Beta Oxidation
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
Once the fatty acyl- CoA is inside the matrix what happens?
It undergoes beta oxidation
Overview of beta oxidation function
Chops the fatty acid two carbons at a time (from the carboxyl end).
Releases acetyl-CoA, which can enter the citric acid cycle.
Generates NADH and FADH₂, which go to the electron transport chain for ATP production.
Beta oxidation cosists of four continuous steps:
Oxidation → makes a double bond
Hydration → adds water
Oxidation → makes a ketone
Thiolysis → cuts off acetyl-CoA (2 carbons)
happens each time the fatty acid is shortened by 2 carbons in β-oxidation.
Step 1 beta oxidation:
Oxidation by FAD forms a double bond between the alpha and Beta carbons of fatty acyl-CoA (alkane → alkene)
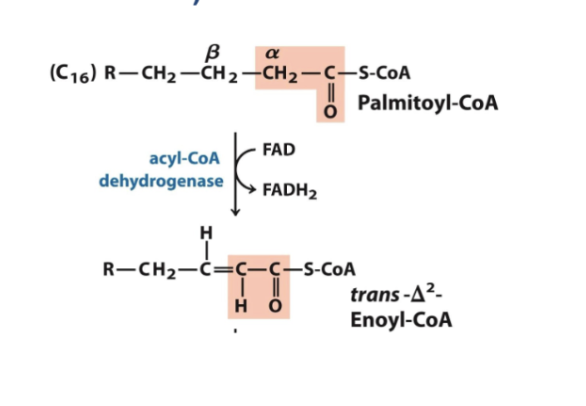
you can see which is alpha (the one beside the carbonyl carbon) thats where
In this process we lose two hydorgens and these 2 hydorgens are used to convert FAD to FADH2.
Step 2 Beta oxidation
Water is added across the double bond to give an alcohol at the beta carbon (hydration → alkene → alcohol)
the double bond is back to saturated
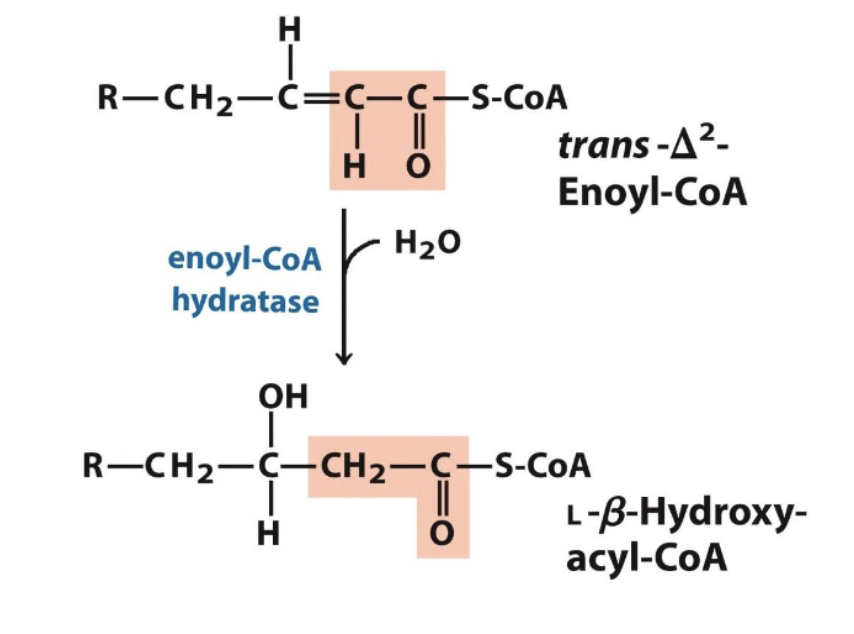
Step 3: Beta oxidation
Oxidation of the alcohol by NAD+ this this causes loss of 2 hydrogens and a ketone at beta carbon
NAD+ becomes NADH + H
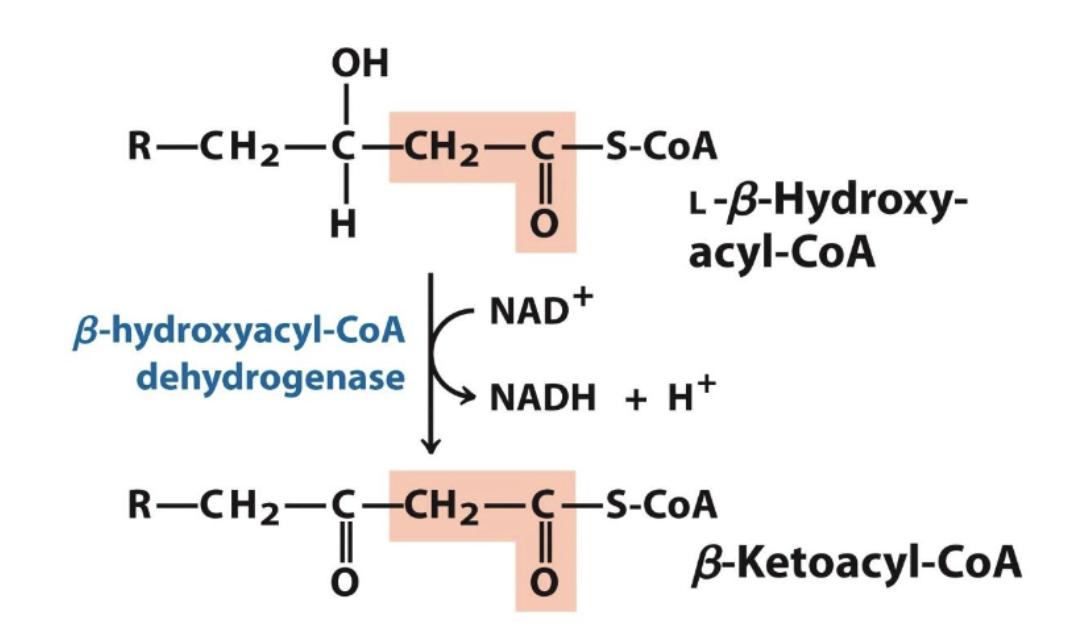
Step 4 beta oxidation:
Lysis of the bond between alpha and beta carbons (thiolysis) a sulfer group is added ot do this
Another Acetyl coA comes in attacks the Beta carbon ketone
Now fatty acid is shortened by 2
the cycle can contineu and shorten the next fatty acids on the chain
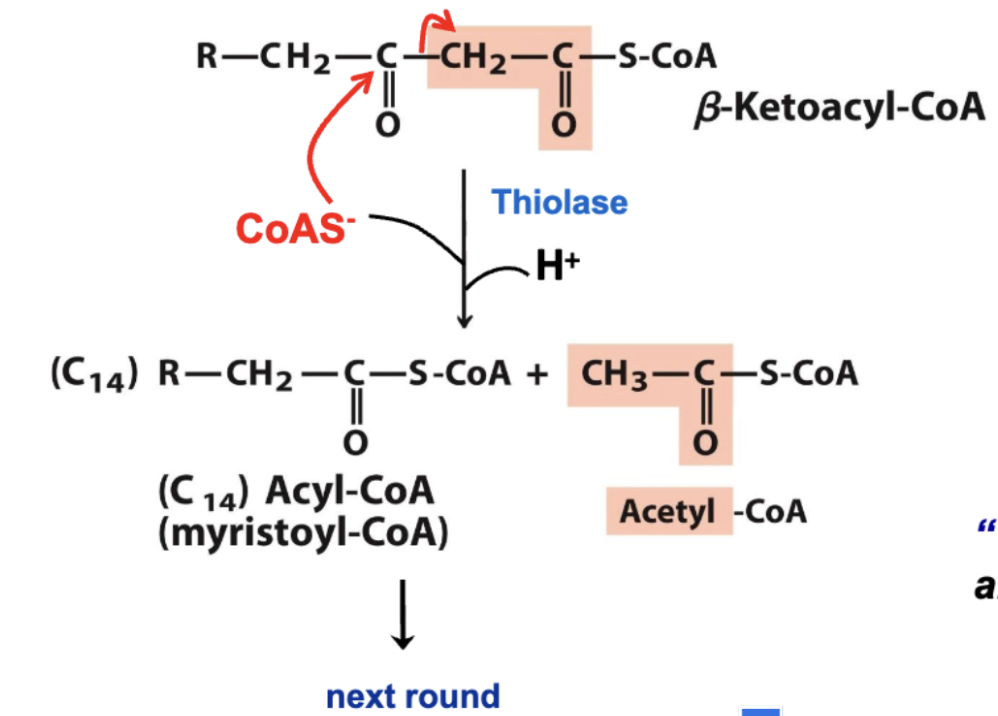
left with 2 products Acetyl-CoA which is the part in orange attached to the S (2 carbons)
the original fatty acid minus two carvbons
Acyl-CoA vs Acetyl-CoA
Acyl-CoA = any length fatty acid attached to CoA → what we start with
Acetyl-CoA = the 2-carbon version (final product of β-oxidation)
Each round of β-oxidation does 4 steps (oxidation, hydration, oxidation, thiolysis) and:
Releases 1 acetyl-CoA (2 carbons)
Shortens the fatty acid by 2 carbons
When does beta oxidation end?
when the entire fatty acid chain is converted into acetyl-CoA units
Palmitic acid Beta oxidation example → 16 carbon fatty acid
requires 7 cycles - BECAUSE IT HAPPENS BETWEEN THE BONDS

16/2-1=7
What does each cycle of Beta oxidation release?
1 FADH₂
1 NADH
These coenzymes enter the electron transport chain to produce ATP.
What happens after beta oxidation?
The acetyl-CoA produced enters the citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle) where it is further oxidized to CO₂, producing additional GTP, NADH, and FADH₂, contributing further to cellular energy.
If you know the number of carbon atoms in a fatty acid (e.g., 16), how can you calculate the number of acetyl-CoA, NADH, and FADH₂ molecules produced during β-oxidation?
Acetyl CoA → divide 16 by 2
NADH and FADH2 would be would ever 16/2 is - 1
Complete beta oxidation of a 20-carbon saturated fatty acid will yield:
10 acetyl coA; 9 NADH, 9 FADH2