Final exam
1/180
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
181 Terms
sweden hunt club
stags compete for hinds, harem polygyny
sweden hunt club
castle that manages animals similarly to the way we do domesticated
sweden hunt club
dominance hierarchy among stags, which is important for "peace"
sweden hunt club
European hunt clubs privately own game
red deer
what animal is most prized in the sweden hunt club
sweden hunt club
had a lottery where people would win a chance to shoot a certain animal
disrupted the social hierarchy, errupting in chaos
what happened when someone illegally shot the largest red deer buck in the sweden hunt club?
rose petal effect
The removal of all deer in one rose-petal cluster may produce a long-term effect at low rates of recruitment and dispersal.
rose petal effect
- local matrilines
- has management implications
- removal/treatment is more long-lasting if conducted by matriline
red wolf (canis rufus)
45-80 lbs
diet: deer, rabbits, raccoons
was reduced to a remnant population by the 1900's
red wolf (canis rufus)
the last remaining of these were captured in 1973 and placed in captivity for captive breeding
red wolf (canis rufus)
- declared extinct in the wild in 1980
- reintroduced in 1987 in 5 counties in North Carolina
red wolf (canis rufus)
these animals reaches a high of 50-75 in the wild but now there is only 15-17 left. There are 240 in captive facilities
human persecution (intentional and accidental) and hybridization with coyotes
two main recovery challenges of the red wolf (canis rufus)
placeholder concept
recovery plan where other species in outside territories are sterilized to prevent hybridization of declining species, essentially creating a buffer
(alpha) coyotes in the surrounding areas of the red wolf territory were sterilized (50) so that that there was no hybridization between them and the red wolves. The sterilized coyotes kept their places, so no new coyotes came into the territories
what is the placeholder concept when applied to the red wolf species?
p22
los angeles mountain lion that the public loved and tracked
separation by urbanization (highways)
what was the issue for the los angeles mountain lions?
- high mortality (intraspecifc strife)
- reduced genetic diversity
lack of dispersal from los angeles mountain lions led to:
land overpass
solution to los angeles mountain lion dispersal issue
fission-fusion social system
group members reside within same home range, maintain closer relations than in other groups, but separate into smaller subgroups on a regular basis.
elephants
what species has a fission-fusion social system?
they are selectively poaching older matriarchs, which disrupts the entire social network and removes critical social partners with ecological knowledge and access to resources
how does poaching harm the social systems of elephants?
elephants
which species exhibits compensatory bonding to build resistance to loss and provide help to orphans
mortality rate
number of deaths
reproductive rate
number of births
immigration
contributing to a population without births
emigration (dispersal)
taking away from population without deaths
reproductive rate and survival (mortality) rate
2 vital rates
number of births, deaths, immigrants, and emigrants
what causes population sizes to change?
dN/dT (size of population divided by time)
change in population formule
birth rate - death rate - immigrants + emigrants
change in population: dN/dT = ...
bN - dN (birth rates minus death rates)
dN/dT (change in population) = ...
positive (increasing)
if B>D (birth rates are greater than death rates), then the population is
stable
if B = D (birth rates equal death rates) then the population is
negative
if B<D (birth rates are less than death rates) then the population is
r
replace term B-D with....
r
population growth rate symbol
dN/dT = rN
population growth rate formula with r
limiting factor
any condition that prevents a population from attaining unlimited growth at r
extrinsic factors
factors that come from outside the individual: weather, water, food, disease
intrinsic factors
factors that come from inside the individual: social behavior, infanticide, reduced reproduction
density dependence
profound influence that a population's density has on the vital rates of individuals in the population; changes in vital rates in turn lead to changes in population growth rate
negative density dependence
high numbers lead to negative feedback, limiting the growth of a population
effect of negative density dependence
increase in density can increase competition
effect of negative density dependence
increase in density can heighten susceptibility to predation and/or disease
direct interference or exploitative
competition can occur as...
type 1
low risk of juvenile death, higher risk in older ages
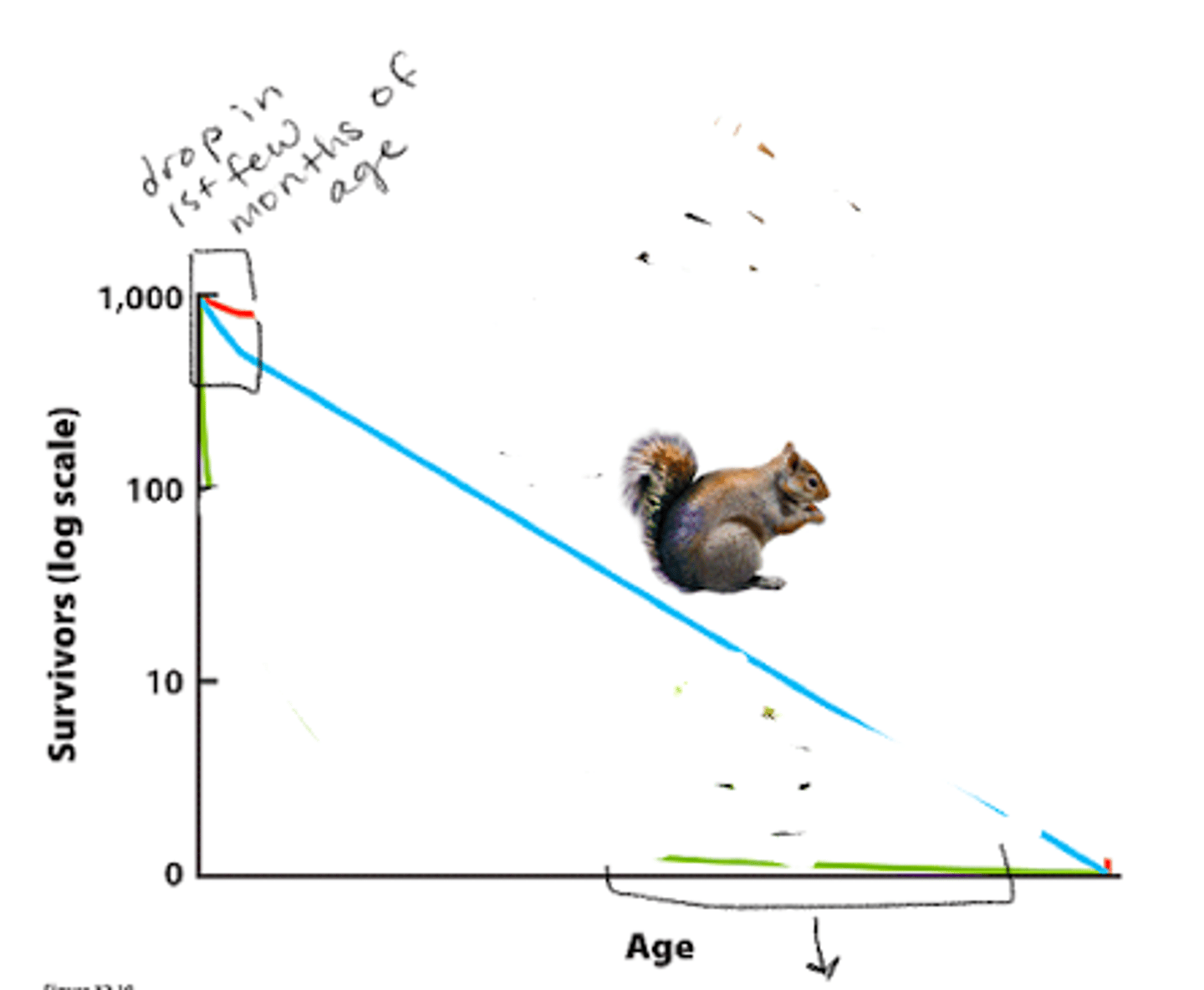
type 2
constant risk of death in all ages (linear)
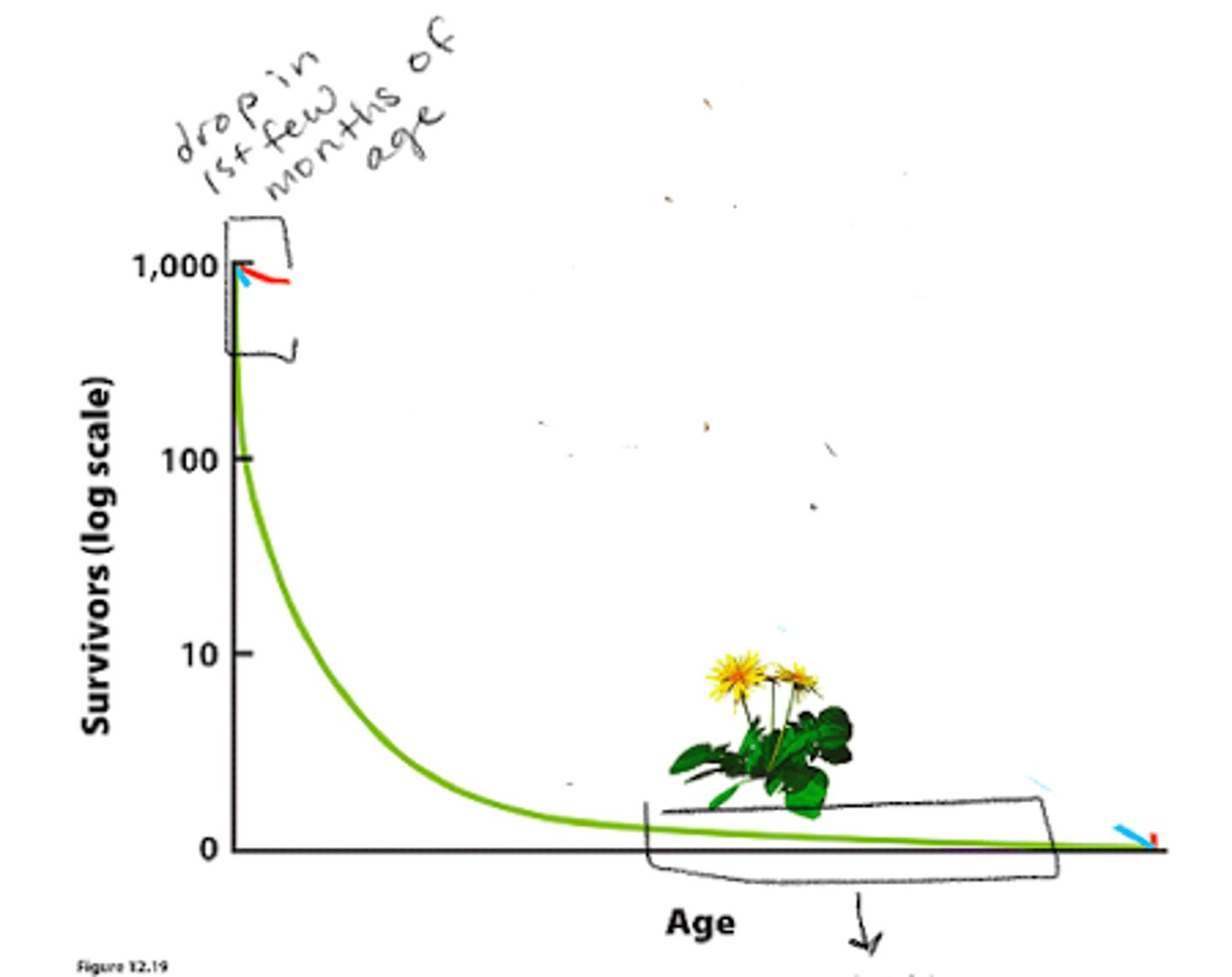
type 3
high risk of juvenile death but long life expectancy
type 1
surivorship curve
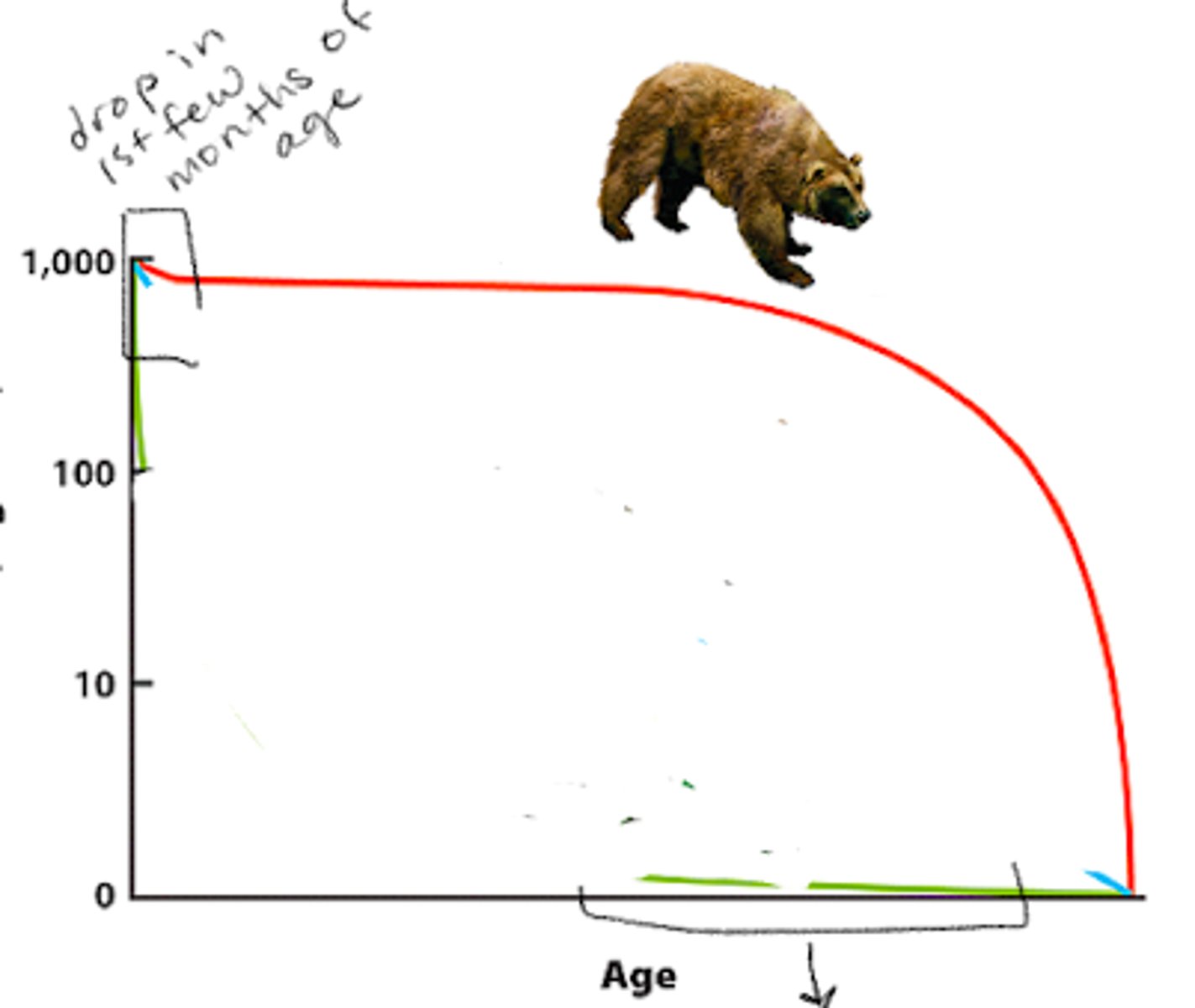
type 3
survivorship curve
type 2
survivorship curve
type 3
what type of survival curve is this?
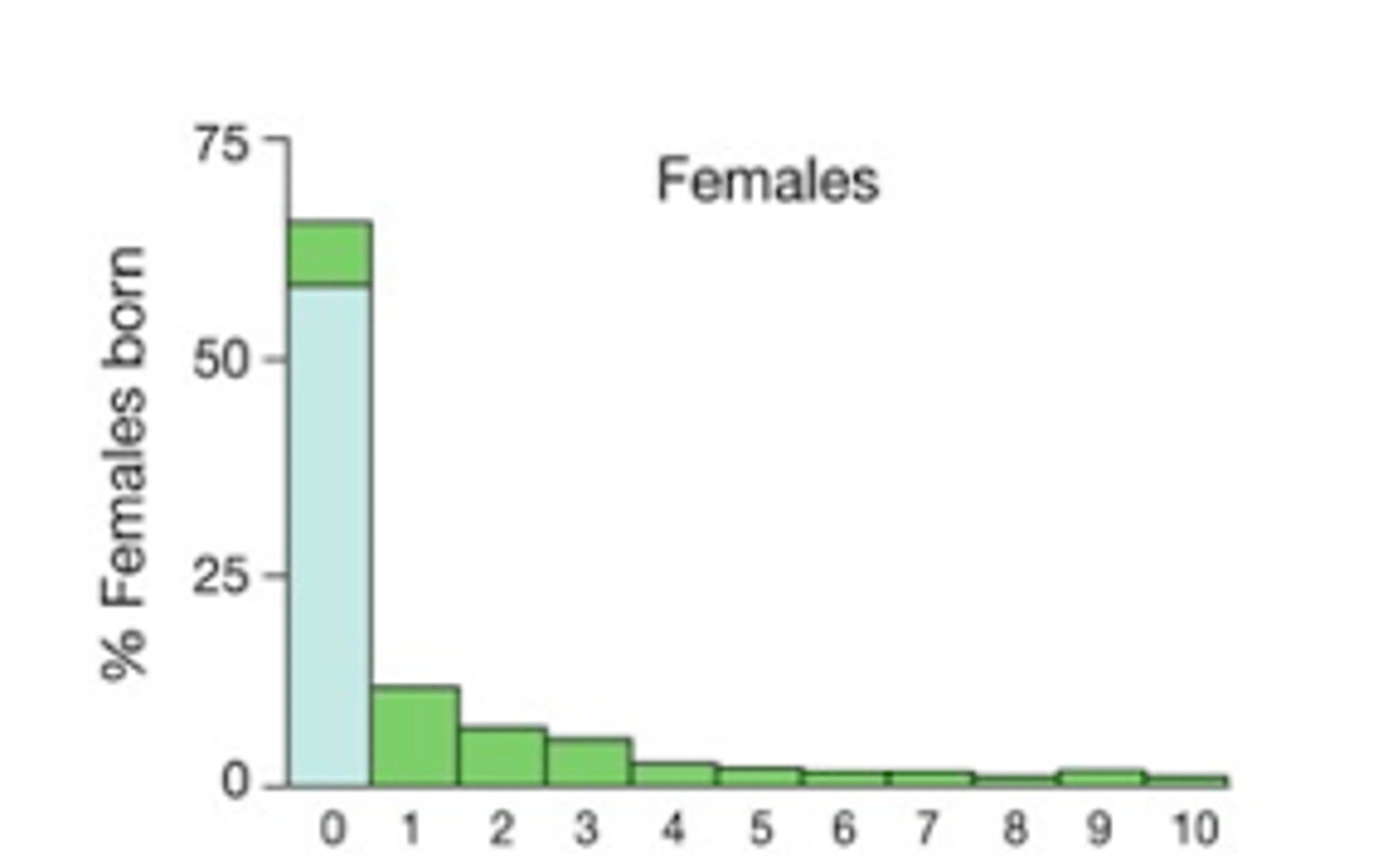
positive density dependence
(very rare) an increase in numbers results in an increase in vital rates or population growth
group hunting by some large predators (african wild dogs in a pack mean higher success rate when hunting)
instance where positive density dependence is possible
minimizing predation, foraging advantages, finding mates and caring for young, and temperature tolerance (huddling for warmth)
possible mechanisms leading to positive density dependence
single-species
logistic model that is useful in understanding carrying capacity and maximum sustained yield concepts
multi-species models
logistic model that is useful for understanding predator-prey relationships
logistic growth curve
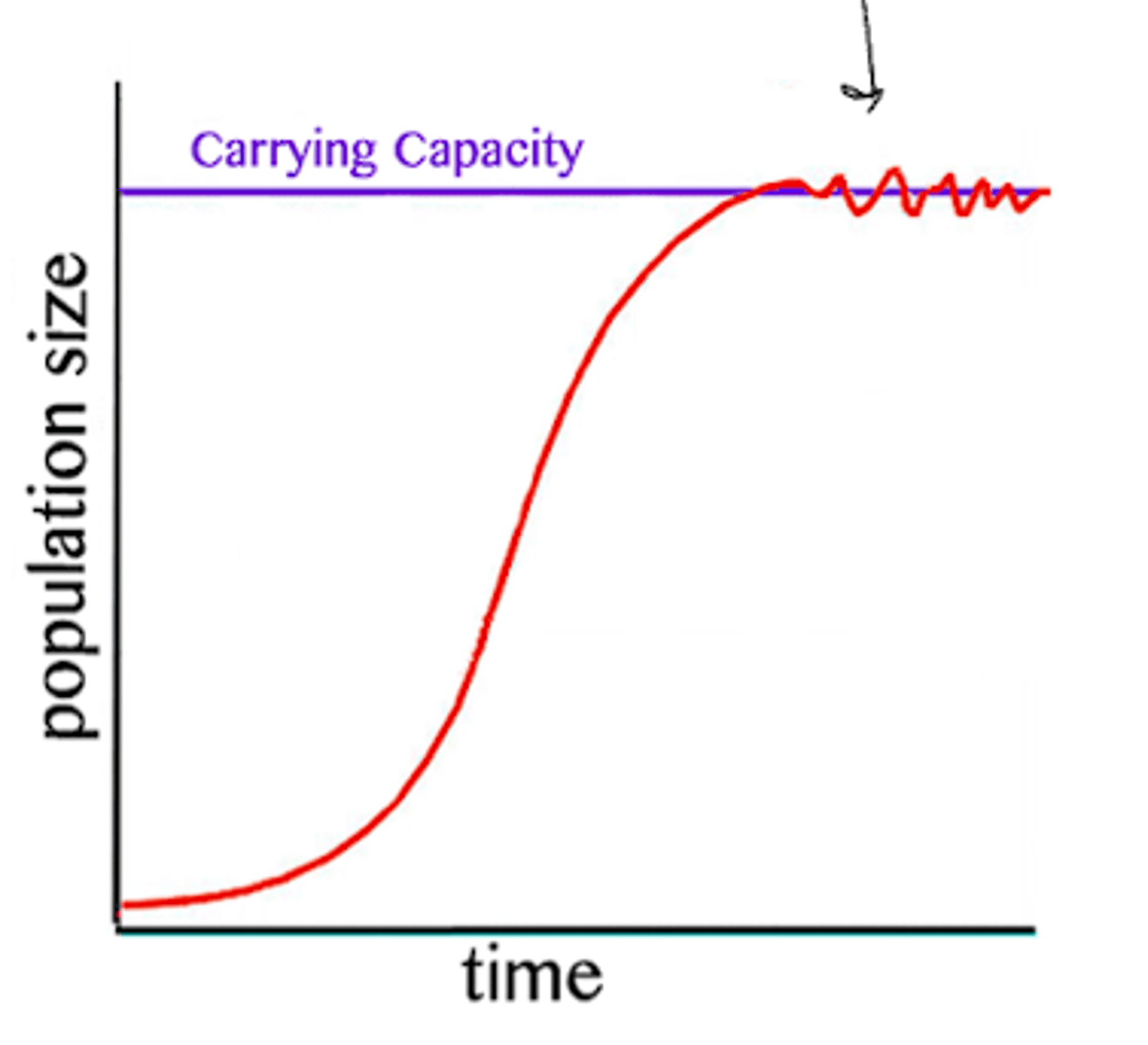
dN/dT = [(rmax)(N)] x [K - N/K]
logistic growth curve equation
population that can exhibit logistic growth
ones that are limited by a consumable resource
population that can exhibit logistic growth
one that is limited by social behavior (territorial animals can't grow if there's no space left)
population that can exhibit logistic growth
one that is limited by availability of a non0renewable resource, like nest sites
r species
species that have an unstable environment, and are density independent
r species
small organism size
r species
low energy used to make each individual
r species
many offspring produced
r species
early maturation
r species
short life expectancy
r species
one lifetime reproductive events
r species
type 3 survivorship curve
k species
species that live in a stable environment, with density depended interactions
k species
large organism size
k species
high amount of energy used to make each individual
k species
few offspring produced
k species
late time of maturation with lots of parental care
k species
long life expectancy
k species
more than one reproductive event in lifetime
k species
type 1 or 2 survivorship curve
r species
known to be "irruptive species"- population quickly explodes and can crash just as quick
muskrat
example of r species that had multiple population booms and crashes
yellowstone national park wolves
in contrast to the muskrat population, this species exhibits consistent levels in their population
prey abundance
strong extrinsic factor that helps regulate yellowstone wolf population
intrinsic factors
when at carrying capacity (K), what regulates the population?
compensatory mortality
the affect of one kind of mortality influences the affect of another source of mortality. this has less impact on the population
additive mortality
the affect of one kind of mortality is independent of other sources of mortality. this has a bigger impact on the population
compensatory
is starvation a compensatory or additive mortality?
taking snapshots of population and looking at their characteristics
population demography
changes in a population over time
population dynamics
intrinsic factors
is rate of change within a season influenced by intrinsic or extrinsic factors?
a high survival rate
species with a low reproductive rate have...
a low survival rate
species with a high reproductive rate have...
fibromatosis
disease in deer where they have giant raised bumps in the skin that are not inherently dangerous but can inhibit eating and vision
bot fly larvae
parasite that affects mice and mammals that buries into their skin and lays eggs. non lethal
disease
an alteration of the state of the body and some of its organs which interrupts or disturbs the proper performance of body functions
zoonotic disease
an animal disease that is transmissible to humans
enzootic disease
an animal disease that occurs almost constantly in a population, but only affects a few individuals at any given time
epizootic disease
an animal disease that attacks large numbers of individuals simultaneously and does not persist long-term
primary pathogens
cause disease as a result of their presence or activity within the normal, healthy host