Chromosomes and Mitosis
1/76
Earn XP
Description and Tags
This set of flashcards covers essential concepts related to chromosomes, mitosis, and cell cycle regulation, aiding in reviewing and reinforcing key ideas from the lecture.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
What is a chromosome composed of?
DNA-binding proteins and DNA
How many different types of chromosomes do humans have?
23
What does haploid number (n) represent?
the number of different types of chromosomes
What is ploidy?
the number of each type of chromosome
What is a haploid cell?
A cell that has one of each type of chromosome
What is a diploid cell?
A cell that has two of each type of chromosome
Define homologous chromosomes.
different versions of the same chromosome type
What are sister chromatids?
The identical copies formed by the replication of a chromosome
What phase of the cell cycle does mitosis occur?
M phase
Why must chromosome replication occur before mitosis?
to ensure each daughter cell receives a complete set of chromosomes
What are transcription factors (TF)?
proteins that regulate the expression of genes
What can TFs recruit?
RNA polymerase and proteins that modify histones
What is feedback inhibition?
a regulatory mechanism where the end product of a biosynthetic pathway inhibits an earlier step in the pathway
What is the role of kinetochores in cell division?
protein structures on chromatids that attach to microtubules to help pull chromosomes apart during mitosis
What happens during prophase of mitosis?
chromosomes condense and become visible
What is the metaphase of mitosis characterized by?
chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell
What happens during anaphase?
sister chromatids are pulled apart to opposite sides of the cell
Describe telophase.
nuclei reform around each set of separated chromosomes, and the chromosomes decondense.
What is cytokinesis?
the process of dividing the cytoplasm and cell membrane to form two separate daughter cells.
What are the two major phases of the cell cycle?
interphase and mitotic phase
What occurs during DNA replication (S phase)?
each chromosome is replicated to produce sister chromatids.
What are microtubules' role during mitosis?
help move chromosomes by forming the mitotic spindle and pulling chromatids apart.
What is a negative feedback loop in biology?
a process where the output of a system reduces its activity
Explain the significance of 'G1' and 'G2' phases.
G1 and G2 are growth phases that occur before and after the S phase of DNA synthesis.
What is the function of cyclins in the cell cycle?
proteins that regulate the progression of the cell cycle by activating cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs).
Why is the cell cycle considered 'deeply conserved' in eukaryotes?
The mechanisms controlling the cell cycle are largely similar across different eukaryotic organisms.
What is the structure of Eukaryotic genomes?
Long, linear chromosomes
What is phosphorylation?
Changes physical structure —> alters protein function
What are kinases?
Proteins that phosphorylate other proteins
What does alternative splicing do?
Generates diverse proteins
Does tryptophan binding to the repressor change its shape?
Yes, its a conformational change
What does transcription of the Trp operon followed by translation of the mRNA produce?
Enzymes that synthesize tryptophan
What can repress transcription?
Trp repressor
What is tryptophan essential for?
Cell growth
Is there any transcription of the Trp operon when tryptophan is present?
No because it regulates its own feedback inhibition
What kind of feedback is tryptophan on a example of?
Negative
What happens if you repress one gene in an operon?
You inhibit the entire genome
What genetic information is present in two homologous chromosomes?
Same genes but different alleles
What genetic information is present in two non homologous chromosomes?
Different genes
What genetic information is present in two sister chromatids?
Identical copies of single chromosome
What genetic information is present in two non-sister chromatids?
Chromatids from homologous chromosomes - similar genes but different alleles
Why must chromosome replication occur before mitosis?
To ensure each daughter cells has only half of necessary DNA
What macromolecules are present in eukaryotic cells?
Histones, DNA, TFs and nucleic acids
What does the term 'tetraploid' mean?
a cell that has four sets of chromosomes.
What is a replicated chromosome?
A chromosome with two identical DNA molecules
What is a gene?
Segment of DNA that codes for a protein or RNA product
What is a chromosme?
Complex of DNA-binding proteins and DNA
How many chromosomes do humans have?
23
How many telomeres does each chromatid and chromosome have?
Chromatid —> 2
Chromosome —> 4
How do you discover amount of chromatids of sperm cells from an image of karyotypes?
Divide by 2 because each sperm cell inherits half of homologous chromosome at each chromosome type
How do you find max allele number?
It is equal to amount of diff versions of each chromosome
What must cells do in order to make a copy of themselves?
Duplicate their DNA
Split evenly (every cell must get a copy of every piece of DNA)
Physically spilt the cell
What is the M phase?
Mitosis: physical splitting of DNA and cells
What is interphase?
Between M phases
What is the name for DNA replication in Interphase?
S phase
Why are the stages of replication of DNA separated from the division of DNA into different cells?
To check for errors
What are G1 and G2 phases?
Growth phases before and after S phase
What is the G0 phase?
When cells are not actively dividing (outside of cell)
What is the order of the cell cycle?
G1 —> S phase —> G2 —> M phase
Problem: chromosomes will get tangled in cell division
Wrap all DNA up to make them compact
Problem: how will we move chromosomes?
Use motor proteins to move chromosomes along microtubules
Problem: how will we attach microtubules?
Kinetochores (one per sister chromatid)
Problem: microtubules outside the nucleus, DNA inside
Dissolve the nucleus
What is an allele?
Type of gene that has portions of its sequence that are different from other alleles
Why does DNA wrap around histones?
Electrical interaction: histone + and DNA -
What is mitosis?
Distribution of each chromosome of parent cells to daughter cells
Why do many anti-cancer drugs target mitosis?
Because without mitosis cells can’t divide
When replicated and condensed chromosomes move to the center of the cell, how are sister chromatids pulled apart?
Microtubules attach to sister chromatids then kinesins pull microtubules and chromosomes into position to pull sister chromatids apart
What are somatic cells?
Rest of cells in body: mitosis and cell division
What are germ cells?
Reproductive cells: meiosis
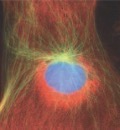
What stage of mitosis?
G2: gap to make sure DNA synthesis is complete
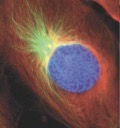
What stage of mitosis?
Prophase
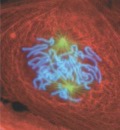
What stage of mitosis?
Prometaphase
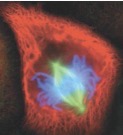
What stage of mitosis?
Metaphase
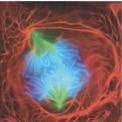
What stage of mitosis?
Anaphase
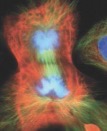
What stage of mitosis?
Telophase