Hit to lead activities 1 (Shr)
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
What is the difference between hit compounds and suitable leads?
Hits show initial activity
Leads are optimized for drug-like properties like potency, safety and efficacy. Can be used in biological models!
What happens during target identification in drug discovery?
"A biological target associated with the disease is identified."
What is the focus of lead identification?
"Validating that a hit binds the correct target and benefits the patient by altering the disease pathway."
What is emphasized in lead optimization?
"Safety and efficacy in biological systems, beyond just target binding, to declare a preclinical/clinical candidate."
What occurs when selecting a development candidate?
"A promising candidate is chosen based on optimization and efficacy, followed by toxicology, ADME, and safety studies."
What is an IND in drug discovery?
An Investigational New Drug - Submitting data to regulatory authorities for clinical trial approval.
What are regenerative chemistry efforts in head optimization?
"Optimizing compound synthesis to reduce steps (e.g., <20) for commercial viability."
Why is oral formulation preferred in in-vivo models?
"It improves pharmacokinetics (PK) and ease of administration."
What are key considerations in hit-to-lead activities?
Improving potency/efficacy – Ensuring the compound binds more strongly to the target and is effective at lower concentrations.
Selectivity – Making sure the drug binds specifically to the target and not to unwanted proteins.
Physicochemical properties – Checking solubility, molecular weight, and ability to cross biological membranes.
Pharmacokinetics (PK) – Studying how the drug is absorbed, distributed, metabolized, and eliminated in the body.
Drug synthesis efficiency – Reducing synthesis steps to make drug production commercially viable (ideally ≤ 7 steps).
What is the target value for aqueous solubility?
">100 micromolar in an aquatic system for therapeutic effect."
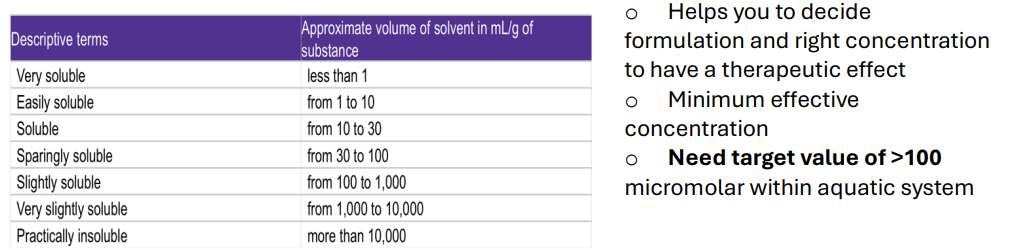
What does very soluble mean?
"Less than 1 mL/g of solvent needed to dissolve the substance."
What does practically insoluble mean?
"More than 10,000 mL/g of solvent needed to dissolve the substance."
What is the target Log D (Distribution Coefficient) value for lipophilicity?
"0-3, especially for BBB penetration."
Measure that accounts for the compound’s ionization state at a specific pH, making it more relevant to physiological conditions.
Why is high lipophilicity (Log D) problematic?
Fat deposition in lipid bilayer
Toxicity - Accumulation of drug
Poor membrane partitioning
Promiscuous binding.
What is the target value for microsomal stability?
"<30 µL/min·mg to resist rapid liver enzyme breakdown."
Why is microsomal stability important?
It ensures the drug stays in the body long enough for a therapeutic effect.
Microsomal stability refers to a compound’s ability to resist metabolism (breakdown) by enzymes in liver microsomes, primarily cytochrome P450 (CYP) enzymes.
What is the target value for P450 inhibition?
">10 µM to avoid inhibiting liver metabolism and causing toxicity."
Why is P450 inhibition a concern?
"It can prevent metabolism of the drug and others, leading to toxic accumulation."
What is the target value for Caco-2 permeability?
">1 × 10⁻⁶ cm/s for good intestinal absorption."
What does the Caco-2 assay measure?
Permeability across intestinal epithelium using a colon carcinoma cell line.
Caco-2 is a human colon adenocarcinoma cell line that, when cultured under specific conditions, differentiates into a monolayer resembling the epithelial cells of the small intestine. These cells form tight junctions and express transporters and enzymes similar to those in the human gut, making them a good model for intestinal absorption.
What is the target value for MDR1-MDCK permeability?
">1 × 10⁻⁶ cm/s to assess efflux pump interaction."
These are Madin-Darby Canine Kidney (MDCK) cells transfected with the human MDR1 gene (ABCB1), which encodes P-glycoprotein (P-gp), a key efflux transporter.
What does MDR1-MDCK measure?
"Permeability with P-glycoprotein efflux pumps in transfected MDCK cells."
What is the target value for Hep G2 hepatotoxicity?
"No effect at 50 × IC50 or EC50 to avoid liver toxicity."
Drug should not cause hepatotoxicity even when it is tested 50 times higher than the IC50
What does Hep G2 screening check?
"In vitro liver cell toxicity, critical since drugs are metabolized in the liver."
What is the target value for cytotoxicity?
No effect at 50 × IC50 or EC50 to minimize cellular toxicity in vivo.
—
IC50 (Inhibitory Concentration 50)
EC50 (Effective Concentration 50): (e.g., receptor activation)
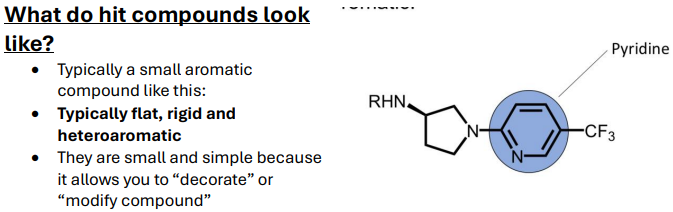
What do hit compounds typically look like?
SIMPLE for modification:
Small
Flat
Rigid
Heteroaromatic compounds
Why is a heterocyclic core important in hit compounds?
Rapid synthesis of analogues:
Heterocyclic core provides flexible scaffold to allow quick modifications
Tweak functional groups to optimise properties and speeds up process
Tuning of properties:
Modification of core allows researchers to fine-tune properties e.g. potency, PK, selectivity and toxicity
Template hopping to novel IP space:
Switching from one core structure to another while retaining biological activity
Pharmacophore which is maintained but change some of the structure so it cannot be considered as same structure
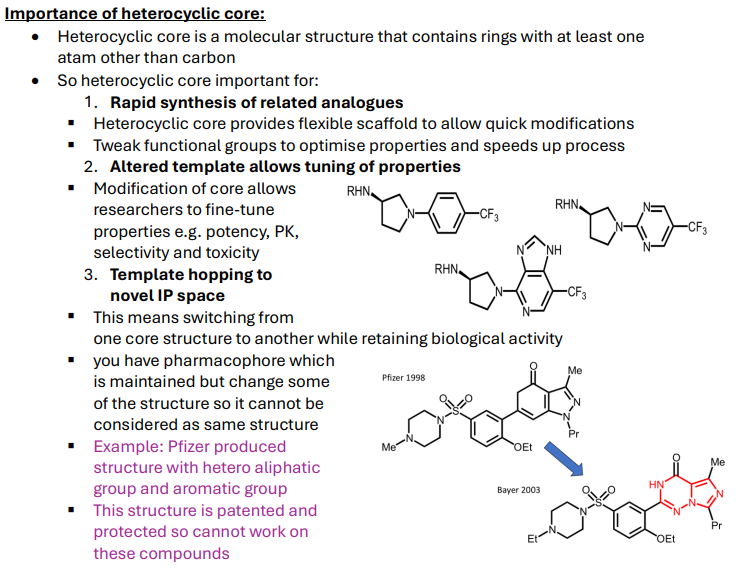
How does a heterocyclic core aid rapid synthesis?
"It provides a flexible scaffold for quick functional group tweaks."
What is template hopping?
"Switching core structures while retaining activity to create novel, patentable compounds."
Why does template hopping matter?
It avoids patent infringement
Creates new IP
Improves drug properties like solubility and selectivity.
What are the criteria for hit compounds to move to lead optimization?
Reproducible in vitro affinity/efficacy: Tested in cell-free or cellular assays where Assay results must be consistent and reliable!
Favorable drug-like properties (cLogP, MW)
Chemical tractability - Easy to synthesise
SAR evidence (Structure-activity relationship): Evidence that related compounds retain activity
Patentability
No significant toxicity
What is the goal of hit-to-lead activities?
Synthesize many compounds to identify modifications with the best properties for lead optimization.
Reduces chance of attrition.
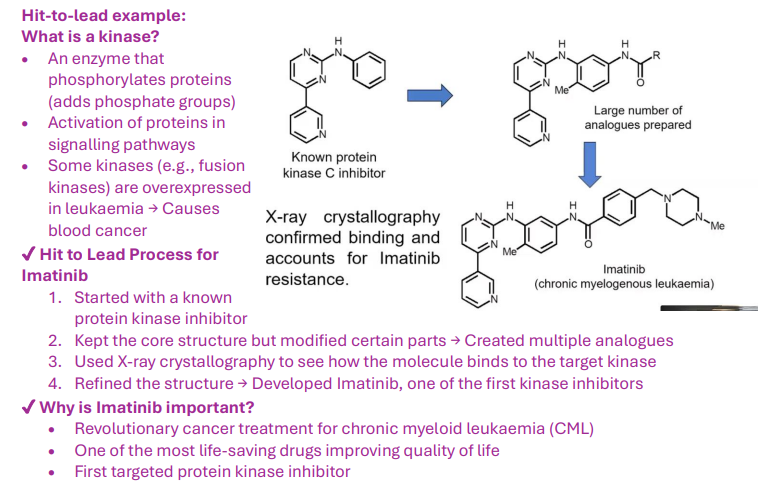
What is a kinase?
"An enzyme that phosphorylates proteins, activating signaling pathways, e.g., overexpressed in leukemia."
How was Imatinib developed in hit-to-lead?
"Started with a kinase inhibitor, modified analogues, used X-ray crystallography, and refined to Imatinib."
Why is Imatinib significant?
"It's a revolutionary CML treatment, the first targeted kinase inhibitor, improving quality of life."
What are DMPK properties assessed in hit-to-lead?
Absorption (Caco-2, IV/PO PK)
Distribution (RBC, PPB, brain/plasma ratio)
Metabolism (microsomes, hepatocytes, CYP, PXR)
Permeability (P-gp).
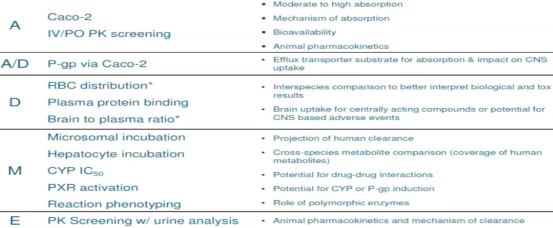
What ensures druggability in hit-to-lead?
Good membrane passage
No liver enzyme inhibition
Sufficient drug stability in the body.
What does the Caco-2 assay evaluate?
"Intestinal absorption by measuring compound passage from apical to basolateral side of a cell monolayer."
What is a good Papp value in Caco-2 assays?
">10⁻⁶ cm/s indicates strong in vivo absorption correlation."
Papp refers to permeability

Why is plasma protein binding (PPB) important?
High binding affects:
Dose
Half-life
Safety by reducing free drug availability.
What is the preferred fraction unbound (fu) for PPB?
">90% to ensure enough free drug reaches the target."
What are criteria to move to lead optimization?
Improved affinity/efficacy
Selectivity over related/non-related targets
Acceptable PPB/CYP/hERG profiles
Animal model efficacy
No toxicity/mutagenicity
Patent strategy
What is a hERG profile concern?
"Binding to heart channels can cause arrhythmias, a major off-target red flag."
What problem does high lipophilicity (Log D = 5.5) pose in the example?
"It causes nonspecific binding, poor solubility, and toxicity from fat accumulation."
What problem does CYP450 inhibition (IC50 = 3 µM) pose?
"It risks drug-drug interactions and toxicity from impaired metabolism."
What problem does poor aqueous solubility pose?
"It limits absorption and bioavailability."
How can lipophilicity be reduced in the example?
"Add polar groups (e.g., hydroxyl, amide) to lower Log D to 0-3."
How can CYP450 inhibition be mitigated?
"Modify aromatic rings or nitrogen groups to reduce binding, targeting >10 µM IC50."
How can aqueous solubility be improved?
"Add hydrophilic groups (e.g., sulfonamides) or use prodrug strategies."
What additional optimization steps are recommended?
"Assess microsomal stability (<30 µL/min·mg), improve PPB (fu >90%), ensure Caco-2 permeability (>1 × 10⁻⁶ cm/s), explore SAR, and use crystallography/template hopping."