KIN 224 Exam 1 (15 & 17)
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
Tear secretions are governed by parasympathetic fibers within which cranial nerve?
III
V
X
IX
VII
VII
Nicotinic receptors bind
a. norepinephrine and allow potassium entry, thereby exciting the cell.
b. acetylcholine and allow chloride ions to exit the cell.
c. muscarine and increase the contractility of intestinal muscle.
d. acetylcholine and allow sodium ions to enter the cell.
e. norepinephrine and can either stimulate or inhibit the cell.
d. acetylcholine and allow sodium ions to enter the cell.
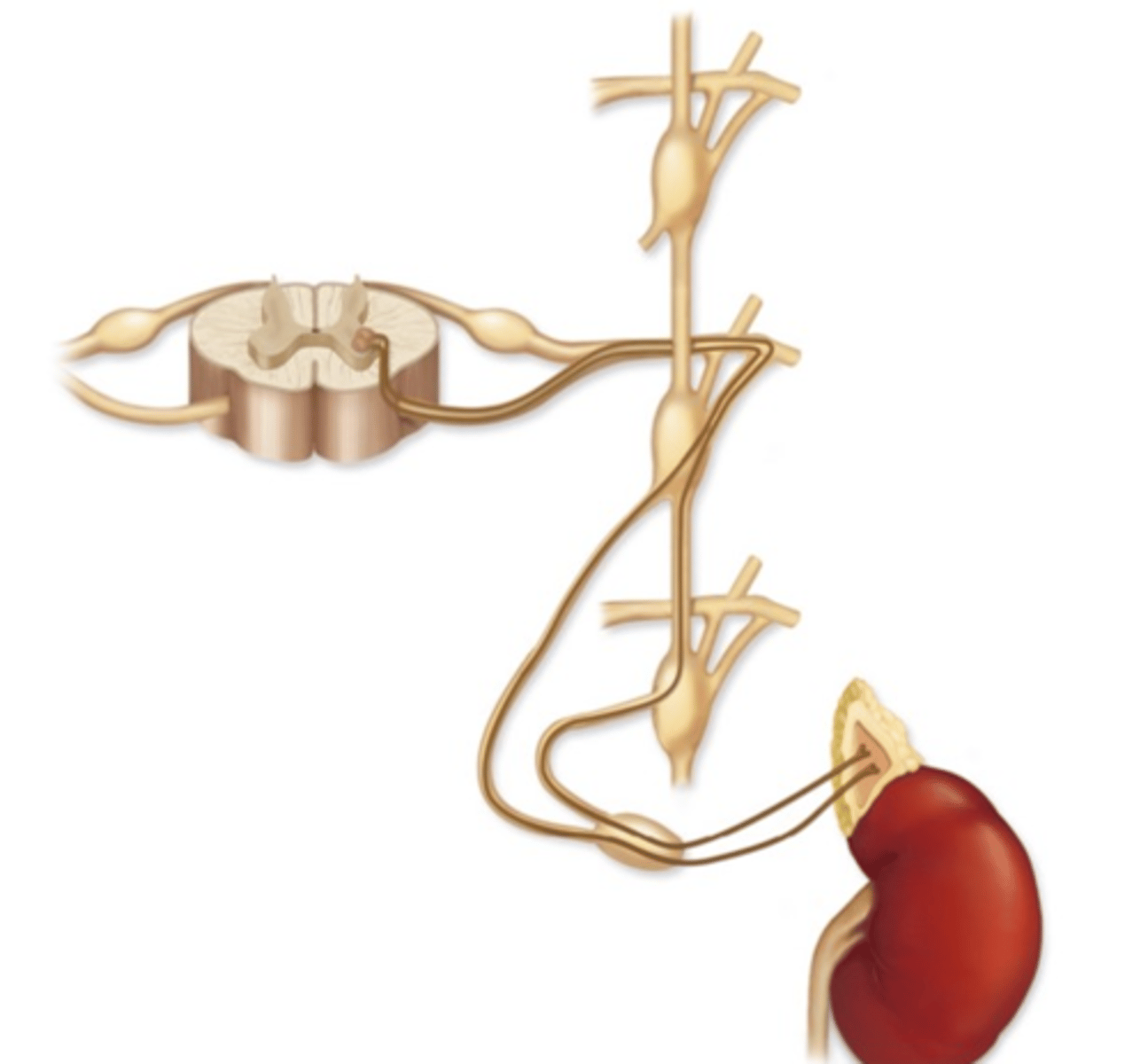
Which type of pathway is illustrated?
a. Postganglionic sympathetic nerve pathway
b. Splanchnic nerve pathway
c. Spinal nerve pathway
d. Adrenal medulla pathway
e. Raynaud nerve pathway
d. Adrenal medulla pathway

The sympathetic postganglionic axons from the superior cervical ganglion innervate
a: Sweat glands in the head
b: Sweat glands in the palms
c: Smooth muscle of blood vessels in the head
d: Smooth muscles of blood vessels in the antebrachial region
e: Superior tarsal muscle of the eye
f: Submandibular salivary gland
b, d
a, c, f
b, d, f
d, e, f
a, c, e
a, c, e
Activation of parasympathetic fibers in pelvic splanchnic nerves leads to
a. decreased secretions in the digestive tract.
b. erection of the male penis and female clitoris.
c. inhibition of urinary bladder contractions.
d. an increase in the heart rate.
e. decreased secretion of adrenaline from the adrenal glands.
b. erection of the male penis and female clitoris.
What visceral sensory stimulus triggers the autonomic reflex causing the reduction of blood pressure?
a. Increased blood CO2CO2
b. Increased body temperature
c. Stretching of large blood vessels
d. Stretching of the urinary bladder
c. Stretching of large blood vessels
Which sympathetic pathway involves a preganglionic neuron that synapses with a ganglionic neuron in a sympathetic trunk ganglion, but the postganglionic axon does not leave the trunk via a gray ramus?
a. Splanchnic nerve pathway
b. Adrenal medulla pathway
c. Postganglionic sympathetic nerve pathway
d. Spinal nerve pathway
e. None of the choices is correct.
c. Postganglionic sympathetic nerve pathway
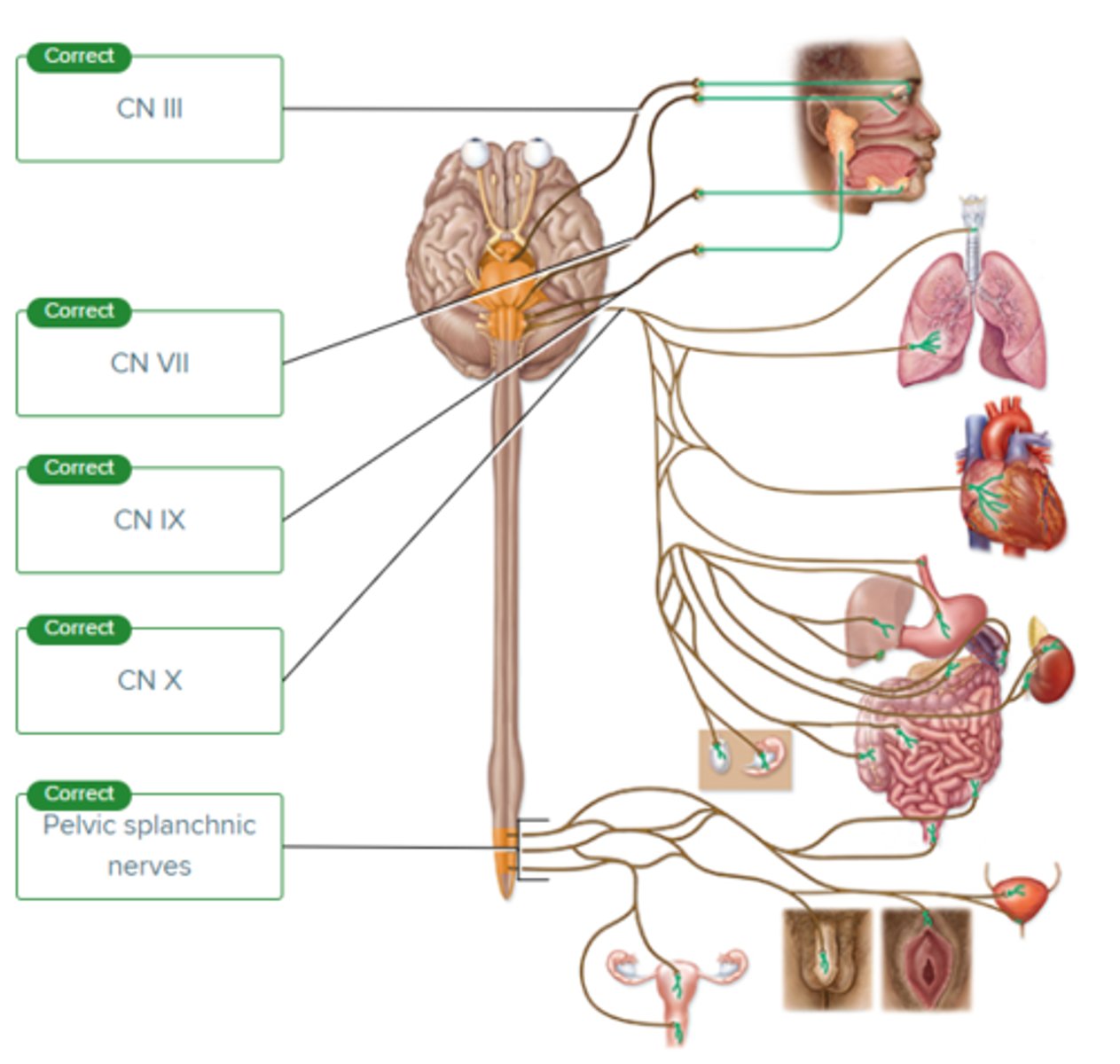
Which of the following parasympathetic nerves controls the production of tears, nasal secretions, and saliva?
Vagus nerve (CN X)
Oculomotor nerve (CN III)
Glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX)
Facial nerve (CN VII)
Facial nerve (CN VII)
Stimulation of β2 receptors in the lung causes
a. bronchoconstriction.
b. bronchodilation.
b. bronchodilation.
Many different neurons can stimulate an autonomic ganglion cell simultaneously due to
convergence.
reciprocity.
divergence.
reverberation.
convergence.
Which of the following is represented in the figure?
Craniosacral (parasympathetic) pathways
Cervicosacral (parasympathetic) pathways
Craniothoracic (sympathetic) pathways
Thoracolumbar (sympathetic) pathways
Cervicolumbar (parasympathetic) pathways
Craniosacral (parasympathetic) pathways
Which system engages in mass activation?
Parasympathetic nervous system
Sympathetic nervous system
Sympathetic nervous system
Sweat glands and arrector pili muscles are controlled
a. by both the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems.
b. by both the autonomic and somatic nervous systems.
c. only by the sympathetic nervous system.
d. only by the parasympathetic nervous system.
c. only by the sympathetic nervous system.
Postganglionic sympathetic axons are carried from the sympathetic trunk to the spinal nerve by the
superior cervical ganglion.
splanchnic nerves.
pterygopalatine ganglion.
white rami communicantes.
gray rami communicantes.
gray rami communicantes.
Typically, alpha adrenergic receptors have
stimulatory effects.
inhibitory effects.
stimulatory effects.
The "fight-or-flight" system is the _________blank nervous system.
sympathetic
parasympathetic
somatic
sympathetic
The sympathetic trunk ganglia are primarily composed of
a. axons of preganglionic neurons.
b. somas of preganglionic neurons.
c. axons of ganglionic neurons.
d. somas of ganglionic neurons.
d. somas of ganglionic neurons.
The type of adrenergic receptor found on the smooth muscle cells of blood vessels in the skin is
α2
α1
β2
β1
α1
Once inside the sympathetic trunk, the sympathetic preganglionic axons
a. follow any of the routes listed
b. travel inferiorly.
c. travel superiorly.
d. remain at the level of entry.
a. follow any of the routes listed
In the brain, the _________blank is the integration and command center for autonomic functions.
brainstem
medulla
cerebral cortex
hypothalamus
spinal cord
hypothalamus
Limited branching of preganglionic axons allows for
mass activation.
rapid changes in numerous structures at once.
local and discrete activation.
local and discrete activation.
Which division functions to conserve energy and replenish the supply of nutrients?
Parasympathetic
Sympathetic
Somatic
Parasympathetic
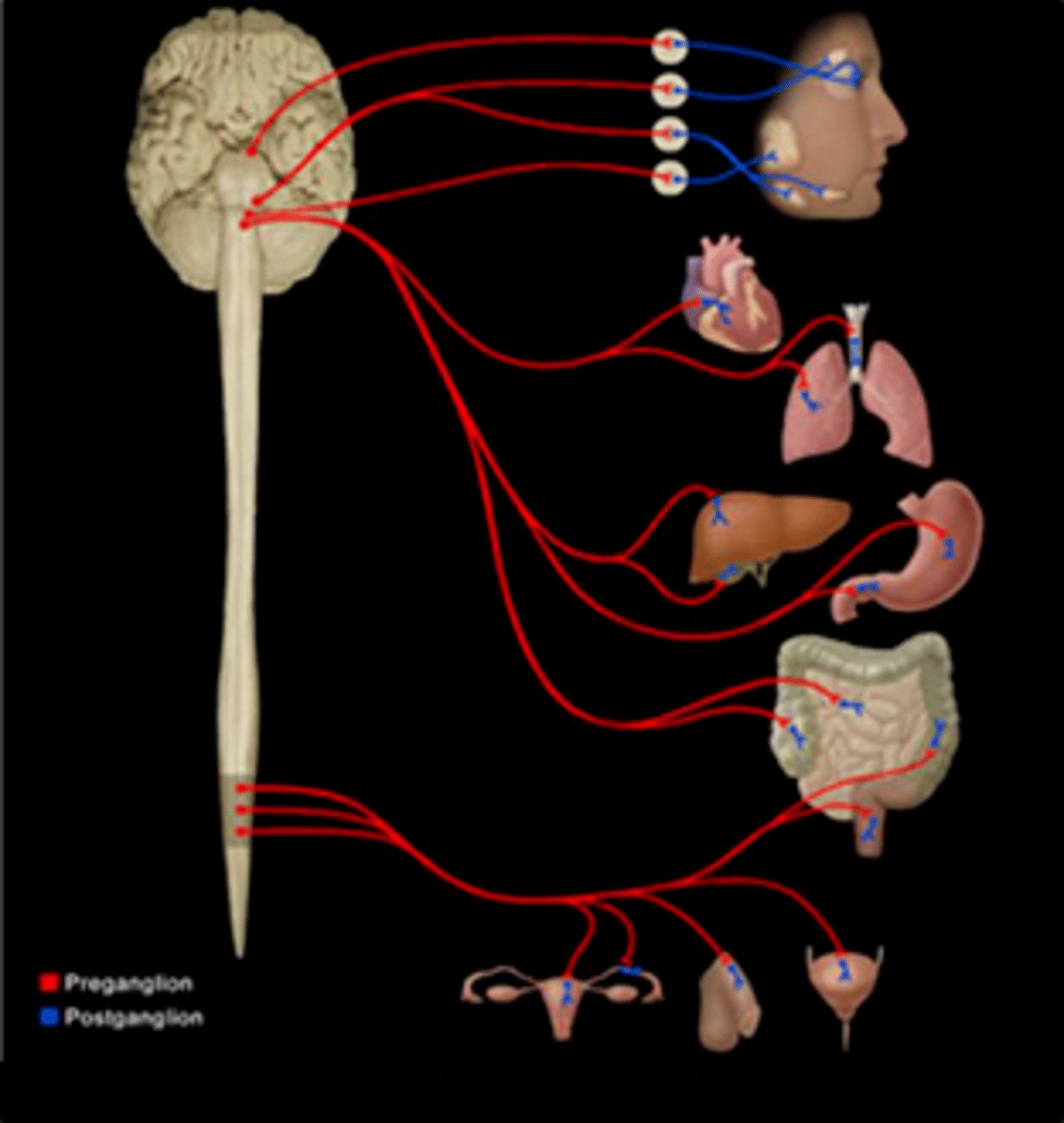
Label the structures in the parasympathetic division illustration.
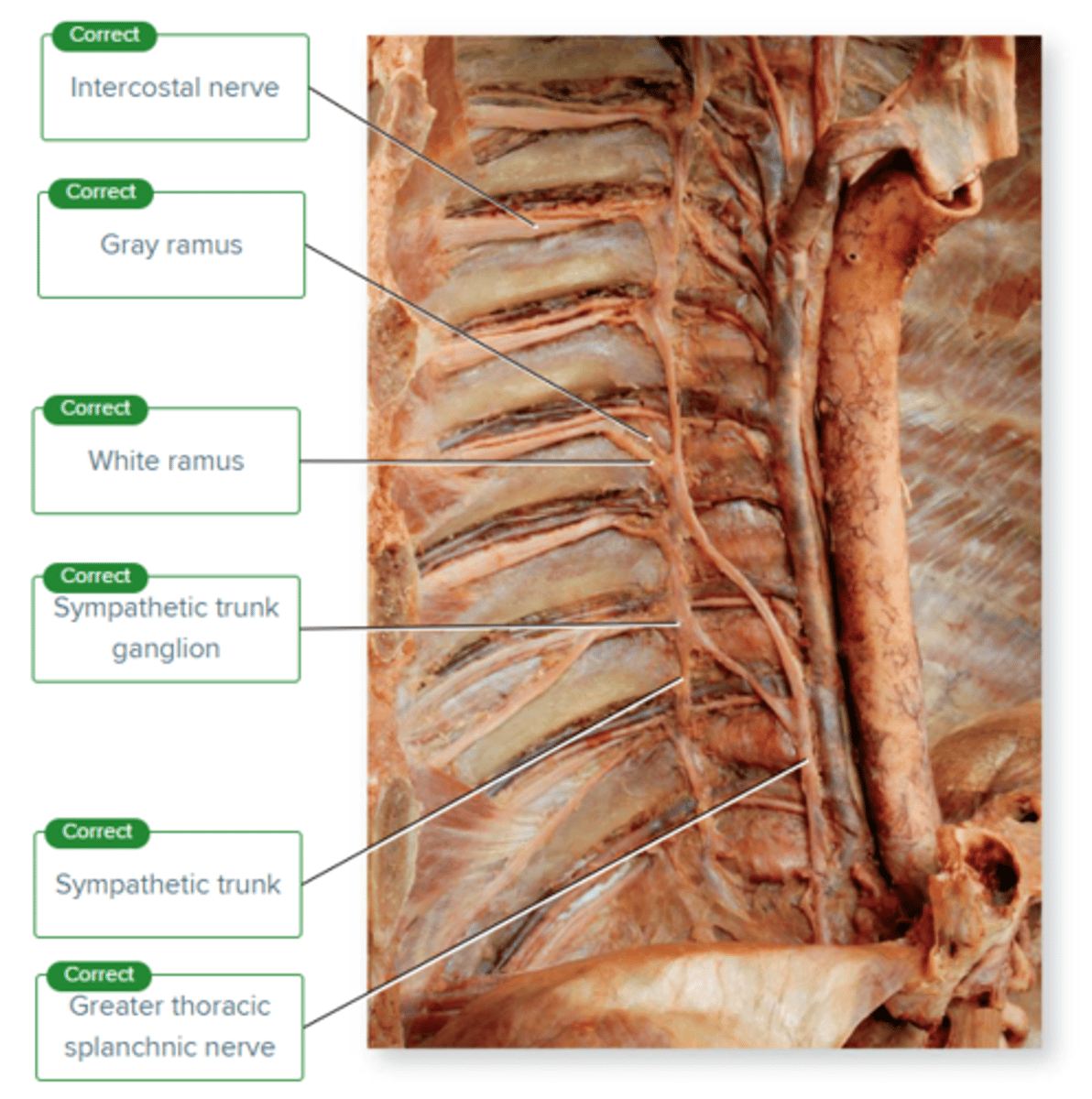
Label the structures associated with the sympathetic trunk.
Match the plexus with its function.
Esophageal plexus
Carries signals that control swallowing
Hypogastric plexus
Carries signals to pelvic region
Pulmonary plexus
Passes signals to bronchi
Abdominal aortic plexus
Composed of celiac and mesenteric plexuses

Insert the correct words into the sentences regarding the location of sympathetic preganglionic neuron cell bodies. Not all terms will be used.
The sympathetic preganglionic neuron cell bodies are housed in the lateral horn of the T1–L2 spinal nerves.
From there, the preganglionic sympathetic axons travel with somatic motor axons to exit the spinal cord.
After this, the preganglionic sympathetic axons enter first the anterior roots and then the spinal nerves .

Click and drag the terms on the left to accurately complete the sentences on the right. Not all terms will be used.

The term down-regulation refers to the process by which
a. a large amount of hormone shuts down all metabolic activity in a target cell.
b. a carrier protein increases the rate of degradation for a hormone and thereby decreases its blood concentration.
c. a carrier protein decreases the rate of degradation of the protein it ferries.
d. a glandular cell decreases the amount of hormone it secretes.
e. a cell decreases the number of receptors it has for a hormone.
e. a cell decreases the number of receptors it has for a hormone.
Generally, the shorter the half-life of a hormone
the more frequently it must be replaced.
the less frequently it must be replaced.
the more frequently it must be replaced.
In the signal transduction pathway that results in the formation of inositol triphosphate, the G protein directly activates
protein kinase A.
adenylate cyclase.
phospholipase C.
calmodulin.
phospholipase C.
Homeostatic mechanisms controlling growth hormone involve negative feedback by GH and what other hormone?
GHIH
GnRH
ACTH
CRH
GHIH
Once a structure is fully grown and mature, it will probably
a. down-regulate its receptors for growth hormone, as it no longer needs to continue to grow at a fast rate.
b. down-regulate its receptors for growth hormone, as it no longer receives as much of the ligand.
c. up-regulate its receptors for growth hormone, as it no longer needs to continue to grow at a fast rate.
d. up-regulate its receptors for growth hormone, as it no longer receives as much of the ligand.
a. down-regulate its receptors for growth hormone, as it no longer needs to continue to grow at a fast rate.
Target cells for releasing hormones are in the
testes.
anterior pituitary gland.
thyroid gland.
hypothalamus.
posterior pituitary gland.
anterior pituitary gland.
ADH and oxytocin are secreted by
a. neurons.
b. neuromuscular cells.
c. neurosecretory cells.
d. neuroendocrine cells.
e. neuroglia.
c. neurosecretory cells.
Thyroid hormone synthesis involves secretion of a glycoprotein called _________blank by the follicular cells.
a. thyroglobulin
b. tetraiodothyronine
c. triiodothyronine
d. thyroxine
e. colloid
a. thyroglobulin
Which hormones are collectively called the gonadotropins?
a. Follicle-stimulating hormone and growth hormone
b. Antidiuretic hormone and oxytocin
c. Follicle-stimulating hormone and luteinizing hormone
d. Thyroid-stimulating hormone and adrenocorticotropic hormone
e. Prolactin and oxytocin
c. Follicle-stimulating hormone and luteinizing hormone
Which hormone induces its target cells to take up glucose, thereby lowering blood glucose levels?
Insulin
Somatotropin
Pancreatic polypeptide
Somatostatin
Glucagon
Insulin
The _________blank secretes triiodothyronine.
a. adrenal gland
b. pineal gland
c. parathyroid gland
d. pancreas
e. thyroid gland
e. thyroid gland
In response to high blood glucose, the pancreas releases insulin to enable glucose to enter body cells. When the blood glucose level returns to normal, insulin release stops. This is an example of regulation by
negative feedback.
positive feedback.
neural regulation.
somatic regulation.
endocrine dysplasia
negative feedback.
Cortisol binds to _________blank receptors and has the effect of _________blank blood glucose levels.
a. membrane-bound, raising
b. membrane-bound, lowering
c. intracellular, lowering
d. intracellular, raising
d. intracellular, raising
GH stimulates liver cells to increase gluconeogenesis; as a result, blood sugar levels
remain unaffected.
fall.
rise.
rise.
Reduced hormone concentration in the blood often causes target cells to
a. up-regulate receptors in order to increase cell sensitivity.
b. up-regulate receptors in order to decrease cell sensitivity.
c. down-regulate receptors in order to increase cell sensitivity.
d. down-regulate receptors in order to decrease cell sensitivity.
a. up-regulate receptors in order to increase cell sensitivity.
Glucagon works by
a. activating second messengers and stimulating glycogenesis.
b. binding to hormone response elements on DNA and stimulating glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis.
c. binding to hormone response elements on DNA and stimulating glycogenesis.
d. activating second messengers and stimulating glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis.
d. activating second messengers and stimulating glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis.
Chemical messengers that influence the activity of the same cell that releases them are _________blank chemical messengers, while chemical messengers that influence the activity of another cell are _________blank chemical messengers
autocrine, paracrine
paracrine, autocrine
merocrine, autocrine
autocrine, merocrine
autocrine, paracrine
Which organ releases secretin and cholecystokinin?
Liver
Kidneys
Stomach
Small intestine
Small intestine
Within the adenylate cyclase signal transduction pathways of target cells, cAMP activates
the G protein.
adenylate cyclase.
transcription of a mRNA.
protein kinase.
the receptor.
protein kinase.
Secretion of insulin causes
a. a decrease in the concentration of blood glucose.
b. a decrease in the permeability of cell membranes to glucose.
c. an increase in the breakdown of glycogen to release glucose.
d. an increase in the concentration of blood glucose.
a. a decrease in the concentration of blood glucose.
The disease called _________blank is caused by excessive secretion of glucocorticoids, and is characterized by redistribution of body fat to produce characteristic features such as "moon face."
pheochromocytoma
Addison disease
androgenital syndrome
Cushing syndrome
Graves disease
Cushing syndrome
The amount of time necessary to reduce the hormone concentration within the blood to one-half of what had been secreted originally is called
terminal-life.
half-life.
semi-life.
lifetime.
half-life.
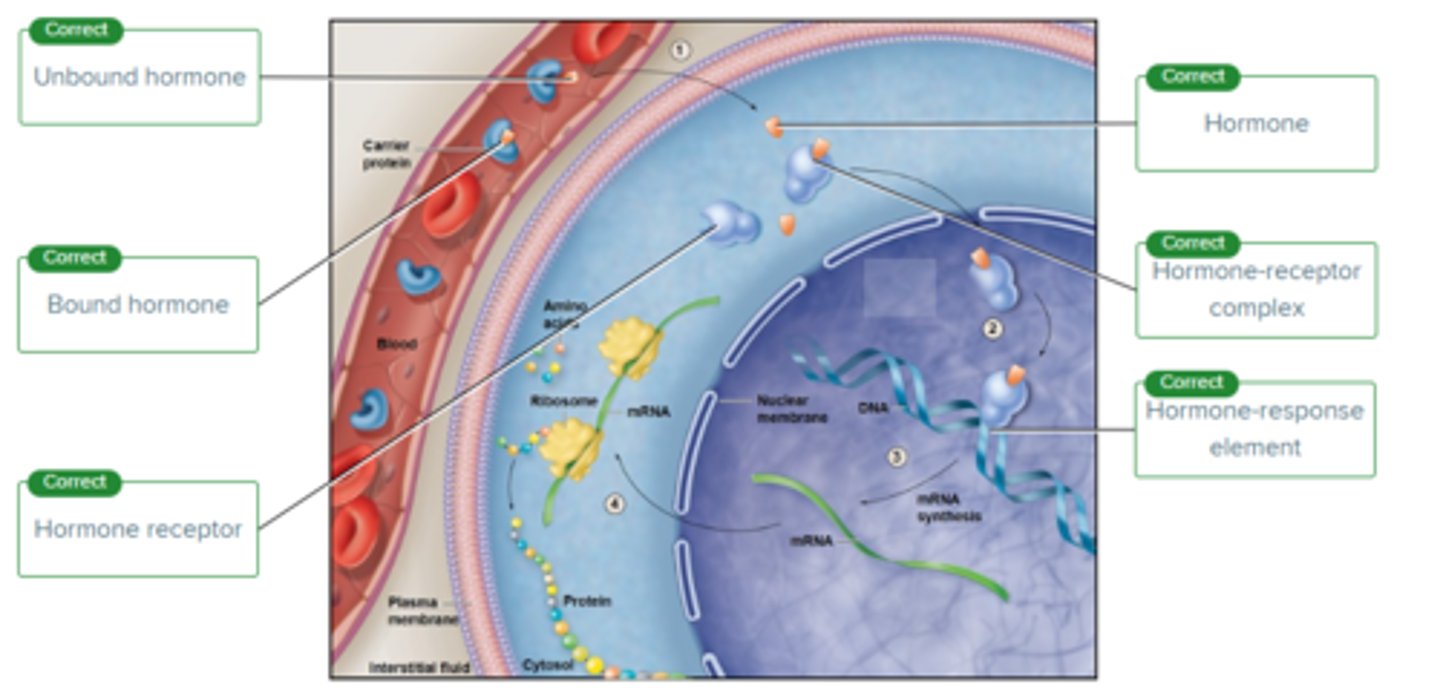
Label the structure involved in stimulation by a steroid hormone.
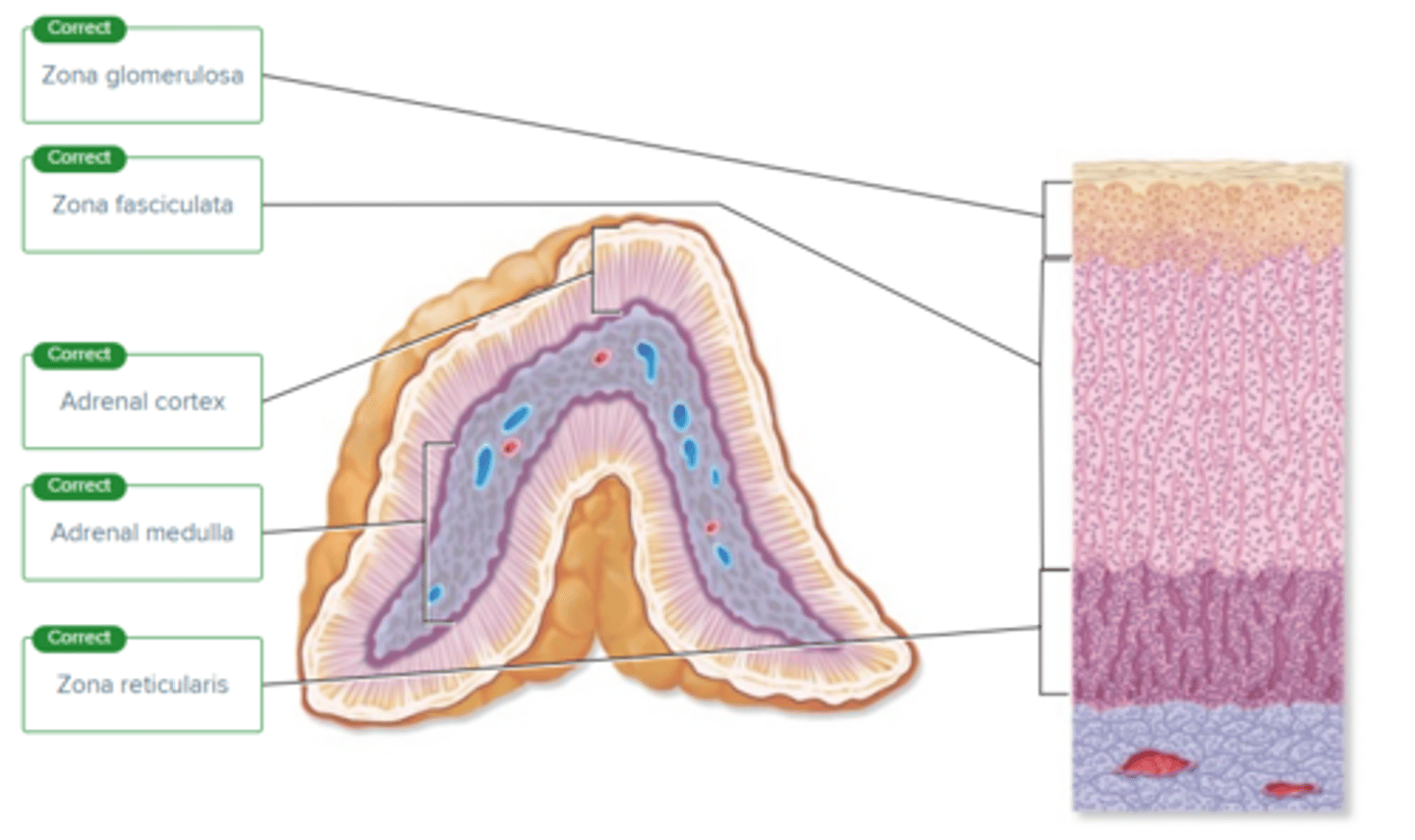
Correctly label the following parts of the adrenal gland.
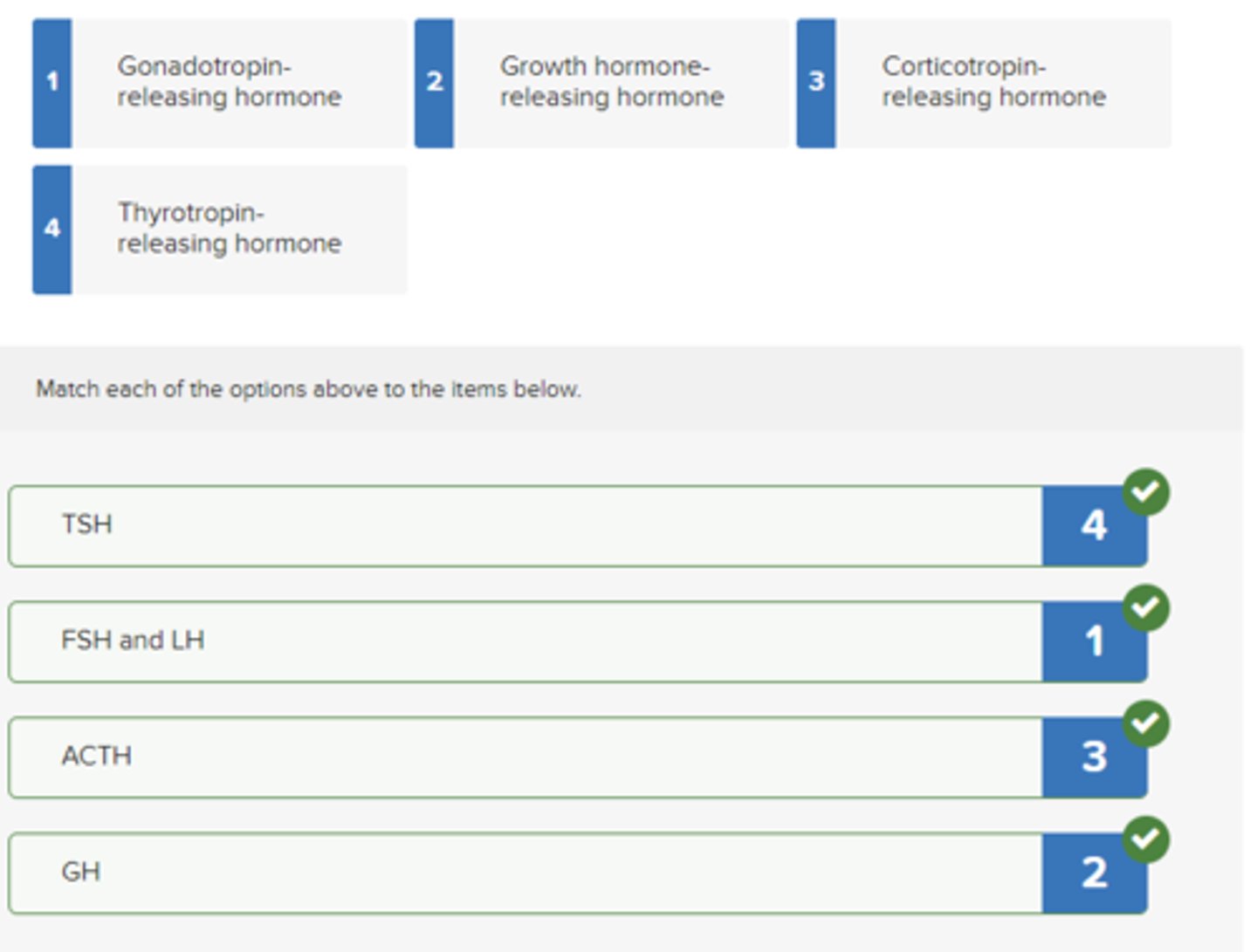
Match the following hypothalamic releasing hormones with the hormone released from the anterior pituitary.
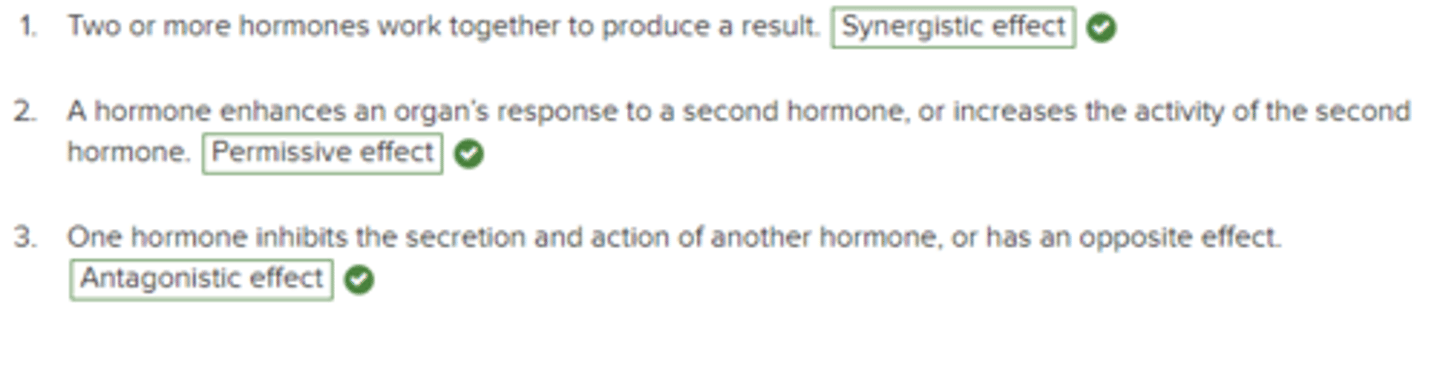
Match the description of the hormone interaction with the correct term.
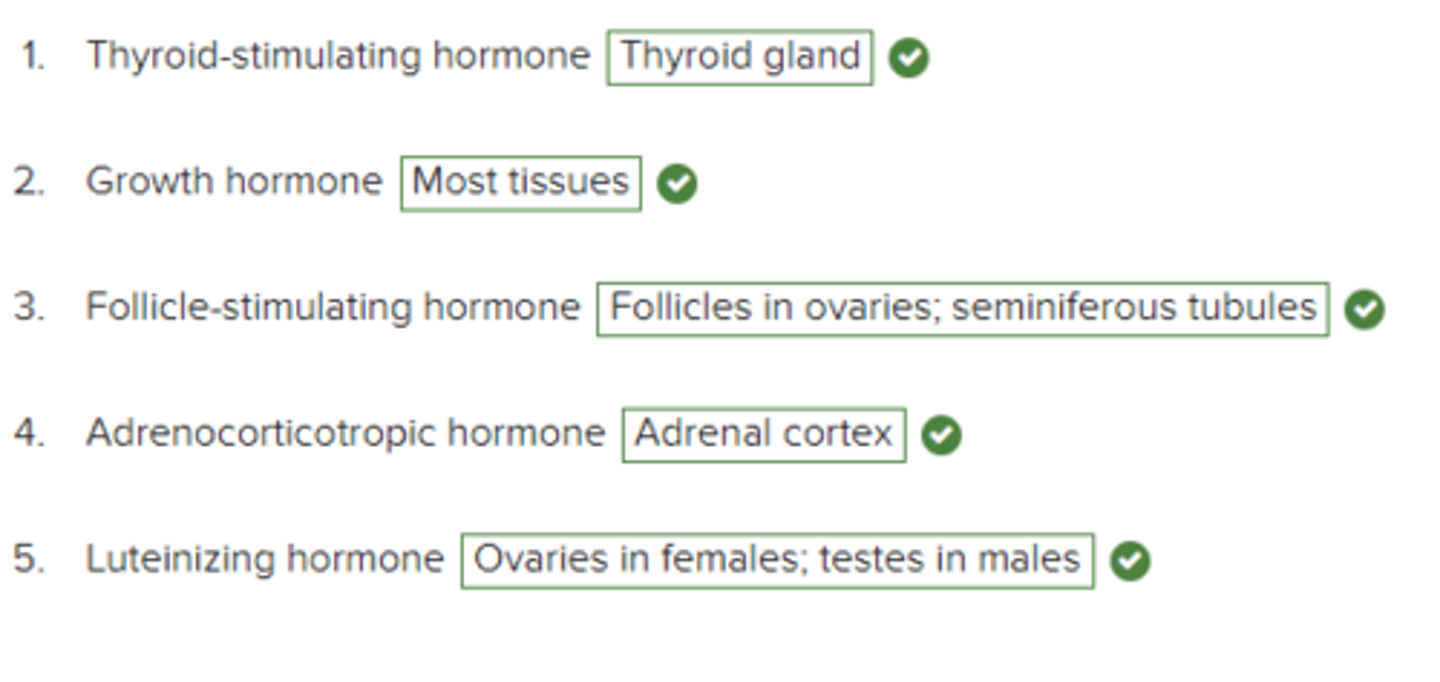
Match the target tissue with the hormone secreted by the anterior pituitary gland.