Regression 2 - term 2 L4
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
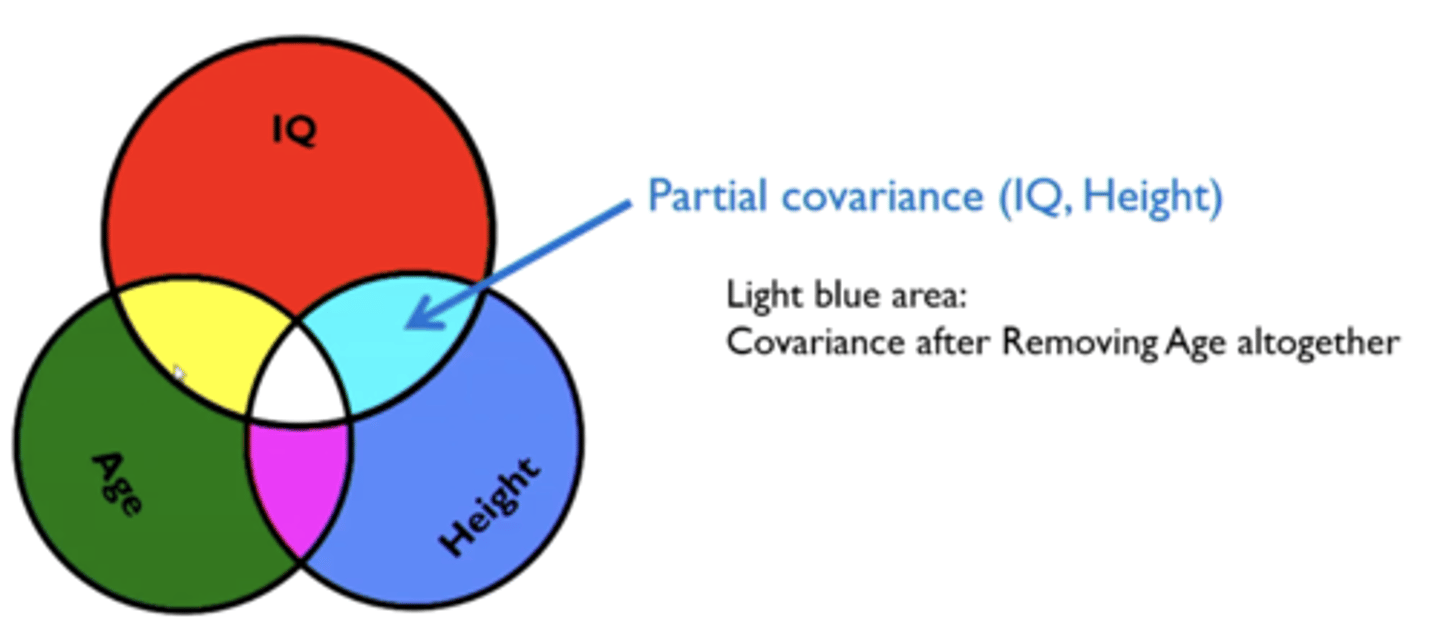
What is a partial correlation?
measures the relationship between two variables, while controlling for the effect of one or more other variables.
- e.g Anxiety (A) and Sleep Problems (S)You also know that Stress (T) is related to both.
- A partial correlation would remove the effect of stress, and show you the "true" correlation between anxiety and sleep problems, without stress as a confound.
What is multiple linear regression?
a single criterion variable but many predictor variables
(partial correlation is just two)
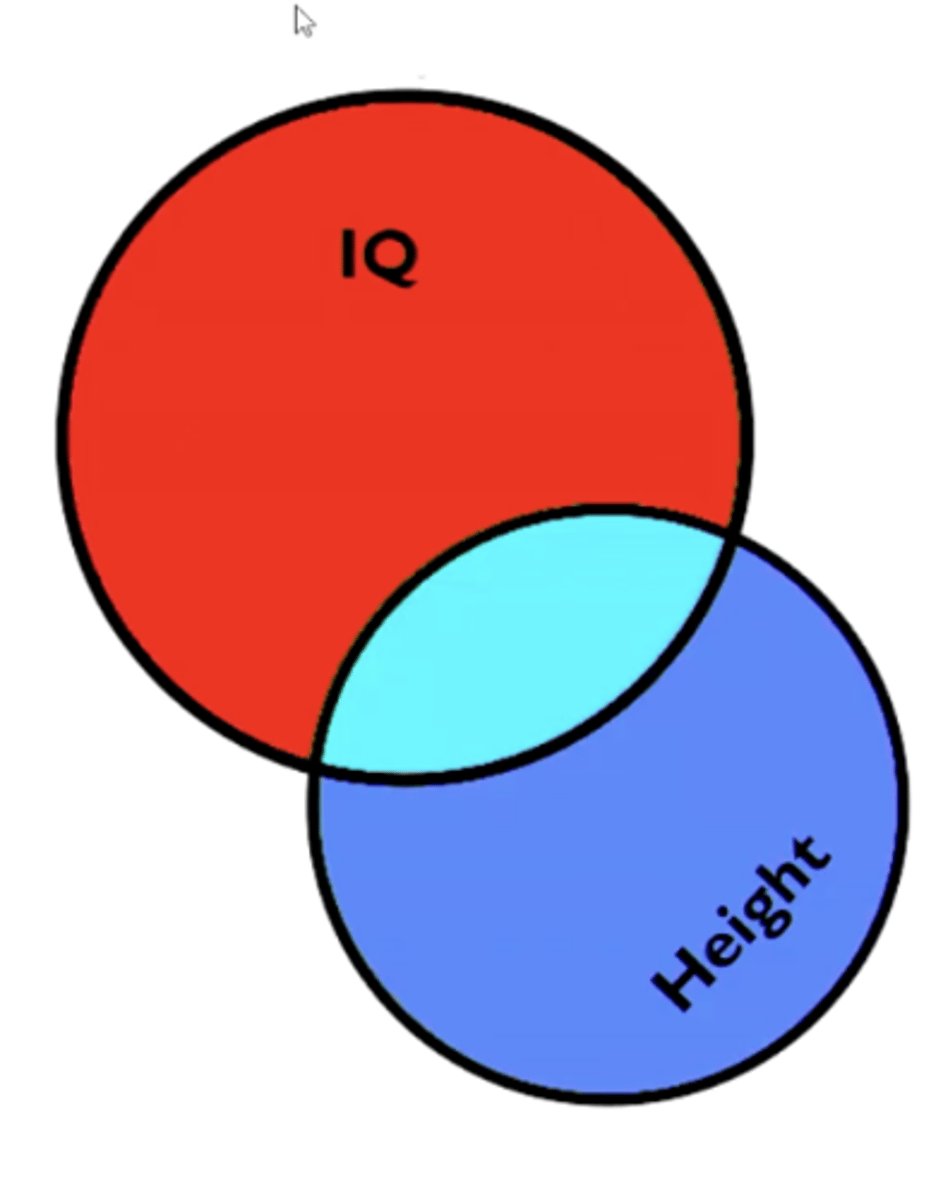
in a regression analysis, what does R^2 reflect? (coefficient of determination)
The proportion of total variance (SST) explained by predictors/model (SSM)
(the proportion of the light blue against the entire circle area of IQ)
- RED area is the residual (unexplained by height)
how does a multiple correlation coefficient link to coefficient of determination?
it is the Square root of R^2 (R).
What is the F ratio in a regression model?
the ratio of explained variance against residual (error) variance.
How is R^2 calculated?
its the model variance (SSM) divides by the total variance SST
How is the F value calculated?
it is the model variance (SSM) divided by the residual SSR (error)
What does a higher F-ratio indicate?
A better model
What is Cohens f?
A way of estimating the effect size for a multiple linear regression
= R^2 / (1-R^2)
What is a small effect size?
0.02
what is a medium effect size?
0.15
What is a large effect size?
0.35
What is multicollinearity?
when there is a high similarity between two or more predictor variables.
What threshold correlation would indicate multicollinearity
r > 0.9 between predictors
What is singularity?
when a variable is entirely redundant because it is a combination of two of more other variables.
- linear dependency.
- extreme form of multicollinearity and impossible to compute.
What are bivariate regression results?
the results between one predictor variable and the criterion variable
what indicated multicollinearity when individual predictor variables are inputted into a full model.
you see completely different results from the full model to the bivariate regression results.
- high correlation between predictor variables.
- if variables are correlated, it changes how much one predictor variable explains the criterion variable.
What is tolerance?
a way of detecting multicollinearity - the goodness of fit of one predictor variable with all the others.
What tolerance scores would suggest that multicollinearity is present?
Low tolerances
< 0.1
What is a simultaneous multiple regression?
when all predictor variables are presented all at once
- if anova is sig, look at individual predictor variables
What is a stepwise multiple regression?
start with one randomly chosen predictor variable and do the regression analysis and then keep randomly adding more.
- then choose the best fitting model.
Why may a stepwise multiple regression be problematic?
risk of a type one error accumulation/over fit of the data
- the more predictor variables inputted, the higher the chance is that one will explain the criterion variable by chance.
- should not be used as a statistical inference tool
What is a Hierachical multiple regression?
- based on priori knowledge of variables (relationship exists) but interested in added explanatory power of a new variable.
- plausible theoretical justification needed for each variable.
What happens in a hierachical multiple regression?
- Several subsequent regression models are analysed
- use this to assess how much better one model explains the criterion variable than another. (delta R^2)
How do outliers affect multiple linear regression?
They are points with deviate substantially from most of the others.
- can have a disproportionate effect on the linear regression fit.
What measures the extremity of an outlier?
Cook's distance
What value of a cooks distance indicates an extreme outlier?
values greater than 1.
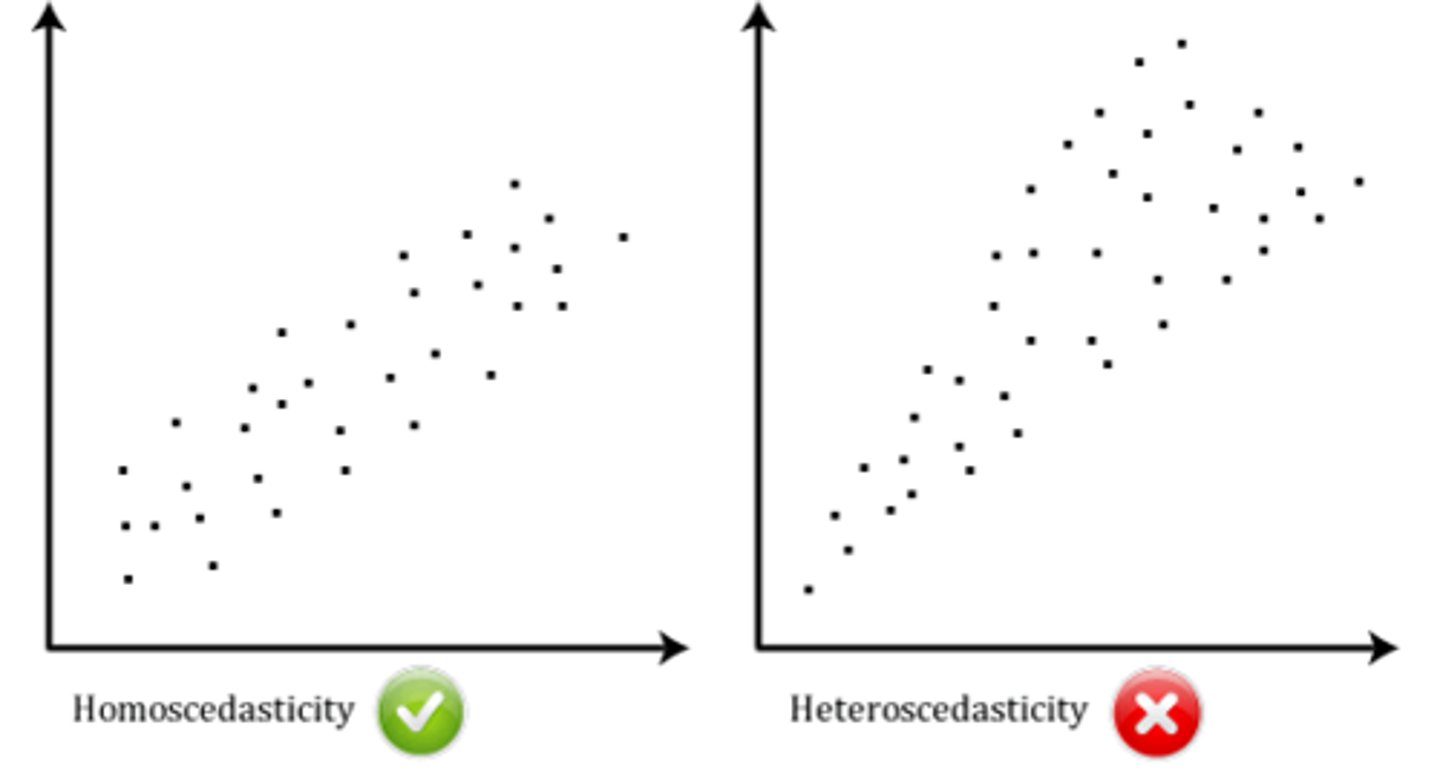
What is Scedasticity?
the distribution of the residual error (relative to the predictor variable)
What is Homoscedasticity?
When residuals stay relatively constant over the range of the predictor variable.
What is Heteroscedasticity?
When residuals vary systematically across the range of the predictor variable.
What should be high compared to the number of predictors?
Number of participants/observations to allow generalisability.
Which test assesses the predictor variables?
The F-test
What correction term corrects for the number of predictor variables?
The adjusted R^2
What is the rule of thumb for the participant to predictor variable ratio?
N > 50 + 8 x m
m = number of predictor variables
What is it called when the number of predictor variables are higher than the number of observations?
Overfitting
In a multiple regression analysis, what has to be normally distributed?
THE RESIDUALS!!
- not the raw data
- an assumption has to be made that the residuals are normally distributed.