sci-of-large-molecules
1/131
Earn XP
Description and Tags
lecture 3
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
132 Terms
What is the only biomolecules that is not made of repeating units of monomers?
lipids
What are important properties of biomolecules?
involved in biological processes that are basic to living organisms
necessary for all forms of life
contribute to the structural integrity of cells and organisms
have been conserved throughout evolution due to their important roles
carry out a variety of different types of functions
complex and have diverse structural variations
What is the polymer of an amino acid?
polypeptide (protein)
What is the polymer of a monosaccharide?
polysaccharide (carbohydrate)
What is the polymer of a nucleotide?
nucleic acid (DNA,RNA)
What are proteins made up of?
long chains of amino acids that folded into three-dimensional structures
What is the function of DNA polymerase?
important enzyme in DNA replication
What is the function of proteases?
catalyze the breakdown of proteins in the cell
What is the function of actin?
part of the cytoskeleton
What is the function of collagen?
fibrous protein in connective tissue, like bone and tendons
What is function of transferrin?
transport of iron in the bloodstream
What is the function of hemoglobin?
transport of oxygen in the bloodstream
What is the function of insulin?
signals cells to take up glucose
What is the function of growth factor receptors?
bind and respond to extracellular signals
What is the function of antibodies?
recognize invaders
What is the function of major histocompatibility proteins (MHC)?
recognition of self vs non-self cells
What does the basic structure of amino acids contain?
side chain (R group), carboxyl group (COOH), central carbon, hydrogen atom, amino group (NH2)
How many different amino acids make up proteins?
20
What does the charge of an amino acid depend on?
the pH
What are the different types of side chains that an amino acid can be classified by?
nonpolar side chains and polar side chains
What does it mean to have nonpolar side chains?
no electrically charged regions are formed, hydrophobic, do not participate in hydrogen bonding
What does it mean to have a polar, negatively charged, acidic side chain?
donate protons at neutral pH and what remains is negatively charged
What does it mean to have a polar, positively charged, basic side chain?
accept protons at neutral pH and what remains is positively charged
What does it mean for amino acids to be essential or non-essential?
essential (we need them in our diet), non-essential (we produce them on our own)
What kind of amide bonds are amino acids linked by?
peptide bonds
What are the different shapes that proteins can fold into?
primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary
What happens to a proteins side chains when folded in an aqueous environment?
polar side chains go on the outside of the molecule and can form hydrogen bonds to water, hydrophobic core region contains nonpolar side chains
What characterizes the primary structure of proteins?
sequence of amino acids
What characterizes the secondary structure of proteins?
folding pattern where short stretches of amino acids interact with each other

Which type of secondary structure is this?
alpha helix
What type of secondary structure is this?
beta pleated sheet

What is the common pattern in secondary structure alpha helixes?
hydrogen bonding in which the carbonyl oxygen (C=O) of an amide group forms a hydrogen bond with the hydrogen on the amide group (N-H) of another amine group four residues ahead (I to i+4), along with the polypeptide backbone
What is the common pattern in beta pleated sheets?
hydrogen bonds form between amino acids that may be far from each other in the primary sequence but are close in the folded protein, hydrogen bonds can also form between the oxygen on the carbonyl groups
What characterizes a tertiary structure?
further folding of the chain, residues with hydrophobic side chains tend to be found on the inside of a protein, while hydrophilic residues tend to be on the outside
What characterizes a quaternary structure?
some proteins consist of multiple polypeptides that come together as one protein
What protein structure is hemoglobin an example of?
four polypeptides
What is cytochrome p450 (Cyp450)?
family of enzymes that have important roles in drug metabolism
What are G protein coupled receptors?
proteins involved in cell signaling
What do beta blockers target?
G protein couples receptors
What are beta blockers used to treat?
hypertension, angina, and other conditions
What are antibodies essential for?
immune responses
What are antibodies produced for?
to treat disease
What is the monoclonal antibody used to treat Her2 positive breast cancer?
Herceptin
What do carbohydrates include?
simple sugars (ex. glucose, fructose), complex carbohydrates (starch, glycogen)
What do all monosaccharides have in terms of molecular structure?
carbonyl group (C=O), chiral center (central carbon), terminal carbon (at the end)
What is the second chiral center in a monosaccharide called?
penultimate carbon
What is a structure of monosaccharides with 3 carbons called?
triose
What is a structure of monosaccharides with 4 carbons called?
tetrose
What is a structure of monosaccharides with 5 carbons called?
pentose
What is a structure of monosaccharides with 6 carbons called?
hexose
What kind of monosaccharides are examples of hexoses?
glucose and fructose
What are the different forms that monosaccharides can cycle through?
linear and cyclic (if 5 or 6 carbons)
What is the linear way that monosaccharides can be illustrated?
fischer projection
What are the circular ways that monosaccharides can be illustrated?
chair conformation, haworth projection
What could glucose be broken down into to use for energy?
ATP
Plants can make what types of energy sources from glucose?
starch and cellulose
What monosaccharide is obtained mostly by food, such as fruits and honey, a role in energy production?
fructose
What monosaccharide is important for synthesis of glycoproteins and glycolipids?
mannose
What monosaccharide is a component of lactose, the sugar in milk?
galactose
What monosaccharide is a component of RNA?
ribose
What monosaccharide is a component of DNA?
deoxyribose
What monosaccharide plays a crucial role in carbohydrate metabolism, specifically in glycolysis and gluconeogenssis?
glyceraldehyde (a triose)
What monosaccharide is uncommon and an intermediate in some metabolic pathways such as the pentose phosphate pathway?
erythrose (a triose)
What monosaccharide is not common in mammalian cells, found in cell walls of plants, found in microorganisms, and obtained in diet in beans and peas?
arabinose
What monosaccharide is found in plants and microbes?
xylose
What monosaccharide is found at low levels in plants and microbes?
lyxose
What monosaccharide is not common in nature and used industrially (cosmetic, tanning)?
erythrulose (a ketotertrose)
What are disaccharides?
two monosaccharide units
What are lactose and sucrose examples of?
disaccharides
What are oligosaccharides?
3-10 monosaccharides
What are polysaccharides?
more than 10 monosaccharides (can be thousands)
What are glycogen, cellulose, and starch examples of?
polysaccharides
What kind of bond are disaccharides bound by?
glycosidic
What is the term for the addition of carbohydrates to proteins, lipids, and other sugars?
glycosylation
What are TAGs?
tumor associated glycoproteins in cancer cells
What are exciptients?
vehicle for drug delivery that often contains carbohydrates
What kind of ingredients are in excipients?
inactive ingredients
What is the use of glucose for energy, or storage of glucose in the form of glycogen?
metabolism
What are the basic components of DNA?
genetic information storage
What are the basic components of RNA?
transcription of genes and translation of proteins
What do nucleotides consist of?
5 carbon sugar, phosphate group, nitrogen base (nucleobase)
What are a nitrogen base and sugar together called?
nucleoside
What are the major bonds in DNA?
phosphodiester bonds (backbone) and hydrogen bonds (base pairing)
How does DNA fit in the cell?
condensed by being packaged with histones, coiled around the histones to become super coiled, takes the form of a chromosome
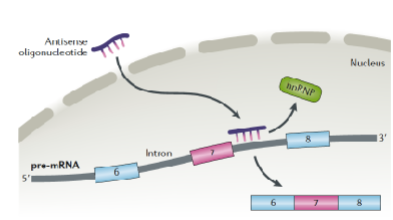
What is an antisense drug that alleviates symptoms of SMA (Spinal Muscle Atrophy)?
spinraza
What condition is caused by a mutation in the SMN1 (survival of motor neuron 1) gene?
SMA (Spinal Muscle Atrophy)
What is SMN2?
gene that can make SMN, but at lower levels and often truncated, due to alternative splicing
What binds the SMN2 RNA (but not the SMN1 RNA) and prevents splicing at the junction between exon 7 and the intron?
hnRNP (heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoproteins)
What kind of nucleotide is Spinraza (nusinersen)?
oglionucleotide
What does Spinraza do?
binds RNA and prevents binding of the hnRNP, restores a splice site so that exon 7 is not removed, then full length SMN can be produced from the SMN2 gene to compensate for the lack of SMN1 gene
What is characteristic of lipids?
include fats, oils, and steroids such as cholesterol, hydrophobic molecules, long hydrocarbon chains or ring systems
What are lipids in terms of energy?
major source of energy storage in the body and stored in adipose tissue as triglycerides (TAG)
What forms the lipid bilayer of the cell membrane?
phospholipids
What do lipids do in terms of insulation and protection?
help to regulate body temperature and cushion organs and tissues
What do lipids do in terms of cell signaling?
regulate cell growth, differentiation, and apoptosis
What do lipids do to apoptotic cells?
remove
What is the simplest form of lipids?
fatty acids
What do fatty acids generally contain?
a carboxyl group (COOH)
What is characteristic about saturated fatty acids?
no double bonds, saturated with H atoms, more difficult to melt, high MP
What is characteristic about cis unsaturated fatty acids?
monosaturated or polyunsaturated, easier to melt because they don’t pack together well