Stem and Secondary growth
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
Primary growth
growth in length; contains primary anatomy; happens firth
Secondary growth
Only in eudicots; growth in width; lateral meristems; contains secondary anatomy; all the wood in the tree is secondary xylem; has thick cellulose walls with lots of lignetn
Primary stem anatomy in Eudicots
Vascular bundles in a ring; clear pith and cortex; residual procambium
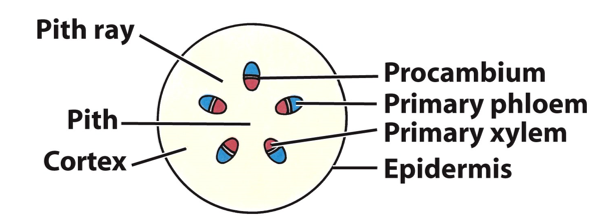
Pith
made up of parenchyma in the middle of the stem
Pith ray
Procambium
Dormant meristem; in-between xylem and phloem; activates to form 2nd growth
Primary growth in monocots
Scattered vascular bundles; no clear pith or cortex; no residual procambium and thus cant make wood
Why secondary growth
Not adequate for shrubs and trees with branching systems; dont provide enough support
Annuals
its life cycle happens in one year, stays over the winter as a seed
Biannuals
its life cycle is over 2 years
Herbecaous perenials
Around all year; Non-woody; areial shoots die in the winter; leave bulbs, tubes, and rhizomes
Palm trees
Are tall but still non-woody; have lots of lignin; lots of vascular bundles with lignin; abscise their leaves to decrease weight; not branching; proprots;
Who does secondary growth
Woody perennials; eudicots and conifers