EXAM 3- Khan (IBD and Pancreatitis)
1/38
Earn XP
Description and Tags
based on sg
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
Sulfasalazine contains ____ bonds, which is broken down by __________________ in the colon.
Sulfasalazine contains azo bonds, which is broken down by bacterial azo-reductase in the colon.
What is the main therapeutic moiety of sulfasalazine? What is the structure of sulfasalazine?
main moiety is 5-ASA (5-amino salicylic acid)
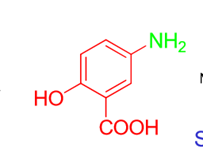
What percentage of an orally administered dose of sulfasalazine reaches the colon?
25%
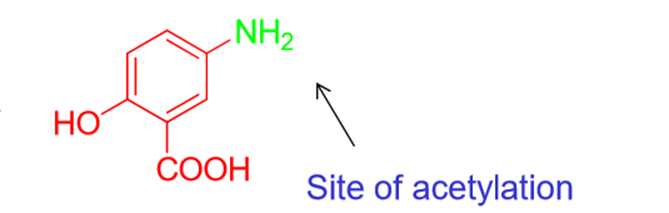
How is 5-ASA metabolized when absorbed systemically? (Be able to also identify on the structure where it is metabolized.)
5-ASA metabolized to N-acetyl-5-ASA through ACETYLATION
What are the ADRs of sulfasalazine caused by the sulfapyridine?
GI (abdominal pain, n/v, anorexia)
rash, HA, oligospermia
INHIBITS folate absorption
hemolytic anemia in G6PDH deficiency
What does the sulfapyridine from sulfasalazine do to glutathione to cause hemolytic anemia?
Sulfapyridine OXIDIZES glutathione. this is not good because the reduced (non-oxidized) form is necessary for fxn as a cellular antioxidant.
What is the name of the 5-ASA drug used for IBS?
Mesalamine
What are the contraindications of 5-ASA or Mesalamine?
salicylate or aminosalicylate allergy
What is the MOA of glucocorticoids?
inhibits production of cytokines and other inflammatory mediators (ex: TNF-a, IL-1)
What are the long-term ADRs of glucocorticoids?
impaired wound healing
IMMUNOSUPPRESION
decrease bone density
What is the advantage of the acetyl group in budesonide?
DECREASES MINERALCORTICOID ACTIVITY
What is the MOA of methotrexate? (Include the specific enzyme) What is the effect?
Inhibits DHF (Dihydrofolate reductase), which depletes folate cofactors needed for DNA synthesis
What is the MOA of infliximab and adalimumab? What is the difference between the 2 drugs?
MOA- inhibit TNF-a
Difference: Infliximab is a mouse-human chimeric antibody, Adalimumab is FULLY humanized
What are the BBW of infliximab and adalimumab?
INFECTIONS (TB reactivation, RTIs, fungal, sepsis)
What is the MOA of natalizumab? What is the BBW?
MOA- humanized antibody alpha-4 integrin
BBW- increases the risk of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (an opportunistic viral infection of the brain)
Natalizumab blocks the adherance of ___ integrin to ________.
alpha-4 integrin to VCAM
What is the MOA of vedolizumab?
humanized antibody a4/b7 integrin
Vedolizumab blocks the adherence of _____ integrins to ___________.
a4/b7 integrins to MAdCAM1
How is vedolizumab different from natalizumab?
vedolizumab is more specific
Vedolizumab is used for UC and CD, while natalizumab can only be used in CD
What are the composition of pancreatic enzymes?
amylase, lipase, protease
How are pancreatic enzymes prescribed?
based on lipase content
What is the indication of pancreatic enzymes?
malnutrition
steatorrhea
pain reduction
How do pancreatic enzymes reduce pain?
basically: we give proteases that degrade CCK, and that stops the pain
CCK is the secretagogue of pancreatic enzymes, when not broken down by trypsin in pancreatitis, it causes pain
What are the ADRs of pancreatic enzymes?
nausea/ abdominal pain, flatulence
mucosal irritation
fibrosing colonopathy
hyperuricemia
hypersensitivity
What is the BBW of NSAIDs?
risk of CV thrombotic event
C/I in CABG surgery
GI bleeding, ulcers, perforation
What is the BBW of Acetaminophen?
risk of errors
hepatoxicity
What is the max daily dose of APAP a day?
≤4 grams/day
What is the difference between opioids and opiates?
o Opioid- any drug, natural or synthetic, with morphine-like actions
o Opiate- natural compound present in opium (morphine, codeine)
What are the effects mediated by mu and kappa receptors?
BOTH RECEPTORS ARE ASSOCIATED WITH ANALGESIA
mu- respiratory depression, sedation, euphoria, physical dependence, decrease GI motility
kappa- sedation, dysphoria, psychotomimetic effects, decrease GI motility
Discuss the mechanism of cellular actions from mu receptor activation PRESYNAPTIC
Inhibit voltage-gated Ca++ channels
Inhibit NT release
Discuss the mechanism of cellular actions from mu receptor activation POSTSYNAPTIC
Causes hyperpolarization
Action potential is inhibited
What neurotransmitters deal with pain transmission?
glutamate
neuropeptide NK
How is pregabalin different from GABA in its effect?
Although they look similar----
Pregabalin binds to alpha2delta-1 subunit of Ca channel
Causes presynaptic effect that was previously discussed (inhibit NT release)
GABA binds to GABA receptors and inhibits nerve transmission
What is the MOA and ADRs of beta-lactam antibiotics?
MOA: bacterial cell wall synthesis inhibitors
ADRs: GI, hypersensitivity, seizures
What is the MOA of fluoroquinolones?
MOA: DNA synthesis inhibitor (Inhibit DNA gyrase and Top IV)
What is the BBW of fluoroquinolones?
BBW: serious ADRs (Tendon rupture, CNS effects, exacerbate myasthenia gravis)
Explain the R6 and R7 positions in the structure of fluoroquinolones:
R6- F Cell Wall Penetration (Fluorine group)
R7- heterocyclic substitution increases spectrum
What are the ADRs of insulin?
HYPOGLYCEMIA!!!!
Insulin allergy
Lipodystrophy atrophy of SQ fat
Weight gain
What is the BBW of antidepressants?
suicidal ideation