cooked
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
93 Terms
how many times did chloroplast originate by endosymbiosis in green plants
one time
what events are examples of primary endosymbiosis
creation of the first chloroplast and mitochondrion
what event was an example of secondary endosymbiosis
red algae becomes chloroplast of ancestry to brown algae and diatoms
which life cycles are haploid dominant?
Chlamydomonas and Spirogyras and Oedogonium
the embryo of the Ginkgo biloba is ____
diploid
the megagametophyte of ginkgo biloba is ____
haploid
true or false - the male gametophyte of gymnosperms produces several antheridia
false
true or false - the female gametophyte of gymnosperms produces triploid endosperm
false
the ovules and seeds of gymnosperms are exposed on the surface of sporophylls
true
does gymnosperm mean “naked seed”?
yes
what type of ovaries does raspberries have?
apocarpous
What is the fundamental difference between the fruits of mulberry and blackberry?
mulberries are multiple fruit from the fusion of many flowers
blackberries are aggregate fruit formed from multiple ovaries of a single flower
largest tree belongs to this group
seqoiadendron giganteum or giant sequoias
tallest tree belongs to this group
sequoia semperviren or coast redwoods
oldest tree belongs to this group
pinus longaeva or Bristlecone Pine
is a monoecious plant bisexual or heterosexual?
bisexual
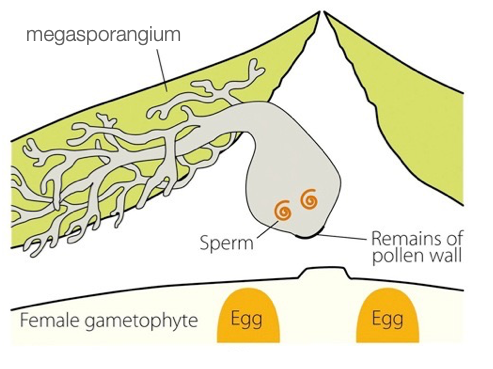
What does the image below indicate?
Growth of haustorial pollen tube in Cycads and Ginkgo
The dominant trees of the carboniferous rain forest were:
Lycophytes and Ferns
The major adaptation by the later plants to thrive on dry areas after 300 mya is the evolution of:
pollen
The tiny microspores produced inside microsporangia are ________ structures which develop into_____________.
haploid, pollen
Which of the following are anatomically equivalent parts between Selaginella strobilus and angiosperm anther?
Y and Z
Which of the following are anatomically equivalent parts between pine (gymnosperm) strobilus and angiosperm flower?
male cone - stamens of flower
female cone - carpels of flower
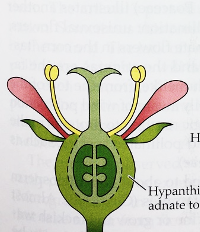
Ovary in this flower is_____
inferior
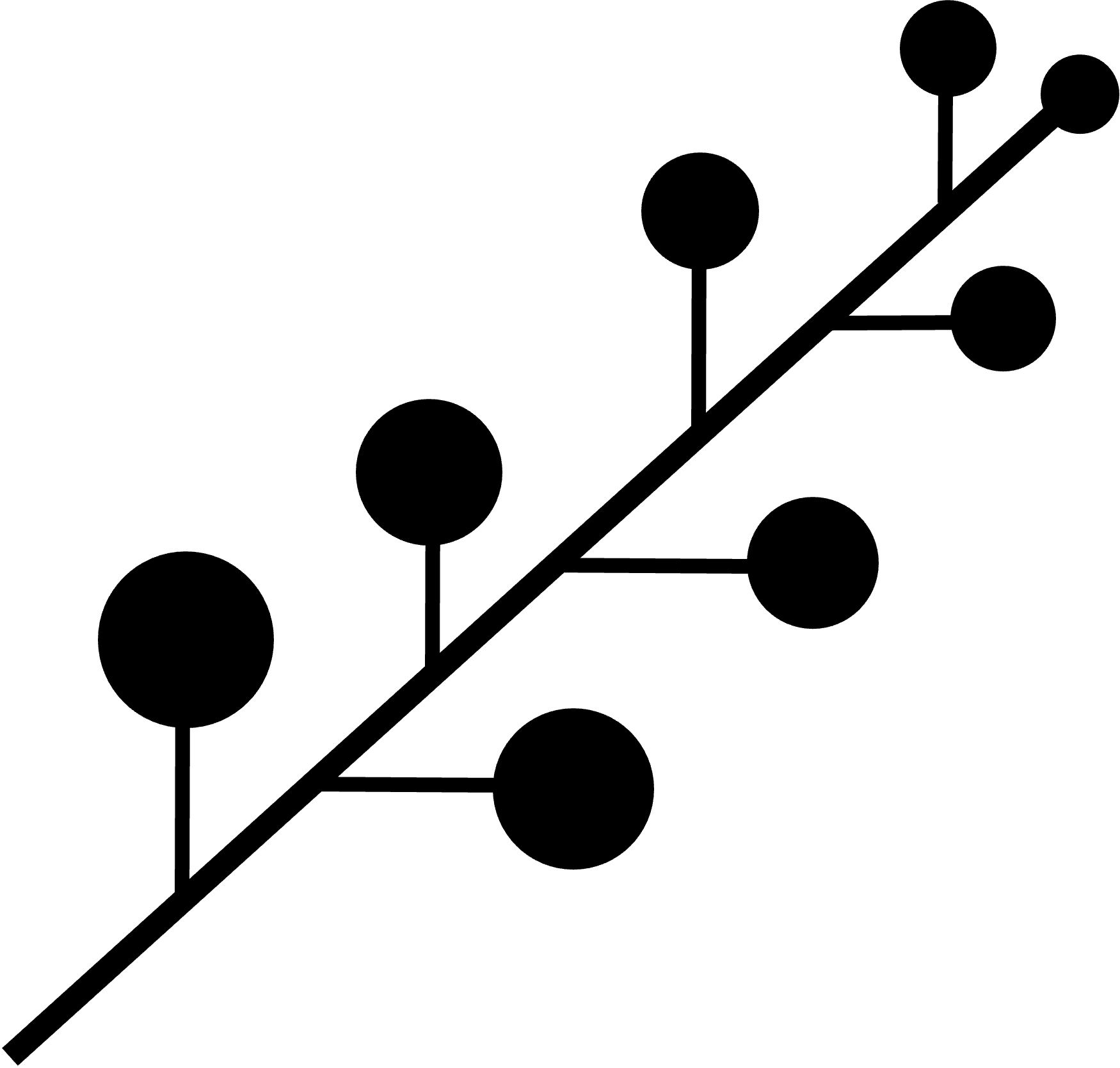
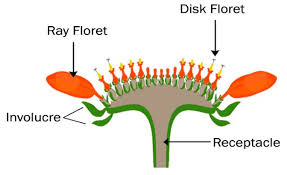
inflorescence represent _____. the inflorescence in this figure below is an ____ type
a cluster of flowers, indeterminate
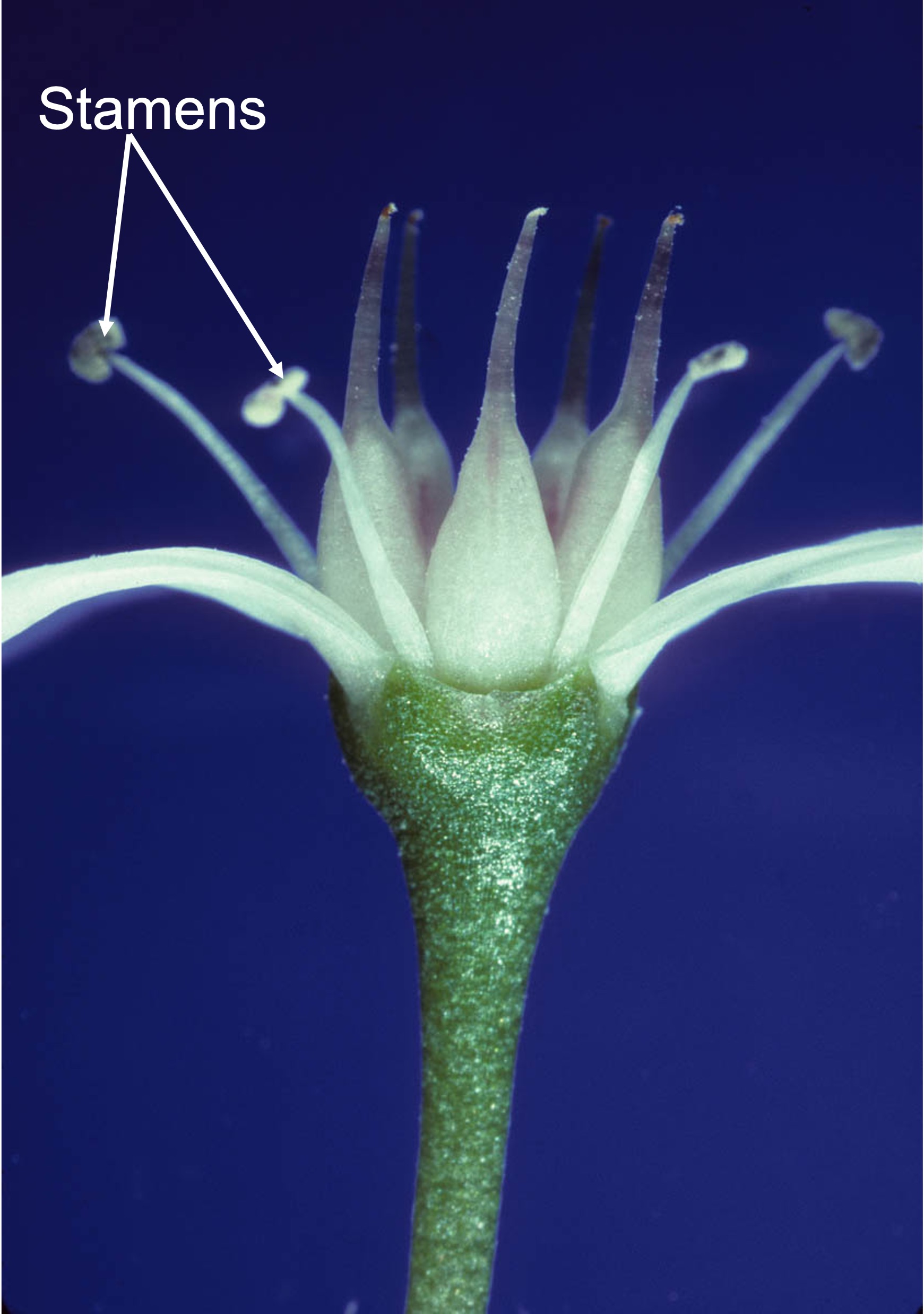
this plant has
apocarpous ovary with multiple carpels.
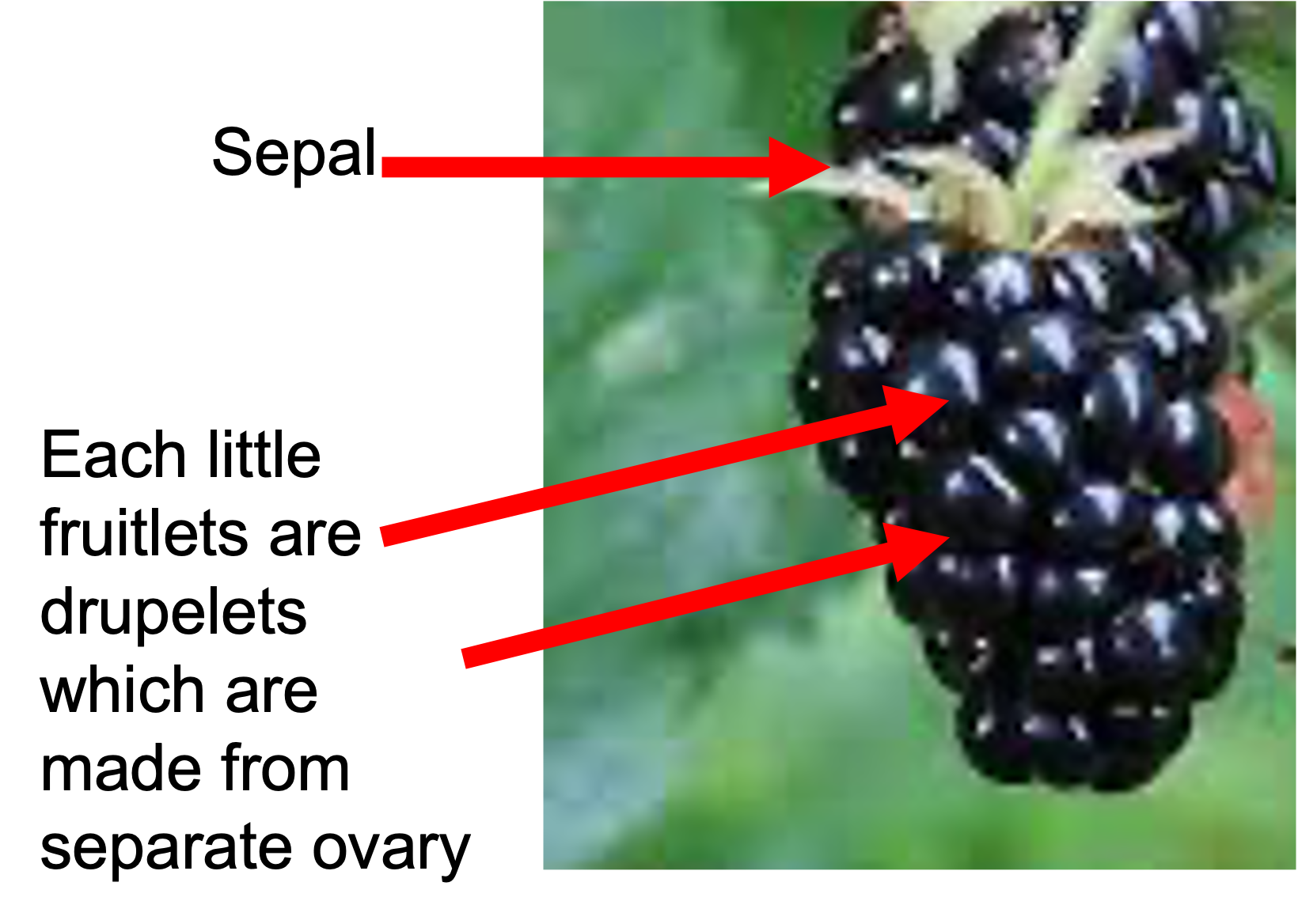
The fruit below is the result of:
a single flower with free carpels
Which of the following statements about Spirogyra is FALSE?
Gametes are anisogamous
what was the effect of early embryophytes on the climate
reduced carbon dioxide in atmosphere so the temp was lower and it was drier
how does a plant reproduce without water?
deliver sperm directly to them and and don’t make them swim
how many cells does a microgametophyte have?
4
are gymnosperms haploid or diploid dominant?
diploid dominant
what makes up an ovule
integument and megasporangium
a tiny megaspore produced inside megasporagium develops into ____ that produces ___ for fertilization
megagametophyte, egg
what doe gymno sperm mean
naked seed
4 types of gymnosperms
conifers, ginkgos, cycads, and gnetophytes
trees with short stubby trunks and very rigid, pinnate leaves and large cones that emerge fromt he top of the trunk
cycads
what does monoecious mean
one house or a plant with make and female parts
what is dioecious
two houses or a plant with only female or male parts
Ovules become ___ and ovaries become ___
seeds and fruit
4 types of whorls
calyx, corolla, androecium, and gynecium
what are whorls made of
modified leaves
another name for gyneocium
pistil
another name for androcium
stamen
another name for the calyx
sepal
another word for corolla
petall
what is in androecium
groups of pollen sacs that contain pollen grains
what is a carpel
modified leaf bearing ovules on the margin of its uppper surface
what is a pistil
one or more carpels fused into a structure having an ovary, style and stigma
what is gyneocium
collective term for all carpels in a flower
what is syncarpous gynoecium
three carpels are fused into a single pistil that separates only at the stigma
what is superior ovary
flower parts attach below it
what is an inferior ovary
sunk below the point where the other flower parts attach.
hypogynous
plant has ovary open and easy to see. it is not covered
perigynous
you can still see the ovary but it has some walls around it
epigynous
the ovary is totally hidden in the hypanthium
what is the only group to do double fertilization
angiosperms
why is endosperm so iportant
the plant does not have to waste any energy making food for the embryo that does not exist
steps of double fertilization
the sperm joins with the egg to make the zygote then another sperm goes for the central cell nuclei to create a 3N cell
what is inflorescene
cluster of flowers
raceme inflorescence
pedicels and internodes
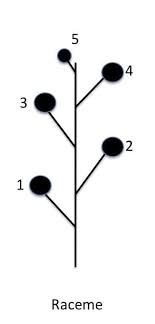
solitary inflorescence
just one flower
umbel
pedicels but no internodes
spike
internodes but no pedicels
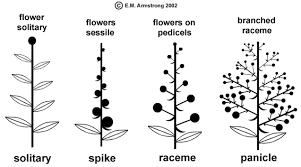
head
neither internodes nor pedicels
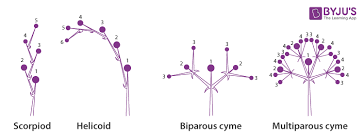
cymose
cyanobacteria pigments
chlosophyll a and phyconilins (phycoerythrin and phycocyanin)
pigments in red algae
chlorophyll a and phycobilins (phycoerythrin and phycocyanin)
important uses of red algae
ice cream
what is megasporophylls
modified leaves bearing sporangia (megasporangia)
what do carpels turn into
fruits
what is apocarpous
3 carpels with 1 locule per carpel
syncarpous
A carpels 3 locule 1 B carpels 2 locule 1 C carpels 4 locules 4
unicarpellous
1 carpel, 1 locule
placenta
all places where ovules attach
simple fruits
produced by syncarpous or unicarpellate gynoecium
types of simple fruits
dry dehiscent and indehiscent and fleshy
simple fleshy fruits are called
berries (ex - grape, tomato, blueberries, eggplant)
pepo
a fruit from the angiosperm plant family called cucubitaceae and are characterized by leathery rind (ex: pumpkin, cucumber, watermelon)
desperidium
a citrus fruit with the fleshy part consisting of juice sacs and also has a rind with oil glands (ex: lemon)
pomes
fruit with fleshy part is hypanthium of epigynous flowers (ex: apple)
drupes
have a hard or woody pit in the center (ex. peach cherry)
follicle
or a dry fruit formed from a single carpel
legume
have 2 seams instead of just one
capsule
multiple carpels
samara
is an achene with winds
grain
fruit that has an achene that cant be seperated
nut
has a very ahrd outer shel and the nut isnt fused to the ovary wall
aggregate fruits
fruits produced by the apocarpous gneocium of a single flower (ex: strawberries and rasperries and blackberries)
multiple fruits
fusion of fruits from several flowers
brown algae (kelp) pigments
chlorophylls a and c and fucoxanthin
diatoms pigments
chlorophylls a and c and fucoxanthin
what makes diatoms unique?
cell walls made of glass
green algae pigments
chlorophylls a and b and carotenoids