Bio Foundations 4.1
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
binary fission
a type of asexual reproduction where a cell splits into two identical daughter cells
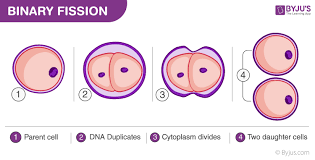
4 steps of binary fission
DNA replication
the chromosome is duplicated so that the cell has two complete copies of its DNA sequences
chromosome segregation
the two copies of the chromosome are physically separated to the opposite ends of the cell
cytokinesis
the cell membrane pinches in the middle to separate the two cells
cell separation
the pinched membrane combines with itself so that the two separate cells are made
interphase
the periods between rounds of mitosis
3 major phases of interphase
first gap (G1) phase
the phase of growth and performing physiological jobs
synthesis (S) phase
the phase where the cell’s chromosomes are copied
second gap (G2) phase
the phase used by the cell to prepare for mitosis
involves DNA proofreading
eukaryotic chromosomes
eukaryotes have multiple
linear in shape
stored in the nucleus
DNA is twisted around proteins called histones
form nucleosomes, which are twisted together into a chromosome by supercoiling

prokaryotic chromosomes
prokaryotes have only one
circular in shape
stored in the nucleotide, a region of the cytoplasm
twisted around itself by supercoiling
human chromosomes
humans have 46 total and 23 nearly identical pairs
every cell in an individual has one complete set from each parent
the 23rd pair may be an XX or XY
How do chromosomes look in interphase vs. mitosis?
During interphase, chromatin spreads out to fill the entire nucleus. During mitosis, chromosomes condense into smaller, densely packed structures.
homologous chromosome
pairs of chromosomes that have the same genes, though not necessarily identical copies of those genes
sister chromatids
identical copies of a chromosome that are attached together
centromere
the constricted region of a chromosome where sister chromatids are joined together
cohesions
proteins that stick sister chromatids together at the centromere
kinetochore
a protein structure that assembles on the centromere of chromosomes and acts as the attachment site for spindle microtubules
6 stages of mitosis
prophase
chromatin condenses into dense, distinct mitotic chromosomes
prometaphase
the nuclear envelope breaks apart and releases the chromosomes into the cytoplasm
the mitotic spindle attaches to the chromosomes
metaphase
the mitotic spindle makes small adjustments that line up each homologous chromosome at the middle
anaphase
digestive enzymes destroy cohesins holding the sister chromatids together
the mitotic spindle pulls the chromatids to the opposite ends of the cell (chromosome segregation)
telophase
the nuclear envelope re-forms around the segregated chromosomes
mitotic chromosomes de-condense into chromatin
cytokinesis
cytokinesis in animal vs. plant cells
animal cells
the mitotic spindle breaks down
a ring of protein attaches to the plasma membrane and pinches the membrane together
the plasma membrane combines with itself to produce two separate cells
cell separation
plant cells
the mitotic spindle remains to assemble vesicles made by the Golgi apparatus at the middle of the cell, which contain the materials needed to build the plant cell wall
vesicles combine together to form a cell plate that creates two separate cells
cell separation
after cell separation, the mitotic spindle breaks down