how competitive markets work (chap 1-2)
1/76
Earn XP
Description and Tags
The economic problem, opportunity cost, allocation of resources, specialisation, trade
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
77 Terms
ceteris paribus
things being equal
positive statement
an objective statement that can be tested and is based on facts, they are not based on value judgements
example of a positive statement
rishi sunak has been in office for two years
normative statement
a subjective statement that is soeley based on an individuals judgement and opinion, cannot be tested
example of a normative statement
we should raise the national minimum wage
value judgement
an assessment if a decision is worthwhile in terms of standards and priorities
what is the basic economic issue
the issue of scarcity and resource distribution
scarcity
where supply does not meet demand
Free good
A good that is not regarded as scarce such as the earths atmosphere
Economic good
A good that is in demand by a consumer
What are the three economic agents
Households, government, firms
What is the aim of a rational consumer
Maximise utility
opportunity cost
the next best thing you give up when making a decision
example of opportunity cost
paying your workers more CAUSING less money to be available for things
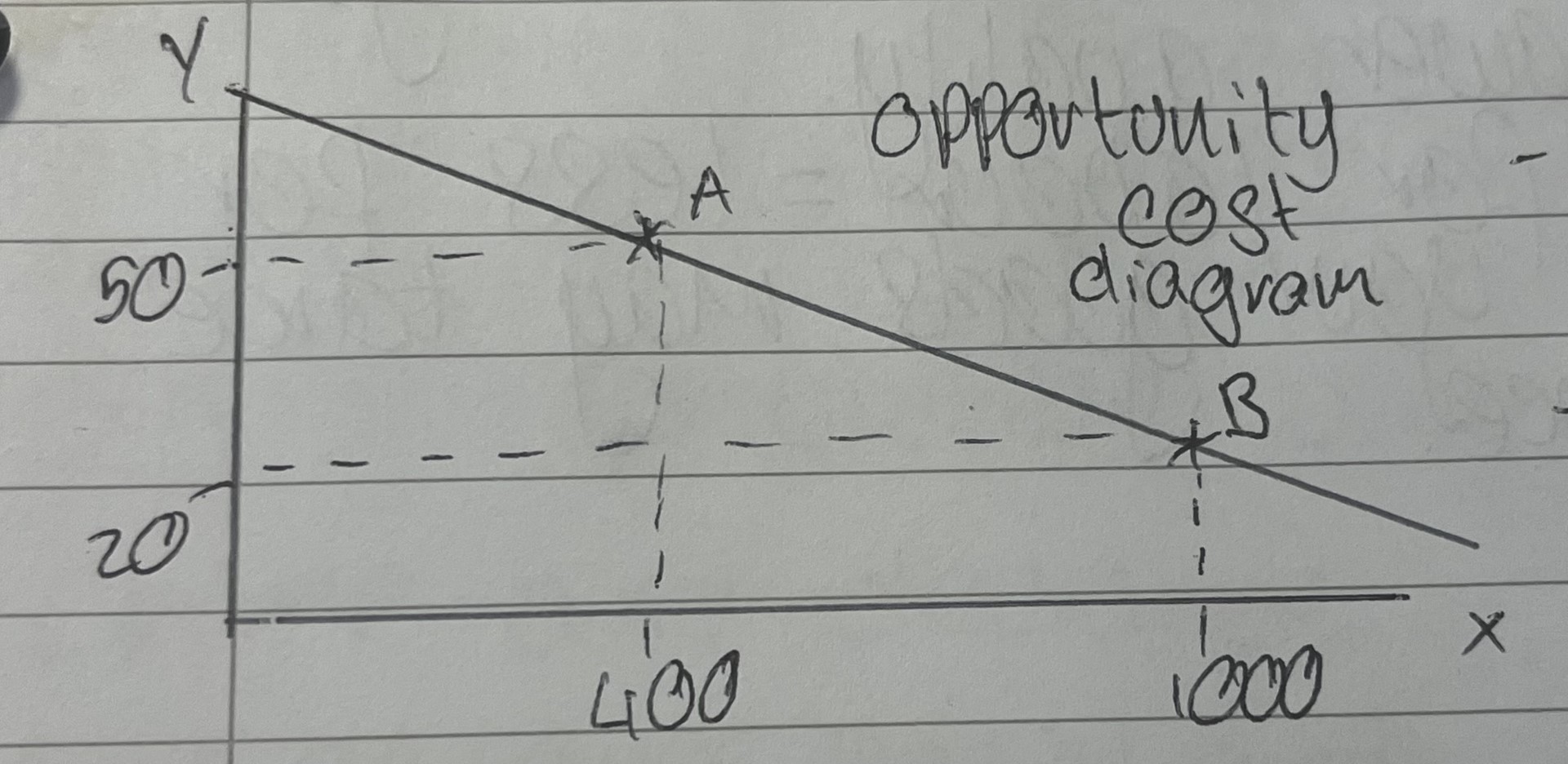
explain the opportunity cost diagram
as you increase x output, you give up some of y output and vice versa
what are the four factors of production
capital, labour, land, enterprise
capital and its rewards
Non Human Resources used in the production process, reward is interest
labour and its rewards
manual work and efforts in order to produce goods and services in an economy, reward is wage
land and its rewards
the space and nature providing the materials and space, reward is rent
enterprise and its rewards
ability to bring all factors of production together and take risks to start business, reward is profit
renewable resource
a resource that can replenished e.g wind energy
non-renewable resource
a resource that cannot be replenished e.g coal
how does opportunity cost link to scarcity
if a firm was to use cheaper materials to combat good quality resources being scarce, they may loose customers as the products quality has dropped
what does ppf stand for
production possibility frontier or curve
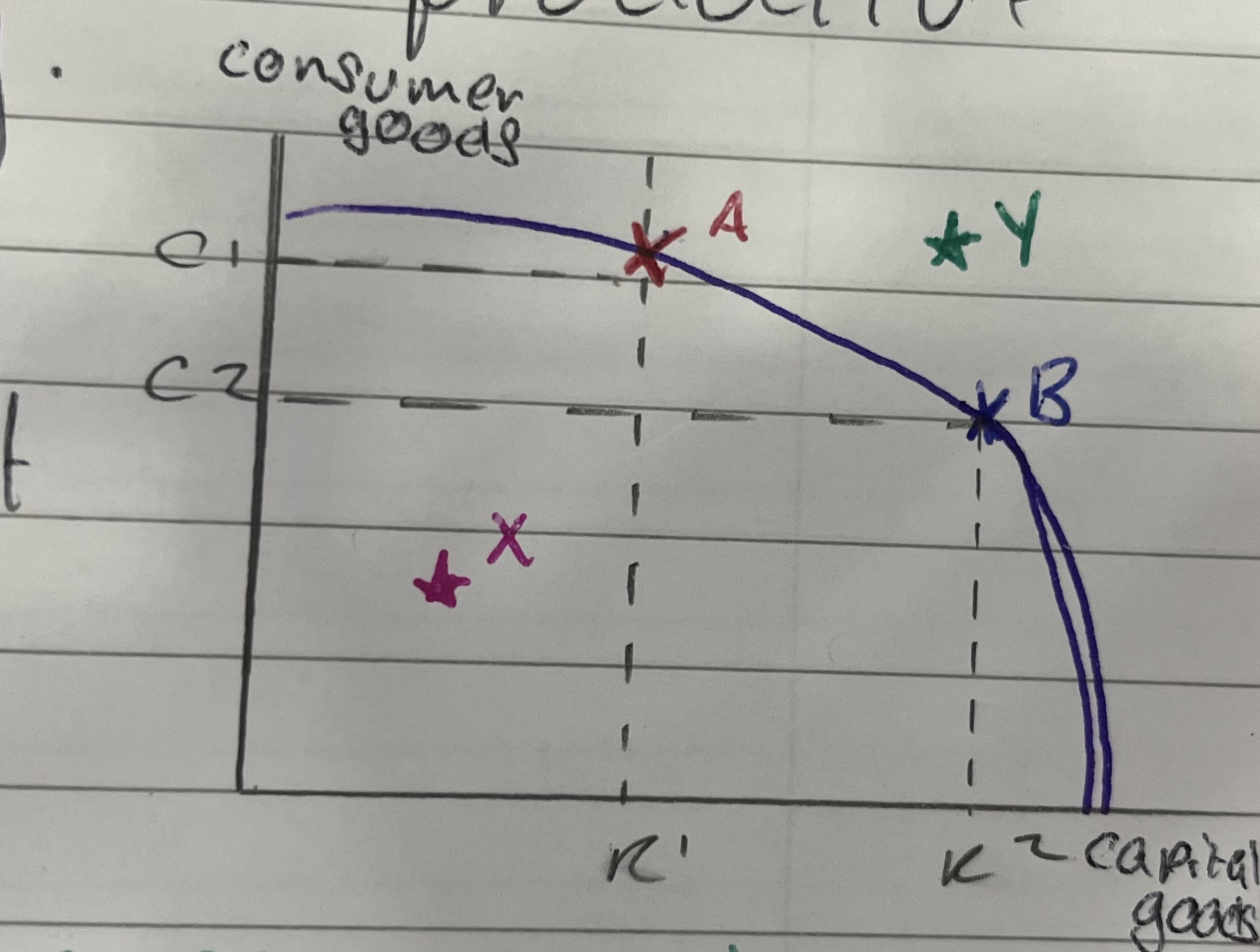
what does a ppf show
the maximum combinations of goods and services that can be produced in a given period with available resources
Trade off
What you give up when making a decision between two objectives, shown on a ppf depending on what amount of what product is being produced
where on a ppf shows maximum possible output
anywhere on the curve
if a point on a ppf is outside the curve, what does this indicate
the goal is unattainable as there is not enough resources e.g raw materials or machinery
if a point on a ppf is inside the curve, what does this indicate
the economic agent is not producing at maximum output e.g having idle machinery
how can efficiency change on a ppf
changes to the factors of production e.g having more labour causing more output
describe opportunity cost in relation to a ppf
as you move from one point on the curve to another, you give up producing more of one product than another so your opportunity cost is one of the good’s output
how can the ppf curve expand outwards
if the overall production increases in volume due to an increase in productive potential, usually in long run economic growth
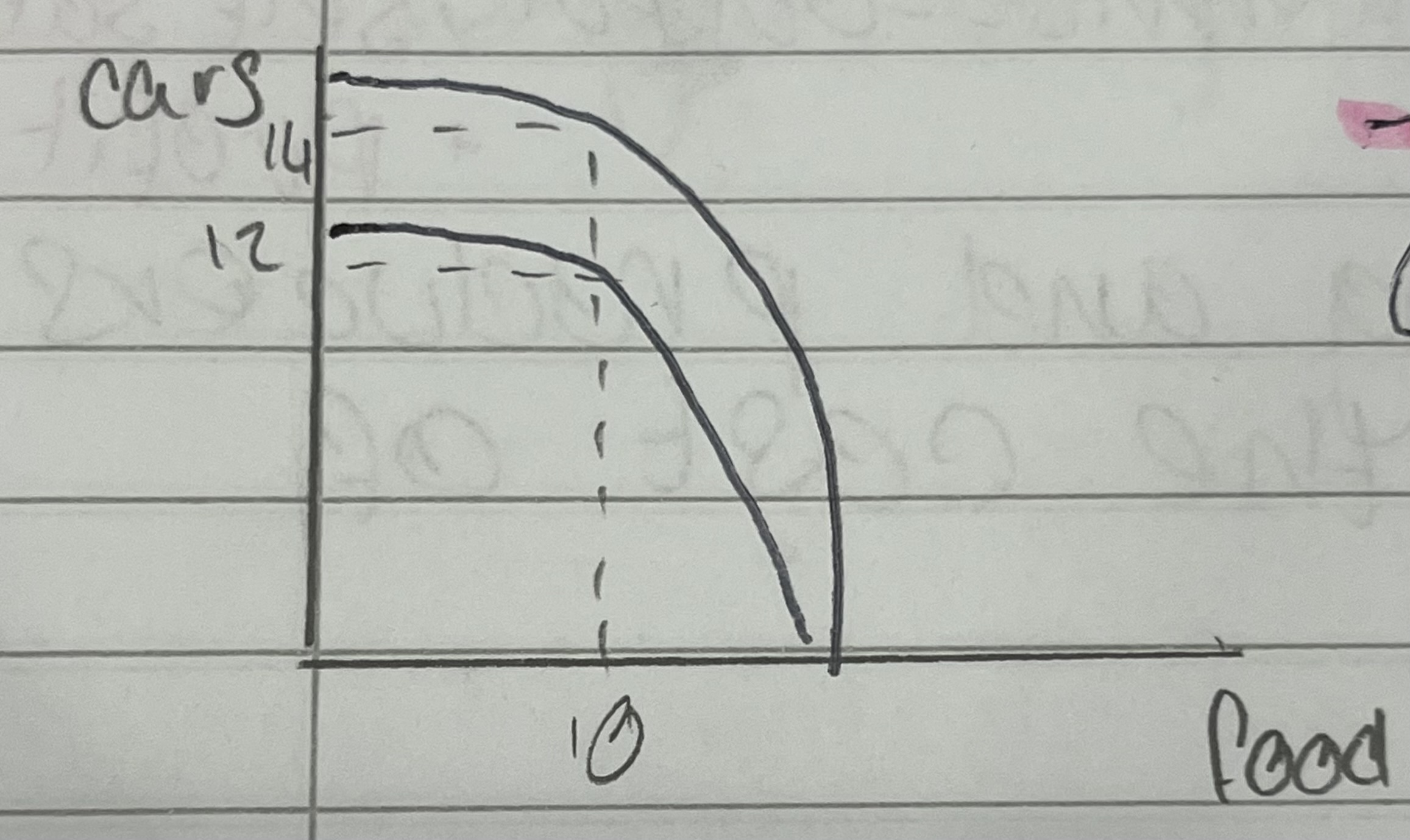
what causes the curve to be presented as such
investment in the production of one product over the other increasing output for only one
Capital good
Good used as part of the production process e.g machinery buildings
Consumer good
Good produced for consumer use
Productive efficiency
Where firms produced at the lowest possible cost
Allocative efficiency
Where firms produce the correct amount of goods in relation to what consumers wish to buy
Incentive
What motivates an economic agent to make a decision e.g a household buying more as prices are lower
What is the main aim of households
Maximise utility
What is the main aim of governments
Improve welfare/ quality of life
What is the main aim of firms
Profit maximisation
rationality
making decisions using assumptions of the consumers feelings and behaviours as the facts may not always be available
explain the rational decision making model
a flow diagram that describes how businesses make rational decisions
first identify the issue, find criteria they are to stick to, weigh out the criteria, generate alternatives, evaluate the alternatives, carry out the best decision
what is a drawback of the rational decision making model
it is a long process that takes time which may not match up with a firms time constraints
Resource allocation
How resources are distributed across society
free market
a type of economy where the decision making about prices is left up to firms and consumers with minimal government intervention
what can a free market also be called
market economy, capitalist economy
pros of a free market *5
high efficiency as firms want to meet customer demands as quick as possible to generate profits, follows the consumers demand, likely to lower production costs as goods are usually being produce in masses, no or little shortages, freedom of consumer choice in production and consumption
cons of a free market *4
monopolies that own almost all the trades territory may raise prices and cause all consumers to loose out, underproduction of merit goods such as welfare and education, overproduction of demerit goods such as alcohol and tobacco leading to societal outbreak, ignores the reality that inequalities as made due to people not being able to afford all goods
realistically, how do government generally intervene in free market economies
they enforce laws and provide public services aswell as goods such as roads
explain Adam Smith’s invisible hand theory
prices in a free economy are determined by consumers spending votes, the wealthy employ the poor to produce their wants, interdependency between the wealthy and poor
laissez faire
what adam smith advocated, where governments can enter and leave economies as they wish to regulate themselves
what did hayek argue
control of the economy by the government leads to the individual loosing out and having no freedom, argues free markets have more liberty and allow for more individual choice
what are some criticisms of hayeks view
free markets still create disadvantaged people as people cannot afford what is needed e.g in event of monopolies raising prices, law is controlled by the rich and power regardless of what economy you are in so you don’t necessarily have choice
what did marx argue
the proletariat are exploited by the bourgeoise and in a free market the drive for lower waged and harder work would increase exploitation and frustration against the bourgeoise causing rebellion, wanted a planned command economy of order and equal distribution
planned economy
economy where government locates all of its scarce resources to its citizens
what is a planned economy also called
command economy
pros of a planned economy *5
better order in times of crisis, ensures all have the basic needs, reduced inequalities and more welfare, prevents abuse of monopolies power, compensation when the market fails as governments can just re-allocate resources
cons of a planned economy *5
governments can fail as they are not informed well of consumer wants, may not meet all of consumer wants, limits democracy and personal freedom, usually poor quality goods and services, slow or no response to consumer demand trends so generally cannot capitalise on profits
mixed economy
where the market is controlled by both consumers and governments, most prevelant in our economy
example of a free market economy
singapore
example of a planned economy
north korea
example of a mixed economy
uk
Specialisation
The process of concentrating on a particular task to become expert in it
Division of labour
Production procedure is broken down into stages and workers are assigned to the stages
Who Introduced the division of labour
Adam smith
Advantages of specialisation for firms
Less training for workers, higher production, minimal time wasting
Disadvantages of specialisation for firms
Workers can’t fill in for each other, mistakes, shock if there is a demand change, repetitive work means boredom and a bad brand image
Advantages of specialisation for workers
Less stressful, expertise developed, sense of achievement
Disadvantages of specialisation for workers
Boredom and specific skills only, hard to gain promotions, easy to be made redundant
Advantages of specialisation for countries
Increased efficiency, greater output, lower costs, can capitalise on high demand and grow economy
Disadvantages of specialisation for countries
Over dependency on specific commodity, overuse of non-renewable resources, more imports
Market
Set of arrangements that allows transactions to take place
Labour productivity
Output per worker / unit of labour
Capital productivity
Output per unit of capital employed
Barter system
Economy where trading goods and services is a coincidence of wants- you trade something you don’t want for something you want with someone who is in the same position
Fiat money
Money that is backed by a government rather than a commodity such as bank notes rather than gold coins