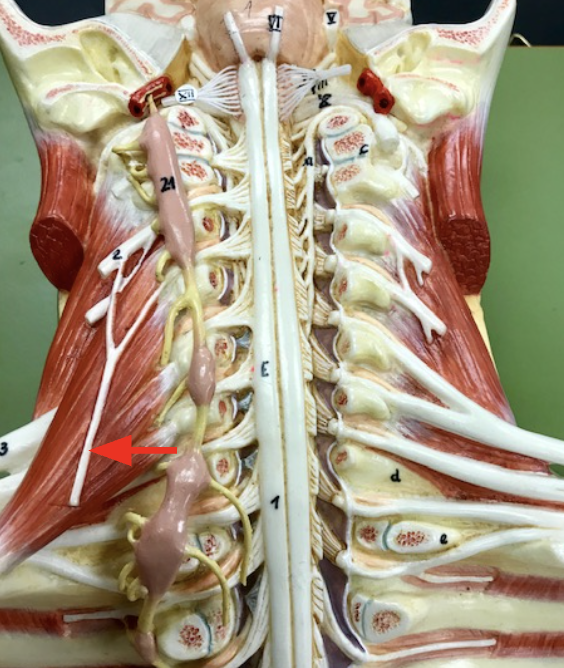
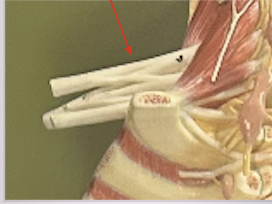
Phrenic nerve
takes motor signals to the diaphragm
Brachial plexus
etwork of nerves that sends signals to the shoulders, arms, and hands
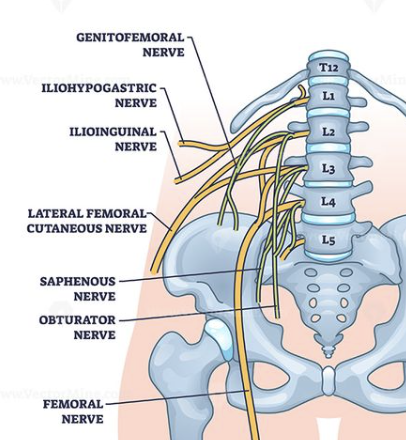
Lumbosacral plexus
a group of nerves that sends signals to the lower back, pelvis, legs, and feet
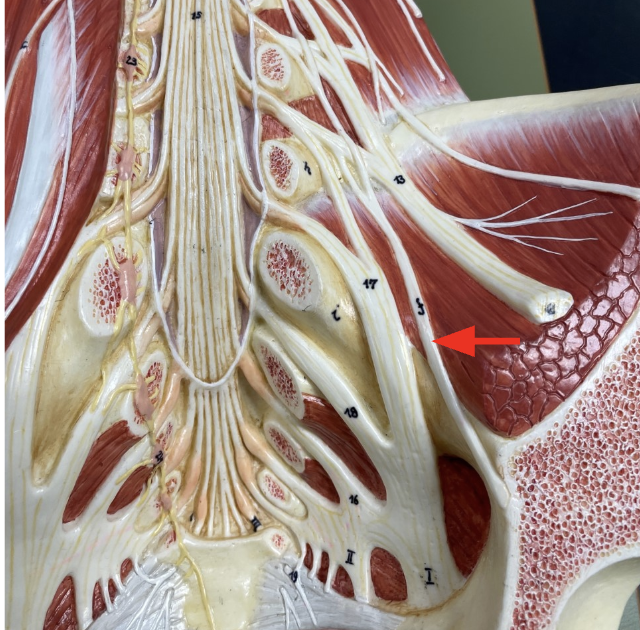
Obturator nerve
Takes motor and sensory signals to/from the medial thigh
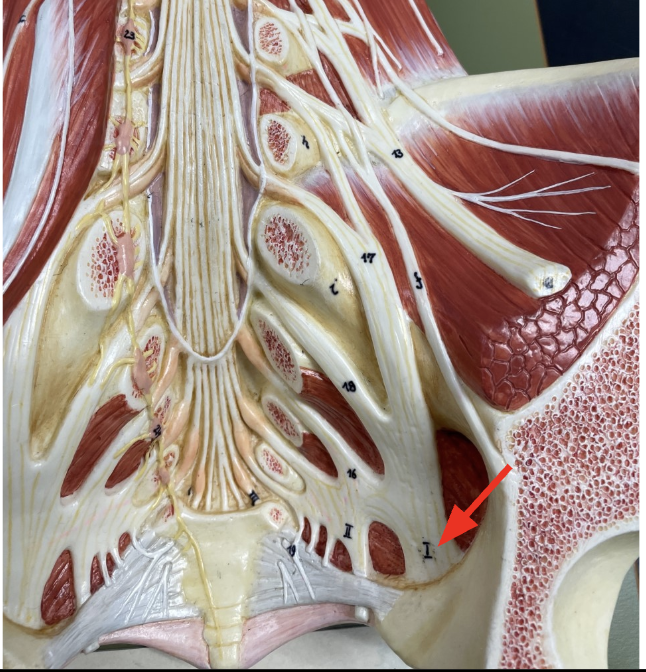
Sciatic nerve
Takes motor signals to the hamstring muscle and carries sensory info from much of the posterior thigh and leg as well as the plantar foot
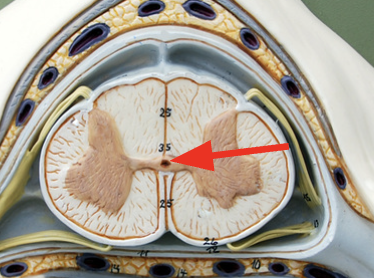
Central canal
Cavity with CSF
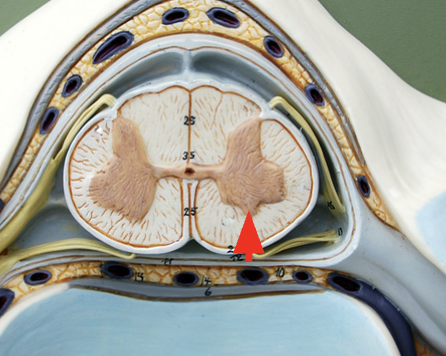
Anterior horn
Contains bodies of somatic motor neurons. the axons of there motor neurons travel to skeletal muscles
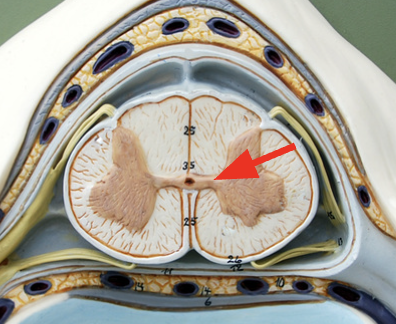
Posterior horn
Axons from sensory neurons bringing info from the body regarding touch and proprioception
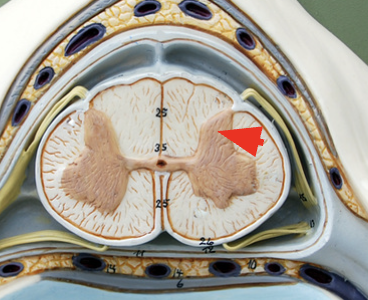
Lateral horn
part of the spinal cord that contains nerve cells involved in controlling involuntary functions like heart rate and digestion
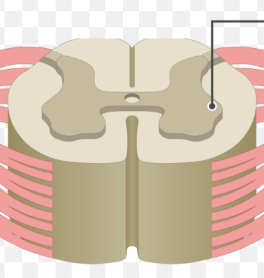
Gray commissure
Connects sides
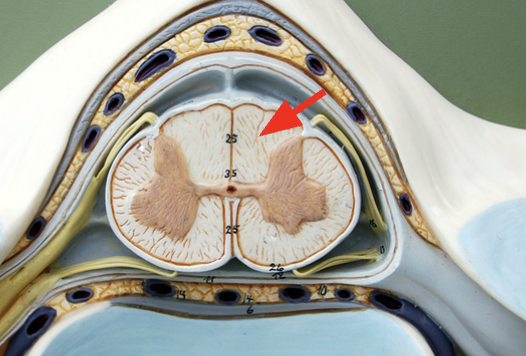
Posterior funiculus
White matter, a group of myelinated axons conveying info from the brain regarding touch, perception, ect
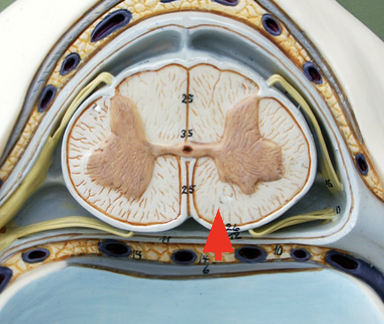
Anterior funiculus
myelinated axons involved in taking sensory signals to the thalamus as well as motor commands involved in balance and coordination
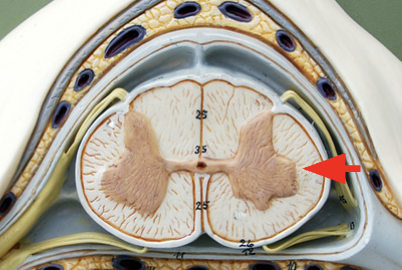
Lateral funiculus
myelinated axons involved in taking sensory signals to the cerebellum and thalamus as well as motor command from the cortex and brain stem
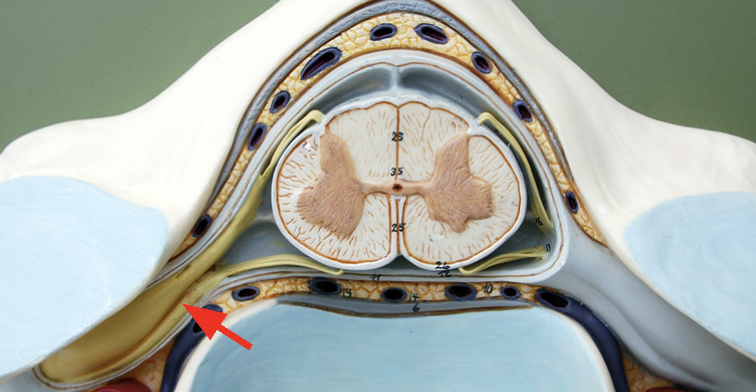
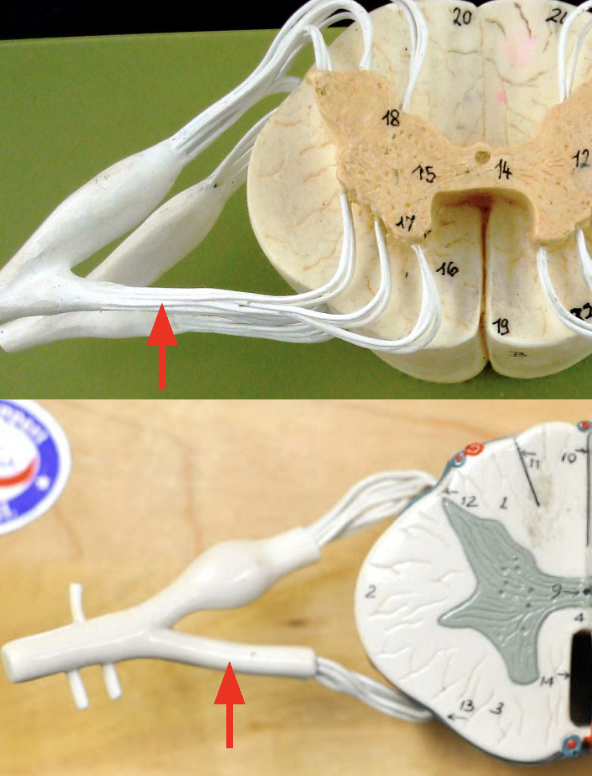
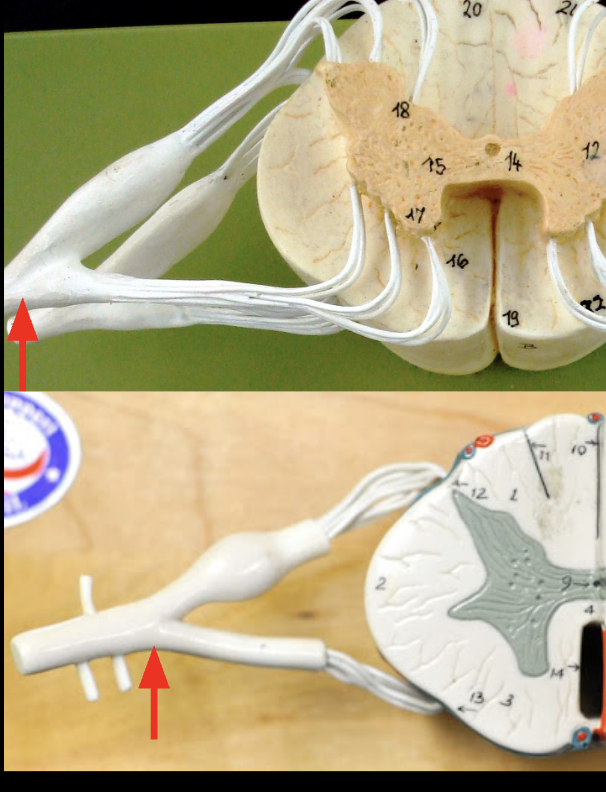
Ventral root
Contains axons if ventral horn motor neurons that will travel to skeletal muscles
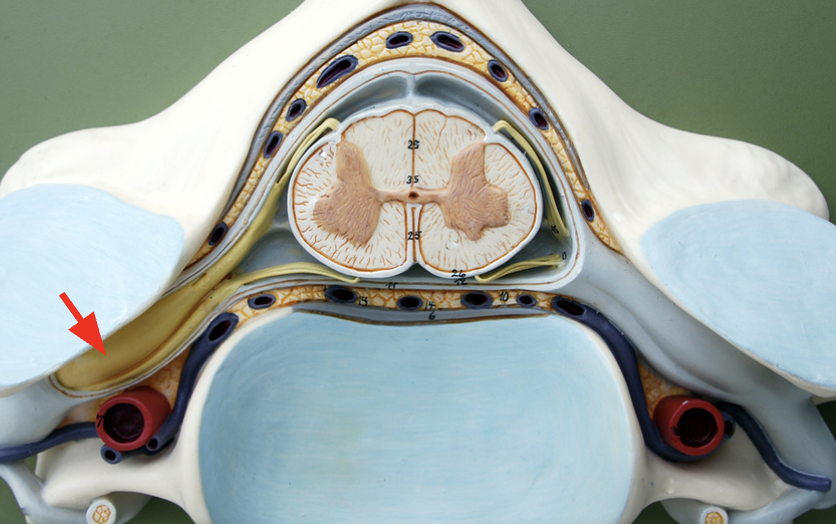
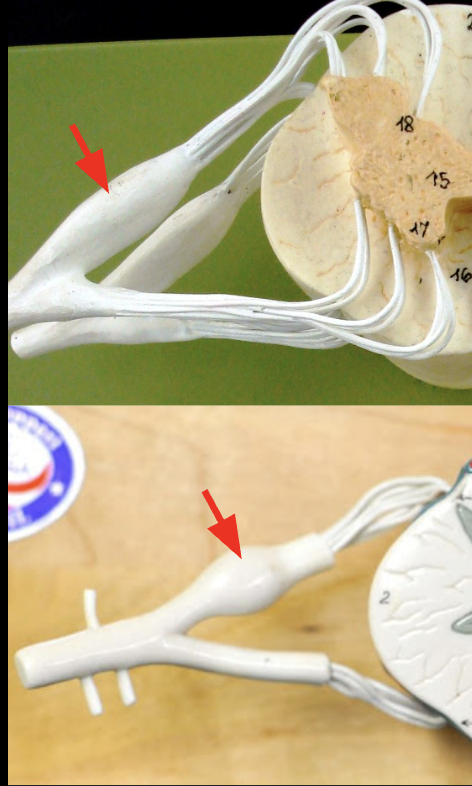
Dorsal root ganglion
Soma of sensory root, brings sensory info into the spinal cord
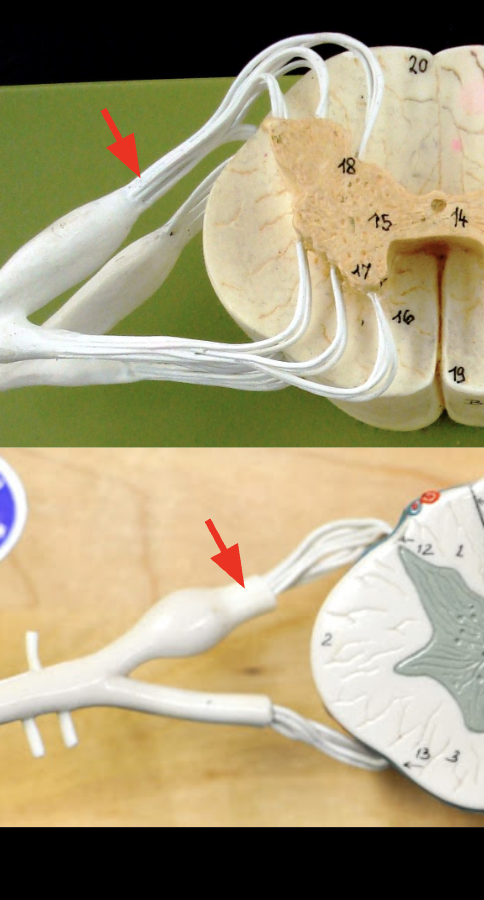
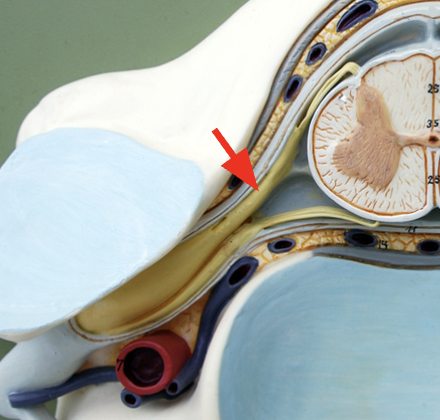
Dorsal root
contains sensory axons bringing sensory info into dorsal horn
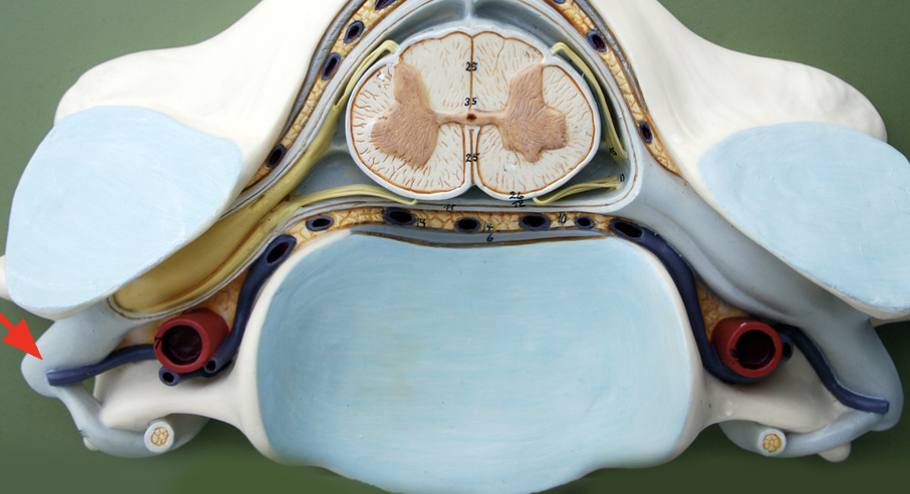
Spinal nerve
Sensory axons of the dorsal root and motor axons of the ventral root, mixed nerve