Lecture 6: Linear Probability Models
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
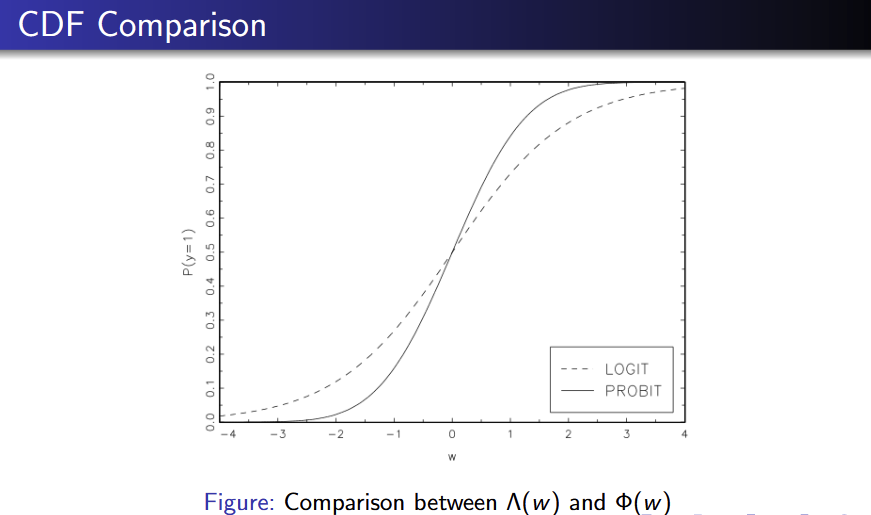
Probit and Logit difference
Probit models the conditional probability as the CDF of standard normal distribution
Logit models it as the CDF of the standard logistic distribution
(both guaranteed to take values between 0 and 1)
what is the logistic function
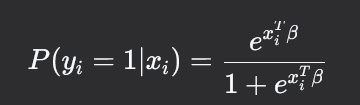
differences between Logit and Probit (function used, error dsitribution, computational simplicity, variance)
page 5
what is MLE used for
to find the β that maximises the likelihood function L(β)
what is maximum likelihood estimation (MLE)
a statistical method used to estimate the parameters (β) of a probability distribution by maximising the likelihood function
ie find the β that make the observed data most probable
how to do MLE
write out likelihood function (start with PMF for single observation then do joint likelihood which is product of all)
then do natural log of L(β) to turn product into sums
find best β using numerical optimisation
page 8
obtaining MLE of Logit model
page 9
marginal effects of probit and logit
page 6
marginal effects vary with xi, smaller effects are closest to extremes 0 or 1
3 ways to calculate marginal effects
page 11