Biology of cells Unit 2: Cell communication Homeostasis Cell signalling Hormones PART 1
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/16
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 1:08 PM on 10/30/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
1
New cards
What is a hormone?
A hormone is a substance secreted directly into the blood by discrete specialised cells in response to a specific stimulus (neural or blood borne) and in amounts which vary with the strength of the stimulus and transported to a distant target tissue where it exerts specific effects
2
New cards
Endocrine glands
• Responsible for the production of hormones • They secrete the hormones to the bloodstream
• Other organs can also produce hormones
• Other organs can also produce hormones
3
New cards
Endocrine substances
(defined as hormones) secreted directly into the blood stream - transported to distant target tissue to exert its actions
4
New cards
Paracrine hormone released by
y a gland cell diffuses through the extracellular space to its target cell within the same gland
5
New cards
Autocrine
hormone released by a cell - exerts its actions on the same cell
6
New cards
Neuroendocrine
A neuronal hormone released into a synaptic cleft adjacent to where the neurone contacts the target cell
7
New cards
Classification of types of hormones
• Protein and peptide hormones eg. Insulin, luteinising hormone (LH)
• steroid hormones eg. Cortisol, oestradiol
• hormones derived from tyrosine eg. thyroxine and norepinephrine
• eicosanoids eg. prostaglandins and leukotrienes
• steroid hormones eg. Cortisol, oestradiol
• hormones derived from tyrosine eg. thyroxine and norepinephrine
• eicosanoids eg. prostaglandins and leukotrienes
8
New cards
Protein and peptide hormones
These hormones are synthesized from amino acids Stored in secretory vesicles until needed Vary in size:
some are very small and consist of only a single chain of amino acids
• Thyrotropin releasing hormone (TRH) consists of only 3 amino acid (aa) residues.
• Gonadotrophin releasing hormone (GnRH) consists of 10 aa.
some are very small and consist of only a single chain of amino acids
• Thyrotropin releasing hormone (TRH) consists of only 3 amino acid (aa) residues.
• Gonadotrophin releasing hormone (GnRH) consists of 10 aa.
9
New cards
Glycoprotein peptide hormones
Glycoprotein hormones are large molecules.
Gonadotrophins (luteinising hormone, LH and follicle stimulating hormone, FSH) and thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) from the anterior pituitary consist of two distinct peptide chains (called a and b subunits) which are linked together by non-covalent bonds.
The α subunit is common to LH, FSH, TSH (also human chorionic gonadotrophin, hCG); biological specificity is conferred by the β subunit
They are glycosylated
Gonadotrophins (luteinising hormone, LH and follicle stimulating hormone, FSH) and thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) from the anterior pituitary consist of two distinct peptide chains (called a and b subunits) which are linked together by non-covalent bonds.
The α subunit is common to LH, FSH, TSH (also human chorionic gonadotrophin, hCG); biological specificity is conferred by the β subunit
They are glycosylated
10
New cards
Protein/peptide hormone action
Hydrophilic Bind to cell surface receptors (which receptor types?)
Initiate downstream signalling pathways that mediate biological effects
Initiate downstream signalling pathways that mediate biological effects
11
New cards
Steroid hormones
The steroids are a large class of lipids which are synthesized mainly in the adrenal cortex, testis, ovary and placenta from a common precursor cholesterol.
They all have a common ring structure which consists of 3 six-membered rings and 1 five membered ring.
They all have a common ring structure which consists of 3 six-membered rings and 1 five membered ring.
12
New cards
Steroid hormone action
• Hydrophobic
• transported in the blood stream bound to carrier proteins
• can pass through the cell membrane
• Bind to receptors either in the cytoplasm or the nucleus
• These receptors move to the nucleus and dimerise in order to regulate gene transcription
• Also, alternative signalling pathways including non genomic action
• transported in the blood stream bound to carrier proteins
• can pass through the cell membrane
• Bind to receptors either in the cytoplasm or the nucleus
• These receptors move to the nucleus and dimerise in order to regulate gene transcription
• Also, alternative signalling pathways including non genomic action
13
New cards
Hormones derived from tyrosine
Include adrenaline, noradrenaline, dopamine and the thyroid hormones thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3)
Whilst these hormones are all derived from tyrosine, they have very different properties.
Whilst these hormones are all derived from tyrosine, they have very different properties.
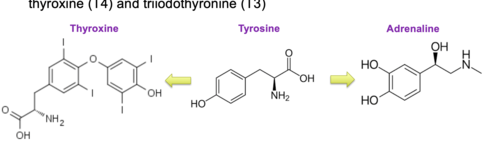
14
New cards
Adrenaline, noradrenaline and dopamine are
e hydrophilic They bind to cell surface receptors (GPCRs)
15
New cards
Thyroid hormones
Thyroid hormones thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3) are hydrophobic
They enter cells (via transporter proteins) and bind to nuclear receptors
They enter cells (via transporter proteins) and bind to nuclear receptors
16
New cards
Eicosanoids
Two major classes of messengers
• Prostaglandins (PGs)
• Leukotrienes (LTs)
They bind to GPCRs on target cells
Derived from arachidonic acid (AA) AA is converted to LTs by the action of 5-lipoxygenase
AA is converted to PGs by the action of cyclooxygenase (COX)
• Prostaglandins (PGs)
• Leukotrienes (LTs)
They bind to GPCRs on target cells
Derived from arachidonic acid (AA) AA is converted to LTs by the action of 5-lipoxygenase
AA is converted to PGs by the action of cyclooxygenase (COX)
17
New cards
Summary
Hormones are produced primarily by endocrine glands • They can act in an endocrine, paracrine, autocrine or neuroendocrine manner
• They can be classified into four groups
• Protein and peptide hormones
• Hormones derived from tyrosine
• Steroid hormones
• Eicosanoids
• They exert their action by binding on receptors on target cells • Hydrophobic hormones are transported in the blood bound to carrier proteins
• They can be classified into four groups
• Protein and peptide hormones
• Hormones derived from tyrosine
• Steroid hormones
• Eicosanoids
• They exert their action by binding on receptors on target cells • Hydrophobic hormones are transported in the blood bound to carrier proteins
Explore top notes
Explore top flashcards
Foundations of govt, British history, DOI, Articles of Confederation
Updated 881d ago