Antibacterial drugs
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
Beta-Lactam MOA
Beta lactams inhibits transpeptidase (its a PBP) (mimics D-ala-D-ala side chain) and prevents crossliking of the peptidoglycans and inhibit cell wall synthesis
Beta lactam post-antibiotic effect
can continue suppression fo antibacterial growth after aministration of antibiotic has stopped
Penicillan G (oral) and V (IV) MOA
Beta lactams
Penicillan G (oral) and V (IV) clinical use
broad spectrum Gram +, Strep pneumo, Strep pyogenes, limited Gram -: Nisseria Menigitis, Spirochete Treponema pallidum
Amoxicillan/Ampicillin MOA
Beta lactams
Amoxicillan/Ampicillin Clinical Use
Broad spectrum Gram + and -:
-H. Flu, E.Coli, Salmonella, Listeria, Proteus, Enterococci
What Beta-lactamase inhibitor do you add to amoxixillin/ampicillin to combact resistance
CLAVULANIC ACID
Nafcillin has what MOA
Beta lactams
Nafcillin clinical Use
Narrow spectrum. MSSA
Piperacillin MOA
Beta lactams
Piperacillin Clinical Use
Broad spectrum. For Pseudonomas
What B-lactamase inhibitor do you pair with Piperacillin
Tazobactam. It protects against degradation
AE of Penicillin
Allergic reaction, contraindicated to anyone allergic to any b-lactam antibiotic.
AE of Naficillin
allergic nephritis
AE of amoxilicillin and ampicillin
GI: diarrhea, vomiting, nausea
Colitis
Imipenem-Carbapenems MOA
beta lactams with broader spectrum d/t sterochemistry and R group position
What generation Cephalosporin is Cefazolin and Cephalexin?
first generation
What generation Cephalosporin is CEFOTAXIME,CEFTAZIDIME, CEFTRIAXONE
3rd gen
Which generation cephalosporin has a wider sprectrum of activity
3rd
What is the MOA of the cephalosporins
Beta-lactams
Imipenem-Carbapenems clinical use
broad spectrum covers most G+ and G- and anaerobes, HELD AS RESERVE TX
1st gen cephalosporins clinical use (cefazolin/cephalexin)
G+ cocci (e.g. Staph and Strep)• G- (E. coli, Proteus mirabilis)
3rd gen cephalosporins clinical use CEFOTAXIME, CEFTAZIDIME, CEFTRIAXONE
-G- (Enterobacter, Serratia, Neisseria gonorrhoeae)
-Pseudomonas
-Meningitis
Aztreonam MOA
its a Monobactam Beta lactam: single ring thats specific for only Gram - aerobes
Aztreonam clinical use
G- aerobes only (aerobic forms of Enterobacter, Pseudomonas)OK for patients with penicillin allergy
AEs of ceftriaxone
billiary sludging
What drugs are Fluoroquinolones (2)
Ciprofolxacin and Levofloxacin
What is a Quniolone's MOA
They are bacterialcidal! they target/inhibit bacterial topoismoerases (gram+ topo IV/Gram - topo II)which increases supercoiling: disrupting DNA/RNA replication/repair/transcription
Clinical use of fluoroquinolones
-UTIs and GI tract infections caused by G- rods (Pseudomonas/ETEC)
-Chlamydial cervicitis/urethritis
-Bacillus anthracis (G+) infections
-streptococcus pneumoniae (G+) with high-level penicillin resistance
fluoroquinolones AEs
-Metals chelate quinolones and blocks their absorption (mg+, iron)
-GI: vomit, nausea, anorexia
CNS: peripheral neuropathy
Heart: prolongs QTc interval
-Tendonitis
Contraindication for Quinolones
avoid in childres/ preg women because they disrupt growing cartilage
What are all the drugs for UTIs (4)
-fluoroquinoloes
-Nitrofuratoin
-Sulfonamides
- TMP/SMX (trimethoprim/sulfamethaozaole)
Nitrofuratoin MOA
produces lots of free radicals in bacteria to kill them ->Bacterialcidal
Nitrofuratoin AE
pulmonary toxicity
TMP/SMX MOA
Bactericidal. Inhibits folic acid synthesis and inhibits bacterial synthesis of dihydrofolic acid. Stops purine synth-Bacteria cannot make DNA/RNA
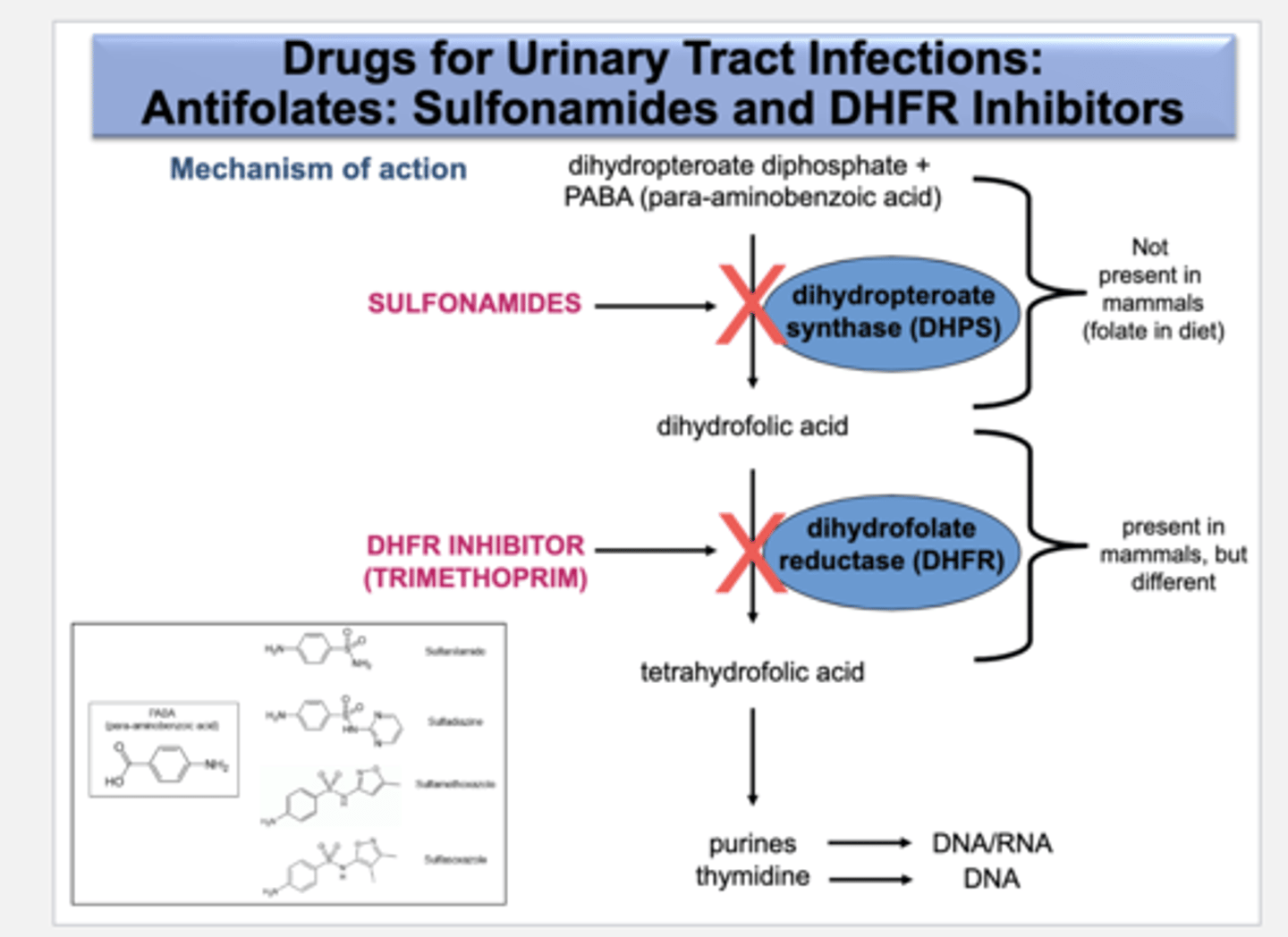
TMP/SMX AEs and contraindications
Contra: avoid in preg women as there is risk of bilirubin displacement
AE: allergic rxns in ppl with G6PD deficiency
-megaloblastic anemia
TMP/SMX clinical use
recurrent UTIs and acute chronic broncitis
Protein Synthesis Inhibitors- Macrolide Antibiotics Drugs (3)
Azithromycin
Clarithromycin
Erythromycin
Macrolide Antibiotics Drugs MOA
Bacteriostatic.
-Inhibit translation of RNA to protein
-Bond to 50s to inhibit trnaslocation
Macrolide clinical use
-accumulate in Gram + and human macrophage (Listeria)
-azithromycin is used for gram -
-legionella, H.flu, Chlamydia, bronchitis, otisis media, mycobacterium avium complex, mycoplasma pneumonia, C.diffe
Macrolide contraindications/AEs
-hepatic impairement
-POTENT INHIBITOR OF CYTOCHROME P450
-GI: nuasea, vom, diarrhea
-cardio: caution w/ pts. prolongs QT
Protein Synthesis Inhibitors- Tetracyclines drugs (1)
doxyclycline
Tetracycline MOA
-Bacteriostatic
-Binds to 30s, blocks binding of aminoacyl tRNA
-Inhibits translation of RNA to protein
Tetracycline(doxy) drug interactions
Antacids: Al, Ca+, Mg+
Iron salts: Fe+
Tetracycline(doxy) AEs/Contrindications
Photosensitivity, GI-GERD
-Contraindication: Preg/Kids bc it binds to bones and teeth
Tetracycline(doxy) Clinical Use
-Brain abscesses (Fragilis/Strep)
- Meningitis (h.flu, N.Men)
-Ricketssia
-Bacterial conjunct
Protein Synthesis Inhibitors- Others (2)
-Chrolramphenicol
-Clindamycin
Chrolramphenicol MOA
Bacteriostatic. its a protein sytnhesis inhibitor (other), it stops the translation of RNA to protein. Esp. mitochondrial protein synthesis
Clindamycin MOA
Bacteriostatic. its a protein sytnhesis inhibitor (other), it stops the translation of RNA to protein. Inhibits 50s ribosome
Chrolramphenicol AEs
-Bone marrow supression
-Grey baby Syndrome (baby will OD=grey bc they cant metabolize drug)
-Drug interactions with Cyt p450
-Ihibits Clindamycin and Erythromycin
Clindamycin clinical use
-Anaerboic Gram - bacilli
-Aerobic Gram + cocci
-Acne
Clindamycin AEs/Contraindications
-GI: diarrhea
-Inhibits Chloramphenicol and macrolides (same 50s)
-inhibits drugs for c.diff like metronidazole
Aminoglycosides (4)
-Gentamycin
-Streptomycin
-Neomycin
-Tobramycin
Aminoglycosides MOA
Bactericidal. Bind to the rRNA of 30s unit; blocks translation initiation anad causes mis coded proteins, also blocks translocation
Aminoglycosides Clinical Use
-Only for Aerobic bacteria
-Gram - aerobics: Enterobacter, Proteus, Klebsiella
-Gram + Aerobics: Strep Viridins, Strep. agalact, Enterococcus
-Mycobacterium, N.Gonorrhoeae
Aminoglycosides AEs
-Nephrotox
-Ototox
Neuromuscular blockade-MG