Chapter 10🧬🔬🫀
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
Exercise helps with…..
maintaining muscle mass and function.
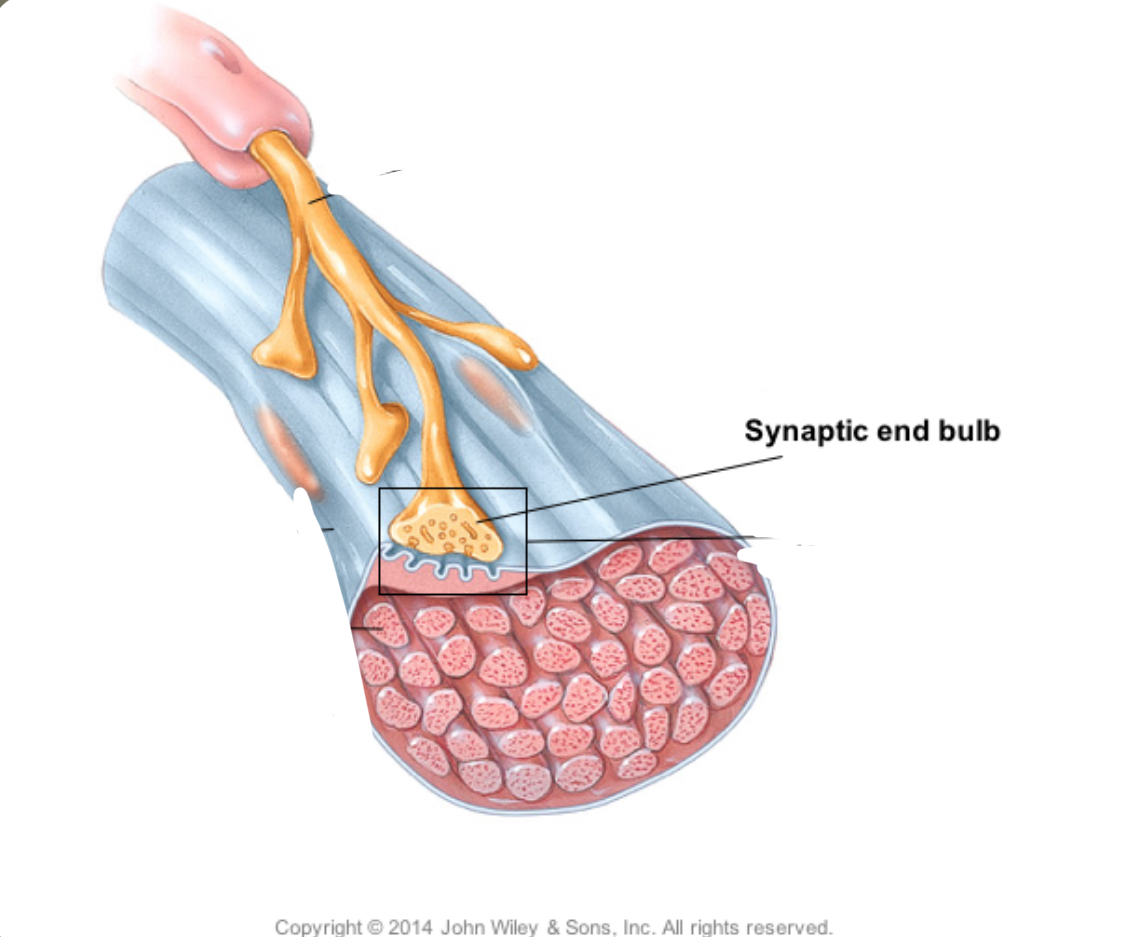
What are the neuromuscular junctions….
Synaptic Knob
Synaptic Vesicles
Motor End Plate
Synaptic Cleft
ACh receptors
AChE
ACh stands for….
Acetylcholine
AChE stands for….
Acetylcholinesterase
Synaptic Knob is thr….
expanded end and surface area of the neuron
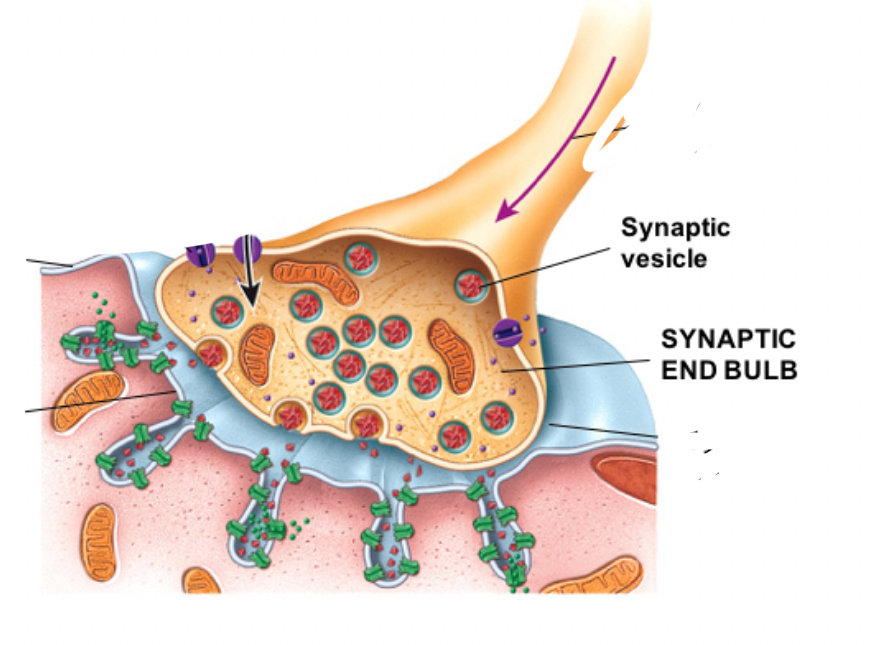
Synaptic Vesicles is the…..
Membrane-bound sacs filled with ACh = neurotransmitters
Motor End Plate is the….
Region on the Sarcolemma to increase surface area.
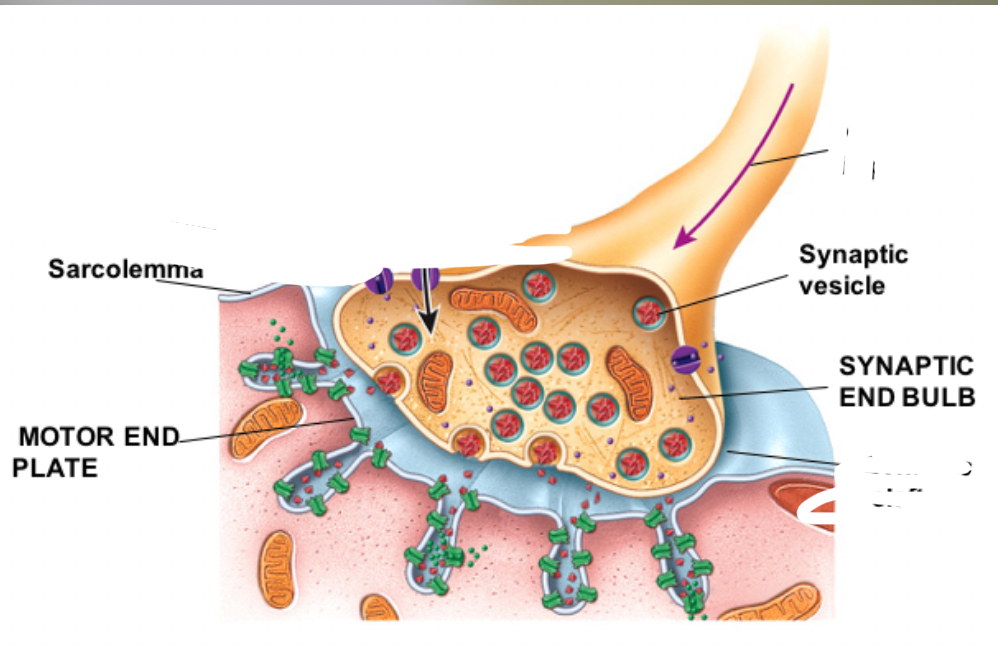
Synaptic Cleft is the…..
Narrow space separating the Synaptic Knob from the Motor End Cleft.
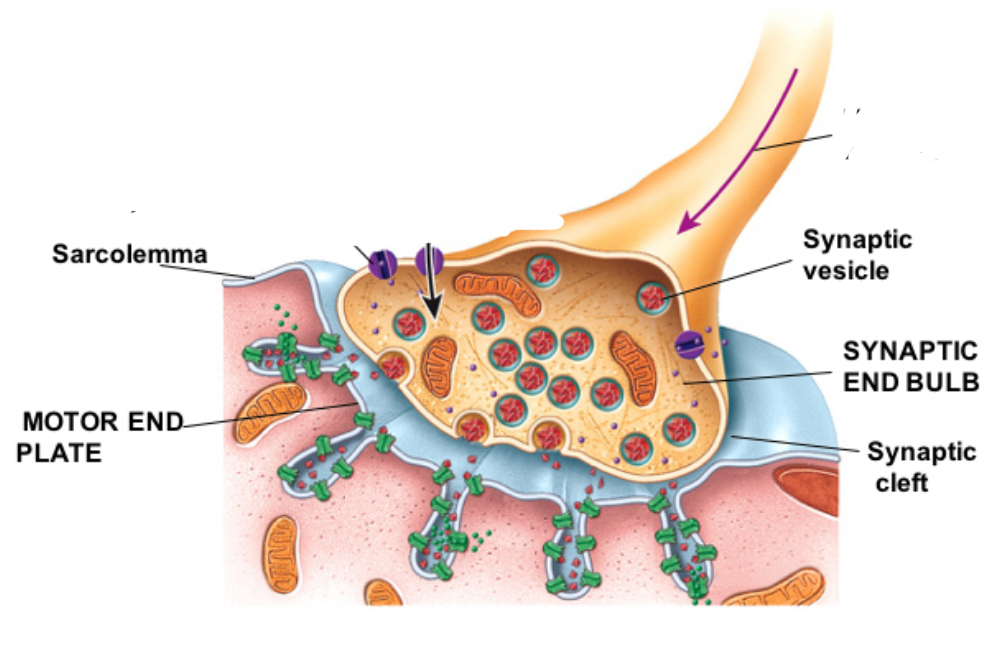
ACh receptors….
are in the Motor End Plate that bind ACh
AChE is….
an enzyme in the Synaptic Cleft, and decomposes ACh
what is the Cross Bridge Cycle???
it is the theory of muscle contraction based on muscle proteins that slide past each other to generate movement
ACh causes the release of….
Calcium from the T Tubules
Calcium is sent to Actin and….
binds with Troponin
Troponin causes the Tropomyosin to….
move off the Actin binding sites
Myosin head attaches to…
Actin active site forms a Cross Bridge
Cross-Bridge pulls the….
Thin Filament towards center of the Sarcomere
ADP and Phosphate are….
released from Myosin
Creatine Phosphate a high energy molecule coverts….
ADP to ATP
ATP then binds to….
Myosin
Muscle contractions involves….
• Sliding movement of Thin Filaments past the Thick Filaments
•Thin filaments slides towards the center of the Sarcomere
Sliding continues until the overlapping of the….
Thin and Thick filaments is complete.
Motor nerve impulse causes….
ACh to be released into the Synaptic Cleft
When ACh binds to receptors in the Motor End Plate….
initiate a muscle impuse along the Sarcolemma and T-tubule Membrane
When Calcium is then released into the Sarcoplam….
Calcium ions bind to Troponin, which causes Tropomyosin to uncover active binding sites.
Mysosin heads bind to Actin and form Cross Bridges…..
Myosin heads detach
What is necessary for detachment???
ATP
Without Motor Units….
nothing happens, muscle doesn’t contract.
what is Muscle Tissue comprised of???
Motor Units that are used for Comtraction.
Motor units are comprised of….
Single Motor Neurons
Neuromuscular junction
Muscle Fibers
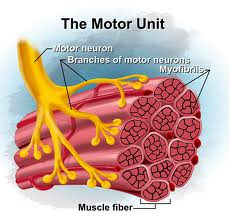
When motor unit is stimulated…
All Muscle Fibers under its control contract.
Recruitment is…
the process by which different Motor Units are activated to produce Muscle Contraction.
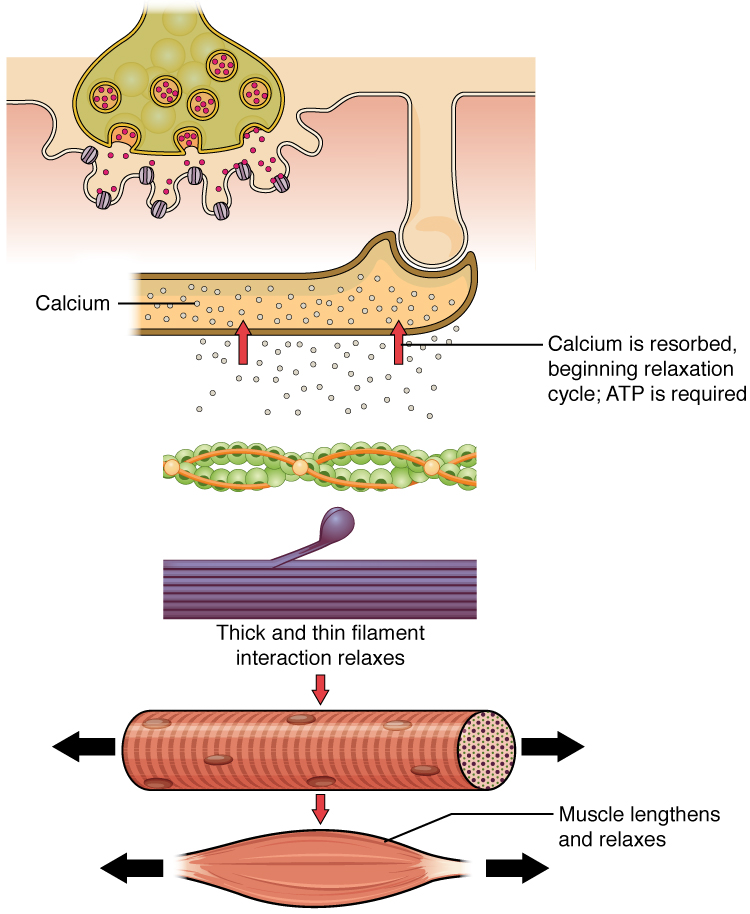
What is needed for muscle relaxation???
ATP
What is Skeletal Muscle Fatigue???
inability to contract a muscle.
what does it cause???
Decreased blood flow
ion imbalances across sarcolemma
Accumulation of lactic acid
What is
sustained contraction and involuntary contraction
Muscle tone is….
Continuous state of a partial muscle contraction.
Sustained Contractions are….
smaller motor units that are recruited first
larger units recruit later
produce smooth movements
Muscle Hypertrophy is….
increase in Muscle Fiber Size
Muscle Atrophy….
wasting of muscle tissue
Skeletal Muscles generate a….
variety of body movements
Skeletal Muscle and bones function as….
mechanical devices = Levers
The action of each muscle mostly depends upon….
• The kind of joint it is associated with
•The way the muscle is attached on either side of the bone
The four types of Muscle movement…
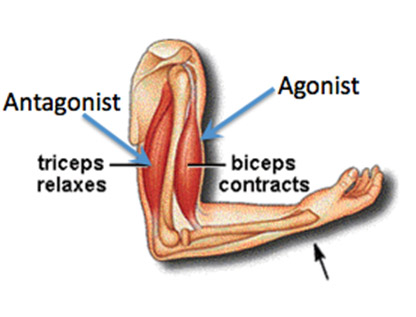
Agonist/Prime mover
Antagonist
Synergist
Fixator
Agonist/ Prime mover
Produces specific movement when contracted
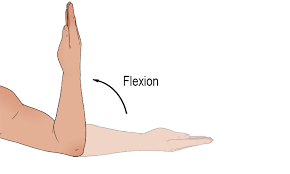
Antagonist
Resists the Prime Mover’s action and causes movement in the opposite direction
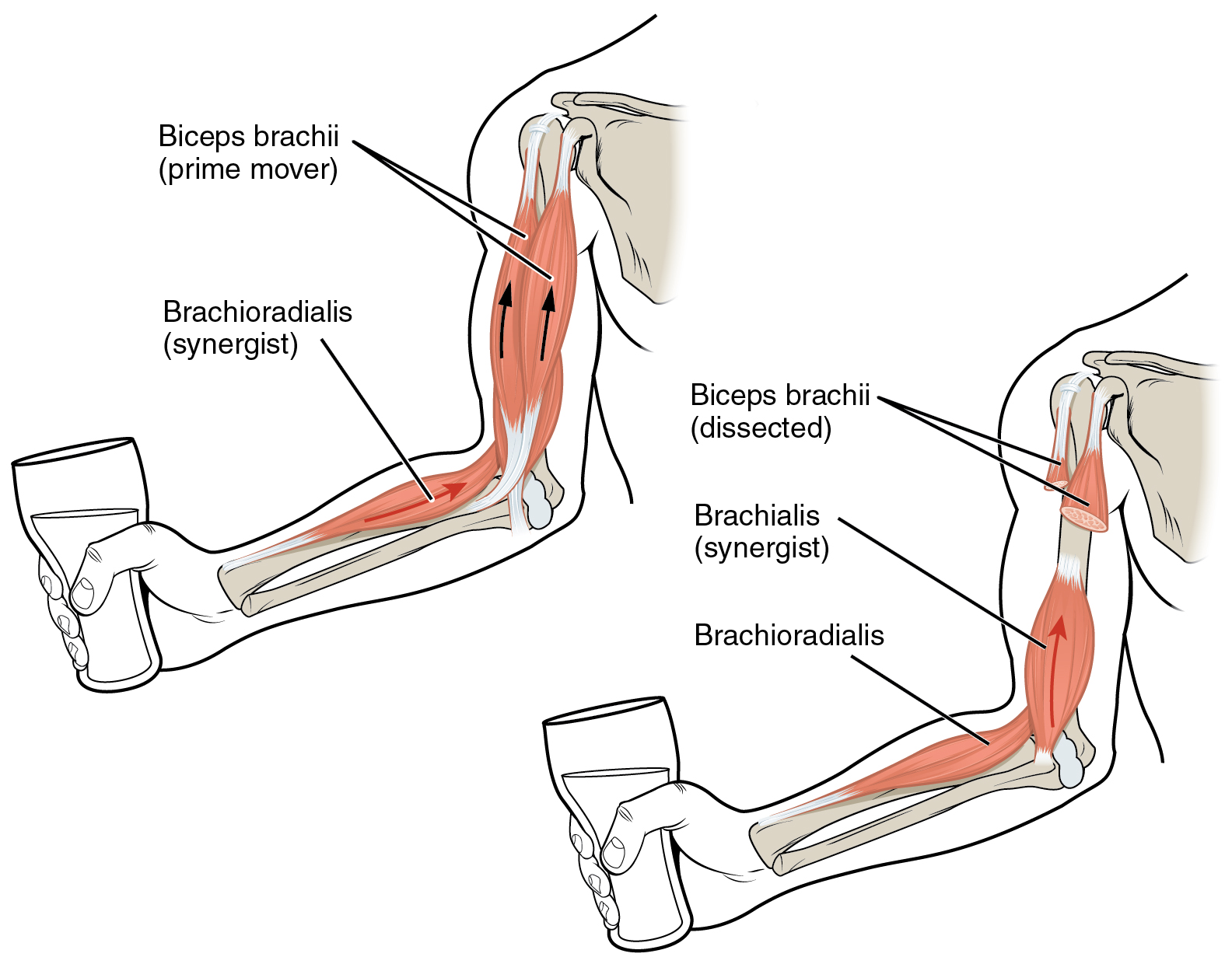
Synergist
A muscle that assists the Agonist or Prime Mover
Fixator
Contracts Isometrically to stabilize the Origin of the Prime Mover
What are the 2 types of muscle contraction
Isotonic and Isometric
Isotonic
Muscle tension equals or is great than resistance
Muscle shortens
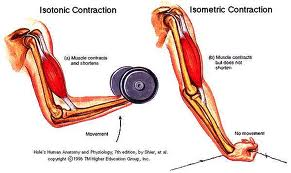
Isometric
Muscle tension is less than the resistance
Muscle does not shorten = no movement