Organizing Society - UCSP 4Q
1/95
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
96 Terms
Group
A bounded collection of interacting individuals who are functionally, cognitively, and structurally interdependent to various degrees. Formed by two or more individuals.
Common ancestry and territorial proximity
Enumerate two (2) typical bases for group formation:
Primary groups
Small group characterized by highly intimate and personal relationships that allow them to thrive and last through cooperation and close association.
Family; Children's play groups; Groups in the community
Enumerate three (3) basic primary groups:
FCG
Secondary groups
Large groups characterized by low intimacy and impersonal relationships. Membership depends on shared aspirations and common objectives. Members don't necessarily interact with everyone. Bound together by shared social identities.
Nations; Corporations; Professional associations
Enumerate three (3) common examples of secondary groups:
NCP
Reference group
Toward forming his/her identity, an individual uses a _____ that serves as a point of reference in evaluating one's attitudes and behavior and making decisions related to those. Influences a person’s behaviour and attitudes, regardless whether they are a member.
In-groups
Group to which a person belongs and feels a sense of identity.
Out-groups
Group to which a person does not belong and feels a sense of hostility towards.
Social network
Group of people who have occasional interactions and who engage in similar or related tasks while remaining unknown, unfamiliar, or only slightly familiar with each other. An example of this is a community formed by one's membership in social media sites.
To help find a job and To receive better medical care
Enumerate two (2) reasons why social networks are significant:
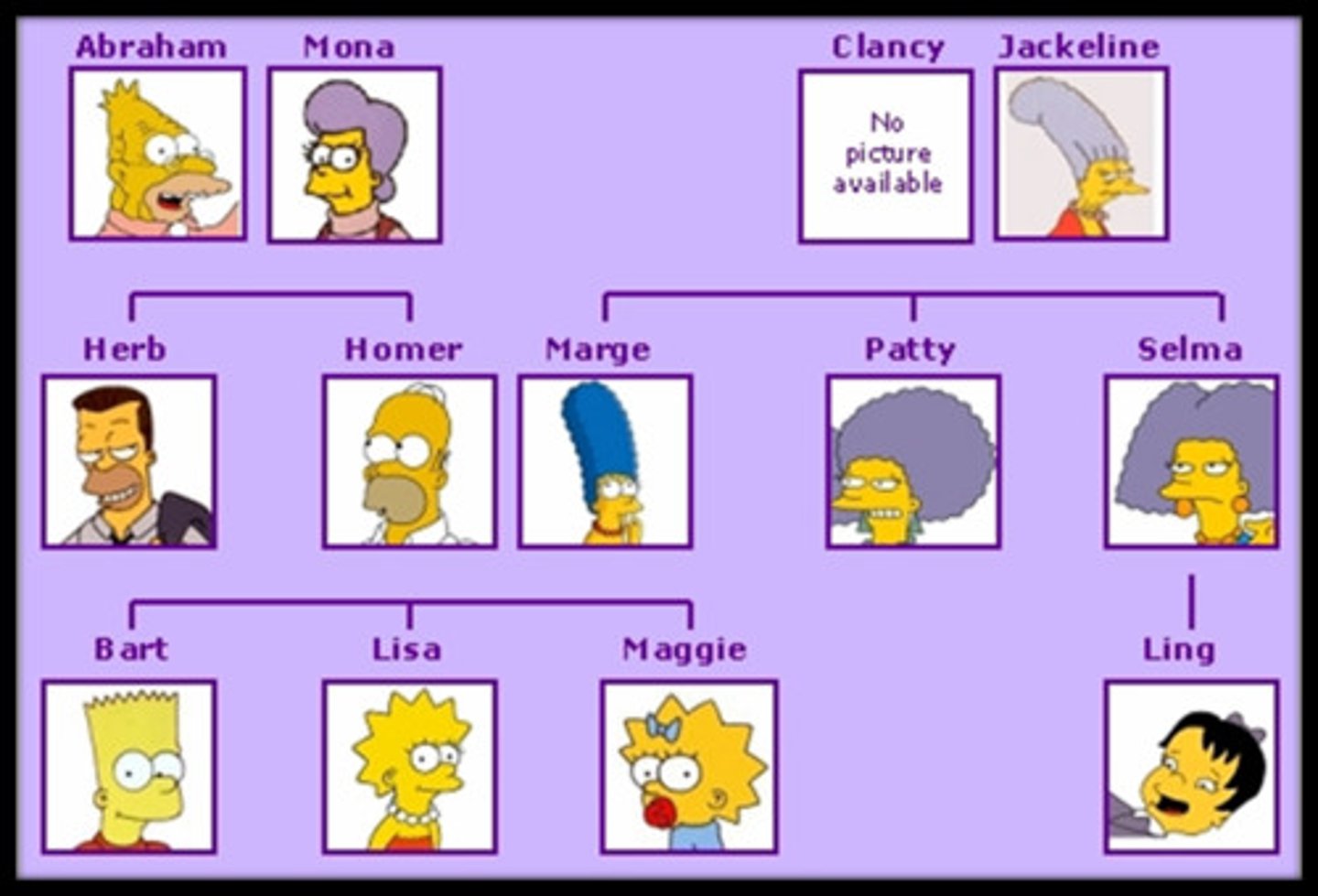
Family
Most basic social unit composed of one or more parents and (a) child/children who typically live together.
Nuclear or conjugal family
A family composed of one or two parents and their child or children.
Extended or consanguine family
A family composed of parents and children, plus other members of their kin.
Reconstituted family
A family where its members differ from the typical members of a nuclear or an extended family.
Female-headed translational family
An example of a reconstituted family which is a household with core members living in at least two nation-states and in which the mother works in another country while some or all of her dependents reside in the Philippines.
Kinship
Family ties with social bond based on common ancestry, marriage, or adoption. It considers both biological relationships and non-biological relationships.
Consanguinity or marriage
Enumerate two (2) possible ways people can be related to be considered part of one's kin group:
Matrilineal kinship
Traced when people are considered members of the mother's group from birth onward.
Patrilineal kinship
Traced when people are considered members of the father's group from birth onward.
Descent
Reckoning of relationship based on a common ancestor. It considers only biological relationships.
Unilineal descent
When descent is traced only either through patrilineal or matrilineal kinship, tracing is _____.
Bilateral descent/Cognatic descent
Both matrilineal and patrilineal descent.
Lineages
Group of people related by a common ancestor.
Public policy and Morality
Enumerate two (2) reasons why cousins aren't allowed to marry each other:
Compadre system/Compadrazgo
It initiates a godparent-godchild relationship that serves to strengthen ties between families (who may or may not be related by blood).
Upper; Middle high; Middle low; Lower
Patterns and strategies in choosing compadres (godparents) differ according to four (4) ranked socio-economic levels, namely:
_____ level consists of older elite and capitalist entrepreneurs
_____ level consists of professionals and bureaucrats
_____ level consists of small-scale businessmen and employees
_____ level consists of fishermen, crewmen, laborers, and market vendors
Political dynasty
When a political family strengthens its hold on political power through such alliances.
Bands
In ancient times and even in some nomadic communities that endured through hundreds of centuries to the modern times, societies are/were typically organized into _____.
Band
A small, egalitarian, kin-based group of perhaps 10-50 people.
Tribe
Comprised a number of bands that were politically integrated (often through a council of elders or other leaders) and shared a language, religious beliefs, and other aspects of culture. Politically weak.
Chiefdoms
Organized through formal structures that integrate several communities (such as tribes) into a distinct political entity led by a council of elders or leaders which typically has a chief, but doesn't always have one.
Ancient barangays led by datus
These can be classified as chiefdoms:
States and nations
Political institutions are typically organized along the lines of _____.
State
Independent, sovereign government exercising control over certain spatially defined and bounded area, whose borders are usually clearly defined and internationally recognized by others.
Nation
Group of people who see themselves as a cohesive and coherent unit based on shared cultural or historical criteria. _____ are socially constructed units that are essentially imagined communities bound together by notions of unity that can pivot around religion, ethnic identity, language, cultural practice and so forth.
Population; Territory; Government; Sovereignty
Enumerate four (4) elements a state typically has:
PTGS
Elements of a nation
Include people living in a specific territory; is distinctly marked by a shared history and culture, most of the times including bonds of linguistic and religious ties as well.
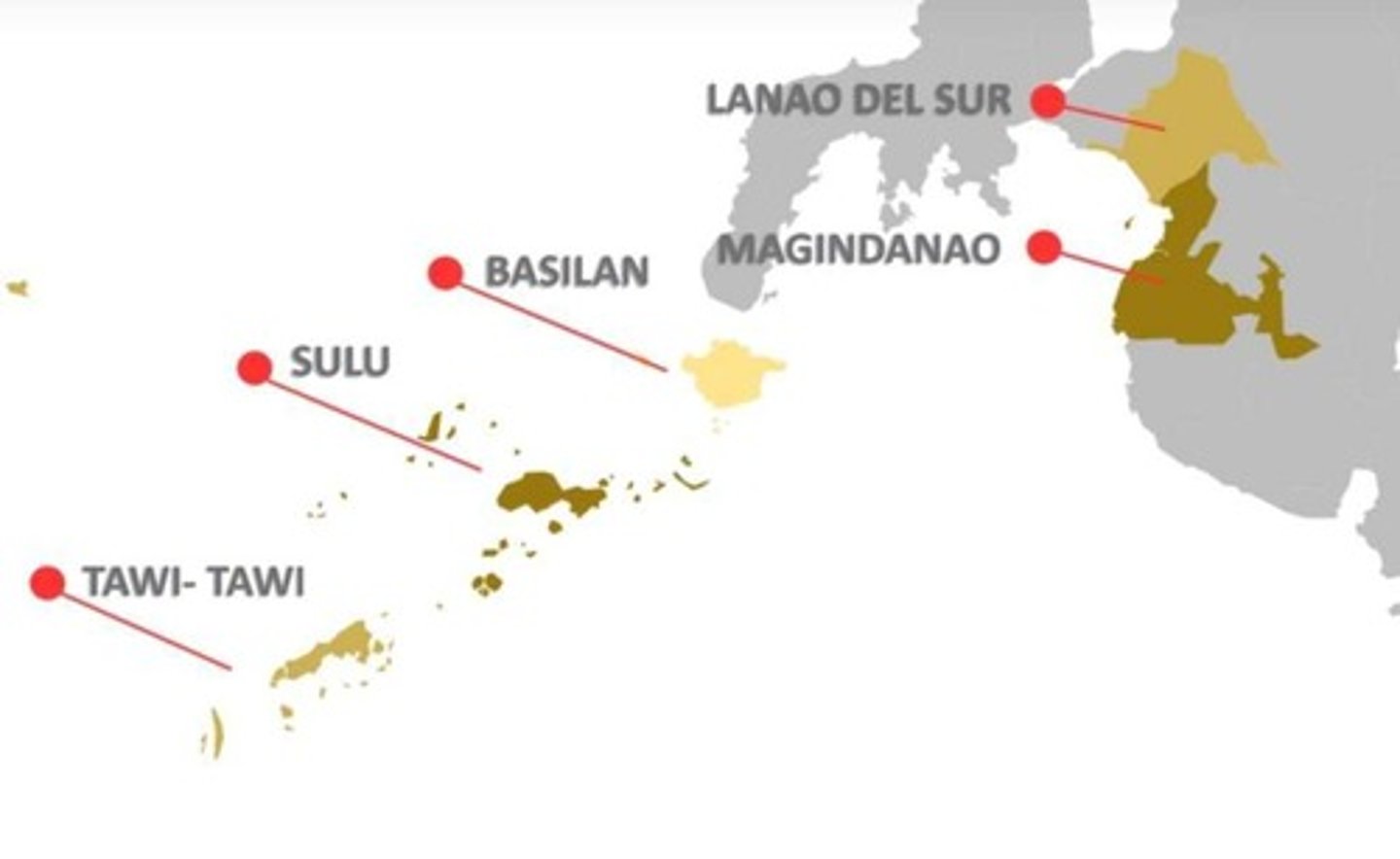
Bangsamoro Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao (BARMM)
The culmination of decades-long attempts to deconstruct the very fabric of a highly centralized, unitary nation-state and rationalize the imperative recognition of a separate nation, the Bangsamoro, albeit still within the Philippine state.
Wielding authority
Political structures in modern nations and states, even in bands, tribes, and chiefdoms are governed through _____.
Traditional; Charismatic; Rational-legal
Enumerate three (3) types of authority:
Traditional authority/Hereditary authority
Authority passed through bloodline of leaders, as in absolute monarchies.
Charismatic authority
Authority drawn from a leader's personal charisma and qualities, like some dictators and cult leaders.
Rational-legal authority
Authority drawn from legal and constitutional mandates that are usually collectively agreed upon by those who are governed, as in what is practiced in democratic countries.
Public sphere
Core of state, economy, and societal relations.
Market economies
Economies that rely on currency to facilitate trade or the exchange of goods and services. An example is typical modern society.
Law of demand and supply
Economies follow the dictates of _____ that influences every public and private sector decision with regard to investments, commodity production, and distribution of goods and services.
Non-market economies
Economies that rely on barter and similar forms of product/commodity exchanges. Has extensive government ownership or control of the means of production, allocation of resources, price and output decisions of enterprises.
Contemporary market economies
Economies that adhere to capitalist free trade and/or where the private sector is either dominant, regulated, or at least relatively strong.
Deregulation
The lifting of government restrictions on business, industry, and professional activities. Meant to free up market forces for accelerated innovation but is complained to be an excuse for price hikes.
Principles of Reciprocity or Redistributions
Traditional non-market economies are governed by _____.
Reciprocity
Direct exchange of goods or services.
Redistribution
Transfer of goods or services from a central authority to redistribute to society.
Market transaction
Indirect exchange of goods facilitated by money.
Stocks and shares
Partial ownership of a corporation.
Profit motive
Maximizing the profitability of a company or business or optimizing an individual's financial gains from a market transaction.
Primary; Secondary; Tertiary
Enumerate three (3) major sectors of economic activity:
Primary sector
Sector engaged in extraction of materials and natural resources.
Secondary sector
Sector engaged in manufacturing or the mass production of goods from raw materials.
Tertiary sector
Sector engaged in providing services, especially those that facilitate the transport, distribution, and sale of goods. Encompasses business process outsourcing, real estate sales, and practicing professions. The current Philippine economy is dominated by this.
Non-state institutions
Institutions that help build and shape societies that include banks and corporations, cooperatives and trade unions, translational advocacy groups, etc. Exists independently from states but operate within regulations and limitations set by them.
Banks
They lend money to businesses, start-ups, entrepreneurs, and the government and play a major role in maximizing the productive potential of money.
Corporations
Private entities led by a board of directors created to manage a company or group of companies.
Corporate social responsibility
The private sector's commitment to upholding the common good.
Landbank
A state-owned bank in the Philippines meant to assist farmers and other beneficiaries of land reform in their financing needs.
Collective bargaining agreement (CBA)
Government-registered labor unions have the power to strike a _____ with the corporate management. Such agreement covers negotiations with respect to wages, hours of work and all other terms and conditions for employment.
Civil society organizations and community organizations
Established to advocate for short-term, medium-term, and long-term reforms in local, national, and international levels. These organizations are typically multi-sectoral, as they draw their power from collective demands of various sectors.
Cooperatives
Organizations formed by citizens to help themselves through providing financial services to its members, in exchange for membership dues or share capital.
Translational advocacy groups
Ensure that governments worldwide maintain transparency in their affairs (especially about public finances in major government projects) and uphold human rights and civil liberties to make democracy function well despite perceived limitations and weaknesses.
Development agencies and lending institutions
Help finance big government projects, especially in developing countries. Critics point out they lack transparency and democratic mechanisms, are times not responsive to voices of communities, and charge interest rates to loans that they facilitate.
Profit motive
____ rather than altruism, seems to be the central function of development agencies like typical private banks.
Interdependence
The necessary order of things for social beings like humans.
International organizations
Through these, nation-states are able to peacefully conduct dialogues on pressing issues, resolve disagreements, and carry out mutually-beneficial economic and socio-cultural activities.
United Nations
Springboard for global governance.
Schools
The main entities in establishing and nurturing educational institutions. Education's functions cover the need for self-actualization (fulfilling or maximizing one's potentials) and society's need for having productive citizenry that contributes knowledge and skills toward improving lives.
Philippine Education Act of 1982
Mandates that country's education system should ensure maximum contribution to attainment of the follow national development goals: (1) to achieve and maintain an accelerating rate of economic development and social progress; (2) to ensure the maximum participation of all the people in the attainment and enjoyment of the benefits of such growth; and (3) to achieve and strengthen national unity and consciousness and preserve, develop and promote desirable cultural, moral and spiritual values in a changing world.
Animism
Belief that everything has a spirit: trees, birds, rainstorms, rocks. "Nature worship" or a nature-based spirituality. Practiced especially in Mindanao, where the Lumad reside.
Lumad
Non-Christian and non-Moslem ethnolinguistic groups.
Polytheism
Belief system that emphasizes belief in the existence of multiple gods.
Monotheism
Belief that only one all-powerful god exists. The Philippines' two dominant religions: Christianity and Islam, fall under this.
Democratic secularism
Lack of official institutionalization of religion in the Philippines, as the country adheres to this. It ensures both democracy and the separation of religion from government affairs.
Dominant religions
Played a major historical role and/or closely linked with certain countries' history and heritage are institutionalized or recognized as official religions.
Western; Traditional; Alternative
Health services rely on three (3) systems of healing:
Alternative healing systems
Incorporate culture-specific discourses related to illnesses, such as binat/bughat, bales/usog/buyag.
Binat/Bughat
Can be translated as "relapse" and it occurs when someone is recovering from illnesses but gets sick again shortly after or even during the recovery period.
Rest
Binat can only be beaten through _____.
Bales
A condition unique to Philippine folk medicine that is believed to be caused by an admiring or complimentary greeting or comment which carries bad wind with it.
Puwera isog
A verbal antidote (pang-kontra) for bales is to say _____.
7107
Number of islands in the Philippine archipelago:
175
Philippines has approximately _____ ethnolinguistic groups with their own unique cultural identity and health practices.
Namamana
A common Filipino cultural belief related to health which pertains to inheritance.
Lihi
A common Filipino cultural belief related to health which pertains to conception or maternal cravings.
Sumpa/gaba
A common Filipino cultural belief related to health which pertains to curse.
Pasma
A common Filipino cultural belief related to health which pertains to hot and cold syndrome.
Namaligno
A common Filipino cultural belief related to health which pertains to mystical and supernatural causes.
Kaloob ng Diyos
A common Filipino cultural belief related to health which pertains to God's will.