ANSC 300 Respiratory System
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
Functions of the Respiratory Tract
Exchange of gases
Respiratory pump
Regulation of body pH
Protection from inhaled pathogens/foreign objects
Vocalization
Water & heat exchange
inhale: warm/humidified
exhale: cool/water
Ventilation and Respiration are Not the Same Thing.
True
Ventilation
mechanics of breathing
Respiration
exchange of gases between and animal and its environment
Upper Respiratory Tract
nasal cavity
pharynx
larynx
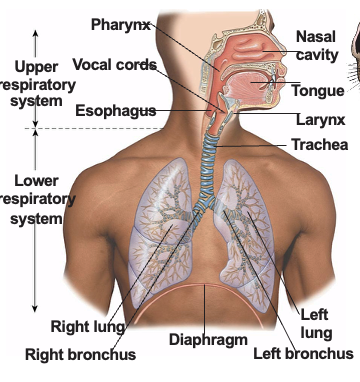
Lower Respiratory Tract
trachea
primary bronchi
lungs
Concha
mucosa-covered turbinate bones
Epiglottis & Vocal Chords
epiglottis: prevents the entrance of food into the trachea
phonation: sound production
located in the upper respiratory tract: larynx
Trachea
cartilage rings incomplete
Bronchi Split into ______ ______
primary bronchi
Bronchioles
smallest airway division
Alveoli
single layer of epithelium
key site of gas exchange = smallest functioning unit of the respiratory tract
Type 1: Gas Echange
Type 2: Secrete Surfactant
Each Branch of the Airway is Called a ________
generation
Why does the Cross-Sectional Area (CSA) Increase with each Generation?
Decreased Velocity = better exchange at capillaries
Decreased Pressure = protects small vessels
Increased Surface Area = increased efficiency of diffusion
Increased Volume Capacity = stabilized blood flow
The Number of Lobes can Vary By Species
L = 2
R = 3/4
Thoracic Cavity
lungs and heart
the pleura lines the chambers
visceral: inner layer, moves with the lungs during breathing
parietal: outer layer, lines the inside of the chest wall
Mediastinal Space: the space between pleural cavities
Pleura
allow for almost friction free movement of the lungs
made of connective tissue
25-30 mL in a 70 kg man
important for “sticking” the lungs to the thoracic cavity
Respiratory Cycle
includes 1 inhale and 1 exhale
actuated by vacuum
Inspiration
pressure drops
muscle contraction
intercostals, 25-40%
diaphragm, 60-75%
Expiration
typically passive
active expiration: during exercise or forced breathing
During INSPIRATION, the Volume of the Thoracic Cavity (and Thus the Lungs) will Decrease.
False
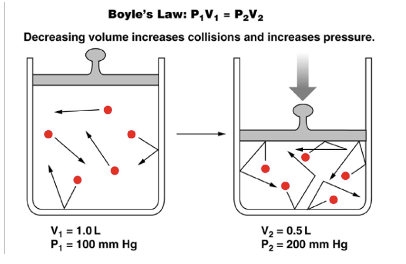
Boyle’s Law
states that the pressure of a gas is inversely proportional to its volume
Dead Space Ventilation
occurs when there is no gas exchange of O2 and CO2 across a membrane
anatomical dead space: nose, pharynx, trachea, bronchioles
functional dead space: alveoli
Respiratory Frequency
body size
age
exercise
excitement
environmental temperature
health status
pregnancy
filling of GI tract
***Cows have a high range of bmp at rest***
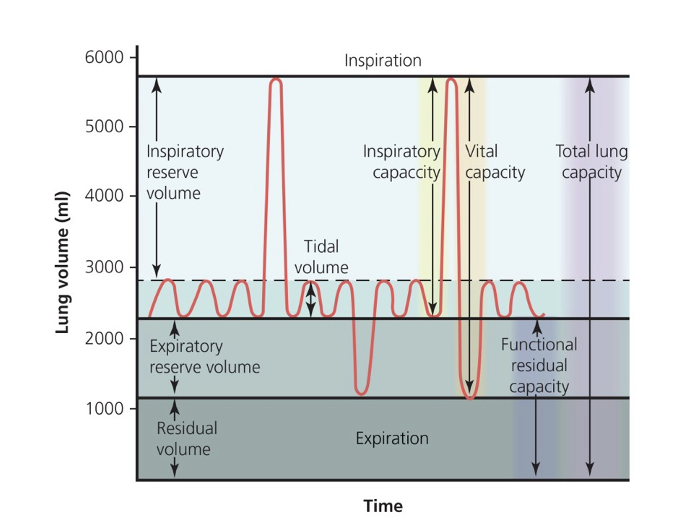
Lung Capacity
is the sum of 2 or more lung volumes
Air
is a mixture of gases; we use partial pressures when talking about O2 and CO2
Fick’s Law
gases diffuses down a concentration gradient
important for understanding how CO2 and O2 diffuse through the body
CO2 is _____ _____ ______ in Water than O2.
20x more soluble
Hemoglobin carries ____
O2
oxyhemoglobin (HbO2)
O2 Carrying Capacity with Hb
200 mL O2/L Blood
O2 Carry Capacity without Hb
3 mL O2/L Blood
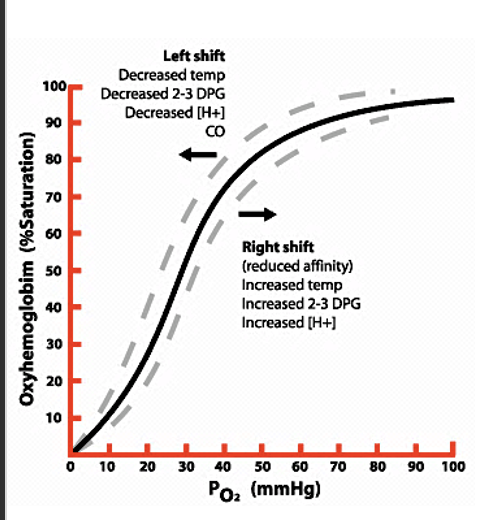
Oxyhemoglobin Dissociation Curve
shows the saturation of hemoglobin with O2
PO2 40 mm Hg = 72% saturation
What are the 3 Ways CO2 is Transported?
Dissolved in plasma (7%)
Converted to bicarbonate (70%)
Bound to hemoglobin (23%)
Carbon Dioxide Transport
from tissues and get removed at the lungs
Oxygen → Carbon Dioxide
Neutral & Humoral Controls Over Breathing
Carotid Receptors: primary chemoreceptors; highly sensitive to changes in oxygen concentration
Aortic Receptors: less sensitive; detect changes in more stuff than carotid receptors
Respiratory Clearance
the removal of harmful particles that been inhaled
Deposition affected by:
inertia: large particles like pollen tend to get stuck in the nose and throat when airflow changes direction quickly
sedimentation: medium-sized particles settle out due to gravity, usually in the bronchi and bronchioles
brownian motion: tiniest particles move randomly and can reach the deepest part of the lungs (alveoli)
Upper Resp. Clearance: moving mucous blanket
Alveolar Clearance:
phagocytosis → macrophages
dissolve
transported to lymph
sequestered