Endocrine Physiology: Hypothalamus & The Anterior Pituitary Gland
1/30
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Week 4: Thursday, September 18th
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
the Egyptians believed that the _______ was not important, and that the _______ and _______ were because they drained mucus from the brain
brain, hypothalamus and pituitary
true or false: future research found that removing the pituitary gland did not lead to endocrine gland atrophy
false. future research found that removing the pituitary gland did lead to endocrine gland atrophy
the _______ is the tube connecting the hypothalamus and pituitary gland, it has blood vessels that send hormones between the two
infundibulum
true or false: hypothalamus hormones are hormones because they’re released in the brain
false. hypothalamus hormones are neurohormones they’re released in the brain
true or false: pituitary gland hormones are hormones because they’re released outside of the brain
true
_______ claims that the hypothalamus releases chemicals into portal blood vessels to regulate pituitary
Neurovascular hypothesis
the pituitary gland is a _______ between the brain and body
relay station
the _______ hangs from our brain in the sphenoid bone within sells turcica (bone depression); below the hypothalamus; and broken into 3 sections
pituitary gland
the _______ pituitary gland is derived from oral ectoderm (mouth cavity) and connected to the hypothalamus via blood
anterior (adenohypopsis)
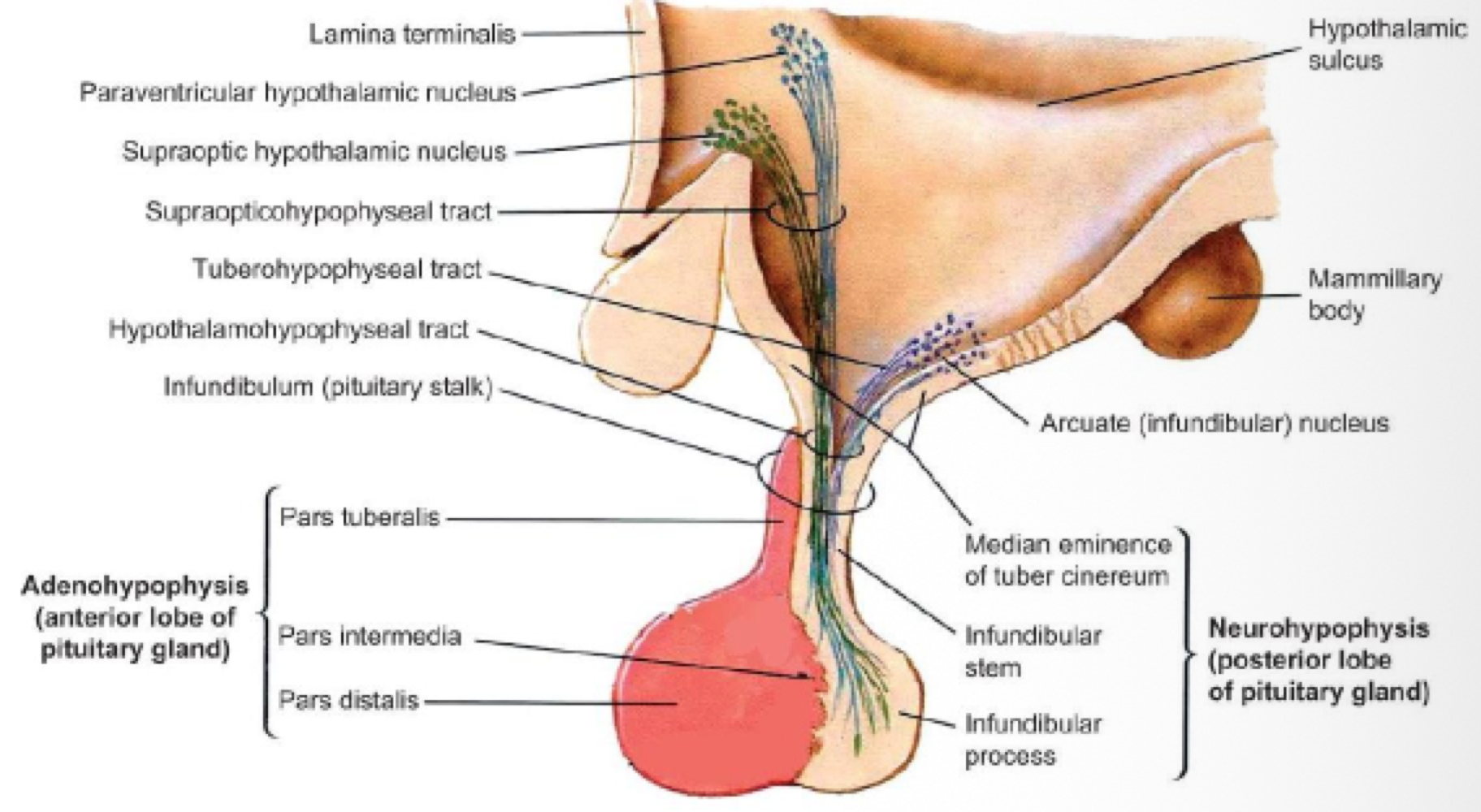
the _______ pituitary gland is derived from neural ectoderm (forebrain) and connected to the hypothalamus via axons
posterior (neurohypopsis)
a _______ causes the inhibition of growth and reduction in size of adrenal glands, gonads, and thyroid glands
hypophysectomy
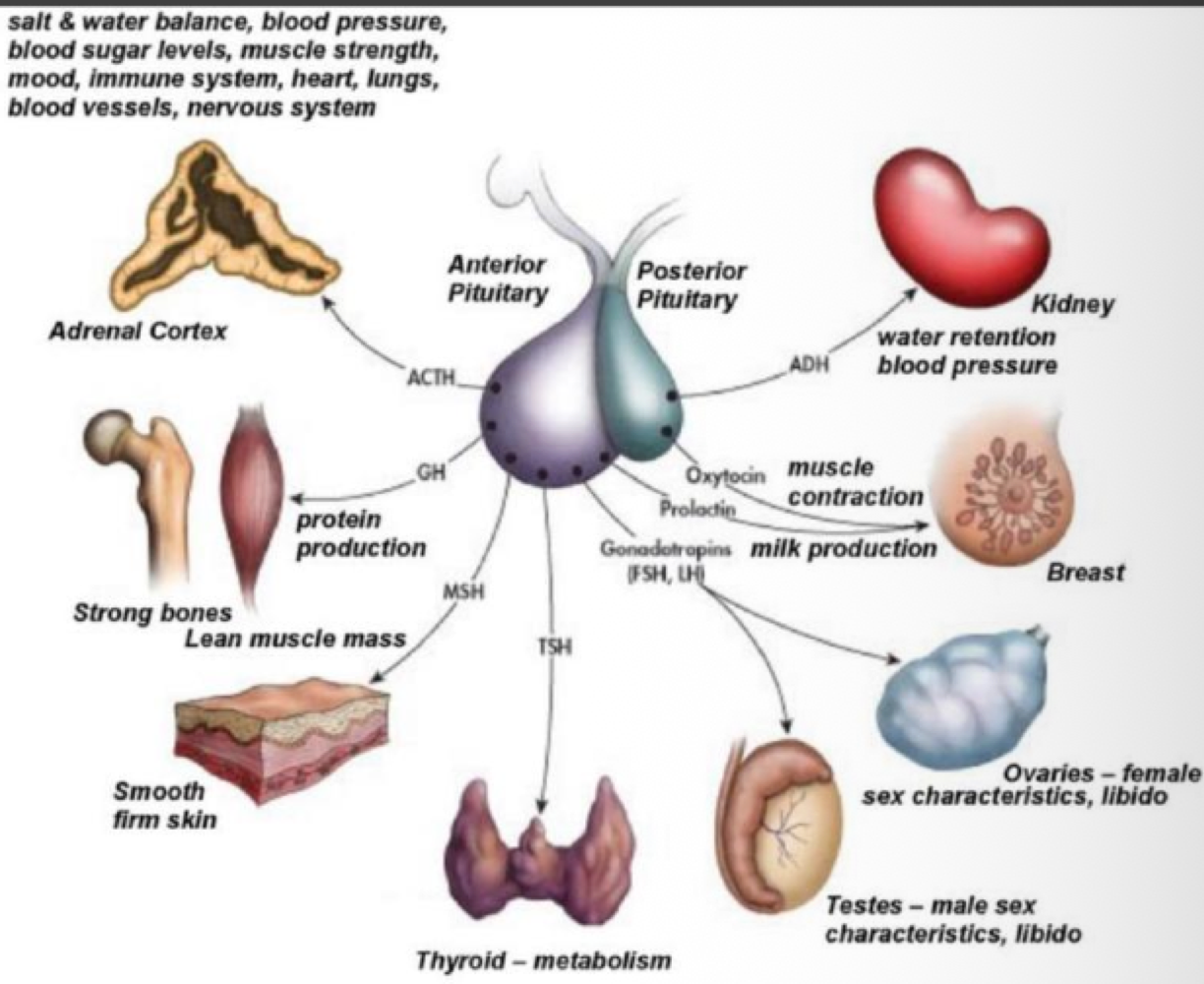
true or false: injection of interior pituitary extracts in hypophysectomy rats restores growth in adrenal glands, gonads, and thyroid glands
true
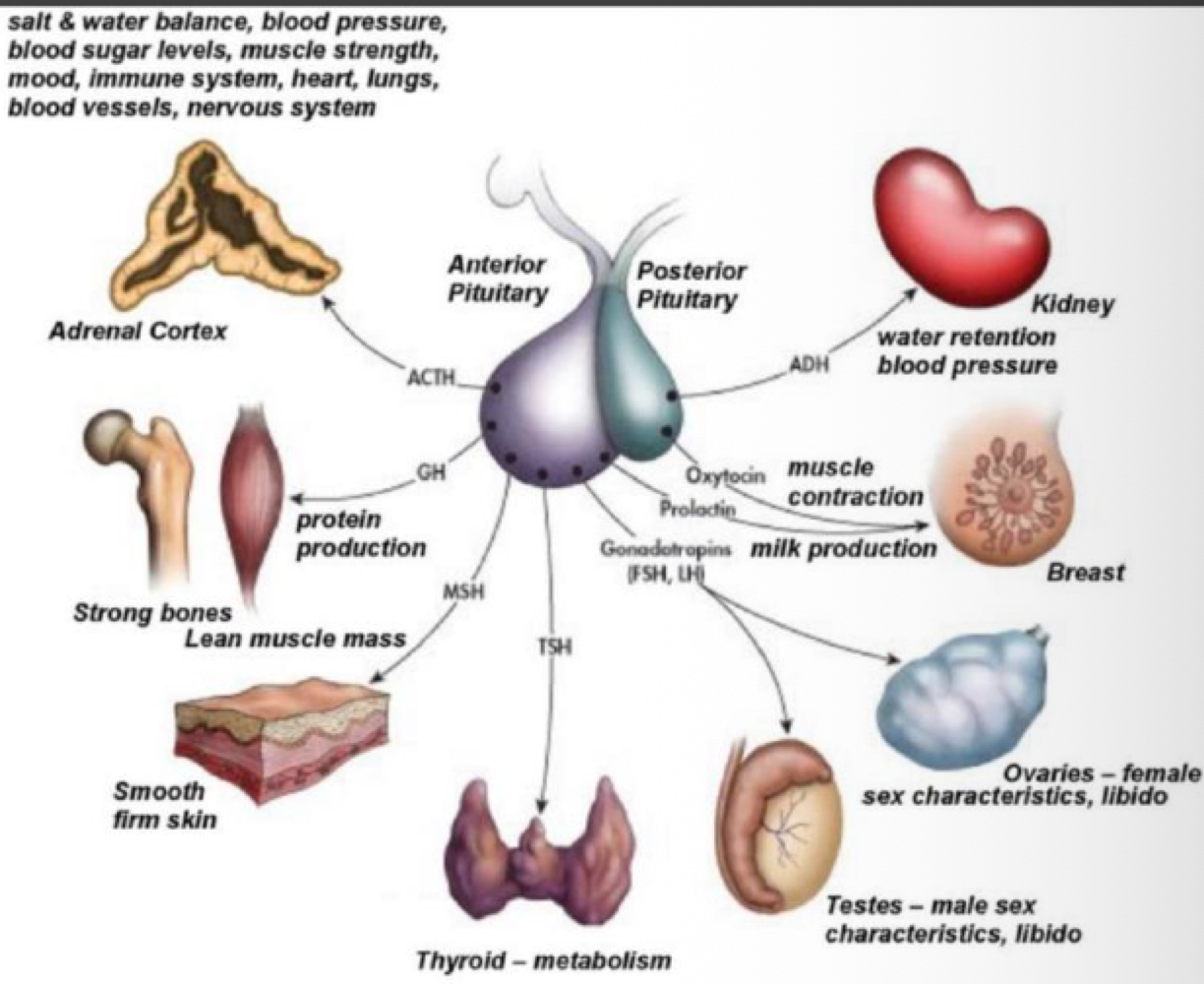
True or false: removal of endocrine glands enlarges the pituitary gland
true
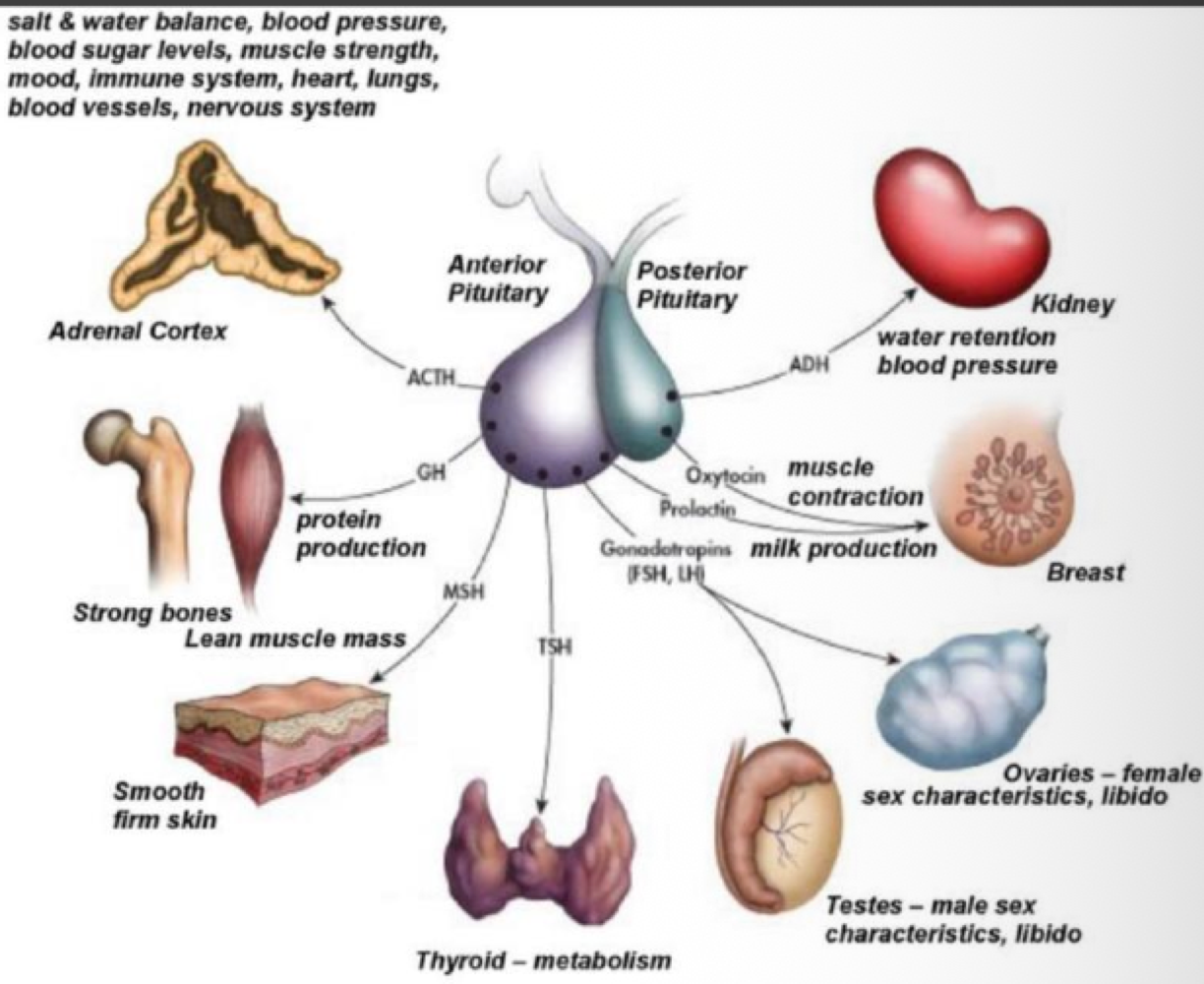
gigantism, cushing’s syndrome, hyperthyroidism, and disruptions of sex hormones are examples of _______
disorders resulting for pituitary tumors
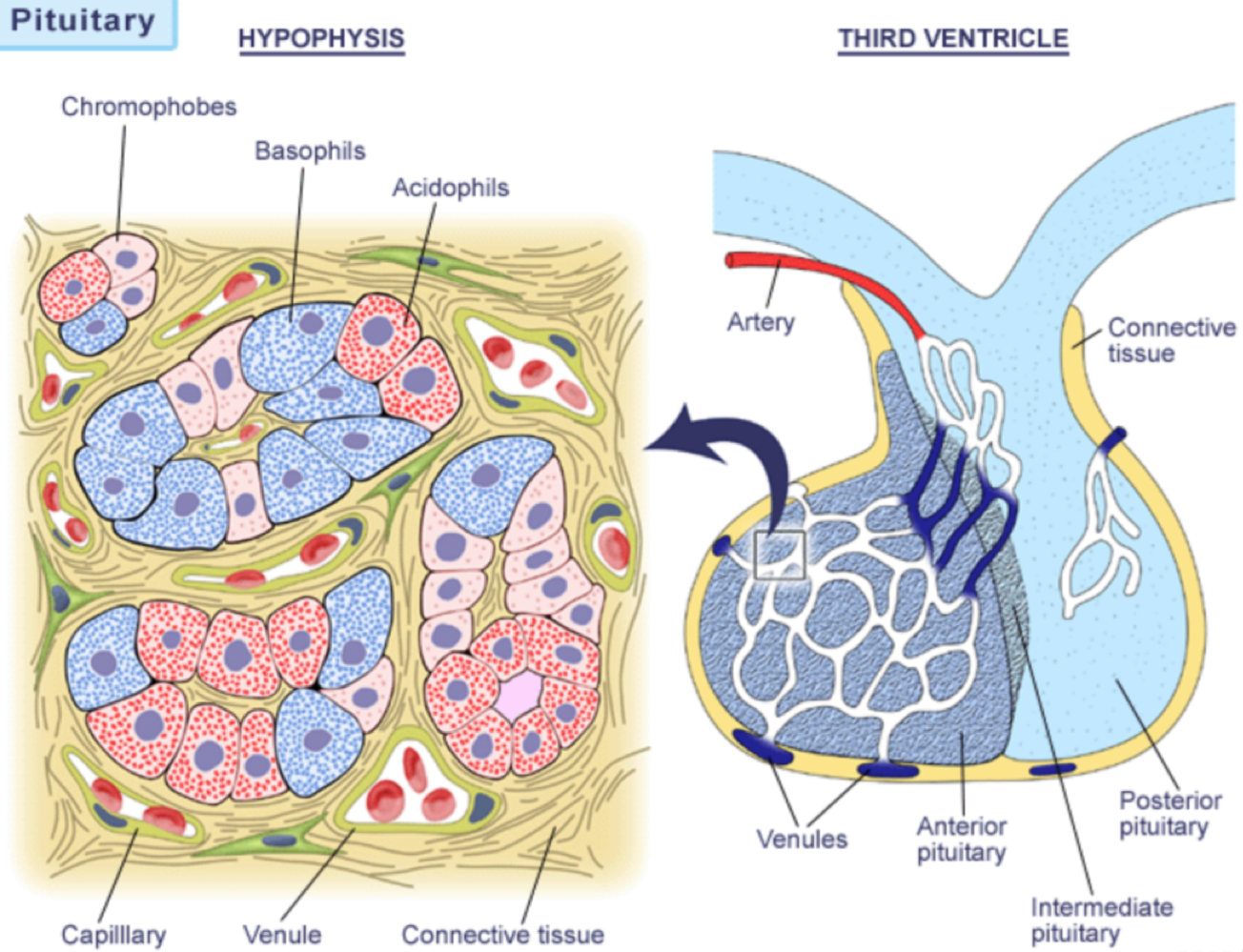
the _______ has different cell types surrounded by sinusodal cappilaries (very permeable)
adenohypopsis
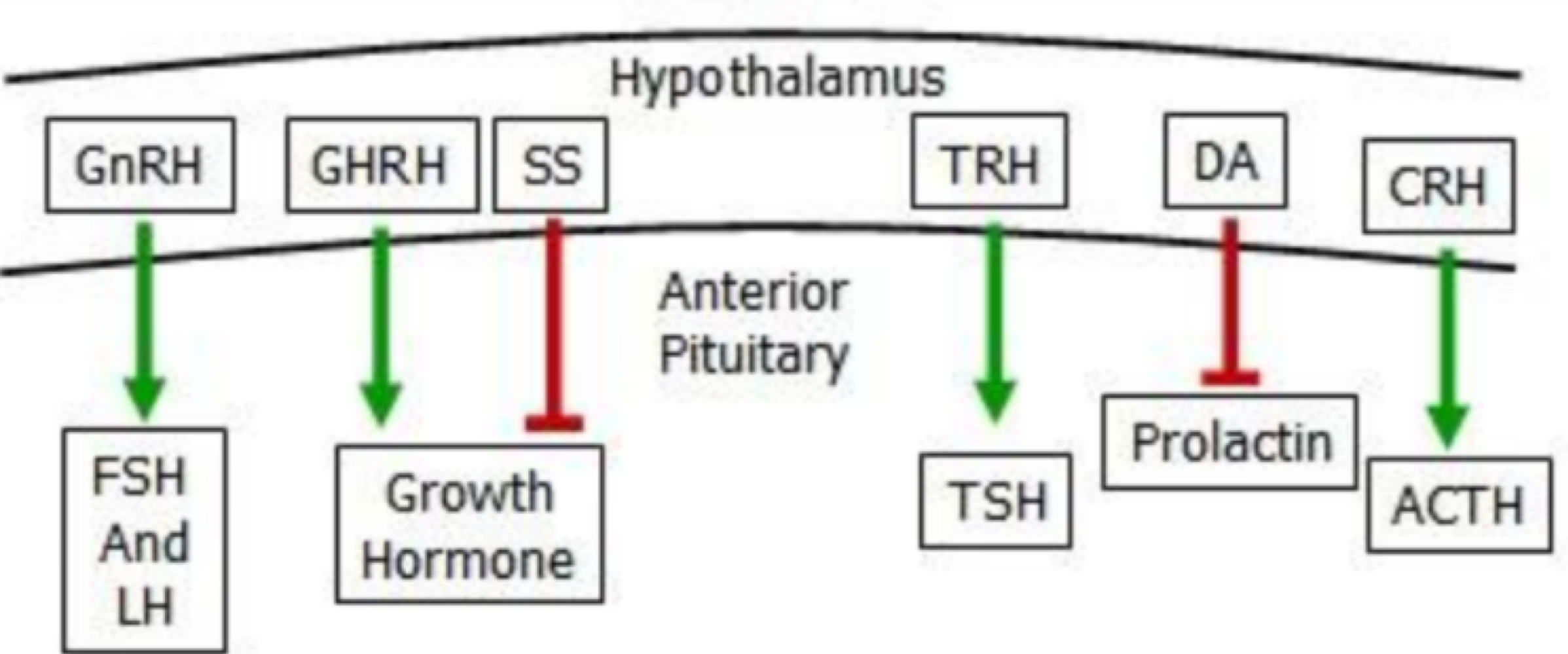
sinusodial capillaries surrounding the adenohypopsis store/release _______, which control glands, and _______, which nourish/help gells grow
tropic hormones, trophic hormones
_______ is an adenohypopsis glycoprotein hormome that releases thyrotropin/thyroid hormone (TSH), and stimulates thyroud hormone secretion
thyrotrope
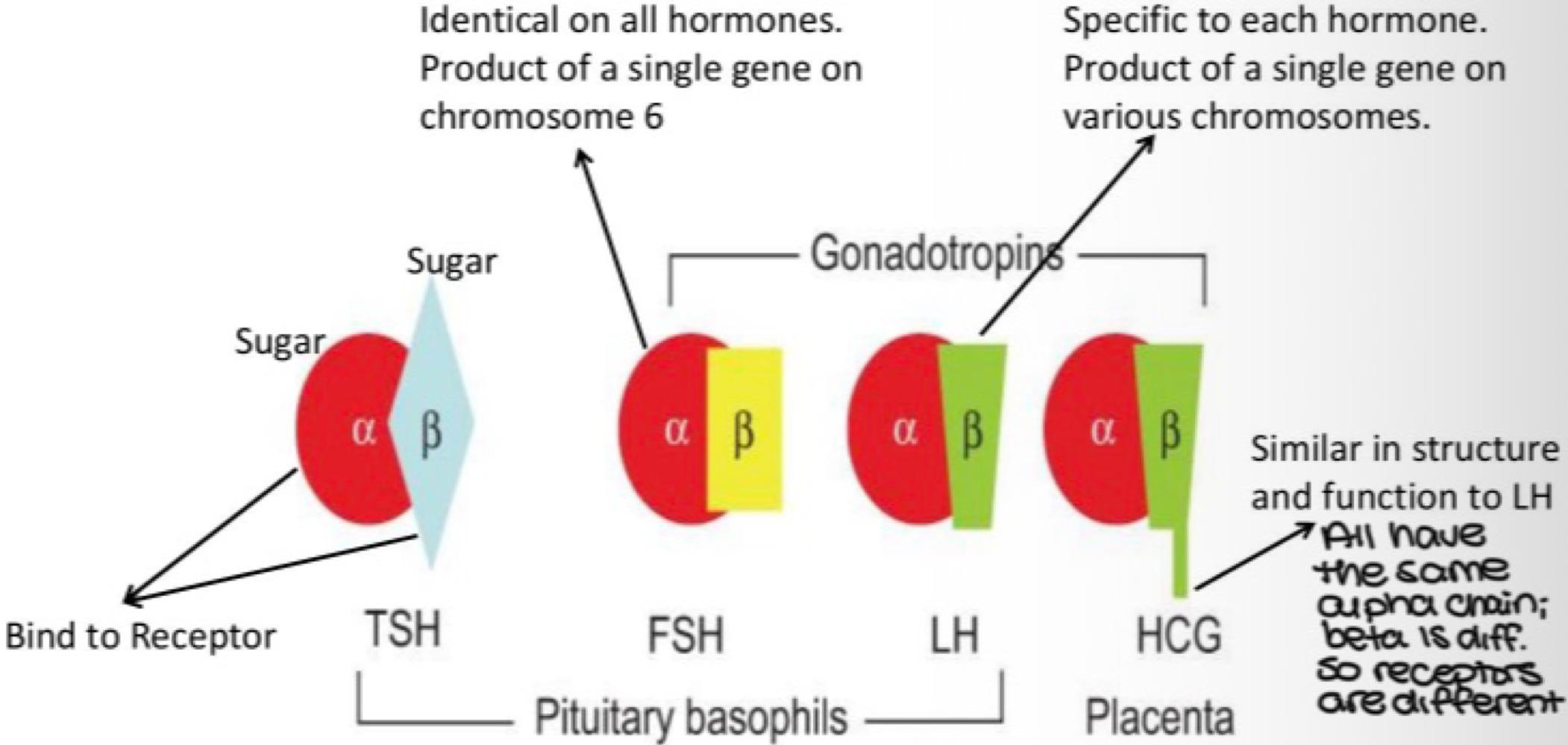
_______ is an adenohypopsis glycoprotein hormome that releases follicle-stimulating hormome (FSH) and leutinizing hormome (LH), and stimulates gonads hormome secretion
gonadotrope
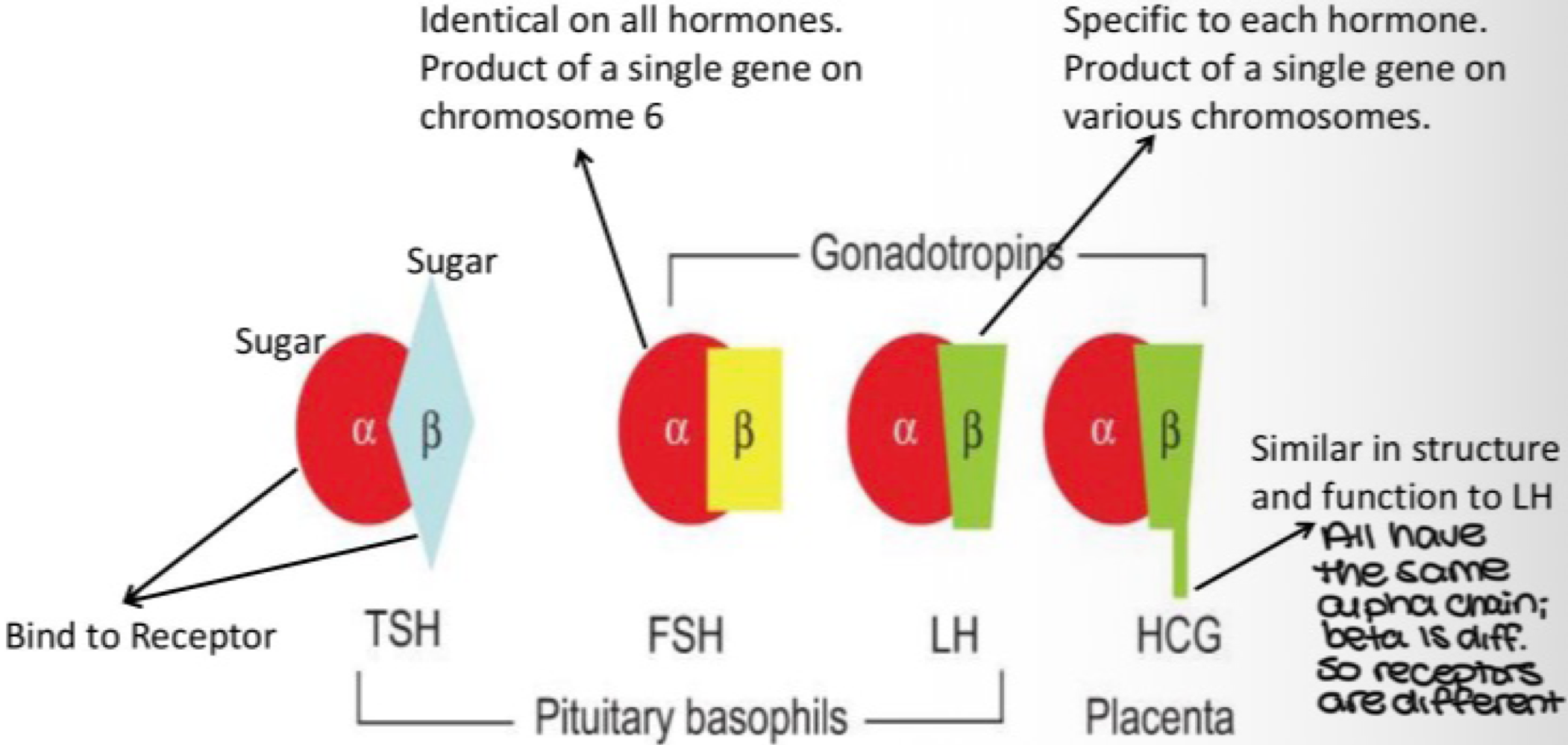
true or false: LH stimulates sperm and egg production, and FSH stimulates corpus luteum formation, estrogen, progesterone, and testosterone
false. FSH stimulates sperm and egg production, and LH stimulates corpus luteum formation, estrogen, progesterone, and testosterone
TSH, FSH, and LH have the same alpha chain, but different _______, and receptors
beta chain
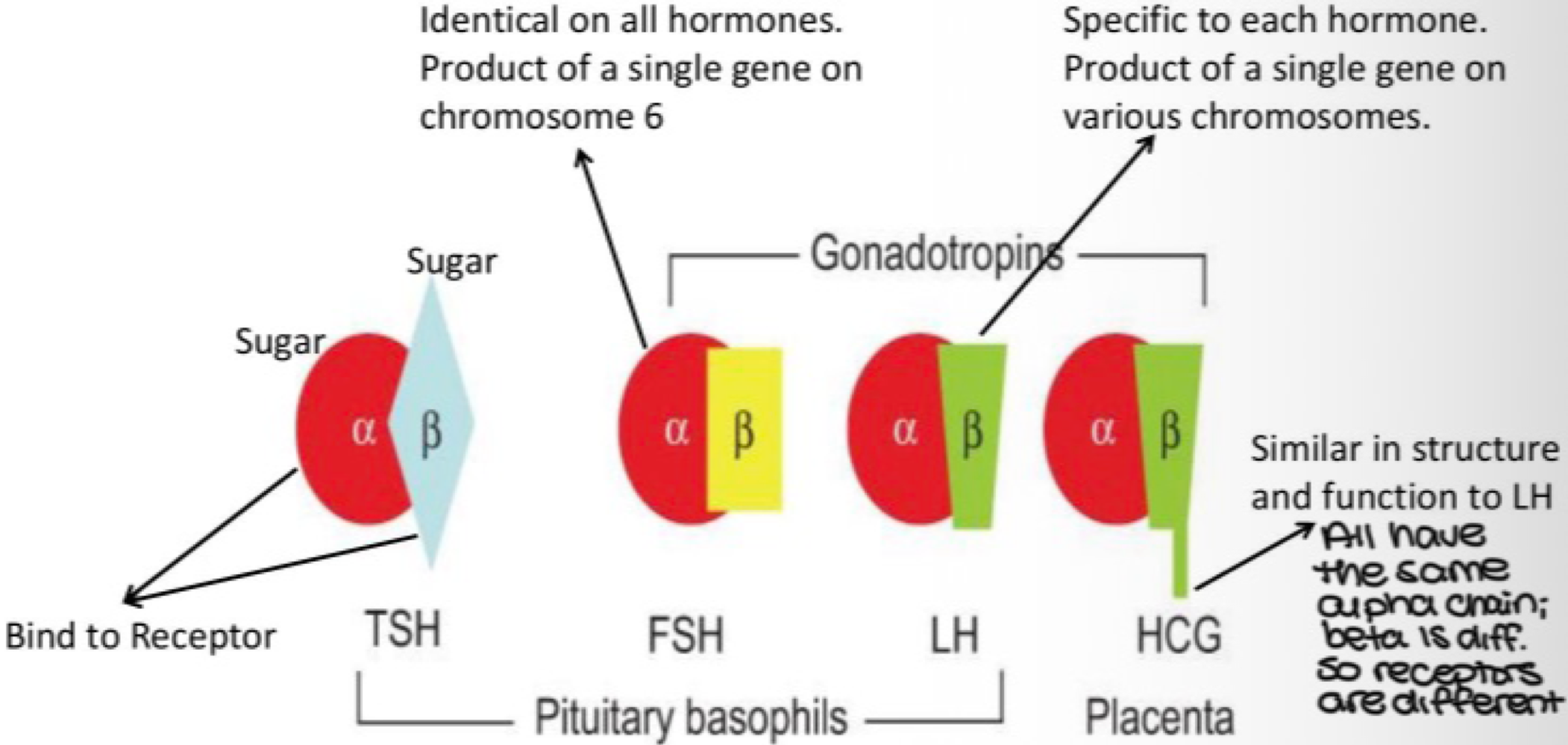
_______ is an adenohypopsis hormome that releases somatotropin (sonatotrophic hormome/growth hormone (GH)), is the most abundant cell, stimulates body cell growth adn development, and affects energy balance and milk production
somatotrope
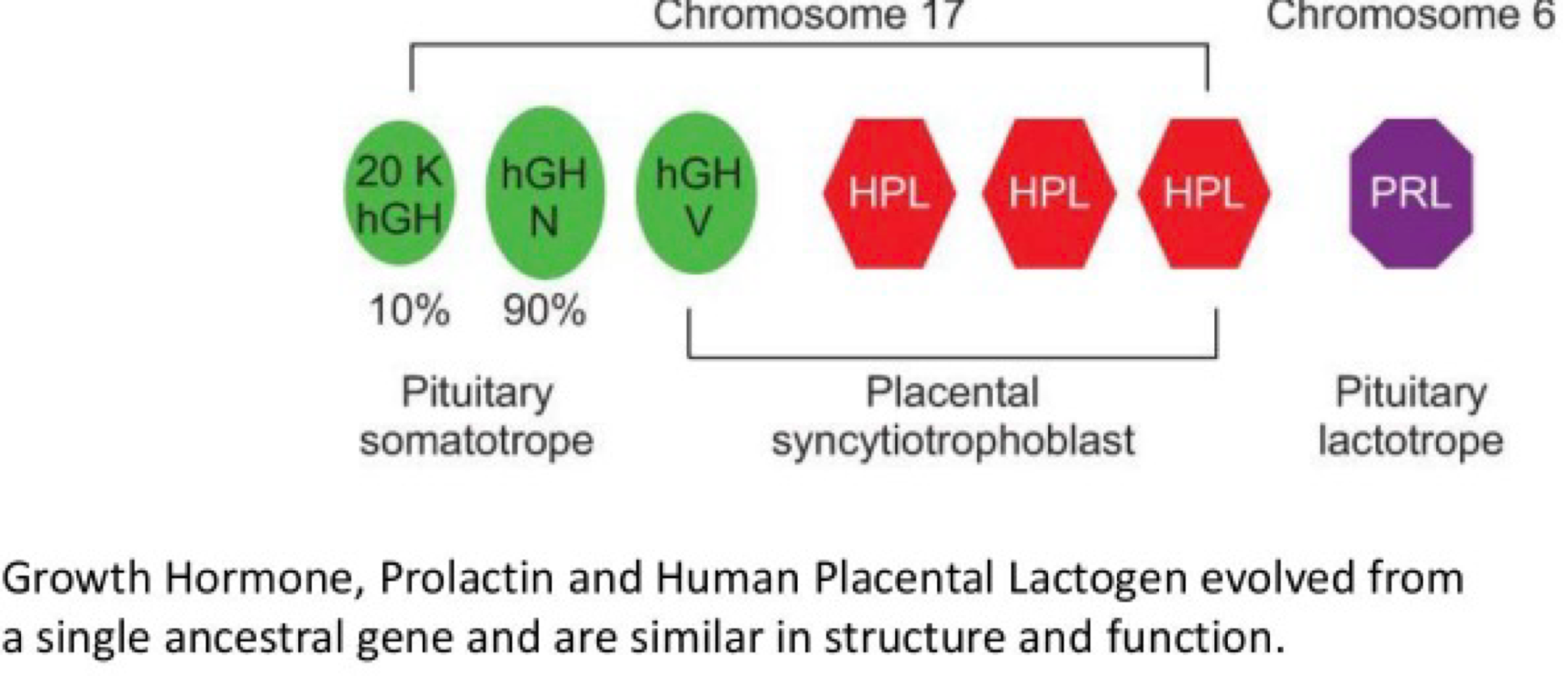
_______ is an adenohypopsis hormome that releases prolactin (PRL), which stimulates mammary gland to produce milk, and immune cells, and is involved in maternal and paternnal behavior
lactotrope
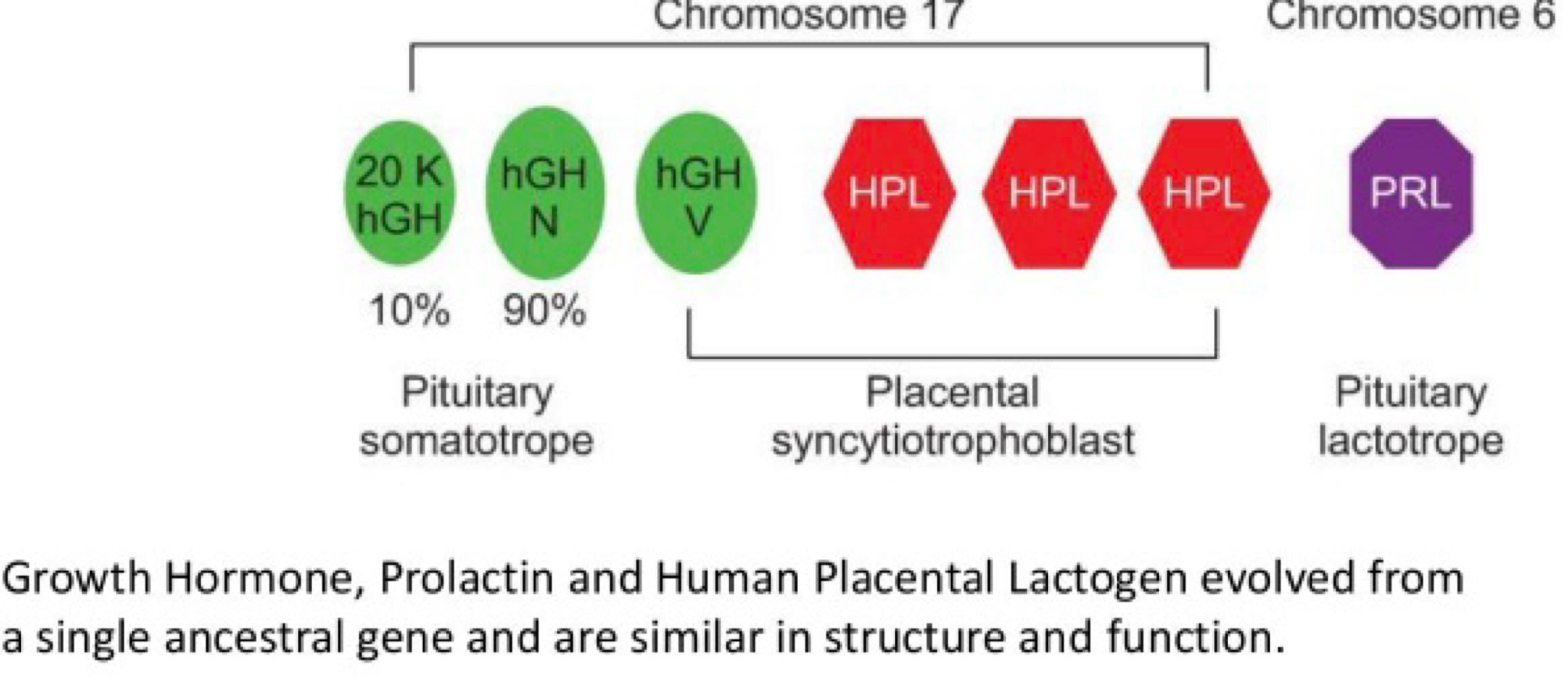
_______ is an adenohypopsis hormome that releases Gh and PRL
somatomammotrope
_______ is an adenohypopsis hormome that releases adrenol corticotropic hormome (ACTH), which stimulates the adrenal cortex (controls fluidds, energy, reproduction)
corticotrope
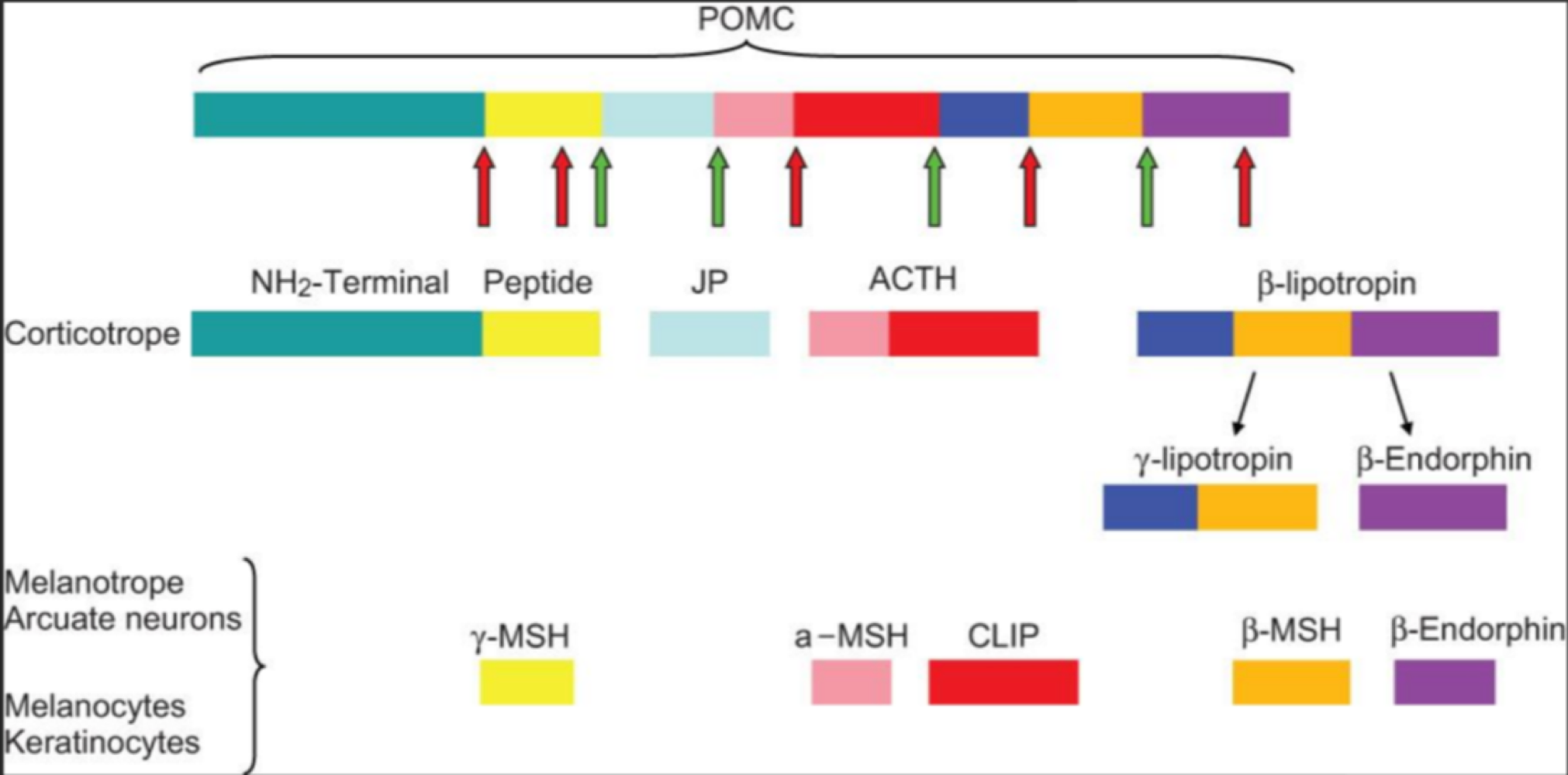
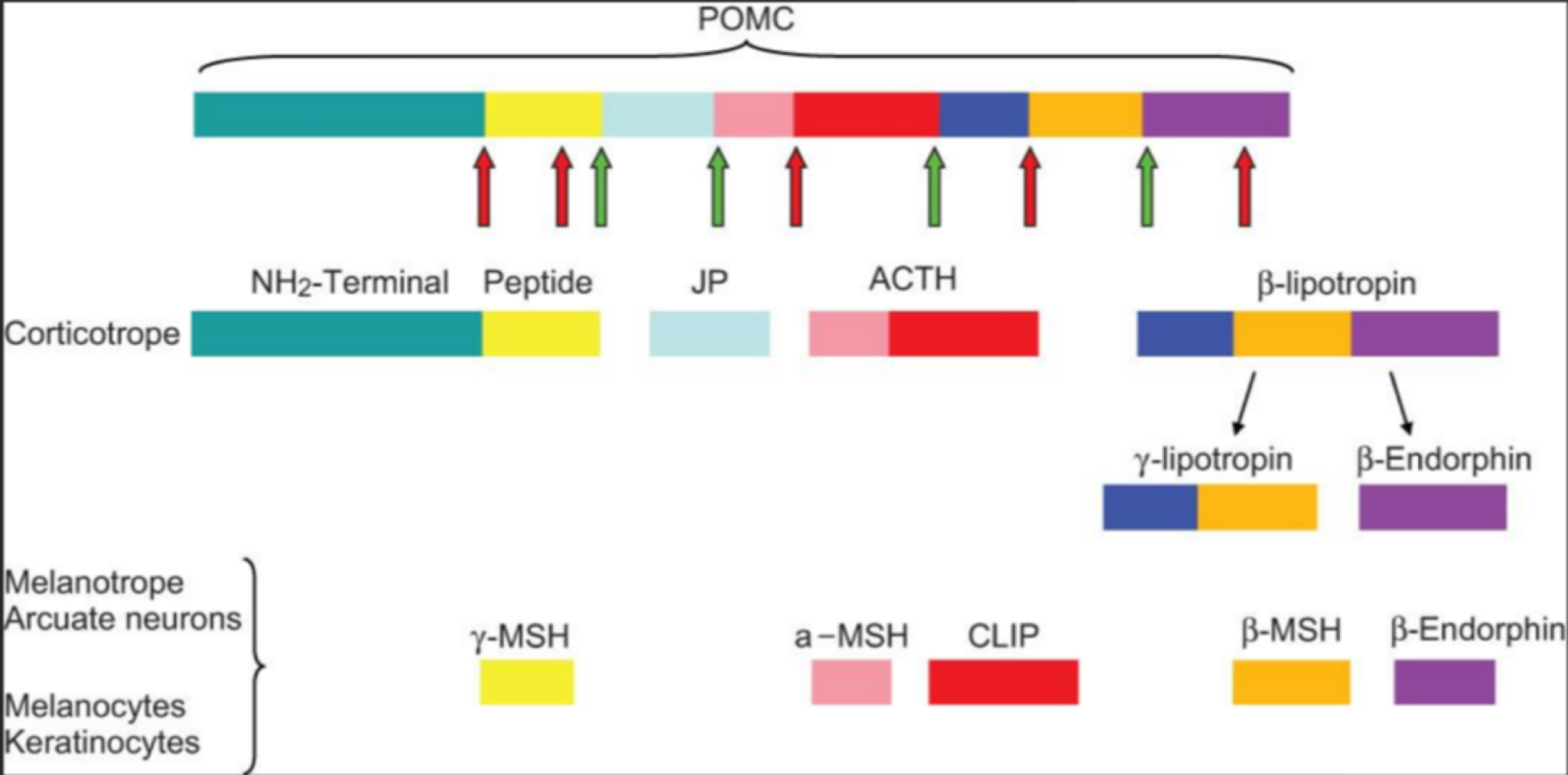
true or false: ACTH-like hormomes come from proopiomelanocortin, and are processed into multiple hormomes
true
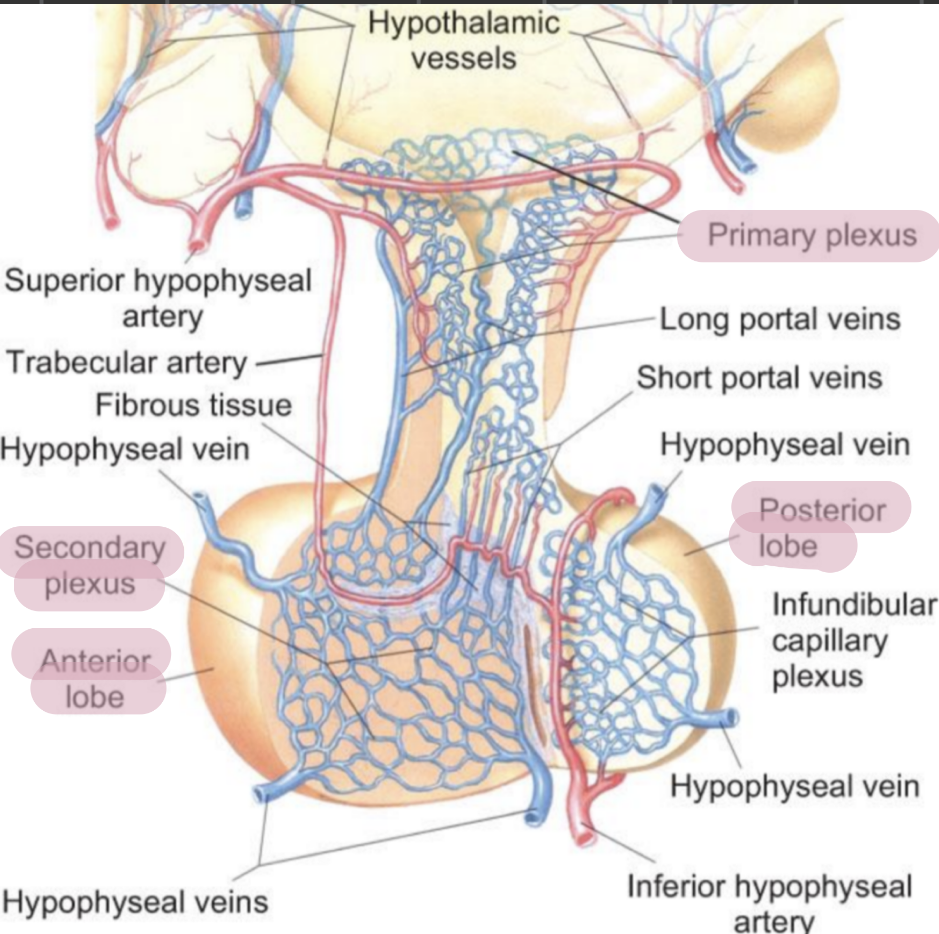
true or false: the adenohypopsis has many nerves but a low blood supply
false. the adenohypopsis has few nerves but a rich blood supply
the adenohypopsis is connected to the hypothalamus by the _______, a blood vessel system containing primary and secondary plexuses
hypothalamohypophyseal portal system
the pituitary gland secretes _______ hormomes
stimulating
secretion in pulses matching hypothamic input, and daily cycles based on activity, sleep, and light/dark, are examples of _______
adenohypopsis regulation
_______ inhibits GH if too much is released
somatostatin
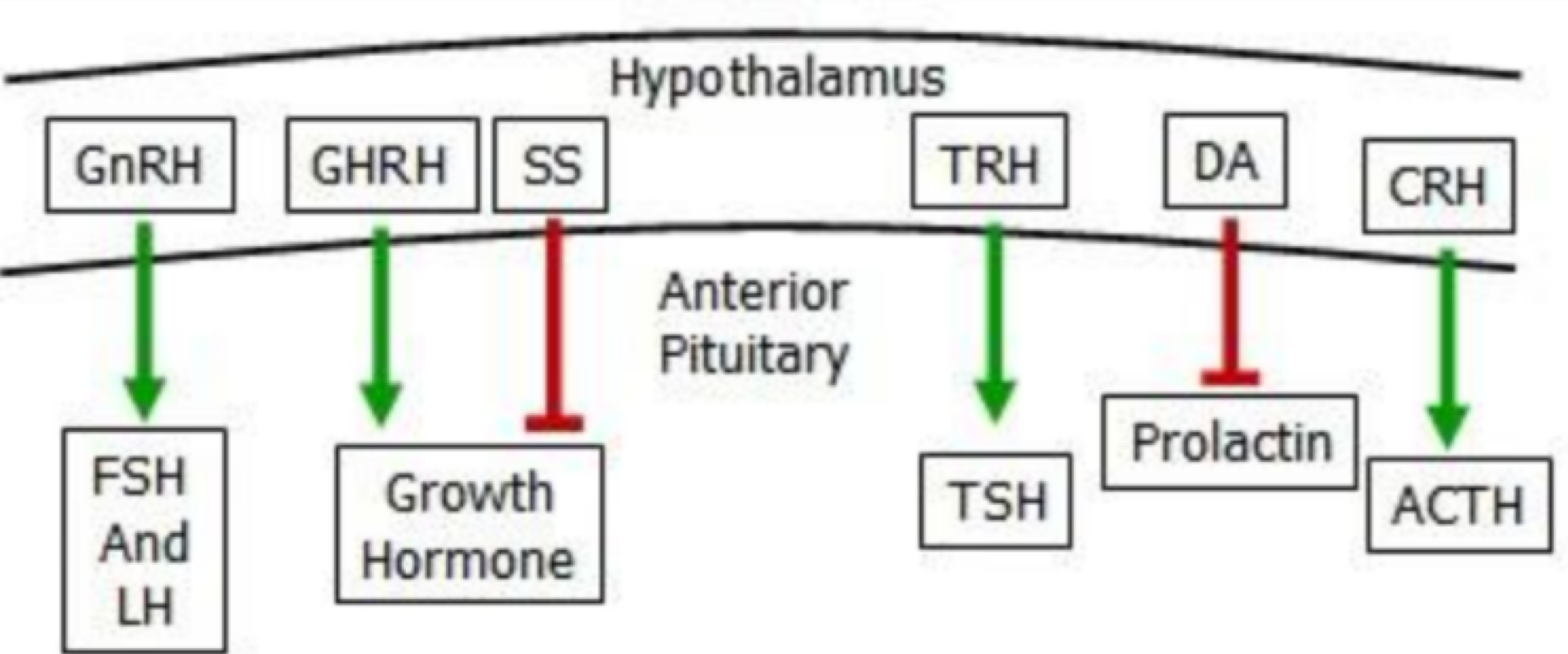
prolactin is always released, unless _______ is present, which will inhibit PRL
prolactin